Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHILOSOPHY tABLE
PHILOSOPHY tABLE
Uploaded by
Arlyn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesThe document discusses several educational philosophies including essentialism, perennialism, progressivism, existentialism, behaviorism, constructivism, and reconstructionism. It provides an overview of the key principles of each philosophy in terms of why they teach, what they teach, and how they teach. The philosophies vary in their views on the purpose of education, appropriate curriculum, and teaching methods but commonly focus on developing students' abilities, knowledge, conduct, or awareness of social issues.
Original Description:
Original Title
PHILOSOPHY-tABLE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several educational philosophies including essentialism, perennialism, progressivism, existentialism, behaviorism, constructivism, and reconstructionism. It provides an overview of the key principles of each philosophy in terms of why they teach, what they teach, and how they teach. The philosophies vary in their views on the purpose of education, appropriate curriculum, and teaching methods but commonly focus on developing students' abilities, knowledge, conduct, or awareness of social issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesPHILOSOPHY tABLE
PHILOSOPHY tABLE
Uploaded by
ArlynThe document discusses several educational philosophies including essentialism, perennialism, progressivism, existentialism, behaviorism, constructivism, and reconstructionism. It provides an overview of the key principles of each philosophy in terms of why they teach, what they teach, and how they teach. The philosophies vary in their views on the purpose of education, appropriate curriculum, and teaching methods but commonly focus on developing students' abilities, knowledge, conduct, or awareness of social issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
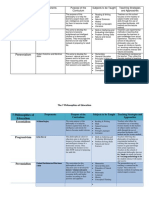
PHILOSOPHY WHY TEACH? WHAT TO TEACH HOW TO TEACH?
• According to • The fundamental • Important
this abilities of reading, teachers
ESSENTIALISM philosophy, writing, mathematics, stress
educators and right conduct, subject-
should focus which are matter
on helping prerequisites for knowledge
students learning higher-level ; they are
grasp or more complicated supposed
fundamenta skills necessary for to serve as
l concepts, preparing for moral and
abilities, and adulthood. intellectual
morals • Traditional subjects role
like arithmetic, the models for
natural sciences, their
history, foreign students.
languages, and
literature are covered
in the curriculum.
• Belief in the • The perennial’s • The
importance curriculum is based perenialist
PERENNIALISM of reason on the premise that classroom
and that all people share a are "
people are fundamental centered
capable of essence. around
making • • Strong humanities instructors
defensible and general " are used
decisions education in
regarding components. perennial’s
the classrooms
goodness of . The
things. professors
don't let
the
students'
experience
s or areas
of interest
heavily
influence
what they
teach.
• Learners are • Need-based, • The
developed pertinent curriculum developme
into that "responds to nt of the
PROGRESSIVISM becoming students' needs" and full kid
educated connects to students' should be
and real-world situations. encourage
intelligent • More focused with d by
citizens in a equipping students instructors
democratic with the ability to , according
society by deal with change. to
progressivist The only thing that progressivi
teachers. stays the same is sts,
Instead of change. through
preparing experientia
students for l learning,
adulthood, exploratio
teachers n, and
aim to help play. We
them live promote
fully in the immersive,
present. emergent,
and group
learning in
our
progressiv
e
classrooms
.
• To enable • Provides many • One-on-
the children possibilities from one
EXISTENSIALISM to recognize which to pick. interaction
and value • The humanities are s with the
themselves highlighted. instructor.
as • Vocational education • Since
distinctive to help kids values are
individuals understand who they individual,
who accept are and what they teachers
full are capable o must avoid
accountabili passing
ty for their judgment
feelings, on their
thoughts, students
and deeds. and take
• And also, care not to
Existence force their
comes own views
before on them.
essence.
• The • Teach pupils how to • Arranges
environmen react positively to the
t a student numerous environme
BEHAVIORISM is in has an environmental cues. ntal
impact on conditions
his conduct. so that
students
can make
the
responses
to stimuli.
• critical • It asserts that rather • Create
thinking than merely cognitive
CONSTRUCTIVISM fosters absorbing dissonance
engaged information, students . Assign
and driven actively generate problems
learning. knowledge. and
• teach us activities
that that will
developing challenge
new students.
concepts is
a necessary • Reflect on
part of learning.
learning
across all
topic areas.
