Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bloom's Taxonomy - Center For Innovative Teaching and Learning - Northern Illinois University
Bloom's Taxonomy - Center For Innovative Teaching and Learning - Northern Illinois University
Uploaded by
Dr. M. Hannan JamilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hanzi Freinacht The Listening SocietyDocument499 pagesHanzi Freinacht The Listening SocietymefastidiasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To Heritage TourismDocument17 pagesModule 1 - Intro To Heritage Tourismcjons delacruz100% (1)
- GrayScale - The Grid Method - Development Resource Workbook - FINAL EDIT Copy 2Document44 pagesGrayScale - The Grid Method - Development Resource Workbook - FINAL EDIT Copy 2Anbarasi SNo ratings yet
- FSAC - Learning Outcomes WorkshpDocument18 pagesFSAC - Learning Outcomes WorkshpQalab E AbbasNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain Was Published in 1956 (Eisner 2000) - Because Many CurriculumDocument6 pagesCognitive Domain Was Published in 1956 (Eisner 2000) - Because Many CurriculumVivian BastoNo ratings yet
- Outcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesDocument6 pagesOutcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesJessel GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson 1Document1 pageEapp Lesson 1Arcel V Luceno100% (2)
- Bloom Objectives Planning WorksheetDocument1 pageBloom Objectives Planning WorksheetMalak ZiyadNo ratings yet
- Teaching With The Revised Bloom'StaxonomyDocument33 pagesTeaching With The Revised Bloom'StaxonomyRebenna Bernaldez Lagahit IINo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's TaxonomyDocument29 pagesRevised Bloom's TaxonomyBitoy AlarconNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationsDocument55 pagesTable of SpecificationsMERCY ABOCNo ratings yet
- KognisainsDocument9 pagesKognisainsnurfifahNo ratings yet
- Sample: Sampling DesignsDocument6 pagesSample: Sampling DesignsLovejoylife Castillo RevecheNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Integrating Problem-Solving Educational SoftwareDocument25 pagesTopic 7 - Integrating Problem-Solving Educational SoftwareChee YinNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument20 pagesChapter Iianglo phileNo ratings yet
- Task Creating Vocabulary Mind Maps On Piagets Cognitive Development TheoryDocument3 pagesTask Creating Vocabulary Mind Maps On Piagets Cognitive Development Theory2010092No ratings yet
- 1 Blooms Taxonomy For OBLTDocument26 pages1 Blooms Taxonomy For OBLTABCNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument17 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesRea GoNo ratings yet
- Revised Blooms Taxonomy Process Verbs Assessments and Questioning StrategiesDocument2 pagesRevised Blooms Taxonomy Process Verbs Assessments and Questioning StrategiesAnup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- Writing Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level Thinking: Login Subscribe!Document8 pagesWriting Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level Thinking: Login Subscribe!api-638514534No ratings yet
- Teacher: Autumn Carter Grade Level: 9 - 12 Date: Lesson Title: Creating An Album Cover Using HarmonyDocument5 pagesTeacher: Autumn Carter Grade Level: 9 - 12 Date: Lesson Title: Creating An Album Cover Using Harmonyapi-546172080No ratings yet
- Mariel DepaudhonDocument18 pagesMariel DepaudhonMariel DepaudhonNo ratings yet
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBloom TaxonomyAmirah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Power Point 2Document20 pagesAssessment 1 Power Point 2dhamiltonNGCSUNo ratings yet
- Success CriteriaDocument14 pagesSuccess CriteriaClive AngusNo ratings yet
- RM-Chapter 2Document81 pagesRM-Chapter 2Wubliker BNo ratings yet
- BIOSCI 109 Lab 6 Student HandoutDocument5 pagesBIOSCI 109 Lab 6 Student HandoutGurleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Mapping To The Common Core StandardsDocument32 pagesMapping To The Common Core StandardsShu'eib HassenNo ratings yet
- Writing Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level ThinkingDocument12 pagesWriting Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level ThinkingmazanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument14 pagesBloom's TaxonomydeepakNo ratings yet
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBloom TaxonomyJeffrey TanNo ratings yet
