Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Docsity General Biology Reviewer
Docsity General Biology Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lancer SignoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Docsity General Biology Reviewer
Docsity General Biology Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lancer SignoCopyright:
Available Formats
General Biology Reviewer
Biology
6 pag.
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
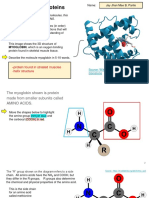
III. LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION OF LIFE - HYDROPHOBIC TAIL: portion of cell membrane
1. ATOMS - smallest particle of an element.
that does not allow water to pass through.
2. MOLECULE - reaction of the combination of atoms - HYDROPHILIC HEAD: portion where water pass
(lipids, protein, nucleic acids, carbohydrates)
through, do not have affinity for nutrients—only
3. CELL - combination of molecules needed by the water.
organisms.
CYTOPLASM
4. TISSUE - group of similar cells that perform specific - jellylike mixture of water, sugars, ions, and proteins.
functions.
ORGANELLE
5. ORGAN - structure usually composed of several - structure that carries out specialized metabolic
tissue types that form a functional unit.
functions inside a cell.
6. ORGAN SYSTEM - two or more organs working ________________________________________________
together in the execution of a specific body function.
PROKARYOTIC CELLS
7. MULTICELLULAR ORGANISM - an individual that
- do not have nucleus.
consists of one or more cells.
CAPSULE - found in some bacterial cells, protects the
8. POPULATION - group of interbreeding individuals of cell when it is engulfed by other organisms.
the same type or species.
CELL WALL - outer covering of most cells that
9. COMMUNITY - two or more populations of different protects bacterial cell.
species living and interacting in the same area.
PILI - hair-like structures on the surface of the cell that
10. ECOSYSTEM - a community together with its attach to other bacterial cells.
nonliving surroundings.
FLAGELLA - long, whip-like protrusion that aids in
locomotion.
11. BIOSYSTEM - part of Earth inhabited by living
organisms, consists of all ecosystems of Earth.
RIBOSOMES - responsible for protein production.
PLASMIDS - gene carrying, circular DNA structures not
IV.A PARTS OF PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC involved in reproduction.
CELLS NUCLEOID REGION - contains the DNA.
CELL THEORY
________________________________________________
- All living organisms are made up of cells.
EUKARYOTIC CELLS
- Cell is the most basic unit of life.
NUCLEUS
- Cells come from pre-existing cells.
- has nuclear pores
- Cells contain DNA which they pass to their - Contains nucleolus, nuclear lamina, and
offspring when they divide.
chromosomes.
Nucleolus: contains RNA
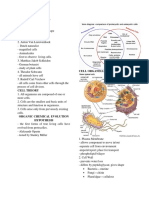
COMPONENTS OF ALL CELLS
Nucleus: contains DNA
PLASMA MEMBRANE/CELL MEMBRANE Functions: Genetic information, assembly of ribosome
- surrounds the cell and controls which substances units, structural support
move in and out.
RIBOSOMES
- Follows a Fluid Mosaic Model
- Complex of RNA and proteins
- It has 2 regions:
Function: Protein synthesis
ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Ma. Jesikah R. Encarnacion (DLSMHSI)
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
- contains receptors for entry of selected proteins.
- Organelle of photosynthesis
- Has ribosomes attached to the surface.
Function: Production of ATP and sugars via
- Flattened sacs
Photosynthesis
Function: Protein synthesis and processing
CYTOSKELETON
SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM - actin filaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
- has enzymes for synthesizing lipids.
Function: Structural support, movement of materials,
- Tube-like sacs.
movement of whole cell.
Function: Lipid synthesis
Microtubules - involved in movement, made of tubulin
GOLGI APPARATUS subunits.
- stack of flattened sacs
Microfilaments - triggers microtubules to use motor
Cis Face: secretory, facing outwards
proteins, made of fibers of actin subunits.
Trans Face: transport, inside
Intermediate filaments - lock cells and tissues together
Function: Protein processing
CILIA - short, harlike structures that project from the
LYSOSOMES plasma membrane.
- acid hydrolases
- With enzymes for intracellular digestion.
IV.B CELL DIVISION
Function: Digestion and recycling
MITOSIS
PEROXISOMES
- enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions.
- Breaks down amino acids, fatty acids, and toxic
substances
Function: Oxidation of fatty acids, ethanol, and other
compounds.
VESICLES
- stores, transports, or degrades its contents
Secretory Vesicle - functions with Golgi bodies
Transport Vesicle - from inside to outside,
transports toward the Smooth ER.
