Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q2 - Week 1 - Day 4
Q2 - Week 1 - Day 4
Uploaded by
Erwin TusiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2 - Week 1 - Day 4
Q2 - Week 1 - Day 4
Uploaded by
Erwin TusiCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
National Capital Region
Schools Division of Quezon City
TORO HILLS ELEMENTARY SCHOOL
LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 3
2nd Quarter-Week 1-Day 4
Date: _________________________________ Day: _______________________________
Section: ______________________________ Time:_______________________________
I. Objectives:
1. Identify the parts of the ears.
2. Describe its parts and functions.
3. Identify the proper ways of caring the ears.
II. Subject Matter:
The Ears
Reference: DBOW, MELC (S3LT-IIab-1) TG pages 53-55
Materials: big poster of the parts of the ear
Integration: MAPEH (Arts and Health)
III. Procedure:
1. Elicit
Ask the following:
Why do we need to take care of our ears?
2. Engage
Never put anything inside the ear
Wear earmuffs to protect the ears from cold
Avoid very noisy places.
Listen to not too loud music, even watching television.
Consult a doctor when suffering from sudden hearing loss.
3. Explore
Let the pupils stand and get a partner and say:
Look at the ears of your partner. Draw the parts that you see.
Give ten minutes to do it.
Let them compare their drawing with their partner and ask:
What to do you want to know about your ears?
4. Explain:
Let the students do their activity.
Let the student present their drawing.
Process their responses to correct misconceptions if there are any and to arrive at the
correct ideas/concepts.
5. Elaborate
What are the parts of your ears?
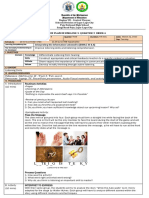
The parts of the ears:
Pinna - is the visible portion of the outer ear. It collects sound waves and channels them into the
ear canal (external auditory meatus), where the sound is amplified. The sound waves then travel
toward a flexible, oval membrane at the end of the ear canal called the eardrum, or tympanic
membrane.
Anvil – Hammer – Stirrup
The middle ear contains three tiny bones:
Hammer – attached to the eardrum.
Anvil – in the middle of the chain of bones.
Stirrup – attached to the membrane-covered that connect the middle ear with the inner ear.
Ear Canal - The ear canal functions as an entryway for sound waves, which get propelled
toward the tympanic membrane, known as the eardrum.
Ear Drum - Your eardrum is a really important part of your ear. Sound waves travel through the
ear canal to reach the eardrum. The eardrum is a thin flap of skin that is stretched tight like a
drum and vibrates when sound hits it. These vibrations move the tiny bones of the middle ear,
which send vibrations to the inner ear.
Auditory Nerve - Auditory nervous system: The auditory nerve runs from the cochlea to a
station in the brainstem (known as nucleus). From that station, neural impulses travel to the brain
– specifically the temporal lobe where sound is attached meaning and we HEAR.
Cochlea - The cochlea is a hollow, spiral-shaped bone found in the inner ear that plays a key role
in the sense of hearing and participates in the process of auditory transduction. Sound waves are
transduced into electrical impulses that the brain can interpret as individual frequencies of sound.
6. Evaluate
Put check (/) if it shows a proper way of caring the ears and put a cross mak (x) if it is not.
_____1. Avoid noisy places.
_____2. Consult a doctor when there is an ear problem.
_____3. Clean the ears with cotton buds.
_____4. Turn the volume high when listening to the music.
_____5. Use earphones when in a place with loud sounds.
7. Extend
Why are the ears are important?
