Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch.5 Straight Line Graphs
Ch.5 Straight Line Graphs
Uploaded by
Antonio Pérez-LabartaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Year 7-10 Formula SheetDocument6 pagesYear 7-10 Formula SheetEvan TranNo ratings yet
- 1600.io Essential SAT Math Study Notes - V1.3Document46 pages1600.io Essential SAT Math Study Notes - V1.3enonumousthekillerNo ratings yet
- CIS LP Gradients of Lines and Curves WK4 Y11 V2Document11 pagesCIS LP Gradients of Lines and Curves WK4 Y11 V2myeboockNo ratings yet
- 11AS - 5.1 YmxcDocument12 pages11AS - 5.1 Ymxcq76hdrfgy6No ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry of The Straight LineDocument6 pagesCoordinate Geometry of The Straight Linereeta ramNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry FormulasDocument6 pagesAnalytic Geometry FormulasHanie FordNo ratings yet
- Higher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSDocument22 pagesHigher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSbrunaalvesbento.1997No ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsDocument40 pagesP1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsSudeepNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument25 pagesAnalytical GeometryowethungcapheNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series s3 Geometric Sequences and Series - Bpns 468-476 v2Document9 pagesSequences and Series s3 Geometric Sequences and Series - Bpns 468-476 v2spengappNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 Review NotesDocument4 pagesChap 6 Review Notesana.j4m180No ratings yet
- P1 Chp5 StraightLineGraphsDocument35 pagesP1 Chp5 StraightLineGraphsHan ZhengNo ratings yet
- Pure 1 Chapter 5 Straight Line GraphsDocument16 pagesPure 1 Chapter 5 Straight Line GraphsrvqskvNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH Matematika Ekonomi Materi Fungsi Permintaan Dan Fungsi PenawaranDocument28 pagesMAKALAH Matematika Ekonomi Materi Fungsi Permintaan Dan Fungsi PenawaranshintaNo ratings yet
- 2 - The LineDocument18 pages2 - The LineRoxanne Chan OzoaNo ratings yet
- P1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 3 DBT 120922 Perp Length Area FFDocument26 pagesP1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 3 DBT 120922 Perp Length Area FFtotallyxai1No ratings yet
- Equation of A LineDocument17 pagesEquation of A LineMatthew JohnNo ratings yet
- MTH 101 CH 3Document56 pagesMTH 101 CH 3Suli FlamencoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Illustrating and Finding The Slope of A Line Given Two Points, Equation, and GraphDocument18 pagesMathematics: Illustrating and Finding The Slope of A Line Given Two Points, Equation, and Graphbabita serraNo ratings yet
- Point A Parallel Point Parallel Form: Ex. Find The Vector and The CartesianDocument7 pagesPoint A Parallel Point Parallel Form: Ex. Find The Vector and The Cartesianriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Math Lesso File 4 (With Exercizes)Document4 pages10th Grade Math Lesso File 4 (With Exercizes)Andrés CuadraNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan1b-Review of Matrix AlgebraDocument21 pagesPertemuan1b-Review of Matrix AlgebraANDI AULIA HUSENGNo ratings yet
- P1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 2 DBT Equations FFDocument24 pagesP1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 2 DBT Equations FFtotallyxai1No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument10 pagesMathematicsROMEO JR RAMIREZ100% (1)
- BC1 Week 7-ModuleDocument17 pagesBC1 Week 7-ModuleEarl PecsonNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Math Lesso File 3 (With Exercizes)Document6 pages10th Grade Math Lesso File 3 (With Exercizes)Andrés CuadraNo ratings yet
- F4 Add Maths Chap8 Vectors (Student)Document50 pagesF4 Add Maths Chap8 Vectors (Student)Khoo Ning EnNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry-PureDocument13 pagesCoordinate Geometry-PureWynter mulyataNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: General Maths - Unit 2Document63 pagesLinear Programming: General Maths - Unit 2Alem Abebe AryoNo ratings yet