- Tips and Tricks ELearning Symposium BookletDocument8 pagesTips and Tricks ELearning Symposium BookletTodd ConawayNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument9 pagesModuleMerry Joy Tauro Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Beauty WeeblyDocument8 pagesUnit Plan Beauty Weeblyapi-450160025No ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionDocument17 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionNur ZaraNo ratings yet
- Daw Mary Associate Professor English Department Maubin UniversityDocument19 pagesDaw Mary Associate Professor English Department Maubin UniversityEmpressMay ThetNo ratings yet
- Real World Algebra Problems Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesReal World Algebra Problems Lesson Planapi-357246840No ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A Practical Approach For Deeper Learning: September 15, 2012Document4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: A Practical Approach For Deeper Learning: September 15, 2012Krishnamurthy RamasubramanianNo ratings yet
- General Principles in Constructing Classroom Test: Original DomainDocument42 pagesGeneral Principles in Constructing Classroom Test: Original DomainVinjel Libradilla100% (1)
- Full Action Research Action Research Proposal Checklist YesDocument3 pagesFull Action Research Action Research Proposal Checklist YesKatherine ChavezNo ratings yet
- Inverse Operations Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesInverse Operations Lesson Planapi-357246840No ratings yet
- Writing Learning Outcomes WorksheetDocument6 pagesWriting Learning Outcomes WorksheetRoxana MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Design Document For Blended Course Design and DeliveryDocument18 pagesDesign Document For Blended Course Design and Deliveryapi-412970899No ratings yet
- ILO GuideDocument3 pagesILO GuideHala BenghasheerNo ratings yet
- Eng 9 HportfoliobookreviewDocument1 pageEng 9 Hportfoliobookreviewapi-257561679No ratings yet
- WRITING STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES - Rev03Document18 pagesWRITING STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES - Rev03hishahNo ratings yet
- Research Method Rm-Chapter 2Document50 pagesResearch Method Rm-Chapter 2GAMEX TUBENo ratings yet
- Project Conceptualization FormDocument2 pagesProject Conceptualization FormJuliette LaMontagneNo ratings yet
- Blooms PresentationDocument31 pagesBlooms PresentationNitin TembhurnikarNo ratings yet
- How To Write Learning Outcomes WorksheetDocument6 pagesHow To Write Learning Outcomes WorksheetAriana Sanchez Alvarez100% (1)
- Revised-Blooms of Taxonomy of ObjectivesDocument2 pagesRevised-Blooms of Taxonomy of ObjectivesStephenNo ratings yet
- Consideration in Writing A Lesson PlanDocument23 pagesConsideration in Writing A Lesson PlanElyss SantiagoNo ratings yet
- SLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsDocument5 pagesSLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsEricka NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Healtheduc 4Document4 pagesHealtheduc 4Mark ApariciNo ratings yet
- CPSVersion6.1B TreffingrDocument8 pagesCPSVersion6.1B TreffingrihwalNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument8 pagesBloom's TaxonomyMarissaM.PerezNo ratings yet
- Maam Hadir2,.0Document4 pagesMaam Hadir2,.0Julius Rusiana CatubigNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design TheoriesDocument51 pagesInstructional Design Theoriescjust0318No ratings yet
- DLL-3rd Q Day 1Document4 pagesDLL-3rd Q Day 1KèlǐsītǎnKǎPángNo ratings yet
- Week 3 21st CLDocument6 pagesWeek 3 21st CLFlorina Nadorra RamosNo ratings yet
- Bloom'S Taxonomy - Lower-Level and Higher-Level Cognitive SkillsDocument1 pageBloom'S Taxonomy - Lower-Level and Higher-Level Cognitive SkillsLeidyDanielaBenitezPantojaNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1 - Intro CHPE - B 4 - 13-10-2022Document17 pages1 - Intro CHPE - B 4 - 13-10-2022Dr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Using Blooms Taxonomy To Write Learning GoalsDocument2 pagesUsing Blooms Taxonomy To Write Learning GoalsDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Course Alignment - Learning in A Flat WorldDocument7 pagesCourse Alignment - Learning in A Flat WorldDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Assess Series 3 Curriculum Mapping 01062020Document26 pagesAssess Series 3 Curriculum Mapping 01062020Dr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives - The Center For Teaching and Learning - UNC CharlotteDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives - The Center For Teaching and Learning - UNC CharlotteDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy - Master Your Learning ObjectivesDocument13 pagesBloom's Taxonomy - Master Your Learning ObjectivesDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Week 2 AssignmentsDocument7 pagesWeek 2 AssignmentsELLA ZHOUNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Social Media On Self Concept of AdolescencesDocument24 pagesThe Influence of Social Media On Self Concept of AdolescencesLakshita GomaNo ratings yet