VACUOLES
- contains transported for selected molecules.
- Fluid-filled organelle that isolates or dispose wastes.
- Bigger than vesicle.
- Acts as storage of water
MITOCHONDRIA
- contains enzymes for ATP production.
Cisternae: external compartment
Matrix: Inner compartment
Function: ATP production
CHLOROPLASTS
- Pigments
Ma. Jesikah R. Encarnacion (DLSMHSI)
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
MEIOSIS
V. HEREDITY AND GENETICS - Most genes program cells to synthesize specific
HEREDITY enzymes and other proteins, whose cumulative
- transmission of traits from one generation to the action produces an organism’s inherited traits.
next.
GAMETES
VARIATION - reproductive cells
- sons and daughters are not identical copies of either - Vehicles that transmit genes from one generation to
parent or of their siblings.
the next.
GENETICS FERTILIZATION
- scientific study of heredity and inherited variation.
- male and female gametes unite.
INHERITANCE OF GENES
GENES
- parents endow their offspring with coded information
in the form of hereditary units.
- Account for family resemblance.
Ma. Jesikah R. Encarnacion (DLSMHSI)
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
VI. HUMAN BIOLOGY AND ANATOMY internal organs. They are not striated and are
Organ Systems
involuntary.
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM
Components: skin, hair, nails, sweat glands
Components: nerves and sense organs, brain and
Function: covers and protects the body spinal cord
Specific features:
Function: receives stimuli from external and internal
- protect against injury
environments, conducts impulses and integrates
- Sensory receptors in skin tell about the environment
activities of other systems
- Prevents drying out of cells
Specific features:
- Helps maintain body temperature
- Central nervous system consists of the brain and
- Sweat glands excrete water and some wastes
spinal cord.
SKELETAL SYSTEM - Peripheral nervous system consists of the sense
Components: bones, cartilage, ligaments
organs and the nerves which connect the spinal cord
Function: supports and protects body with the rest of the body.
Specific features:
- Somatic division: consists of receptors and nerves
- supports body via bony framework
concerned with changes in the outside
- Protects delicate vital organs
environment.
- Bones are levers that transmit muscular forces
- Autonomic division: regulates the internal
- Muscles are attached to bones by bands of environment, primarily the sympathetic and
connective tissue called tendons. parasympathetic systems of the efferent system of
- Marrow inside some bonds produces blood cells.
nerves.
- Bones serve as banks for storage and release ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
minerals like Calcium and Phosphorus.
Components: Pituitary gland, adrenal gland, thyroid
MUSCULAR SYSTEM gland, hypothalamus gland, pineal gland, kidney,
Components: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth pancreas, ovaries, testes
muscle
Function: regulates body chemistry and many body
Function: moves parts of the skeleton, locomotion, functions.
pumps blood, aids movement of internal materials
Specific features:
Specific features:
- information about hormone levels or their effect is
- muscle cells contract and become shorter and fed back to the gland to regulate the hormone’s
thicker
release.
- Long and narrow muscles are called fibers. - Endocrine activity is controlled by the hypothalamus
- Voluntary muscles are skeletal muscles attached to gland. This gland links nervous and endocrine
bones which make our bodies move, they are striped systems.
or striated in appearance.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
- Cardiac muscles are found in the walls of the heart, Components: heart, blood vessels, blood
it contracts involuntarily and is striated in Function: transports materials from one part of the
appearance.
body to another, defends body against diseases
- Smooth muscles are found in the walls of the
digestive tract, uterus, blood vessels and other
Ma. Jesikah R. Encarnacion (DLSMHSI)
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
Specific features:
Function: reproduction
- consists of cardiovascular system (consists of the
heart which pumps the blood through the blood Facts about the Human Body
vessels) and lymphatic system (helps to preserve Largest organ of the body Skin
fluid balance and protects the body against disease)
Largest internal organ Liver
- Transport nutrients all over the body from the
digestive system.
Total no. of muscles 630+
- Transports oxygen from lungs to all cells of the body.
Longest bone Femur
- Helps maintain normal body temperature.
Smallest bone Stapes/Stirrup
- Helps maintain fluid balance.
Hardest bone Teeth
RESPRIRATORY SYSTEM
Components: lungs and air passageways
Smallest muscle Stapes muscle
Function: exchanges gases between blood and the Largest muscle Gluteus Maximus
external environment
Total no. of bones 206
Specific features:
Filter of the body Kidney
- respiration includes breathing, gas exchange
between lungs and blood, transport of gases through Pump of the body heart
the body by the blood.
