Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy and Heat Transfer Answers To Study Guide
Energy and Heat Transfer Answers To Study Guide
Uploaded by
Josie KileyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- POGIL - Heat TransferDocument4 pagesPOGIL - Heat TransferDon SekarNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesMeteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions Manualsaturnagamivphdh100% (20)
- Exercises - Sheet - Lesson-11 Heat and Temperature PDFDocument5 pagesExercises - Sheet - Lesson-11 Heat and Temperature PDFMaría Esperanza Velázquez CastilloNo ratings yet
- En - 13384 2 EnglishDocument61 pagesEn - 13384 2 Englishbadmike71No ratings yet
- Astm d2216 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm d2216 PDFemmanuel0% (1)
- Major Project PPT GGBSDocument20 pagesMajor Project PPT GGBSNaReN KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseDocument5 pagesPhysics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseRB100% (1)
- Transfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesTransfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersUsman babarNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesTransfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersUsman babarNo ratings yet
- Loiweza Abaga Beed 2A QuizDocument5 pagesLoiweza Abaga Beed 2A QuizLoiweza AbagaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter NotesDocument9 pagesHeat Chapter NotesMaanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Science TestDocument2 pagesScience TestJeist HideNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Conduction, Convection, and Radiation ConductionDocument16 pagesDefinitions of Conduction, Convection, and Radiation ConductionAnita MeghaniNo ratings yet
- 699908fe-9802-4080-ae15-004131ad3c25Document10 pages699908fe-9802-4080-ae15-004131ad3c25Herton FotsingNo ratings yet
- Radiation ProcessesDocument20 pagesRadiation ProcessesAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument32 pagesHeatAndreiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 4 Heat PDF DownloadDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 4 Heat PDF Downloadpravin161079No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer 2Document24 pagesHeat Transfer 2AshMere MontesinesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1 - Heat ConductionDocument51 pagesLecture 1-1 - Heat ConductionBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics: Class 9th (KPK)Document13 pagesPhysics: Class 9th (KPK)Jawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Heat End of Unit TestDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Heat End of Unit TestJayNo ratings yet
- Module Thermodynamics 1-4: Colorado State UniversityDocument28 pagesModule Thermodynamics 1-4: Colorado State UniversityAsyifa Rizqi UtamiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2019 C Captainstryouts-Enloe TestDocument4 pagesThermodynamics 2019 C Captainstryouts-Enloe Testjeetchoudhary7890No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Meteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Meteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions Manual PDFtaylorloganptglt100% (13)
- Presentation On Heat and Temperature: Our MembersDocument19 pagesPresentation On Heat and Temperature: Our Membersdavid jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat TransferDocument7 pagesTemperature and Heat TransferAhmed HashkarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument27 pagesHeat TransferOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban San Jose, Rodriguez, Rizal: Institute of EducationDocument4 pagesColegio de Montalban San Jose, Rodriguez, Rizal: Institute of EducationVOLANTE, EDLYN JOYCENo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat Transfer: OjectiveDocument7 pagesMethods of Heat Transfer: OjectiveNadine BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiationnavketsharma6280100% (1)
- Energy and Heat CentersDocument4 pagesEnergy and Heat CentersmceldowneaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: ENERGY: Stop Monkey-N-ing Around and Go Green Already! P.S. I'm Mookie The MonkeyDocument167 pagesUnit 1: ENERGY: Stop Monkey-N-ing Around and Go Green Already! P.S. I'm Mookie The MonkeyhemajanarthananNo ratings yet
- ThermoelectricDocument8 pagesThermoelectricChandan MulherkarNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument78 pagesThermodynamicsHarold Jan R. TeranoNo ratings yet
- 2 Conduction Convection RadiationDocument24 pages2 Conduction Convection RadiationSyed Inam UllahNo ratings yet
- REVALIDAAAADocument4 pagesREVALIDAAAAmeccabryjoreyNo ratings yet
- 7 Heat SolutionsDocument7 pages7 Heat Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Science Script: Scene 1Document4 pagesScience Script: Scene 1Mikaela MercadoNo ratings yet
- HEAT ActivityDocument20 pagesHEAT ActivityFernan SibugNo ratings yet
