Professional Documents
Culture Documents
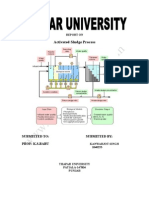
Activated Sludge Process
Activated Sludge Process
Uploaded by
Akshay Uday0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesActivated sludge refers to a mixed culture of microorganisms grown in an aeration tank to break down organic matter in wastewater. It consists mainly of bacteria but also contains fungi, protozoa, and invertebrates. The activated sludge process was developed in 1914 and works by suspending sludge flocs in an aerated tank where they use organic pollutants for growth, transforming the waste into new cell material, water, carbon dioxide, and energy. It is a multi-chamber process that uses highly concentrated microbes to degrade organics and remove nutrients, producing high-quality effluent.
Original Description:
A
Original Title
activated sludge process
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentActivated sludge refers to a mixed culture of microorganisms grown in an aeration tank to break down organic matter in wastewater. It consists mainly of bacteria but also contains fungi, protozoa, and invertebrates. The activated sludge process was developed in 1914 and works by suspending sludge flocs in an aerated tank where they use organic pollutants for growth, transforming the waste into new cell material, water, carbon dioxide, and energy. It is a multi-chamber process that uses highly concentrated microbes to degrade organics and remove nutrients, producing high-quality effluent.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesActivated Sludge Process
Activated Sludge Process
Uploaded by
Akshay UdayActivated sludge refers to a mixed culture of microorganisms grown in an aeration tank to break down organic matter in wastewater. It consists mainly of bacteria but also contains fungi, protozoa, and invertebrates. The activated sludge process was developed in 1914 and works by suspending sludge flocs in an aerated tank where they use organic pollutants for growth, transforming the waste into new cell material, water, carbon dioxide, and energy. It is a multi-chamber process that uses highly concentrated microbes to degrade organics and remove nutrients, producing high-quality effluent.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Activated Sludge
Activated sludge refers to a flocculent
culture of organisms developed in
aeration tanks under controlled
conditions, according to WEF.
Activated sludge is typically brown in
color. Activated sludge is also known as
waste activated biosolids or waste
activated solids.
The sludge consists of a mixed blend of
microorganisms, 95% of which are a
variety of mostly aerobic species of
bacteria, according to Science Direct.
Activated sludge also contains
populations of fungi, protozoa and higher
forms of invertebrates.
Equipment
According to Dokuz Eylill University, the
basic function of the activated sludge
process is to establish and maintain a
viable population of microorganisms.
There are several stages necessary for
treatment.
Aeration Tank
An aeration tank provides the required
detention time and ensures that the
activated sludge and the influent
wastewater are thoroughly mixed.
Mechanical or Diffused Aeration
Mechanical aeration systems use agitators
or mixers to mix air and mixed liquor.
Diffused aeration systems use pressurized
air released through diffusers near the
bottom of the tank.
Settling Tank
Activated sludge systems are equipped
with plain settling tanks designed to
provide approximately 2 to 4 hours of
hydraulic detention time.
Return Sludge & Activated Sludge
The return sludge system includes pumps,
a timer or variable speed drive, and a
flow measurement device. An activated
sludge system consists of the same
components but in some cases, the waste
activated sludge withdrawal is
accomplished by adjusting valves on the
return system.
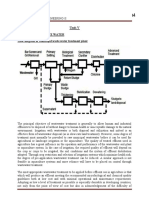
The Activated Sludge Process
The activated sludge process is designed
to speed up the rate of decomposition of
waste material in water and was first
developed in 1914, according to the
International Water Association.
The activated sludge process was first
tested at the Manchester - Davyhulme
Wastewater Treatment Plant, in a
"mobile" pilot-plant. Most parts of the
pilot-plant unit were made of wood, but
the installation already exhibited most
characteristic features of the activated
sludge process used today. This includes
the continuous-flow arrangements with
separate clarifiers and activated sludge
recycle and the fill-and-draw
arrangement, also known as a sequencing
batch reactor (SBR), according to the
International Water Association.
The activated sludge process is a means of
treating both municipal and industrial
wastewater.
The activated sludge process is a multi-
chamber reactor unit that uses highly
concentrated microorganisms to degrade
organics and remove nutrients from
wastewater, producing quality effluent.
The goal is to maintain aerobic conditions
and to keep the activated sludge
suspended. To achieve this, a continuous
and well-timed supply of oxygen is
re uired.