Total no. of vertebrae 33
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Normal body temperature 37C
Components: mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines,
Normal heart beat 72 per minute
liver, pancreas
Function: ingests and digests foods, absorbs them into No. Of ribs 12pairs
blood Total no. of bones in arm 30
Specific features:
total no. of bones in leg 29
- Salivary glands, liver and pancreas are NOT part of
Strongest muscle Masseter (Jaw), Tongue,
the digestive system but secrete digestive juices into
Uterus
it.
Largest element (amount) oxygen
URINARY SYSTEM
Spinal nerves 31 pairs
Components: kidney, bladder, and associated ducts
Function: excretes metabolic wastes, removes Volume of blood 5-6 liters
substances present in excess from the blood Most common blood type O and A
Specific features:
Largest part of brain cerebrum
- urine is made by the kidneys
- Transported from the kidneys to the bladder by the Largest Cell Nerve cell
ureters, the bladder stores the urine then urine Largest vein Inferior vena cava
leaves the bladder and exits via the urethra.
Largest artery Aorta
- 95% of urine is water.
Joints in human body 230
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Components: testes, ovaries, and associated pH of blood 7.3-7.4
structures
Ma. Jesikah R. Encarnacion (DLSMHSI)
Document shared on www.docsity.com
Downloaded by: lancer-signo-1 (signolancer929@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Proteins Guided LearningDocument17 pagesProteins Guided LearningMel MasculinoNo ratings yet
- Previous IB Exam Essay QuestionsDocument58 pagesPrevious IB Exam Essay QuestionsDah Lin J91% (11)
- Biology Cells Microscopy 1Document14 pagesBiology Cells Microscopy 1Andrea Trish NicolasNo ratings yet
- Structure and TaxonomyDocument4 pagesStructure and Taxonomymhiee maaaNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and StructureDocument4 pagesCell Theory and StructureKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- Biology Principles Review11-20-14Document19 pagesBiology Principles Review11-20-14Afidah CamarNo ratings yet
- Parts of The CellDocument3 pagesParts of The CellMa Claire TumboconNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Cell StructureDocument31 pagesCh.4 Cell StructureEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- C3 - Cell StructureDocument4 pagesC3 - Cell StructureLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- BioNOTES Midterm Study GuideDocument14 pagesBioNOTES Midterm Study Guidebro jo lolNo ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJoyce GuintoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 1Document9 pagesGeneral Biology 1 1manansalastarringNo ratings yet
- Genbio ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio ReviewerAnne Carmel PinoNo ratings yet
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- Genbio I ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenbio I Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- Bot 1Document16 pagesBot 1Lawrence SarmientoNo ratings yet
- (Zoolone) Animal CellDocument5 pages(Zoolone) Animal CellRenee Margarette GrapilonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Parts and Functions of The CellDocument26 pagesLesson 2 Parts and Functions of The CellDavid BayaniNo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- Physio Compiled NotesDocument9 pagesPhysio Compiled Notesthtu.sint.swuNo ratings yet
- Botany ReviewerDocument10 pagesBotany ReviewerJARISSA DIZON GALLAZANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CytogeneticsDocument13 pagesChapter 2 CytogeneticsKathleen TanateNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Biochemistry Review Notes: MembraneDocument18 pagesBiochemistry Review Notes: MembraneRanielle Samson100% (1)
- A Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodyDocument1 pageA Sub-Cellular Structure That Has One or More Specific Jobs To Perform in The Cell, Much Like An Organ Does in The BodySarthepandabearNo ratings yet
- Biology: Cell StructureDocument3 pagesBiology: Cell StructureFernanda AntonialliNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewerabijaneee11No ratings yet
- Cells: Simple or Complex CellsDocument2 pagesCells: Simple or Complex CellsMary Jean BoNo ratings yet
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review in GenbioDocument5 pagesPointers To Review in GenbioLouie BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Week 1Document3 pagesGen Bio Week 1Lucy AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Biology Principles Review11!20!14!1!11Document18 pagesBiology Principles Review11!20!14!1!11shashaNo ratings yet
- IB Bio Notes MasterDocument45 pagesIB Bio Notes MasterE. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure2Document6 pagesCell Structure2CRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Pre Lim BioDocument5 pagesPre Lim BioJanica SamsonNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio CH 1 - S24Document26 pagesCell Bio CH 1 - S24corniecehallNo ratings yet