- Kant's A Priori in The Critique of JudgmentDocument4 pagesKant's A Priori in The Critique of JudgmentteletoniqNo ratings yet
- Theories On Human Behavior (UCSP)Document2 pagesTheories On Human Behavior (UCSP)jc nerNo ratings yet
- q1 Week1 Etech DLLDocument4 pagesq1 Week1 Etech DLLBrendzNo ratings yet
- TUGAS 1 - Rizqa Alysya RafianidaDocument200 pagesTUGAS 1 - Rizqa Alysya RafianidaRizqa AlysyaNo ratings yet
- (UCSP 1) 1st Periodic ExamDocument3 pages(UCSP 1) 1st Periodic ExamKrisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - MetacognitionDocument14 pagesModule 1 - MetacognitionMarisol MipantaoNo ratings yet
- Validating The University Entrance English Test To The Vietnam National University: A Conceptual Framework and MethodologyDocument11 pagesValidating The University Entrance English Test To The Vietnam National University: A Conceptual Framework and MethodologyThị Phương Quyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: Bachelor of Science in Information SystemsDocument1 pageJose Rizal Memorial State University: Bachelor of Science in Information Systemsdonz borjNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Crim 7Document11 pagesModule 3 Crim 7Geronimo BazarNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Inverter System Based On Fuzzy ControlDocument8 pagesThree Phase Inverter System Based On Fuzzy ControlNaresh Kumar NNo ratings yet
- Sympathy - WikipediaDocument1 pageSympathy - WikipediaBadhon Chandra SarkarNo ratings yet
- A Short Pause From A School LeaderDocument2 pagesA Short Pause From A School LeaderLG BaganiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem PhiloDocument6 pages2nd Sem PhiloOnin MatreoNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Teacher Mobility and Retention Guidance and Considerations Report 2. REL 2021081Document28 pagesAnalyzing Teacher Mobility and Retention Guidance and Considerations Report 2. REL 2021081Vina YaaqubNo ratings yet
- I. Factors Affecting Academic Planning (Stark & Lattuca, 1997)Document4 pagesI. Factors Affecting Academic Planning (Stark & Lattuca, 1997)ROSANA0% (1)
- ActivitySheet DISS CadawasDocument45 pagesActivitySheet DISS CadawasRheyjhen Cadawas100% (1)
- 03 SA 2022 VRMMM Executive Summary ReportingTemplate 20220329Document24 pages03 SA 2022 VRMMM Executive Summary ReportingTemplate 20220329Melody ShekharNo ratings yet
- g8 PPT Religion and Ideology Karl MarxDocument36 pagesg8 PPT Religion and Ideology Karl Marxaishareyjumawan29No ratings yet
- Mps 3 - Desain Studi Kohort - Dr. Budi Utomo, DR., M.kes.Document43 pagesMps 3 - Desain Studi Kohort - Dr. Budi Utomo, DR., M.kes.putri permata SariNo ratings yet
- AI Final ReportDocument29 pagesAI Final ReportVishesh BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking Course Day 1Document43 pagesDesign Thinking Course Day 1dharam123_904062105No ratings yet
- Formseminar Module13Document56 pagesFormseminar Module13BharathiNo ratings yet
- Speech Based Parkinson's Disease Detection Using Machine LearningDocument7 pagesSpeech Based Parkinson's Disease Detection Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology GuidebookDocument382 pagesIntroduction To Psychology Guidebooktahsali100% (1)
- Unit 1.1 - Introduction To EpidemiologiDocument21 pagesUnit 1.1 - Introduction To EpidemiologiBENNY BAKARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Change ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Change ManagementPrincess Czarina Delas AlasNo ratings yet
Bloom's Taxonomy - Center For Innovative Teaching and Learning - Northern Illinois University
Bloom's Taxonomy - Center For Innovative Teaching and Learning - Northern Illinois University
Uploaded by
Dr. M. Hannan JamilOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bloom's Taxonomy - Center For Innovative Teaching and Learning - Northern Illinois University
Bloom's Taxonomy - Center For Innovative Teaching and Learning - Northern Illinois University
Uploaded by
Dr. M. Hannan JamilCopyright:
Available Formats
11/2/22, 10:36 PM Bloom's Taxonomy | Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning | Northern Illinois University
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Center for Innovative
Teaching and Learning
Bloom's Taxonomy
Benjamin Bloom (1913-1999) was an educational psychologist who was interested in improving student learning.