Inihanda ni:
MARICAR L. QUIZON
Guro sa Ikatlong Baitang Iniwasto ni:
GNG. EVELYN N. DIAZ
Gurong Tagapayo /MT-II
GNG. BIBIANA D. CONCEPCION
Gurong Tagapayo/MT-I
GEORGE C. MELEGRITO
Principal IV
You might also like
- Navajo Medicine Man Remedy For Hearing Loss PDFDocument44 pagesNavajo Medicine Man Remedy For Hearing Loss PDFgerald nacinopaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Modyul 1 Organo Sa PagbatiDocument16 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Modyul 1 Organo Sa PagbatiAngel Limbo100% (1)
- Science Module For Grade 3Document22 pagesScience Module For Grade 3NabongJoanKate100% (6)
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 3Document3 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 3Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 5Document3 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 5Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 3Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Science 3Caren Pogoy ManiquezNo ratings yet
- Science 3 DLP 4 - Parts of Ears and Their FunctionsDocument11 pagesScience 3 DLP 4 - Parts of Ears and Their Functionsmary grace musni100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Science 3Document5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 3Josenia Constantino78% (9)
- Lesson Plan in Science 3 Parts and Functions of The EarDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Science 3 Parts and Functions of The EarMark Anthony TubioNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document1 pageActivity 2Gryl CrntsNo ratings yet
- Cot in Science 3 Q. 2Document2 pagesCot in Science 3 Q. 2Maguyepyep Elementary School (CAR - Abra)No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IIIDocument12 pagesLesson Plan in Science IIIAllyn Misa JarabeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan 2api-248521749No ratings yet
- Science3 - q3 - Mod2 - Uses of Sound Light HeatDocument32 pagesScience3 - q3 - Mod2 - Uses of Sound Light Heatsuper trapsiNo ratings yet
- Group 2: Amaliani Laraswati Dewi Andini Fifi Kurniawati Gita Rianti Nelly Marta Nadeak Nury Andriani Nur AnisahDocument15 pagesGroup 2: Amaliani Laraswati Dewi Andini Fifi Kurniawati Gita Rianti Nelly Marta Nadeak Nury Andriani Nur Anisahjihan salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - The Listening ProcessDocument5 pagesModule 4 - The Listening ProcessRyan Fer GomezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 6.6Document5 pagesLesson Plan 6.6Josh ArgonzaNo ratings yet
- Project of Thesis - Listening ComprehensionDocument25 pagesProject of Thesis - Listening ComprehensionSonia Chauca50% (2)
- Kent Marianito-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesKent Marianito-WPS OfficeKent Andojar MarianitoNo ratings yet
- Parts of EarDocument3 pagesParts of Earapi-307692959No ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 1Document2 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 1Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 4 Module 7Document19 pagesQ3 Science 4 Module 7Rica PuzonNo ratings yet
- Week 5 LessonsDocument18 pagesWeek 5 LessonsAngela Louise SmithsNo ratings yet
- 2303 Final Exam Q&A 2023Document39 pages2303 Final Exam Q&A 2023dietubrowNo ratings yet
- Cot Science6Document4 pagesCot Science6Jaime DailegNo ratings yet
- Bohol English6 Q2 Week1Document11 pagesBohol English6 Q2 Week1Cindy Florabel Mirzi I. MugaNo ratings yet
- VI HEALTH 2 Q2 Week2 Day1 MELCDocument4 pagesVI HEALTH 2 Q2 Week2 Day1 MELCJULIE ANN DEVELOSNo ratings yet
- Lesson Guides 1st GradingDocument108 pagesLesson Guides 1st GradingLuxûry Francisco PinedaNo ratings yet
- TEXTO 7 Ingl I What Is Hearing Loss 2CDocument4 pagesTEXTO 7 Ingl I What Is Hearing Loss 2Ccande cáceresNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (Ears)Document4 pagesLesson Plan (Ears)Art Montallana PomarejosNo ratings yet
