Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wetlnd Model
Wetlnd Model
Uploaded by
chandni ShuklaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wetlnd Model
Wetlnd Model
Uploaded by
chandni ShuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION:
Wetland are distinct ecosystem, where dry land is Wetlands are also known as the kidneys of Earth. The wetland is rich in biodiversity and has
saturated by water.The primary factor that They purify the waters that pass through them and species representing both India's Western
distinguishes wetlands from other landforms or water distil out poisonous sediments, chemicals, and Ghats and the Deccan Plateau Bio Geographical
Zones. To date, 536 species of aquatic and
bodies is the characteristic vegetation of pollutants. terrestrial plants, eight species of mammals, 265
aquatic plants, adapted to the unique hydric soil. species of birds, 24 species of freshwater fish,
Wetlands provide a wide range of important resources and 41 species of butterflies from the area have
and ecosystem services such as food, water, fibre, been reported. Mumbai's Central Institute of
groundwater recharge, water purification, flood Fisheries Education reported 24 fish species in
moderation, erosion control the Nandur Madhameshwar wetland from ten
and climate regulation. families. However, it was only in 1994 that the
Wildlife Wing of the Forest Department began
efforts to protect, maintain and conserve it. The
State of Maharashtra has a large number of problems in settling the claims of local people,
unrecognized wetland bodies which require immediate other agencies and departments on the land,
attention before they degrade and dry Deccan Plateau the resource study of the area fluctuations in
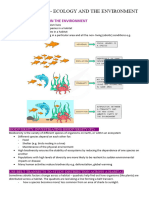
faces shortage of water during the summer season and Conceptual model of formation of Wetlands. the population of migratory birds.
thus to overcome this scarcity of water the British Wetland protection aimed at protecting and
Government had designed Godavari Canal System by restoring areas such as swamps, marshes, and
constructing dams across the river Dama at Nandgaon bogs where water occurs at or near the Earth's
and at the confluence of rivers Godavari and Kadva at surface. Wetlands occupy at least six percent of
Nandur Madhameshwar in the years 1907-1913. The the Earth and, because of the ecological services
water stored in this canal is later then released to
they offer, have become a focal issue for
nearby areas like Aurangabad and Ahmednagar for
conservation With a large number of coastal and
irrigation and drinking purposes. This Wetland was
inland wetlands, the state of Maharashtra is
formed due to continuous deposition of silt and
blessed. These are one coastal Wetland in
organic matter which was carried by the Godavari and
Mumbai's Sewri and five inland wetlands in the
Kadva river streams.
districts of Ujni in Pune, Nandur Madhyameshwar
in Nashik Jayakwadi in Aurangabad, Lonar in
This has led to the most distinctive and biologically rich
Buldhana, and Navegaon in Gondia. The Nandur
Wetland in the state of Maharashtra This Wetland
Madhyameshwar in Nashik is one of the most
Ecosystem is a home for major migratory birds and
significant ones. The flow of water carries a lot of
thus there is a need of high global conservation for the
silt and organic matter and the same is deposited
bio-diversity
in Nandur Madhameshwar Lake For the last few
years, the deposition process has been going on
and the water level in the lake has been shallow.
The deposition of silt has also enriched the
agricultural lands surrounding it and enriched the
BACKGROUND STUDY: habitats in and around body of water.
Wetlands are distinct ecosystems where water meets
land. It is flooded by water either permanently or
seasonally where there is sudden depression in land
Wetlands are also considered the most biologically
diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide
range of plant and animal life.