• Reconstructi • Reconstructionist • First, focus your
onist work educators focus on a opening lesson on
RECONSTRUCTIONISM to identify curriculum that the recently freed.
and address highlights social • Second, discuss
a number of reform as the aim of the brutality of the
significant education. time period with
societal your pupils,
issues that especially if they
face our are familiar with
country in the
addition to #BlackLivesMatter
their campaign.
primary goal • Reconsider the
of educating periodization,
the next third.
generation
of problem
solvers.
You might also like
- Philosophy Theory of Truth Methodolog y To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Available/ Good Goal of Teaching and LearningDocument4 pagesPhilosophy Theory of Truth Methodolog y To Arrive at The Truth Theory of What Is Available/ Good Goal of Teaching and LearningIan Dante Arcangeles73% (15)
- Plan de Lectie Clasa A 3 A FamilyDocument4 pagesPlan de Lectie Clasa A 3 A FamilyTibi Dan100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentlya natasyaNo ratings yet
- Phil of Education Matrix PDFDocument2 pagesPhil of Education Matrix PDFmarichu apilado100% (2)
- Teaching ProfDocument23 pagesTeaching ProfKayla Marie Cago92% (13)
- The Oxford Handbook of Cognitive Neuroscience, Vol. 1 PDFDocument1,111 pagesThe Oxford Handbook of Cognitive Neuroscience, Vol. 1 PDFandrewlan000No ratings yet
- The Teaching ProfessionDocument44 pagesThe Teaching ProfessionAnjeanette Baltazar Cayote100% (3)
- 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pages7 Philosophies of Educationmei rose puyat50% (6)
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument4 pagesThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument6 pagesPhilosophies of EducationJake FundalNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Document4 pagesProf. Ed 13 - The Teaching Profession Modular Lesson No. 2Mish LimNo ratings yet
- Seven Philosophies of Education Philosophies Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach EmphasisDocument6 pagesSeven Philosophies of Education Philosophies Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach EmphasisFranz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- The Seven Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesThe Seven Philosophies of EducationGIRLIE M. JABONITENo ratings yet
- College of Teacher Education: Mariano Marcos State UniversityDocument12 pagesCollege of Teacher Education: Mariano Marcos State UniversityJazzel Jane A UlepNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2.1Document4 pagesAssessment 2.1ashNo ratings yet
- Kapu YaaaaDocument6 pagesKapu YaaaaJenny Rose BaculadNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EdDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of EdJoefryQuanicoBarcebalNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To TeachDocument4 pagesPhilosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To TeachAMABELLE MITZI S. NO-OTNo ratings yet
- Mangahas, James Moses (Bped 3-A)Document49 pagesMangahas, James Moses (Bped 3-A)James Sanchez MangahasNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT #3 - Matrix of The Different PhilosophiesDocument6 pagesASSIGNMENT #3 - Matrix of The Different Philosophiesngitngit.jjtNo ratings yet
- fs4 (Episode 4)Document11 pagesfs4 (Episode 4)Ces Reyes50% (2)
- Tugasan Kuliah - Perkembangan Falsafah Pendidikan BaratDocument5 pagesTugasan Kuliah - Perkembangan Falsafah Pendidikan BaratFiona TiehNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of Education Matrix 2Document3 pagesPhilosophies of Education Matrix 2Rey Crtz II50% (2)
- Educational Philosophies Examples Strengths WeaknessDocument3 pagesEducational Philosophies Examples Strengths WeaknessSheena Claire dela Pe?No ratings yet
- EDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONDocument5 pagesEDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- ANSCHAPTER 1 - Module 1 - The Philosophical HeritageDocument5 pagesANSCHAPTER 1 - Module 1 - The Philosophical HeritageDivine CardejonNo ratings yet