- NFVtb3NDbHJOVk94Q0JuODFJV0I2UHN0VUpUdXJ5eWpWRXc0SzdqcklLTQMathematics I Week 1Document14 pagesNFVtb3NDbHJOVk94Q0JuODFJV0I2UHN0VUpUdXJ5eWpWRXc0SzdqcklLTQMathematics I Week 1a21a21911aNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument48 pagesConic SectionsJames Vhon ReyesNo ratings yet
- CG-1 (Basic) : Xis EducationDocument5 pagesCG-1 (Basic) : Xis EducationAbrar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Pure Matheatics 1: Straight LineDocument22 pagesPure Matheatics 1: Straight LineLaughing HyenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR Week 2 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 2)Document14 pages2nd QTR Week 2 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 2)Erwin dela PuntaNo ratings yet
- Systems of Linear Equations. Part IIDocument16 pagesSystems of Linear Equations. Part IIYE KONo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1ggomo15100% (1)
- Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesAnalytic GeometryJennifer JumaquioNo ratings yet
- GEEC107 Module IVDocument55 pagesGEEC107 Module IVEzekiel Jude VilogNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument7 pagesAnalytic GeometrySamNo ratings yet
- Finding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsDocument9 pagesFinding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsParikNo ratings yet
- 1A CER1 Analytic GeometryDocument2 pages1A CER1 Analytic GeometryJenie EscandorNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Document133 pagesAnalytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Edward RamosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Tangent Line and The DerivativesDocument10 pagesTangent Line and The DerivativesandreaNo ratings yet
- Module Week 5Document3 pagesModule Week 5Carla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Equations and InequalitiesDocument1 pageEquations and InequalitiesMazvitaishe MudamburiNo ratings yet
- MODULE-3 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY - LMS MaterialDocument21 pagesMODULE-3 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY - LMS MaterialKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Complex Integration - ImportantDocument48 pagesComplex Integration - Importantstudy.aaaashishhhNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation 1Document25 pagesLinear Equation 1yaw197100% (1)
- MathematicsDocument41 pagesMathematicsbabita serraNo ratings yet
- M03 The Tangent Lines and The DerivativesDocument30 pagesM03 The Tangent Lines and The DerivativesDa YongNo ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS Quarter 1 Module 3Document6 pagesPRECALCULUS Quarter 1 Module 3alohajilljarabe123No ratings yet
- Orthogonal TrajectoryDocument2 pagesOrthogonal TrajectoryArmenion Mark AllenNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Vectors: Prepared by G. ManuwereDocument41 pagesTopic 2: Vectors: Prepared by G. Manuweretinotenda zirevaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For GeometryDocument2 pagesReviewer For GeometryAlice AsmodeusNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-15 at 12.00.05 PMDocument104 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-15 at 12.00.05 PMEva VentroneNo ratings yet
- Equation of Straight LineDocument5 pagesEquation of Straight LineF4C32 Josephine TamNo ratings yet
- Slope of The Tangent Line and Normal Line To The CurveDocument2 pagesSlope of The Tangent Line and Normal Line To The CurveFrill DropNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ch.6 Projectile MotionDocument1 pageCh.6 Projectile MotionAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.7 Trigonometry and ModellingDocument1 pageCh.7 Trigonometry and ModellingAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 ProbabilityDocument1 pageCh.5 ProbabilityAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Measures of Location and SpreadDocument1 pageCh.2 Measures of Location and SpreadAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 Algebraic ExpressionsDocument1 pageCh.1 Algebraic ExpressionsAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- BEARD, R. Quadrotor Dynamics and Control. Brigham Young University, 2008 - Rev 0.1Document48 pagesBEARD, R. Quadrotor Dynamics and Control. Brigham Young University, 2008 - Rev 0.1Wanderson TeotonioNo ratings yet