- EEKJADocument16 pagesEEKJABrianna LedgisterNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter HeatDocument10 pagesClass 7 Chapter HeatBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Document20 pagesThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MaterialsDocument11 pagesThermal Properties of Materialsjacklog600No ratings yet
- Olp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Document17 pagesOlp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Shabbir H. KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HeatDocument32 pagesChapter 5 HeatbcggNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I: Introduction To Heat Transfer Methods of Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument83 pagesCHAPTER I: Introduction To Heat Transfer Methods of Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationSruthi ChallapalliNo ratings yet
- HSPTA - QP - Chapter 11-HssreporterDocument9 pagesHSPTA - QP - Chapter 11-HssreportersumeeshkNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - AssignmentDocument17 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - AssignmentAhmad Ali MirNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics 6: Last TimeDocument6 pagesThermal Physics 6: Last TimekewancamNo ratings yet
- Basics of Heat Transfer: 1.1 Difference Between Heat and TemperatureDocument179 pagesBasics of Heat Transfer: 1.1 Difference Between Heat and TemperatureJam Arun Kumar100% (2)
- Physics Notes (Heat Part - 2)Document5 pagesPhysics Notes (Heat Part - 2)mitaliNo ratings yet
- 5 Lesson Plan On HeatDocument4 pages5 Lesson Plan On HeatJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The RelationshipsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The Relationshipslarison09No ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Solutions Manual 1Document5 pagesIntroduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Solutions Manual 1bill100% (57)
- Water in The AirDocument5 pagesWater in The AirAlDellovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Jonathan Jay-r RestOr100% (1)
- General Instructions:: G10 Chemistry 2, Introduction To Organic Chemistry/General Inorganic Chemistry IIDocument3 pagesGeneral Instructions:: G10 Chemistry 2, Introduction To Organic Chemistry/General Inorganic Chemistry IIHernan Acut ChavezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesR4iDNo ratings yet
- Homework Will Be Posted at The Phys5D Website: Course Schedule Date Topic ReadingsDocument49 pagesHomework Will Be Posted at The Phys5D Website: Course Schedule Date Topic ReadingsMissChristianaNo ratings yet
- Igcse 42 ThermalenergyDocument43 pagesIgcse 42 ThermalenergyHany ElGezawy75% (4)
- ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesThermodynamicsSabyasachiNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS to Chem B Final exam 56Document13 pagesANSWERS to Chem B Final exam 56jr.zamora1380No ratings yet
- ChemQuest 29Document4 pagesChemQuest 29Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- ACT Balancing Equations PhetDocument3 pagesACT Balancing Equations PhetJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 SG and Answers ChemDocument8 pagesCHP 3 SG and Answers ChemJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- Gizmos Ch. 2 Twostepeqse-2 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGizmos Ch. 2 Twostepeqse-2 Lesson 2Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Review Answer KeyDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Review Answer KeyJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- ChemQuest 26Document4 pagesChemQuest 26Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Honors Final Review Answer KeyDocument2 pagesGeometry Honors Final Review Answer KeyJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- .Lab Beanium IsotopesDocument3 pages.Lab Beanium IsotopesJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- ChemQuest 28Document3 pagesChemQuest 28Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 in PpeDocument4 pagesActivity 1 in PpeJenny Mae Pomeda100% (1)
- MMO titanium anodes, cathodes, HHO Generator, Fuel Cell Kits, Dry Cell Kit , H2O statuary engines, fuel benefits pollution free exhaust, Water4gas, fuel saver, wate car, Hydrogen and Oxygen, Green Gas, Brown's Gas, Rhodes Gas, Bubbler, Hydrogen Generator, Water reservoir, dryer, Increase the Mileage, electrolyzer.Document24 pagesMMO titanium anodes, cathodes, HHO Generator, Fuel Cell Kits, Dry Cell Kit , H2O statuary engines, fuel benefits pollution free exhaust, Water4gas, fuel saver, wate car, Hydrogen and Oxygen, Green Gas, Brown's Gas, Rhodes Gas, Bubbler, Hydrogen Generator, Water reservoir, dryer, Increase the Mileage, electrolyzer.Mr. Velappan JeyakummarNo ratings yet
- BeeswaxDocument6 pagesBeeswaxmuahdib11No ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument11 pagesSteam TablesARNOUXNo ratings yet