In the late 1940s, Bloom and other educators worked on a way to classify educational goals and objectives, which
resulted in three learning categories or "domains" and the taxonomy of categories of thinking:
Cognitive domain (knowledge): verbal or visual intellectual capabilities
Affective domain (attitudes): feelings, values, beliefs
Psychomotor domain (skills): physical skill capabilities
Each of the three domains requires learners to use different sets of mental processing to achieve stated outcomes
within a learning situation. Thus, instructional goals and objectives should be designed to support the different
ways learners process information in these domains.
Each of the three domains requires learners to use different sets of mental processing to achieve
stated outcomes
Original and Revised Taxonomies
The "original" Bloom's taxonomy is still widely used as an educational planning tool by all levels of educators. In
2001, a former student of Bloom published a new version the taxonomy to better fit educational practices of the
21st century. At that time, the six categories were changed to use verbs instead of nouns because verbs describe
actions and thinking is an active process. Both models are portrayed as hierarchical frameworks where each level
is subsumed by the higher, more complex level—students who function at one level have also mastered the
level(s) below it. Using the revised taxonomy, for example, a student who has reached the highest level,
"Creating," has also learned the material at each of the five lower levels. Thus, a student has achieved a high level
of thinking skill.
Bloom’s Taxonomy 1956 Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy 2001
Evaluation
Creating
Synthesis
Evaluating
Analysis
Analyzing
Application
Applying
Comprehension
Understanding
Knowledge Remembering
Why Use Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s Taxonomy can be useful for course design because the levels can help you move students through the
process of learning, from the most fundamental remembering and understanding to the more complex evaluating
and creating (Forehand, 2010).
The taxonomy can assist you as you develop assessments by helping you match course learning objectives to any
given level of mastery. When teaching lower-division, introductory courses, you might measure mastery of
objectives at the lower levels, and when teaching more advanced, upper division courses, you would likely be
assessing students’ abilities at the higher levels of the taxonomy.
Using Bloom's Taxonomy to plan instruction
Instructional objectives are more effective if they include specific verbs that can tell students what they are
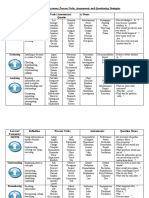
expected to do. The verbs listed in the table below are linked with each level of thinking.
To develop effective and meaningful instruction further, design activities and assessments that challenge students
to move from the most basic skills (remembering) to more complex learning which leads to higher order thinking
(creating).
The table below demonstrates the connections between the levels of thinking, verbs you might use in a learning
objective, sample questions or prompts to generate thinking at that level, and
https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/blooms-taxonomy.shtml#:~:text=Bloom's Revised Taxonomy is one,activities%3B and develop authentic assessments. 1/5
11/2/22, 10:36 PM Bloom's Taxonomy | Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning | Northern Illinois University
Level of Verbs Sample Question / Activities, Products,
Thinking
Statement Stems Outcomes
(Highest to
Lowest)
Creating change
Design a… to… Design a computer
combine
How would you lab for your program
Making compare
improve…? Invent a machine to
Something New compose
Formulate a theory do a specific task
construct
for…? Imagine a new
create
Predict the outcome product
design
of…? and plan a marketing
devise
How would you campaign
formulate
test…? Design a cover image
generate
How would you for a film
hypothesize
estimate the results Formulate a
imagine
for…? hypothesis for…
improve
If you had access to Compose a musical
invent
all resources how score for …
plan
would you deal Devise a problem set
predict
with…? for…
propose What would happen Plan a system of
if…? governance for a
How many ways can utopian society
you…?
Develop a new
proposal which
would…
Create new and
unusual uses for…
Construct a new
model that would
change…
https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/blooms-taxonomy.shtml#:~:text=Bloom's Revised Taxonomy is one,activities%3B and develop authentic assessments. 2/5
11/2/22, 10:36 PM Bloom's Taxonomy | Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning | Northern Illinois University
Evaluating argue
What is your opinion Debate the merits
appraise
of…? of…
Making assess
How would you Write a letter to…
Judgments
check
prove or disprove...? defending your views
Based on
debate
Would it be better on …
Criteria decide
if…? Write an end-of-the-
defend
What would you year report in which
determine
recommend…? you appraise…
dispute
How would you rate Recommend a
editorialize
the…? solution to the
judge
What would you cite problem of…
justify
to defend the Justify a proposal
prioritize
actions…? for…
rate
How could you Select the most
recommend
determine…? useful products for…
select
How would you Prioritize spending
support
prioritize…? for local government
verify Based on what you Assess the credibility
know, how would of sources
you explain…?