= vtWD
- WATER &WASTESOIGEST
Floes of bacteri a are suspen ded and
mixed with wastew ater in an aerated
tank, and the bacteri a use the organic
polluta nts to grow and transfo rm it to
energy, water, CO2 and new cell materia l.
The floes can be remove d in the
second ary clarifie r by gravity settling and
some of this sludge is recycle d from the
clarifie r back to the reactor . The effluen t
can then be dischar ged to final polishin g.
Challenges
Activated sludge sewage treatme nt is
ideally comple ted in a central ized
treatme nt facility and the treatme nt of the
sludge can occur in most climates. Colder
environ ments reduce the treatme nt
capacit y, howeve r.
According to the Pennsy lvania
Depart ment of Enviro nmenta l Protect ion
(DEP), the conven tional activat ed sludge
process is suscept ible to failure from
sbock ]aa d ~ n11 P tn it
You might also like
- The EZ Guide to Aeroponics, Hydroponics and AquaponicsFrom EverandThe EZ Guide to Aeroponics, Hydroponics and AquaponicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Ijciet 08 09 044 PDFDocument7 pagesIjciet 08 09 044 PDFnivedhithaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Suspended Treatment ProcessDocument2 pagesAerobic Suspended Treatment ProcessMinjdeDiosNo ratings yet
- Actvated Sludge Process SSWMDocument28 pagesActvated Sludge Process SSWMGREENLAB ECL TECHNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi Secondary Treatments: Chapter - 12 Biological Unit ProcessesDocument9 pagesUnit Vi Secondary Treatments: Chapter - 12 Biological Unit ProcessesAdesh DeshbhratarNo ratings yet
- Sludge ProcessDocument16 pagesSludge ProcessArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Survey of Materials and Technologies Developed byDocument18 pagesSurvey of Materials and Technologies Developed bySredha BabyNo ratings yet
- Activated SludgeDocument11 pagesActivated SludgeMuhammad Hafizh AzhariNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument15 pagesWater727822tucv025No ratings yet
- Active Sludge PDFDocument8 pagesActive Sludge PDFDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Disinfection of Treated Waste WaterDocument30 pagesDisinfection of Treated Waste WaterHCAG01No ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument24 pagesWaste Water TreatmentNaevisweloveuNo ratings yet
- 109.05 SEO DisinfAection Uv Sterilizer & FlowmeterDocument97 pages109.05 SEO DisinfAection Uv Sterilizer & FlowmeteribrahimNo ratings yet
- 109.03 SEO Blower & Diffusers Biological TreatmentDocument52 pages109.03 SEO Blower & Diffusers Biological TreatmentibrahimNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge - Print VersionDocument5 pagesActivated Sludge - Print VersionAnurag SatyarthNo ratings yet
- Activity On CGMPDocument6 pagesActivity On CGMPmaxi1162No ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesWaste Water Treatmentstylish eagle100% (1)
- Glossary of Wastewater TermsDocument9 pagesGlossary of Wastewater TermsEmina ŠaćirbegovićNo ratings yet
- Layman's ReportDocument9 pagesLayman's ReportIRTANo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge Treatment Process - Concept and System DesignDocument7 pagesActivated Sludge Treatment Process - Concept and System DesignSaiteja NethaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Treatment Technologies For Recycle Reuse of Domestic WastewaterDocument9 pagesAdvanced Treatment Technologies For Recycle Reuse of Domestic Wastewaterنيرمين احمدNo ratings yet
- Post - Seafood Processing UnitDocument4 pagesPost - Seafood Processing UnitRavishankar ANo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesWastewater Treatment Thesis Topicsshannongutierrezcorpuschristi100% (2)
- Group1 Mine EnvironmentDocument18 pagesGroup1 Mine EnvironmentLAURENT JIBUNGENo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Part-1 - RCE602Document6 pagesUnit 5 Part-1 - RCE602Amit Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Dauzuc en PDFDocument14 pagesDauzuc en PDFdan ivanNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocument67 pagesEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNo ratings yet
- Activated SludgeDocument26 pagesActivated SludgeNoshaba NoreenNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument23 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsEnrique MartinezNo ratings yet
- WATER Treatment ProcessDocument41 pagesWATER Treatment ProcessPrakash VermaNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument5 pagesActivated Sludge ProcessshambhavipathakNo ratings yet
- Terminology: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument27 pagesTerminology: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleHaider Al-kadhimiNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument32 pagesSewage Treatment Plantjamroze496114100% (2)
- Treatment of Water: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No.: Semester: DepartmentDocument8 pagesTreatment of Water: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No.: Semester: DepartmentFraz AliNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatment of Wastewater Using PDFDocument9 pagesBiological Treatment of Wastewater Using PDFPhạm LinhNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument12 pagesActivated Sludge Processtvijayaraja100% (1)