- F8 DP 2015 Chlumsky Viktor Thesis PDFDocument89 pagesF8 DP 2015 Chlumsky Viktor Thesis PDFmmihir82No ratings yet
- 3d Transformation MatricesDocument3 pages3d Transformation Matricesvirk_70No ratings yet
- Assignment3 Writeup PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment3 Writeup PDFLeonardo KnuppNo ratings yet
- Robotics BIT Bank-PapersDocument17 pagesRobotics BIT Bank-PapersVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Multiple Choice QuestionDocument46 pagesEngineering Drawing Multiple Choice QuestionARGHA ROYNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Dynamics Homework 1Document6 pagesSpacecraft Dynamics Homework 1TrevorNo ratings yet
- Quotient Space PDFDocument5 pagesQuotient Space PDFritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- Cyclic PolygonsDocument2 pagesCyclic Polygonskepler1729No ratings yet
- DLP Grade 6 MathDocument7 pagesDLP Grade 6 Mathgalange267No ratings yet
- 2 Circular Motion Ex 1 5Document19 pages2 Circular Motion Ex 1 5Kanishk mishraNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Scan Line Conversion AlgorithmDocument25 pagesUnit-3 Scan Line Conversion AlgorithmBinod AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Exercise Congruency Prepare Daily TestDocument3 pagesExercise Congruency Prepare Daily TestmareninopiyaNo ratings yet
- Answers Dubai Tests Math IIDocument10 pagesAnswers Dubai Tests Math IIMMMNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Calc Paper 3Document17 pagesUnit 3: Calc Paper 3MissMillerNo ratings yet
- OMO Spring 2020 ProblemsDocument7 pagesOMO Spring 2020 ProblemsS.M.A NahianNo ratings yet
- The Lagrangian MethodDocument15 pagesThe Lagrangian MethodОгњен Гроздановић100% (1)
- Ellipse Solutions PDFDocument159 pagesEllipse Solutions PDF07 mathsNo ratings yet
- Differential Drive KinematicsDocument8 pagesDifferential Drive KinematicsPratik PatelNo ratings yet
- JEE Adv 2023 Paper 1 MathsDocument10 pagesJEE Adv 2023 Paper 1 MathsDaksh DarjiNo ratings yet
- Mosp2006 HomeworkDocument87 pagesMosp2006 Homeworkmohsen281No ratings yet
- Moment Area MethodDocument6 pagesMoment Area Methodritesh_rajput_10No ratings yet
- 11th National ISMO Class 7 Question Paper With SolutionsDocument10 pages11th National ISMO Class 7 Question Paper With SolutionsMohammad100% (4)
- Basic MathematicsDocument5 pagesBasic MathematicsHamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- TOM Cam & FollowerDocument19 pagesTOM Cam & FollowerRAHUL SOLANKENo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Mathematics 4Document3 pagesPre-Test - Mathematics 4Holly May MontejoNo ratings yet
- Motion in Plane-SubjectiveDocument4 pagesMotion in Plane-Subjective21- VARNIKA DALALNo ratings yet
- MATH Enhancement CDocument2 pagesMATH Enhancement CRoland AcejoNo ratings yet
- Approximation TheoryDocument159 pagesApproximation Theoryvahid100% (1)
Ch.5 Straight Line Graphs
Ch.5 Straight Line Graphs
Uploaded by
Antonio Pérez-LabartaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch.5 Straight Line Graphs
Ch.5 Straight Line Graphs
Uploaded by
Antonio Pérez-LabartaCopyright:
Available Formats
Straight Line Graphs Cheat Sheet Edexcel Pure Year 1
𝒚 = 𝒎𝒙 + 𝒄 Parallel and Perpendicular lines
The gradient 𝑚 of straight-line graphs can be found by taking two random points A (𝑥1 , 𝑦1 ) and B (𝑥2 , 𝑦2 ) on the line and • Parallel lines have the same gradient
considering the horizontal and vertical distance between these two points. • Perpendicular lines are normal to each other. In other words, they make right angles when they intersect.
The formula to calculate any given straight line’s gradient is:
𝑦 −𝑦
• 𝑚 = 𝑥2 −𝑥1
2 1
Straight line equations come in the form of
• 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐, 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑚 𝑖𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑐 𝑖𝑠 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑦 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡.
Or
• 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦 + 𝑐 = 0, 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑎, 𝑏 & 𝑐 𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑙 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟𝑠.