What data were used
to make the
conclusion?
How would you
compare the ideas
…?
How would you
compare the people?
How would you
justify...?
Analyzing advertise
What are the parts or Analyze data
analyze
features of …? according to …
Distinguishing
appraise
How is ___ related to Troubleshoot
Different Parts attribute
…? problems with lab
of a Whole
categorize
What is the theme equipment
compare
…? Arrange a
contrast
List the parts … conference and
differentiate
What inferences can sequence all
distinguish
you make …? necessary steps
examine
How would you Make an
identify
classify …? organizational chart
infer
How would you of your unit or
investigate
categorize …? department
organize
What evidence can (categorize)
outline
you find …? Write an ad
separate
What is the campaign for your
sequence
relationship between organization
test …? (advertise)
What is the function Distinguish between
of …? ethical and unethical
What motive is there behavior
…?
Differentiate the
distinct parts of …
https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/blooms-taxonomy.shtml#:~:text=Bloom's Revised Taxonomy is one,activities%3B and develop authentic assessments. 3/5
11/2/22, 10:36 PM Bloom's Taxonomy | Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning | Northern Illinois University
Applying classify
How would you Construct a
construct
use…? marketing strategy
Using
complete
What examples can for your organization
Information in
demonstrate
you find to? Develop a
New Situations dramatize
How would you solve storyboard of digital
examine
___ using what images to
execute
you’ve learned? demonstrate a
illustrate
What approach process
implement
would you use to…? Draw a flow chart
practice
What would result that illustrates a
show
if…? system
solve
What elements Perform the scene
use would you choose to Practice the task
change …? Use the tool to…
What questions Graph the parabola
would you ask in an
interview with …?
Understanding calculate
How would you Explain what you
compare
classify the type think is the main idea
Explaining
define
of...? Identify what you
Information and describe
How would you think are the most
Concepts
discuss
compare or important supporting
distinguish
contrast…? details
expand
How would you Restate the story in
explain
rephrase the your own words
identify
meaning of...? Compare the events
interpret
What facts or ideas leading up to the
locate
show…? two wars
outline
Which statements Interpret the artwork
predict
support…? Translate the
report
What can you say passage into English
restate
about…? Calculate the
translate Which is the best solution using the
answer to…? appropriate formula
How would you
summarize…?
Remembering describe
What is…? List the main events
duplicate
Where is ? Write a timeline of
Recalling or
find
How did ___ events for…
Recognizing list
happen? Recite a poem
Information locate
How would you Locate the parts of
name
describe…? __ on a diagram
recall
Who was…? Underline all the
recognize
Who were the adverbs
reproduce
main…? Define the scientific
state
When did…? terms
tell
Recall… Describe the Fourth
underline
Amendment
write
Verbs and Products/Outcomes Based on the Six Levels of Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy
Adapted from "Bloom's Bakery, an Illustration of Bloom’s Taxonomy" by Argiro, Forehand,
Osteen, & Taylor (2007) and Extending Children’s Special Abilities: Strategies for Primary
Classrooms by Dalton & Smith (1987, pp. 36-37)
Summary
https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/blooms-taxonomy.shtml#:~:text=Bloom's Revised Taxonomy is one,activities%3B and develop authentic assessments. 4/5
11/2/22, 10:36 PM Bloom's Taxonomy | Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning | Northern Illinois University
Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy is one of many tools that faculty can use to create effective and meaningful
instruction. Use it to plan new or revise existing curricula; test the relevance of course goals and objectives;
design instruction, assignments, and activities; and develop authentic assessments.
References
Argiro, M., Forehand, M., Osteen, J., & Taylor, W. (2005). Bloom’s bakery: An illustration of Bloom’s taxonomy.
https://epltt.coe.uga.edu/index.php?title=Bloom%27s_Taxonomy
Dalton, J. & Smith, D. (1987). Extending children’s special abilities: Strategies for primary classrooms. Melbourne,
Australia: Ministry of Education.
Forehand, M. (2010). Bloom’s taxonomy. In M. Orey (Ed.), Emerging perspectives on learning, teaching, and
technology (pp. 41-47). Retrieved from
https://textbookequity.org/Textbooks/Orey_Emergin_Perspectives_Learning.pdf
Smaldino, S. E., Lowther, D. L., & Russell, J. D. (2008). Instructional technology and media for learning. Upper
Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0
International License.