- Biological Treatment Checklist - Suspended Growth - Activated Sludge, Oxidation DitchesDocument14 pagesBiological Treatment Checklist - Suspended Growth - Activated Sludge, Oxidation DitchesMagin Idelfonso TorreblancaNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Advance C-Tech Technology For Reuse of Sewage in Sewage Treatment Plants of Navi MumbaiDocument3 pagesUtilization of Advance C-Tech Technology For Reuse of Sewage in Sewage Treatment Plants of Navi MumbaiJammi NagrajNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1Document11 pagesLecture - 3 - Wastewater Treatment - Aerobic and Anaerobic-1negaathanipalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Rozelle 1987Document7 pagesRozelle 1987Nermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- Article Fil Conducteur EautarcieDocument5 pagesArticle Fil Conducteur EautarcieGérardNo ratings yet
- Dunne TheuseofStreamingCurrentMonitorsinoptimisingcoagulantdosageinWater CERIProceedings PDFDocument7 pagesDunne TheuseofStreamingCurrentMonitorsinoptimisingcoagulantdosageinWater CERIProceedings PDFAna Carolina FrançaNo ratings yet
- Caustic RecoveryDocument7 pagesCaustic RecoverysivachemtechNo ratings yet
- Sewage-Fed AquacultureDocument15 pagesSewage-Fed Aquacultureapi-3803371100% (2)
- Classification of Water PollutantsDocument11 pagesClassification of Water PollutantsNaveenNo ratings yet
- Shambhunath Institute of Engineering and Technology AllahabadDocument20 pagesShambhunath Institute of Engineering and Technology AllahabadabhishekNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment PlantsDocument11 pagesWater Treatment PlantsamshafirozNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Watch The Video MaterialsDocument4 pagesInstructions: Watch The Video MaterialslkjhsldNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge Process De..Document4 pagesActivated Sludge Process De..emmaNo ratings yet
- Waste Water TreatmentDocument7 pagesWaste Water TreatmentBusi_SeleshoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0011916400900018 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0011916400900018 MainAnita YunusNo ratings yet
- Sewage TreatmentDocument21 pagesSewage TreatmentFemal Rambhiya100% (1)
- Treatment of Water: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No.: Semester: DepartmentDocument7 pagesTreatment of Water: Submitted To: Submitted By: Registration No.: Semester: DepartmentFraz AliNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Digestion-Deo KnjigeDocument16 pagesAerobic Digestion-Deo Knjigemilenaknezevic.mikanaNo ratings yet
- Four Years Experience With A New Chlorine Dosing Regime Against MacrofoulingDocument7 pagesFour Years Experience With A New Chlorine Dosing Regime Against MacrofoulingyvbssvNo ratings yet
- Science Educational Activity at TheDocument4 pagesScience Educational Activity at ThemoiiifitbituserNo ratings yet
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROFrom EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial RORating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Aquaponics system, fish. Volume 1: Sistemas de acuaponíaFrom EverandAquaponics system, fish. Volume 1: Sistemas de acuaponíaNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- Standard methods for the examination of water and sewageFrom EverandStandard methods for the examination of water and sewageNo ratings yet
- 7 - AnalysisDocument5 pages7 - AnalysisAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- 2pce7101 Process Equipment DesignDocument2 pages2pce7101 Process Equipment DesignAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- STUCOR - UG Higher Semester Except Sem IIIDocument1 pageSTUCOR - UG Higher Semester Except Sem IIIAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Modes of Mass TransferDocument20 pagesModes of Mass TransferAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Prob and Stats unit-IIIDocument5 pagesProb and Stats unit-IIIAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Annexure 1Document1 pageAnnexure 1Akshay UdayNo ratings yet
- GE6351 Environmental Science and EngineeringDocument261 pagesGE6351 Environmental Science and EngineeringAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: CH8491 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis 2019-2020Document24 pagesUnit 2: CH8491 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis 2019-2020Akshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Spectroscopical Methods of AnalysisDocument28 pagesUnit I Introduction To Spectroscopical Methods of AnalysisAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Separations: Unit OperationDocument5 pagesMechanical Separations: Unit OperationAkshay UdayNo ratings yet
- Pleurobrachia & Cydippid LarvaDocument18 pagesPleurobrachia & Cydippid LarvaAkshay UdayNo ratings yet