- General Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document37 pagesGeneral Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument13 pagesMicropara ReviewerEmhnaly Kae AggalutNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument106 pagesCell Structure and Cell Organisationwienna1987No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemsitry HandoutDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Biochemsitry HandoutMatthew Elleison Baño100% (1)
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument28 pagesCell StructureBANQUERIGO I.G. (2201427)No ratings yet
- The Cell and Its BeginningDocument6 pagesThe Cell and Its BeginningZarc VenturaNo ratings yet
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Cell The Modern Cell Theory: Rudolph Virchow-1858Document5 pagesCell The Modern Cell Theory: Rudolph Virchow-1858Lindsay GabrielNo ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument31 pages2 CellsRashed NadaNo ratings yet
- STM123 OutlineDocument19 pagesSTM123 OutlineNur-Aiza AlamhaliNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant CellDocument6 pagesCell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant Celljean magallonesNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its StructureDocument5 pagesCell and Its Structureim bored -w-No ratings yet
- Sunlight For Energy. Chloroplast - Is Where Photosynthesis HappenDocument4 pagesSunlight For Energy. Chloroplast - Is Where Photosynthesis HappenSamantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyEarl Nikko ChingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1EricNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Immunology Notes From Uworld, DR-KYDocument16 pagesImmunology Notes From Uworld, DR-KYLayan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Prokariotik Dan Eukariotik 2Document22 pagesProkariotik Dan Eukariotik 2hanumNo ratings yet
- Nav Structure-IntroductionDocument26 pagesNav Structure-IntroductionLorraine Joy dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Role of C Kit SCF System in Hematological MalignanciesDocument5 pagesA Review On The Role of C Kit SCF System in Hematological MalignanciesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 2 Cells and Control - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument10 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 2 Cells and Control - Edexcel Biology GCSEAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Fergusson College (Autonomous) PuneDocument15 pagesFergusson College (Autonomous) PuneAAANo ratings yet
- 2019MackinSJMPhD PDFDocument184 pages2019MackinSJMPhD PDFLuciani Magdalena Palacios GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Cell LineDocument3 pagesCell LineMelvin Thien Wei FattNo ratings yet
- Lesson 28: Bionergetics Utilization of EnergyDocument25 pagesLesson 28: Bionergetics Utilization of EnergyFlorence GuzonNo ratings yet
- Effects of Oleic Acid: Review Article Doi: 10.17546/msd.25609Document8 pagesEffects of Oleic Acid: Review Article Doi: 10.17546/msd.25609Radwan AjoNo ratings yet
- Botany M.C.Q.SDocument86 pagesBotany M.C.Q.SMalik TAHIR100% (2)
- Question Bank 25Document9 pagesQuestion Bank 25archismanmaity3376No ratings yet
- 337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologyDocument166 pages337 Pdfsam NMS PhysiologydrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Histologi EpitelDocument70 pagesHistologi EpitelAndre Christian Sopacua100% (1)
- Car-T Cell 2 (7757)Document8 pagesCar-T Cell 2 (7757)Saradha PellatiNo ratings yet
- Foundations in Microbiology: Nonspecific Host Defenses TalaroDocument35 pagesFoundations in Microbiology: Nonspecific Host Defenses TalaroOdurNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA MCQDocument6 pagesRecombinant DNA MCQChaze WaldenNo ratings yet
- Outlines in PathologyDocument200 pagesOutlines in PathologyLisztomaniaNo ratings yet
- Cosphatec Lecithin FolderDocument7 pagesCosphatec Lecithin FolderfitriasarassNo ratings yet
- BIO 310 Midterm 1 PackageDocument28 pagesBIO 310 Midterm 1 PackageNerdy Notes Inc.100% (1)
- Skin Basics: Biology and Physiology: BY Precious U. Imam, RN, MDDocument31 pagesSkin Basics: Biology and Physiology: BY Precious U. Imam, RN, MDprecyusmanNo ratings yet
- Lets Build A Plant CellDocument5 pagesLets Build A Plant CellSabsNo ratings yet
- Food Allergens - Biochemistry and Molecular NutritionDocument217 pagesFood Allergens - Biochemistry and Molecular NutritionHien PhamNo ratings yet
- Effects of Viral ReplicationDocument3 pagesEffects of Viral ReplicationSamuel OgaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CoordinationDocument3 pagesChapter 10 CoordinationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Biologi Molekluler s1 Farmasi Kapsel SttifDocument40 pagesBiologi Molekluler s1 Farmasi Kapsel SttifFuji Iting RahayuNo ratings yet
- Protein SortingDocument27 pagesProtein SortingNabeel MohammedNo ratings yet
- Branch of Biology: ExampleDocument2 pagesBranch of Biology: ExampleMaría LuévanoNo ratings yet