1
The lines 𝑦 = − 𝑥 + 2 and𝑦 = 2𝑥 are perpendicular. If
The lines 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 2 and 𝑦 = 2𝑥 are parallel 2
as they have the same gradient 𝑚 = 2. you know the gradient 𝑚1 of one of the lines, then the
Example 1: Calculate the gradient of the following line. Point A has coordinate (4,3) and point B has coordinate (7,5). The
gradient of the line perpendicular to it is
line passes through both point A and B. 1
• 𝑚2 = − 𝑚
2 1
To calculate any gradient, we need know any two points which the line passes Example 4: Line 𝑙1 is perpendicular to the line 𝑦 = − 𝑥 + 4 and passes through the point (4,6). Find the equation of line 𝑙1 .
3
through. We are given two points, point A (4,3) and point B (7,5). The vertical 1
To find the gradient of the line 𝑙1 , we need to use the rule 𝑚2 = − . The gradient of the line that it is perpendicular
distance between point A and B needs to be divided by the horizontal distance 𝑚1
2
between the points. to is 𝑚1 = − 3
𝑦 −𝑦 5−3 2
• 𝑚 = 𝑥2 −𝑥1 = 7−4 = 3 Hence, the gradient of 𝑙1 is
2 1
1 1 3
𝑚2 = − =− =
𝑚1 2
−3 2
The line passes through the point (4,6)
Example 2: A line 𝑙 has gradient 2 and 𝑦 intercept at (0, −7). The line has equation 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦 + 𝑐 = 0. Find the values of 𝑎, 𝑏
𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 )
and 𝑐. 3
Straight line equations come in the form of 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐, where 𝑚 is the gradient and 𝑐 is the 𝑦 intercept. In the question we 𝑦 − 6 = (𝑥 − 4) → 2𝑦 − 12 = 3𝑥 − 12
2
are given that the gradient is 2, hence 𝑚 = 2, and that the 𝑦 intercept is at (0, −7), hence 𝑐 = −7. Substituting these values 3
into 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐 we get 𝑦= 𝑥
2
𝑦 = 2𝑥 − 7 Length and Area
However, the question asks us to find the values of 𝑎, 𝑏 and 𝑐 on the form of 𝑎𝑥 + 𝑏𝑦 + 𝑐 = 0. Hence, we need to rearrange We can calculate the distance between two points on the line by using the concept of Pythagoras theorem
our equation into this form.
2𝑥 − 𝑦 − 7 = 0 To calculate the distance 𝑑 between points A and B we can use the formula
Therefore, the solutions to this question are 𝑎 = 2, 𝑏 = −1 and 𝑐 = −7.
• 𝑑 = √(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )2 + (𝑦2 − 𝑦1 )2
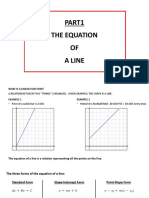
Equations of Straight Lines 1
Instead of relying on using 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑐 to find the equation of a line, in some cases it may be useful to find the equation of a Example 5: 𝑙1 has equation 𝑦 = − 2 𝑥 + 2 and 𝑙2 has equation 𝑦 = 2𝑥. Lines 𝑙1 & 𝑙2 are
line using the following method. perpendicular and intersect at point B. Find this intersection point and area of the
If you know one point on the line and the gradient or two distinct points on the line, we can find the equation of the line by triangle 𝐴𝐵𝑂.