WETLAND CONSERVATION AND RESEARCH CENTER SAI .S. SHEVDE 05-AR-18-48
You might also like
- Uae Dubai Local Order 61 (1991)Document46 pagesUae Dubai Local Order 61 (1991)DaiNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment Plant Boq Unit 128Document6 pagesEffluent Treatment Plant Boq Unit 128shekharshindeNo ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of PlumbingDocument11 pagesThe Basic Principles of PlumbingJoyce Lapuz100% (1)
- Introduction To Ramsar and WetlandsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ramsar and WetlandsNitish ChiniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ramsar and WetlandsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ramsar and WetlandsNitish ChiniaNo ratings yet
- 1905-1910 (4257) HokersarDocument6 pages1905-1910 (4257) HokersarstoicNo ratings yet
- The Lost Paradise (Manchar Lake) : Environmental Protection Agency, Government of Sindh, Karachi, PakistanDocument11 pagesThe Lost Paradise (Manchar Lake) : Environmental Protection Agency, Government of Sindh, Karachi, PakistanHamzaNo ratings yet
- HiiiDocument27 pagesHiiiHarshit BishtNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of PakistanDocument56 pagesWetlands of Pakistanlajbarkhan balochNo ratings yet
- Community Involvement in Conservation of Natural Resources: Case Studies From Rajasthan, IndiaDocument4 pagesCommunity Involvement in Conservation of Natural Resources: Case Studies From Rajasthan, IndiaAdvanced Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - Impact On The Sundarbans:: A Case StudyDocument9 pagesClimate Change - Impact On The Sundarbans:: A Case StudyAshok GopaleNo ratings yet
- Environment EcologyDocument20 pagesEnvironment EcologyPriya KumariNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentMurali SambhuNo ratings yet
- E Paper Published On Env. & EcologyDocument9 pagesE Paper Published On Env. & EcologyMrigangka MalakarNo ratings yet
- Sangat Sindh Report On DEh Akro-11 Wetland Seminar Report - Doc WWFDocument5 pagesSangat Sindh Report On DEh Akro-11 Wetland Seminar Report - Doc WWFjavedkk83No ratings yet
- WetlandDocument45 pagesWetlandnawin1234No ratings yet
- Lecture PPT - 13Document24 pagesLecture PPT - 13Kawsar Jahan Binti 1511787030No ratings yet
- Mini-Forest Revolution: Woods & Water (Chapter 3)Document14 pagesMini-Forest Revolution: Woods & Water (Chapter 3)Chelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- Environment and EcologyDocument31 pagesEnvironment and EcologySuresh VermaNo ratings yet
- Wetland and Its ConservationDocument4 pagesWetland and Its ConservationHarish RaasuNo ratings yet
- Ichthyofaunal Diversity and Anthropogenic Stress On Naitara-Chautara Wetland of Goalpara, Assam, India.Document4 pagesIchthyofaunal Diversity and Anthropogenic Stress On Naitara-Chautara Wetland of Goalpara, Assam, India.jugalNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Wetland Environment: A Case Study of Dora Beel of Kamrup District AssamDocument7 pagesDegradation of Wetland Environment: A Case Study of Dora Beel of Kamrup District AssamInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- WILDLIFEDocument35 pagesWILDLIFEnayab gulNo ratings yet
- Ramsar Wetlands of India 02.02.2021 GreatDocument298 pagesRamsar Wetlands of India 02.02.2021 GreatSYNERGY SIDDHARTH IAS ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- Env 118 187Document70 pagesEnv 118 187Jeffrish raidnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Tourism Impact On The Environment: Preserve, Conserve, Enhance or Even RejuvenateDocument16 pagesChapter 3 Tourism Impact On The Environment: Preserve, Conserve, Enhance or Even RejuvenateJUN GERONANo ratings yet