- WLL LS1English Q2W1M1L1 ATTENTIVELISTENINGDocument3 pagesWLL LS1English Q2W1M1L1 ATTENTIVELISTENINGAlhena ValloNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper On Effective ListeningDocument8 pagesA Research Paper On Effective ListeningAngelique Rae AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Sci101 Prefinal M3L1Document22 pagesSci101 Prefinal M3L1Ej PunlaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lesson 1 and 2-FINALDocument18 pagesModule 3 - Lesson 1 and 2-FINALRANIE MAY V. PIÑERONo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Ringing of Spoon For StudentsDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Ringing of Spoon For StudentsLeyah NallaNo ratings yet
- Q2 G3 Science M1Document40 pagesQ2 G3 Science M1Maricar AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Science 3Document6 pagesLesson Plan For Science 3Dinah DimagibaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ListeningDocument9 pagesLesson Plan ListeningChlarize Gutierrez Mailom-CustodioNo ratings yet
- 4 170502181330 PDFDocument9 pages4 170502181330 PDFRawand AwniNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument9 pagesListening SkillsRawand AwniNo ratings yet
- CO-1-7Es TLEDocument5 pagesCO-1-7Es TLEJohnsaloma100% (1)
- Special Senses: Submitted ToDocument10 pagesSpecial Senses: Submitted ToEliza TuazonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanDencie CabarlesNo ratings yet
- WK6 Lec. LinguisDocument4 pagesWK6 Lec. LinguisAbegail GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Science 3.1Document5 pagesScience 3.1Jelou ApareceNo ratings yet
- Aranilla - Laboratory No. 3Document4 pagesAranilla - Laboratory No. 3Mamamo157No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Children With Hearing ImpairmentDocument69 pagesRehabilitation of Children With Hearing ImpairmentPreeti SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Lesson 1 and 2Document18 pagesModule 3 - Lesson 1 and 2RANIE MAY V. PIÑERONo ratings yet
- Resource Pack - Science - Year 1 - Human Body and SensesDocument19 pagesResource Pack - Science - Year 1 - Human Body and SenseslinguistAiaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II: Listening: I. Course DescriptionDocument16 pagesChapter II: Listening: I. Course DescriptionJohn Marlo DolosoNo ratings yet
- English 8 - Q2 - M9Document15 pagesEnglish 8 - Q2 - M9Wenzel Joy JudillaNo ratings yet
- DLP E9Q3 Week 6 DlpsDocument15 pagesDLP E9Q3 Week 6 DlpsPeter CuevasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 2Document5 pagesLesson Plan in English 2Mary Gwyn Gagaboan100% (1)
- Special Senses WSDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses WSJamaica LunaNo ratings yet
- Team Evana - 1128 Azizah - 1129 Lesson Plan Five SenseDocument7 pagesTeam Evana - 1128 Azizah - 1129 Lesson Plan Five SenseAzizah Baiti LestariNo ratings yet
- Lesson Nose Quarter 2Document23 pagesLesson Nose Quarter 2Lorife Jean ViescaNo ratings yet
- DLP Template ShaneDocument5 pagesDLP Template ShaneEj PunlaNo ratings yet
- Inti Proposal QRMDocument11 pagesInti Proposal QRMEliyana Nur HafidhahNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 3Document3 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 3Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Investiture Camping ProgramDocument2 pagesInvestiture Camping ProgramErwin Tusi100% (1)
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 5Document3 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 5Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 1Document2 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 1Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Week 1 - Day 2Document2 pagesQ2 - Week 1 - Day 2Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- New TIP Course 5 DepEd TeacherDocument98 pagesNew TIP Course 5 DepEd TeacherErwin TusiNo ratings yet
- October 19,20,21Document3 pagesOctober 19,20,21Erwin TusiNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Week 10 DLLDocument7 pages1ST Quarter Week 10 DLLErwin TusiNo ratings yet
- ECD ScheduleDocument2 pagesECD ScheduleErwin TusiNo ratings yet