using the formula: The intersection point of the lines are at B
• 𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) 1 5 4 4 8 4 8
2𝑥 = − 𝑥 + 2 → 𝑥 = 2 → 𝑥 = 𝑦 =2× = 𝐵( , )
Example 3: Find the equation of the line that passes through the points (7,2) and (8,5). 2 2 5 5 5 5 5
2
First, we need to work out the gradient 𝑚 4 8
Length AB is 𝐴𝐵 = √(5 − 0)2 + (5 − 2) =
2√5
𝑦2 − 𝑦1 5 − 2 3 5
𝑚= = = =3 4 8 2 4√5
𝑥2 − 𝑥1 8 − 7 1 Length OB is 𝑂𝐵 = √(5 − 0)2 + (5 − 0) =
We can take the point (7,2) or (8,5) to use in the formula. Let us take point (7,2): 5
1 1 2√5 4√5 4
𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) Hence, the area of the triangle 𝐴𝐵𝑂 is 2 × 𝐴𝐵 × 𝑂𝐵 = 2 × × 5 =5
5
𝑦 − 2 = 3(𝑥 − 7)
𝑦 − 2 = 3𝑥 − 21 → 𝑦 = 3𝑥 − 19
https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
https://bit.ly/pmt-edu https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
You might also like
- Year 7-10 Formula SheetDocument6 pagesYear 7-10 Formula SheetEvan TranNo ratings yet
- 1600.io Essential SAT Math Study Notes - V1.3Document46 pages1600.io Essential SAT Math Study Notes - V1.3enonumousthekillerNo ratings yet
- CIS LP Gradients of Lines and Curves WK4 Y11 V2Document11 pagesCIS LP Gradients of Lines and Curves WK4 Y11 V2myeboockNo ratings yet
- 11AS - 5.1 YmxcDocument12 pages11AS - 5.1 Ymxcq76hdrfgy6No ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry of The Straight LineDocument6 pagesCoordinate Geometry of The Straight Linereeta ramNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry FormulasDocument6 pagesAnalytic Geometry FormulasHanie FordNo ratings yet
- Higher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSDocument22 pagesHigher Mathematics Checklist ZETA MATHSbrunaalvesbento.1997No ratings yet
- P1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsDocument40 pagesP1 Chapter 5::: Straight Line GraphsSudeepNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument25 pagesAnalytical GeometryowethungcapheNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series s3 Geometric Sequences and Series - Bpns 468-476 v2Document9 pagesSequences and Series s3 Geometric Sequences and Series - Bpns 468-476 v2spengappNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 Review NotesDocument4 pagesChap 6 Review Notesana.j4m180No ratings yet
- P1 Chp5 StraightLineGraphsDocument35 pagesP1 Chp5 StraightLineGraphsHan ZhengNo ratings yet
- Pure 1 Chapter 5 Straight Line GraphsDocument16 pagesPure 1 Chapter 5 Straight Line GraphsrvqskvNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH Matematika Ekonomi Materi Fungsi Permintaan Dan Fungsi PenawaranDocument28 pagesMAKALAH Matematika Ekonomi Materi Fungsi Permintaan Dan Fungsi PenawaranshintaNo ratings yet
- 2 - The LineDocument18 pages2 - The LineRoxanne Chan OzoaNo ratings yet
- P1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 3 DBT 120922 Perp Length Area FFDocument26 pagesP1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 3 DBT 120922 Perp Length Area FFtotallyxai1No ratings yet
- Equation of A LineDocument17 pagesEquation of A LineMatthew JohnNo ratings yet
- MTH 101 CH 3Document56 pagesMTH 101 CH 3Suli FlamencoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Illustrating and Finding The Slope of A Line Given Two Points, Equation, and GraphDocument18 pagesMathematics: Illustrating and Finding The Slope of A Line Given Two Points, Equation, and Graphbabita serraNo ratings yet
- Point A Parallel Point Parallel Form: Ex. Find The Vector and The CartesianDocument7 pagesPoint A Parallel Point Parallel Form: Ex. Find The Vector and The Cartesianriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Math Lesso File 4 (With Exercizes)Document4 pages10th Grade Math Lesso File 4 (With Exercizes)Andrés CuadraNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan1b-Review of Matrix AlgebraDocument21 pagesPertemuan1b-Review of Matrix AlgebraANDI AULIA HUSENGNo ratings yet