- The Seven Philosophies of Education PhilDocument2 pagesThe Seven Philosophies of Education PhilArnold C. LasitNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Education Second ActivityDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of Education Second Activitymaria1jennizaNo ratings yet
- 07 - Module 7 - English - DumulagDocument10 pages07 - Module 7 - English - DumulagKaren Kate DumulagNo ratings yet
- Seven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaDocument3 pagesSeven Philosophies - Rocel NavajaRocel NavajaNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument5 pagesPhilosophies of EducationArianne KehNo ratings yet
- 3rd Evaluation PhiloDocument4 pages3rd Evaluation PhiloBerlin Tingson LabianoNo ratings yet
- The Seven Philosophies of Education PhilDocument2 pagesThe Seven Philosophies of Education PhilJohn Patrick ArciteNo ratings yet
- Asyncronous Assignment TTP...Document17 pagesAsyncronous Assignment TTP...Kim alexandraNo ratings yet
- EDUC 11A 1st Exam and Activity1-4 ExercisesDocument3 pagesEDUC 11A 1st Exam and Activity1-4 ExercisesDanilo Malbueso Ebol Jr.No ratings yet
- Jenny D. Napuran - Activity 1Document5 pagesJenny D. Napuran - Activity 1Johnpaul Macapugas50% (2)
- Educational Philosophy Questionnaire: Statements 1 2 3 4Document6 pagesEducational Philosophy Questionnaire: Statements 1 2 3 4JoefryQuanicoBarcebal100% (1)
- ED101Document2 pagesED101Rodie lyn SueltoNo ratings yet
- Educ 2Document5 pagesEduc 2Jhonalyn ManubagNo ratings yet
- 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pages7 Philosophies of EducationZaib Rehman73% (11)
- LA 1 of SG 2Document5 pagesLA 1 of SG 2Junellie Toledo EgotNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Philosophy in LifeDocument8 pagesAssignment - Philosophy in LifeArjay PascuaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: The Seven Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: The Seven Philosophies of EducationJohn RaymondNo ratings yet
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument25 pagesThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNo ratings yet
- Teacher Education Department: EpistemologyDocument5 pagesTeacher Education Department: EpistemologyIvanne MeinelNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophies of EducationErica LeysonNo ratings yet
- EDUC 122 - Lesson 1 To 5Document17 pagesEDUC 122 - Lesson 1 To 5Webster III M. OpiasaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Learning TheoriesDocument8 pagesComparing Learning Theoriesfimmee2006No ratings yet
- Essentailis M Perennialis M Progressivis M Sosial Reconstructio N Behaviouris M ExistentialismDocument2 pagesEssentailis M Perennialis M Progressivis M Sosial Reconstructio N Behaviouris M ExistentialismNARMATHA A/P LINGAM (L221161032)100% (1)
- ACTIVITY THE TEACHING PROFESSION 1.odtDocument20 pagesACTIVITY THE TEACHING PROFESSION 1.odtAlwin AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Why Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismDocument2 pagesWhy Teach What To Teach How To Teach: EssentialismSunako Claes0% (1)
- Do The Progressivist Teachers Strive To Simulate in The Classroom Life in TheDocument4 pagesDo The Progressivist Teachers Strive To Simulate in The Classroom Life in ThestudentNo ratings yet
- Different Type of Educ PhilosophyDocument6 pagesDifferent Type of Educ PhilosophyThet SalazarNo ratings yet
- Philosophies Advocator(s) Role of The Students Role of The Teachers Role of The CommunityDocument3 pagesPhilosophies Advocator(s) Role of The Students Role of The Teachers Role of The Communityflory mae gudiaNo ratings yet
- Urop Poster PPTX PPTX 2Document1 pageUrop Poster PPTX PPTX 2api-345776304No ratings yet
- The 7 Philosophies of EducationDocument23 pagesThe 7 Philosophies of EducationJonamay CarantoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: Philosophical Perspectives: Classical PhilosophiesDocument5 pagesActivity 2: Philosophical Perspectives: Classical PhilosophiesKrystelle Mae Salas AbuyogNo ratings yet
- Module in TPDocument9 pagesModule in TPQuenie De la CruzNo ratings yet