- 10-Ascending Sensory PATHWAYSDocument12 pages10-Ascending Sensory PATHWAYSMai OssamaNo ratings yet
- ASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESDocument13 pagesASSESSING MOUTH, THROAT, NOSE and SINUSESKenneth Andre Batuyog TecsonNo ratings yet
- Temporal Os Mastoid & PetrosumDocument34 pagesTemporal Os Mastoid & PetrosumAyuning SinchittaNo ratings yet
- Billote, CymarcDocument16 pagesBillote, CymarcEllen Bahatan SinahonNo ratings yet
- Oral Anatomy ReviewerDocument7 pagesOral Anatomy ReviewerWyneth Marie SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia in Lateral Medullary Syndrome ObjavljenDocument10 pagesDysphagia in Lateral Medullary Syndrome ObjavljenMala MirnaNo ratings yet
- Skin AssessmentDocument50 pagesSkin AssessmentNayel ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- LYNX Hair CareDocument34 pagesLYNX Hair CareayushdigitalfruitsNo ratings yet
- (H.a.) Chapter 15 - Neurologic SystemDocument9 pages(H.a.) Chapter 15 - Neurologic SystemLevi Sebastian T. CabiguinNo ratings yet
- 4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveDocument49 pages4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveGeronimo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Physical Examination of The SkinDocument17 pages2022 Physical Examination of The SkinMarian FracNo ratings yet
- Eye Care IntroductionDocument66 pagesEye Care IntroductionEdeti RoneNo ratings yet
- Management of A Coronally Advanced Lingual Flap in Regenerative Osseous Surgery: A Case Series Introducing A Novel TechniqueDocument11 pagesManagement of A Coronally Advanced Lingual Flap in Regenerative Osseous Surgery: A Case Series Introducing A Novel TechniqueAnita PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Historical Evolution of Periodontal Flap SurgeryDocument13 pagesHistorical Evolution of Periodontal Flap Surgeryvishrutha purushotham100% (1)
- Asda Floss - Google SearchDocument1 pageAsda Floss - Google SearchMohammed Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Comparing My Character TraitsDocument1 pageComparing My Character TraitsYana StvolovayaNo ratings yet
- HearDocument1 pageHearVanessa MatillanoNo ratings yet
- Tooth TransplantationDocument38 pagesTooth TransplantationmacmaciiNo ratings yet
- Acne & Rosasea: Patomekanisme Gejala Terapi DD/KomplikasiDocument9 pagesAcne & Rosasea: Patomekanisme Gejala Terapi DD/KomplikasiSholeha KhuldyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Maxillary and Mandibular Base Lengths in Class II Malocclusions in Patients Visiting Tertiary Care HospitalDocument8 pagesRelationship Between Maxillary and Mandibular Base Lengths in Class II Malocclusions in Patients Visiting Tertiary Care HospitalRehana RamzanNo ratings yet
- Tla1 Midterm BSC100Document3 pagesTla1 Midterm BSC100AXCEL V. ANTOQUENo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment of The Skin, Head, and NeckDocument81 pagesPhysical Assessment of The Skin, Head, and NeckPark chin-haeNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation Perdev by Haillie and JericDocument15 pagesPowerPoint Presentation Perdev by Haillie and JericTetzie Sumaylo100% (1)
- LandmarksDocument71 pagesLandmarksayeshaNo ratings yet
- Linguistics - Neurolinguistics - PPT DownloadDocument7 pagesLinguistics - Neurolinguistics - PPT Downloadusama aliNo ratings yet
- FAMM FlapDocument12 pagesFAMM FlapSilverline TeamNo ratings yet
- Photoprotection Patient LeafletDocument4 pagesPhotoprotection Patient LeafletAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- FPD - lec.SAS.11 Complete Crown and Posterior PVCDocument11 pagesFPD - lec.SAS.11 Complete Crown and Posterior PVCDian Alaissa MencianoNo ratings yet
- NQVH The Hall Technique ManualDocument19 pagesNQVH The Hall Technique Manualpriti adsulNo ratings yet
- Class II Division 1 Adolescence Treated With Extraction and TADsDocument9 pagesClass II Division 1 Adolescence Treated With Extraction and TADsAnurtha AnuNo ratings yet