- P1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 2 DBT Equations FFDocument24 pagesP1-Chp5-StraightLineGraphs 2 DBT Equations FFtotallyxai1No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument10 pagesMathematicsROMEO JR RAMIREZ100% (1)
- BC1 Week 7-ModuleDocument17 pagesBC1 Week 7-ModuleEarl PecsonNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Math Lesso File 3 (With Exercizes)Document6 pages10th Grade Math Lesso File 3 (With Exercizes)Andrés CuadraNo ratings yet
- F4 Add Maths Chap8 Vectors (Student)Document50 pagesF4 Add Maths Chap8 Vectors (Student)Khoo Ning EnNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry-PureDocument13 pagesCoordinate Geometry-PureWynter mulyataNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: General Maths - Unit 2Document63 pagesLinear Programming: General Maths - Unit 2Alem Abebe AryoNo ratings yet
- NFVtb3NDbHJOVk94Q0JuODFJV0I2UHN0VUpUdXJ5eWpWRXc0SzdqcklLTQMathematics I Week 1Document14 pagesNFVtb3NDbHJOVk94Q0JuODFJV0I2UHN0VUpUdXJ5eWpWRXc0SzdqcklLTQMathematics I Week 1a21a21911aNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument48 pagesConic SectionsJames Vhon ReyesNo ratings yet
- CG-1 (Basic) : Xis EducationDocument5 pagesCG-1 (Basic) : Xis EducationAbrar ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Pure Matheatics 1: Straight LineDocument22 pagesPure Matheatics 1: Straight LineLaughing HyenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd QTR Week 2 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 2)Document14 pages2nd QTR Week 2 Module 3 Linear Equations in Two Variables (Part 2)Erwin dela PuntaNo ratings yet
- Systems of Linear Equations. Part IIDocument16 pagesSystems of Linear Equations. Part IIYE KONo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 1Document2 pagesAnalytic Geometry 1ggomo15100% (1)
- Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesAnalytic GeometryJennifer JumaquioNo ratings yet
- GEEC107 Module IVDocument55 pagesGEEC107 Module IVEzekiel Jude VilogNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument7 pagesAnalytic GeometrySamNo ratings yet
- Finding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsDocument9 pagesFinding The Equation of A Line From Two PointsParikNo ratings yet
- 1A CER1 Analytic GeometryDocument2 pages1A CER1 Analytic GeometryJenie EscandorNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Document133 pagesAnalytic Geometry 2019 - JKCG - Lecture (Final)Edward RamosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesDocument10 pagesMathematics KSSM Form 3: Chapter 9:straight LinesNUR RAIHAN BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MoeNo ratings yet
- Tangent Line and The DerivativesDocument10 pagesTangent Line and The DerivativesandreaNo ratings yet
- Module Week 5Document3 pagesModule Week 5Carla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Equations and InequalitiesDocument1 pageEquations and InequalitiesMazvitaishe MudamburiNo ratings yet
- MODULE-3 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY - LMS MaterialDocument21 pagesMODULE-3 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY - LMS MaterialKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Complex Integration - ImportantDocument48 pagesComplex Integration - Importantstudy.aaaashishhhNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation 1Document25 pagesLinear Equation 1yaw197100% (1)
- MathematicsDocument41 pagesMathematicsbabita serraNo ratings yet
- M03 The Tangent Lines and The DerivativesDocument30 pagesM03 The Tangent Lines and The DerivativesDa YongNo ratings yet
- PRECALCULUS Quarter 1 Module 3Document6 pagesPRECALCULUS Quarter 1 Module 3alohajilljarabe123No ratings yet
- Orthogonal TrajectoryDocument2 pagesOrthogonal TrajectoryArmenion Mark AllenNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Vectors: Prepared by G. ManuwereDocument41 pagesTopic 2: Vectors: Prepared by G. Manuweretinotenda zirevaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For GeometryDocument2 pagesReviewer For GeometryAlice AsmodeusNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-15 at 12.00.05 PMDocument104 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-15 at 12.00.05 PMEva VentroneNo ratings yet