- Water History, Art, and Culture Water History, Art, and CultureDocument51 pagesWater History, Art, and Culture Water History, Art, and CultureDrn PskNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Its Conservation in The SundarbanDocument28 pagesBiodiversity and Its Conservation in The SundarbanŠå Ňđ ÏpNo ratings yet
- 2 WetlandmanagementDocument12 pages2 WetlandmanagementM suleman DarvishNo ratings yet
- SundarbansDocument30 pagesSundarbansSadia Afrin Lipa 2235335660No ratings yet
- ST - John's Water ConservationDocument19 pagesST - John's Water ConservationAbhishekShubhamGabrielNo ratings yet
- Wetland ConservationDocument1 pageWetland ConservationShiven KanodiaNo ratings yet
- The Sunderbans Biosphere A Study On Uncertainties PDFDocument9 pagesThe Sunderbans Biosphere A Study On Uncertainties PDFArchita DuttaNo ratings yet
- WetlandDocument35 pagesWetlandaqsaatahir786No ratings yet
- Natural ResourceDocument30 pagesNatural ResourcejdidiwoodkdorNo ratings yet
- Kawar Lake Bird Sanctuary - 02Document23 pagesKawar Lake Bird Sanctuary - 02Bipin SinghNo ratings yet
- Wetland of GujaratDocument24 pagesWetland of Gujaratvishal makwanaNo ratings yet
- 21950-Article Text-78643-3-10-20160113 PDFDocument7 pages21950-Article Text-78643-3-10-20160113 PDFMd.Faisal Ahmed Anik 1530127630No ratings yet
- Water Resources: Unit III Unit III Unit III Unit III Unit IIIDocument12 pagesWater Resources: Unit III Unit III Unit III Unit III Unit IIIMRINMOY SARMANo ratings yet
- Legy 206Document12 pagesLegy 206praveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Wetlands Ecosystem The AnniversaryDocument3 pagesWetlands Ecosystem The Anniversarykaushik247No ratings yet
- Art20197913 PDFDocument8 pagesArt20197913 PDFAnannya RNo ratings yet
- WetlandsDocument10 pagesWetlandsRaviteja VallamsettiNo ratings yet
- Modeste Natural Infrastructure Project - ALUS - 2022Document32 pagesModeste Natural Infrastructure Project - ALUS - 2022Gull GillNo ratings yet
- Wetlands: Why Should I Care ?Document2 pagesWetlands: Why Should I Care ?Rishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Human Impact On Mangrove ForestDocument30 pagesHuman Impact On Mangrove Forestash100% (1)
- Eec 58Document10 pagesEec 58Mayurakshi BhuyanNo ratings yet
- FreshwaterHydrological Cycle PDFDocument1 pageFreshwaterHydrological Cycle PDFSara ScarlatescuNo ratings yet
- WetDocument8 pagesWetSuresh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Madayi paraDocument4 pagesMadayi paraNikilsha K0% (1)
- SUPW Project Prisha Dalal 10-bDocument14 pagesSUPW Project Prisha Dalal 10-bprisha dalalNo ratings yet
- Sjees V1 E1 1013Document8 pagesSjees V1 E1 1013Cristina MendozaNo ratings yet
- ENV 305 Final QuestionsDocument5 pagesENV 305 Final QuestionsAfsin RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Water HarvestingDocument7 pagesWater HarvestingPradip TripuraNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of PakistanDocument11 pagesWetlands of Pakistanbutterfily75% (4)
- Ecological Understanding of Anchar, Lake, KashmirDocument12 pagesEcological Understanding of Anchar, Lake, KashmirESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNo ratings yet
- Env. NotesDocument104 pagesEnv. NotesVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Day-62 WebDocument22 pagesDay-62 Websubhadeep sarkarNo ratings yet
- Ecological Zones and Succession in The SundarbansDocument19 pagesEcological Zones and Succession in The Sundarbanstanjidur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Prof. Mrinal K. Sen, Director, CSIR-NGRI, Hyderabad Dr. M.J.Nandan, Sr. ScientistDocument27 pagesProf. Mrinal K. Sen, Director, CSIR-NGRI, Hyderabad Dr. M.J.Nandan, Sr. ScientistSharad MusaleNo ratings yet
- Prospects of Ornamental Fish Culture in Seasonal Water Bodies AssamDocument6 pagesProspects of Ornamental Fish Culture in Seasonal Water Bodies AssamBalakrishna GopinathNo ratings yet