SUGGESTED CITATION
Northern Illinois University Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. (2020). Bloom's taxonomy. In
Instructional guide for university faculty and teaching assistants. Retrieved from
https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide
Contact Us
Center for Innovative
Teaching and Learning
Phone: 815-753-0595
Email: citl@niu.edu
Connect with us on
©
2022
Board of Trustees of Northern Illinois University. All rights reserved. Privacy Notice
1425 W. Lincoln Hwy., DeKalb, IL 60115
https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/blooms-taxonomy.shtml#:~:text=Bloom's Revised Taxonomy is one,activities%3B and develop authentic assessments. 5/5
You might also like
- Hanzi Freinacht The Listening SocietyDocument499 pagesHanzi Freinacht The Listening SocietymefastidiasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To Heritage TourismDocument17 pagesModule 1 - Intro To Heritage Tourismcjons delacruz100% (1)
- GrayScale - The Grid Method - Development Resource Workbook - FINAL EDIT Copy 2Document44 pagesGrayScale - The Grid Method - Development Resource Workbook - FINAL EDIT Copy 2Anbarasi SNo ratings yet
- FSAC - Learning Outcomes WorkshpDocument18 pagesFSAC - Learning Outcomes WorkshpQalab E AbbasNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Domain Was Published in 1956 (Eisner 2000) - Because Many CurriculumDocument6 pagesCognitive Domain Was Published in 1956 (Eisner 2000) - Because Many CurriculumVivian BastoNo ratings yet
- Outcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesDocument6 pagesOutcome Statement That Captures Specifically What Knowledge, Skills, AttitudesJessel GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson 1Document1 pageEapp Lesson 1Arcel V Luceno100% (2)
- Bloom Objectives Planning WorksheetDocument1 pageBloom Objectives Planning WorksheetMalak ZiyadNo ratings yet
- Teaching With The Revised Bloom'StaxonomyDocument33 pagesTeaching With The Revised Bloom'StaxonomyRebenna Bernaldez Lagahit IINo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's TaxonomyDocument29 pagesRevised Bloom's TaxonomyBitoy AlarconNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationsDocument55 pagesTable of SpecificationsMERCY ABOCNo ratings yet
- KognisainsDocument9 pagesKognisainsnurfifahNo ratings yet
- Sample: Sampling DesignsDocument6 pagesSample: Sampling DesignsLovejoylife Castillo RevecheNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Integrating Problem-Solving Educational SoftwareDocument25 pagesTopic 7 - Integrating Problem-Solving Educational SoftwareChee YinNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiDocument20 pagesChapter Iianglo phileNo ratings yet
- Task Creating Vocabulary Mind Maps On Piagets Cognitive Development TheoryDocument3 pagesTask Creating Vocabulary Mind Maps On Piagets Cognitive Development Theory2010092No ratings yet
- 1 Blooms Taxonomy For OBLTDocument26 pages1 Blooms Taxonomy For OBLTABCNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument17 pagesBloom's Revised Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesRea GoNo ratings yet
- Revised Blooms Taxonomy Process Verbs Assessments and Questioning StrategiesDocument2 pagesRevised Blooms Taxonomy Process Verbs Assessments and Questioning StrategiesAnup S. Vibhute DITNo ratings yet
- Writing Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level Thinking: Login Subscribe!Document8 pagesWriting Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level Thinking: Login Subscribe!api-638514534No ratings yet
- Teacher: Autumn Carter Grade Level: 9 - 12 Date: Lesson Title: Creating An Album Cover Using HarmonyDocument5 pagesTeacher: Autumn Carter Grade Level: 9 - 12 Date: Lesson Title: Creating An Album Cover Using Harmonyapi-546172080No ratings yet
- Mariel DepaudhonDocument18 pagesMariel DepaudhonMariel DepaudhonNo ratings yet
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBloom TaxonomyAmirah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Power Point 2Document20 pagesAssessment 1 Power Point 2dhamiltonNGCSUNo ratings yet
- Success CriteriaDocument14 pagesSuccess CriteriaClive AngusNo ratings yet
- RM-Chapter 2Document81 pagesRM-Chapter 2Wubliker BNo ratings yet
- BIOSCI 109 Lab 6 Student HandoutDocument5 pagesBIOSCI 109 Lab 6 Student HandoutGurleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Mapping To The Common Core StandardsDocument32 pagesMapping To The Common Core StandardsShu'eib HassenNo ratings yet