- 7 Philosophies of Education: EssentialismDocument3 pages7 Philosophies of Education: EssentialismChandu PanditNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUTIVISMDocument4 pagesCONSTRUTIVISMAlama,Shenna Mea OroscoNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Educ 202 MaedDocument4 pagesAssignment in Educ 202 MaedEmlyne Nicole Pineda ColotNo ratings yet
- Horn Te302 FinalassignmentDocument8 pagesHorn Te302 Finalassignmentapi-340221764No ratings yet
- Teacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8From EverandTeacher Guide for A Girl Called Echo: Learning About the History and Culture of the Métis Nation in Grades 6–8No ratings yet
- English 8-15Document10 pagesEnglish 8-15ArlynNo ratings yet
- Campus Journalism EnglishDocument29 pagesCampus Journalism EnglishArlynNo ratings yet
- My Personal Moral Development of MoralityDocument2 pagesMy Personal Moral Development of MoralityArlynNo ratings yet
- Tos m4 3RDDocument2 pagesTos m4 3RDArlynNo ratings yet
- Childrens Lit BookDocument106 pagesChildrens Lit BookArlynNo ratings yet
- 111 - 113 - 115 - Critical ReadingDocument1 page111 - 113 - 115 - Critical ReadingthouSANd foodNo ratings yet
- Intervention in English 10Document3 pagesIntervention in English 10Alangilan HighNo ratings yet
- The Ludic Strategy 15 06 2022Document2 pagesThe Ludic Strategy 15 06 2022SARA FRANCCESCA ORTEGA OBANDONo ratings yet
- METHODSandSTRATEGIES CBRCDocument21 pagesMETHODSandSTRATEGIES CBRCCherrie Mae cedillaNo ratings yet
- Cheerfulness and Life Satisfaction Mediated by Self-Esteem and BehavioralDocument4 pagesCheerfulness and Life Satisfaction Mediated by Self-Esteem and BehavioralMagda RossatoNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Exam PerdevDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Exam PerdevRea Aguilar San PabloNo ratings yet
- The Theory Practice Relationship in Nursing From The Perspective of The Student Nurse. (PDFDrive)Document264 pagesThe Theory Practice Relationship in Nursing From The Perspective of The Student Nurse. (PDFDrive)HasNo ratings yet
- Presentation, Practice and Production (PPP) : 1. Read About Teaching Techniques Teaching TechniquesDocument4 pagesPresentation, Practice and Production (PPP) : 1. Read About Teaching Techniques Teaching TechniquesЕлизавета ВыблаяNo ratings yet
- Basic Psychological Needs in The ClassroomDocument22 pagesBasic Psychological Needs in The Classrooms1151312No ratings yet
- Written Assignment - Unit 5Document10 pagesWritten Assignment - Unit 5James HingaNo ratings yet
- Invisible Manipulators of Your MindDocument14 pagesInvisible Manipulators of Your MindNatalia SzatkoNo ratings yet
- Phillips 66 - Chapter 1-3Document37 pagesPhillips 66 - Chapter 1-3Cindy GacutanNo ratings yet
- Meditation Visualization ExerciseDocument7 pagesMeditation Visualization ExerciseBININo ratings yet
- Chenny Fs2ep4Document4 pagesChenny Fs2ep4CHENNY BETAIZARNo ratings yet
- The Proficiency Level of Solving Mathematical Problem of Grade 10 Students in Matutum View Baptist Academy IncDocument19 pagesThe Proficiency Level of Solving Mathematical Problem of Grade 10 Students in Matutum View Baptist Academy IncSpIdIcYNo ratings yet
- Per Dev 8Document6 pagesPer Dev 8sheridan dimaano100% (1)
- Faelangca Eng 1ST 22 23Document2 pagesFaelangca Eng 1ST 22 23Hazel FaelangcaNo ratings yet
- Assess 2 Module 2Document10 pagesAssess 2 Module 2jezreel arancesNo ratings yet
- Math 5e Lesson Plan Final Carrie FordDocument11 pagesMath 5e Lesson Plan Final Carrie Fordapi-623400193No ratings yet
- Speaking To InformDocument7 pagesSpeaking To InformWem GamingNo ratings yet
- Post Observ Tool Form 3Document6 pagesPost Observ Tool Form 3Sha SumagangNo ratings yet
- EDUC 107a Module 3 - REPORTDocument6 pagesEDUC 107a Module 3 - REPORTReal Deal IIINo ratings yet
- The Critical Importance of Retrieval For LearningDocument4 pagesThe Critical Importance of Retrieval For Learning林瑜璿No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan Year 3 GemilangDocument8 pagesDaily Lesson Plan Year 3 GemilangZura ZalinNo ratings yet
- 3580 8614 1 SMDocument8 pages3580 8614 1 SMastutikNo ratings yet
- Five Homework Strategies For Teaching Students With DisabilitiesDocument9 pagesFive Homework Strategies For Teaching Students With Disabilitiesogtahbtif100% (1)
- Sales CV2Document1 pageSales CV2cyber bouneNo ratings yet