- Equation of Straight LineDocument5 pagesEquation of Straight LineF4C32 Josephine TamNo ratings yet
- Slope of The Tangent Line and Normal Line To The CurveDocument2 pagesSlope of The Tangent Line and Normal Line To The CurveFrill DropNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ch.6 Projectile MotionDocument1 pageCh.6 Projectile MotionAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.7 Trigonometry and ModellingDocument1 pageCh.7 Trigonometry and ModellingAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 ProbabilityDocument1 pageCh.5 ProbabilityAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Measures of Location and SpreadDocument1 pageCh.2 Measures of Location and SpreadAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- Ch.1 Algebraic ExpressionsDocument1 pageCh.1 Algebraic ExpressionsAntonio Pérez-LabartaNo ratings yet
- BEARD, R. Quadrotor Dynamics and Control. Brigham Young University, 2008 - Rev 0.1Document48 pagesBEARD, R. Quadrotor Dynamics and Control. Brigham Young University, 2008 - Rev 0.1Wanderson TeotonioNo ratings yet
- F8 DP 2015 Chlumsky Viktor Thesis PDFDocument89 pagesF8 DP 2015 Chlumsky Viktor Thesis PDFmmihir82No ratings yet
- 3d Transformation MatricesDocument3 pages3d Transformation Matricesvirk_70No ratings yet
- Assignment3 Writeup PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment3 Writeup PDFLeonardo KnuppNo ratings yet
- Robotics BIT Bank-PapersDocument17 pagesRobotics BIT Bank-PapersVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Multiple Choice QuestionDocument46 pagesEngineering Drawing Multiple Choice QuestionARGHA ROYNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Dynamics Homework 1Document6 pagesSpacecraft Dynamics Homework 1TrevorNo ratings yet
- Quotient Space PDFDocument5 pagesQuotient Space PDFritik dwivediNo ratings yet
- Cyclic PolygonsDocument2 pagesCyclic Polygonskepler1729No ratings yet
- DLP Grade 6 MathDocument7 pagesDLP Grade 6 Mathgalange267No ratings yet
- 2 Circular Motion Ex 1 5Document19 pages2 Circular Motion Ex 1 5Kanishk mishraNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Scan Line Conversion AlgorithmDocument25 pagesUnit-3 Scan Line Conversion AlgorithmBinod AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Exercise Congruency Prepare Daily TestDocument3 pagesExercise Congruency Prepare Daily TestmareninopiyaNo ratings yet
- Answers Dubai Tests Math IIDocument10 pagesAnswers Dubai Tests Math IIMMMNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Calc Paper 3Document17 pagesUnit 3: Calc Paper 3MissMillerNo ratings yet
- OMO Spring 2020 ProblemsDocument7 pagesOMO Spring 2020 ProblemsS.M.A NahianNo ratings yet
- The Lagrangian MethodDocument15 pagesThe Lagrangian MethodОгњен Гроздановић100% (1)
- Ellipse Solutions PDFDocument159 pagesEllipse Solutions PDF07 mathsNo ratings yet
- Differential Drive KinematicsDocument8 pagesDifferential Drive KinematicsPratik PatelNo ratings yet
- JEE Adv 2023 Paper 1 MathsDocument10 pagesJEE Adv 2023 Paper 1 MathsDaksh DarjiNo ratings yet
- Mosp2006 HomeworkDocument87 pagesMosp2006 Homeworkmohsen281No ratings yet
- Moment Area MethodDocument6 pagesMoment Area Methodritesh_rajput_10No ratings yet
- 11th National ISMO Class 7 Question Paper With SolutionsDocument10 pages11th National ISMO Class 7 Question Paper With SolutionsMohammad100% (4)
- Basic MathematicsDocument5 pagesBasic MathematicsHamza KahemelaNo ratings yet
- TOM Cam & FollowerDocument19 pagesTOM Cam & FollowerRAHUL SOLANKENo ratings yet
- Pre-Test - Mathematics 4Document3 pagesPre-Test - Mathematics 4Holly May MontejoNo ratings yet
- Motion in Plane-SubjectiveDocument4 pagesMotion in Plane-Subjective21- VARNIKA DALALNo ratings yet
- MATH Enhancement CDocument2 pagesMATH Enhancement CRoland AcejoNo ratings yet
- Approximation TheoryDocument159 pagesApproximation Theoryvahid100% (1)