- Writing Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level ThinkingDocument12 pagesWriting Multiple-Choice Questions For Higher-Level ThinkingmazanNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument14 pagesBloom's TaxonomydeepakNo ratings yet
- Bloom TaxonomyDocument7 pagesBloom TaxonomyJeffrey TanNo ratings yet
- Tips and Tricks ELearning Symposium BookletDocument8 pagesTips and Tricks ELearning Symposium BookletTodd ConawayNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument9 pagesModuleMerry Joy Tauro Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Beauty WeeblyDocument8 pagesUnit Plan Beauty Weeblyapi-450160025No ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionDocument17 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: Note That The Top Two Levels Are Essentially Exchanged From The Old To The New VersionNur ZaraNo ratings yet
- Daw Mary Associate Professor English Department Maubin UniversityDocument19 pagesDaw Mary Associate Professor English Department Maubin UniversityEmpressMay ThetNo ratings yet
- Real World Algebra Problems Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesReal World Algebra Problems Lesson Planapi-357246840No ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy: A Practical Approach For Deeper Learning: September 15, 2012Document4 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: A Practical Approach For Deeper Learning: September 15, 2012Krishnamurthy RamasubramanianNo ratings yet
- General Principles in Constructing Classroom Test: Original DomainDocument42 pagesGeneral Principles in Constructing Classroom Test: Original DomainVinjel Libradilla100% (1)
- Full Action Research Action Research Proposal Checklist YesDocument3 pagesFull Action Research Action Research Proposal Checklist YesKatherine ChavezNo ratings yet
- Inverse Operations Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesInverse Operations Lesson Planapi-357246840No ratings yet
- Writing Learning Outcomes WorksheetDocument6 pagesWriting Learning Outcomes WorksheetRoxana MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Design Document For Blended Course Design and DeliveryDocument18 pagesDesign Document For Blended Course Design and Deliveryapi-412970899No ratings yet
- ILO GuideDocument3 pagesILO GuideHala BenghasheerNo ratings yet
- Eng 9 HportfoliobookreviewDocument1 pageEng 9 Hportfoliobookreviewapi-257561679No ratings yet
- WRITING STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES - Rev03Document18 pagesWRITING STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES - Rev03hishahNo ratings yet
- Research Method Rm-Chapter 2Document50 pagesResearch Method Rm-Chapter 2GAMEX TUBENo ratings yet
- Project Conceptualization FormDocument2 pagesProject Conceptualization FormJuliette LaMontagneNo ratings yet
- Blooms PresentationDocument31 pagesBlooms PresentationNitin TembhurnikarNo ratings yet
- How To Write Learning Outcomes WorksheetDocument6 pagesHow To Write Learning Outcomes WorksheetAriana Sanchez Alvarez100% (1)
- Revised-Blooms of Taxonomy of ObjectivesDocument2 pagesRevised-Blooms of Taxonomy of ObjectivesStephenNo ratings yet
- Consideration in Writing A Lesson PlanDocument23 pagesConsideration in Writing A Lesson PlanElyss SantiagoNo ratings yet
- SLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsDocument5 pagesSLOs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cognitive, Psychomotor, and Affective DomainsEricka NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Healtheduc 4Document4 pagesHealtheduc 4Mark ApariciNo ratings yet
- CPSVersion6.1B TreffingrDocument8 pagesCPSVersion6.1B TreffingrihwalNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument8 pagesBloom's TaxonomyMarissaM.PerezNo ratings yet
- Maam Hadir2,.0Document4 pagesMaam Hadir2,.0Julius Rusiana CatubigNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design TheoriesDocument51 pagesInstructional Design Theoriescjust0318No ratings yet
- DLL-3rd Q Day 1Document4 pagesDLL-3rd Q Day 1KèlǐsītǎnKǎPángNo ratings yet
- Week 3 21st CLDocument6 pagesWeek 3 21st CLFlorina Nadorra RamosNo ratings yet