- Class10 Geography Assignment 7Document7 pagesClass10 Geography Assignment 7Binode Sarkar100% (1)
- Floodplain Wetland Biota in the Murray-Darling Basin: Water and Habitat RequirementsFrom EverandFloodplain Wetland Biota in the Murray-Darling Basin: Water and Habitat RequirementsKerrylee RogersNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution ProjectDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Pollution ProjectSarang MagarNo ratings yet
- An Bord Pleanala Observation From Puckane Development Association May 17th 2011Document17 pagesAn Bord Pleanala Observation From Puckane Development Association May 17th 2011Puckane PocanNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Water PurificatioDocument39 pagesCase Study On Water Purificatiopankaj100% (1)
- Scaleban BrochureDocument20 pagesScaleban BrochureherikNo ratings yet
- Design Criteria SBRDocument8 pagesDesign Criteria SBRmah61No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 - Ecology and EnvironmentDocument9 pagesBiology Unit 4 - Ecology and Environmentthisismashael07No ratings yet
- Waste Water Treatment 2014Document81 pagesWaste Water Treatment 2014ankur neogNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Cardboard Plant WastewaterDocument3 pagesTreatment of Cardboard Plant WastewaterBryan Alberto Cueva VásquezNo ratings yet
- st15122 PDFDocument10 pagesst15122 PDFJose María Ureta UrzúaNo ratings yet
- HEALTH9 SLeM2 Q1Document10 pagesHEALTH9 SLeM2 Q1venice pitallarNo ratings yet
- Scale and Dirt Control - Munters - PWDocument3 pagesScale and Dirt Control - Munters - PWDon GivsyitNo ratings yet
- Water Supply CalculationDocument21 pagesWater Supply CalculationsmsarchNo ratings yet
- Where Is Location of Socket Outlet AC?: PLC Room FFL. EL. (+) 8.800 LWS Electrical Control Room FFL. EL. (+) 8.800 LWSDocument1 pageWhere Is Location of Socket Outlet AC?: PLC Room FFL. EL. (+) 8.800 LWS Electrical Control Room FFL. EL. (+) 8.800 LWSharisNo ratings yet
- EHS Accomplishments - Kennedy Valve CoDocument1 pageEHS Accomplishments - Kennedy Valve CoRaza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- RunoffDocument19 pagesRunoffفردوس سليمانNo ratings yet
- On The Effectiveness of Watermelon Seeds As Coagulant For Removal of Turbidity and Colour in Beverage Industry WastewaterDocument2 pagesOn The Effectiveness of Watermelon Seeds As Coagulant For Removal of Turbidity and Colour in Beverage Industry WastewaterAbiodun GbengaNo ratings yet
- RRB Junior Engineer Civil Solved Model Question Paper 4Document21 pagesRRB Junior Engineer Civil Solved Model Question Paper 4Naruttam DasNo ratings yet
- Sewage Treatment PlantDocument9 pagesSewage Treatment PlantMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- Water Purification System. Oquin, Jervin.Document8 pagesWater Purification System. Oquin, Jervin.Jervin Ray OquinNo ratings yet
- BQS667 - Task 3 - Project Report PM-03 CaaDocument76 pagesBQS667 - Task 3 - Project Report PM-03 CaaSiti Aisyah IleyesNo ratings yet
- Otonabee Conservation 2023 Watershed Report CardDocument11 pagesOtonabee Conservation 2023 Watershed Report CardPeterborough ExaminerNo ratings yet
- KM Flushing and Sterilization GuideDocument8 pagesKM Flushing and Sterilization GuideLuwalhati TomilasNo ratings yet
- Case Study ExerciseDocument2 pagesCase Study ExerciseayethNo ratings yet
- DewateringtechniquesDocument30 pagesDewateringtechniquesCarol TumanengNo ratings yet
- Especial Sialex Medio Ambiente, Sialex Contra Del SalDocument11 pagesEspecial Sialex Medio Ambiente, Sialex Contra Del SalnascasNo ratings yet
- Reverse OsmosisDocument3 pagesReverse OsmosisJOSEPH HERBERT MABELNo ratings yet
- Complete Water Supply Treatment PlantDocument27 pagesComplete Water Supply Treatment PlantMario Sajulga Dela Cuadra100% (9)