- Bloom'S Taxonomy - Lower-Level and Higher-Level Cognitive SkillsDocument1 pageBloom'S Taxonomy - Lower-Level and Higher-Level Cognitive SkillsLeidyDanielaBenitezPantojaNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1 - Intro CHPE - B 4 - 13-10-2022Document17 pages1 - Intro CHPE - B 4 - 13-10-2022Dr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Using Blooms Taxonomy To Write Learning GoalsDocument2 pagesUsing Blooms Taxonomy To Write Learning GoalsDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Course Alignment - Learning in A Flat WorldDocument7 pagesCourse Alignment - Learning in A Flat WorldDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Assess Series 3 Curriculum Mapping 01062020Document26 pagesAssess Series 3 Curriculum Mapping 01062020Dr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives - The Center For Teaching and Learning - UNC CharlotteDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives - The Center For Teaching and Learning - UNC CharlotteDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy - Master Your Learning ObjectivesDocument13 pagesBloom's Taxonomy - Master Your Learning ObjectivesDr. M. Hannan JamilNo ratings yet
- Week 2 AssignmentsDocument7 pagesWeek 2 AssignmentsELLA ZHOUNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Social Media On Self Concept of AdolescencesDocument24 pagesThe Influence of Social Media On Self Concept of AdolescencesLakshita GomaNo ratings yet
- Kant's A Priori in The Critique of JudgmentDocument4 pagesKant's A Priori in The Critique of JudgmentteletoniqNo ratings yet
- Theories On Human Behavior (UCSP)Document2 pagesTheories On Human Behavior (UCSP)jc nerNo ratings yet
- q1 Week1 Etech DLLDocument4 pagesq1 Week1 Etech DLLBrendzNo ratings yet
- TUGAS 1 - Rizqa Alysya RafianidaDocument200 pagesTUGAS 1 - Rizqa Alysya RafianidaRizqa AlysyaNo ratings yet
- (UCSP 1) 1st Periodic ExamDocument3 pages(UCSP 1) 1st Periodic ExamKrisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - MetacognitionDocument14 pagesModule 1 - MetacognitionMarisol MipantaoNo ratings yet
- Validating The University Entrance English Test To The Vietnam National University: A Conceptual Framework and MethodologyDocument11 pagesValidating The University Entrance English Test To The Vietnam National University: A Conceptual Framework and MethodologyThị Phương Quyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: Bachelor of Science in Information SystemsDocument1 pageJose Rizal Memorial State University: Bachelor of Science in Information Systemsdonz borjNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Crim 7Document11 pagesModule 3 Crim 7Geronimo BazarNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Inverter System Based On Fuzzy ControlDocument8 pagesThree Phase Inverter System Based On Fuzzy ControlNaresh Kumar NNo ratings yet
- Sympathy - WikipediaDocument1 pageSympathy - WikipediaBadhon Chandra SarkarNo ratings yet
- A Short Pause From A School LeaderDocument2 pagesA Short Pause From A School LeaderLG BaganiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem PhiloDocument6 pages2nd Sem PhiloOnin MatreoNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Teacher Mobility and Retention Guidance and Considerations Report 2. REL 2021081Document28 pagesAnalyzing Teacher Mobility and Retention Guidance and Considerations Report 2. REL 2021081Vina YaaqubNo ratings yet
- I. Factors Affecting Academic Planning (Stark & Lattuca, 1997)Document4 pagesI. Factors Affecting Academic Planning (Stark & Lattuca, 1997)ROSANA0% (1)
- ActivitySheet DISS CadawasDocument45 pagesActivitySheet DISS CadawasRheyjhen Cadawas100% (1)
- 03 SA 2022 VRMMM Executive Summary ReportingTemplate 20220329Document24 pages03 SA 2022 VRMMM Executive Summary ReportingTemplate 20220329Melody ShekharNo ratings yet
- g8 PPT Religion and Ideology Karl MarxDocument36 pagesg8 PPT Religion and Ideology Karl Marxaishareyjumawan29No ratings yet
- Mps 3 - Desain Studi Kohort - Dr. Budi Utomo, DR., M.kes.Document43 pagesMps 3 - Desain Studi Kohort - Dr. Budi Utomo, DR., M.kes.putri permata SariNo ratings yet
- AI Final ReportDocument29 pagesAI Final ReportVishesh BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking Course Day 1Document43 pagesDesign Thinking Course Day 1dharam123_904062105No ratings yet
- Formseminar Module13Document56 pagesFormseminar Module13BharathiNo ratings yet
- Speech Based Parkinson's Disease Detection Using Machine LearningDocument7 pagesSpeech Based Parkinson's Disease Detection Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology GuidebookDocument382 pagesIntroduction To Psychology Guidebooktahsali100% (1)
- Unit 1.1 - Introduction To EpidemiologiDocument21 pagesUnit 1.1 - Introduction To EpidemiologiBENNY BAKARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Change ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Change ManagementPrincess Czarina Delas AlasNo ratings yet