- Slow Drips: Another FREE SAMPLE LAB From Tops Learning Systems!Document1 pageSlow Drips: Another FREE SAMPLE LAB From Tops Learning Systems!Ismah WinahNo ratings yet
- CH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelDocument21 pagesCH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelSubhash SinhaNo ratings yet
- XI Science PDFDocument26 pagesXI Science PDFCreative GamingNo ratings yet
- The Corrosion Inhibitor Availability Model 51300 00034 SG PDFDocument13 pagesThe Corrosion Inhibitor Availability Model 51300 00034 SG PDFrachedNo ratings yet
- For Biology, Food & Cosmetics, Drug Discovery, Chemistry: Dolomite - A One-Stop Shop For Microfluidic SolutionsDocument11 pagesFor Biology, Food & Cosmetics, Drug Discovery, Chemistry: Dolomite - A One-Stop Shop For Microfluidic SolutionsWang CharlesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Power PointDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Power PointTai PanNo ratings yet
- F 008 741 Blank Oral Troche (0.9 ML Mold)Document5 pagesF 008 741 Blank Oral Troche (0.9 ML Mold)J C Torres FormalabNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument19 pagesFracture Mechanics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchReeverse MasterminddNo ratings yet
- FM IS Standard 3600Document14 pagesFM IS Standard 3600SureshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry Viva QuestionsShivamNo ratings yet
- Compressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockDocument10 pagesCompressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockPalak ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Manual Visible Dye Penetrant PDFDocument16 pagesManual Visible Dye Penetrant PDFAndik SetyawanNo ratings yet
- A Plastic Solar Water Purifier With High Output: John WardDocument5 pagesA Plastic Solar Water Purifier With High Output: John WardDrEmadEl-SaidNo ratings yet
- Failures Analysis of E-Glass Fibre Reinforced PipeDocument11 pagesFailures Analysis of E-Glass Fibre Reinforced PipeScarllett Lalesca Santos LimaNo ratings yet
- Mining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowDocument3 pagesMining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowBoonsita NammanaNo ratings yet
- Peka 1 (Activity 2.4)Document9 pagesPeka 1 (Activity 2.4)Zarina Idris50% (2)
- Science 9 Module 3Document3 pagesScience 9 Module 3cherish calachanNo ratings yet
- Floor Cleaner Making ClassesDocument8 pagesFloor Cleaner Making ClassesMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Biological MethodsDocument91 pagesBiological MethodsnahomNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshDocument27 pagesPpt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshHegdeVenugopalNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Viscocities 140hDocument8 pagesLubricant Viscocities 140hPablo Gaspar D'Agostini AmengualNo ratings yet
- FDA Stability TestingDocument114 pagesFDA Stability TestingAmalia Riska GNo ratings yet
Energy and Heat Transfer Answers To Study Guide
Energy and Heat Transfer Answers To Study Guide
Uploaded by
Josie KileyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy and Heat Transfer Answers To Study Guide
Energy and Heat Transfer Answers To Study Guide
Uploaded by
Josie KileyCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy and Heat Transfer Study Guide-Answer Key
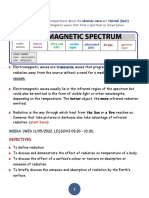
Go through the 10 questions below. The answer to each will be either conduction, convection, or radiation.
__CONV___ 1. During the summer it’s cooler in the basement of your home than the upstairs.
____RAD__ 2. You sit in front of a fireplace and feel the warmth coming from it.
__COND__ 3. Your feet burn when you walk barefoot on a black road on a hot summer day.
___RAD___ 4. The reason why the black top is hot in the first place.
__COND___ 5. The handle of metal spatula gets hot while sitting in a hot skillet.
___COND___ 6. Eric the cat heats himself on a cold winter day by sitting on the hood of a warm engine.
___CONV___ 7. The best place to put a heater is at floor level.
___CONV___ 8. The red alcohol in a thermometer rises when the bulb of it is put in boiling water.
__RAD____ 9. Sunlight is absorbed by the Earth after it has made a 100,000,000 mile journey through space.
___COND___ 10. Packing cans of soda in a cooler full of ice will cause them to become very cold.
11. What is heat transfer? THE MOVEMENT OF HEAT FROM WARMER TO COOLER
12. Define the 3 Types of Heat Transfer and give an example of each type:
CONDUCTION-TOUCHING A HOT IRON
CONVECTION-WARM AIR GOING TO THE CEILING
RADIATION-LIGHT FROM A LAMP KEEPING FOOD WARM
13. What is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles in an object called?
TEMPERATURE
14. Where does the energy in fossil fuels originally come from?
SUN
15. Describe the relationship between the mass of an object and the amount of thermal energy an object has.
AS MASS INCREASES, THERMAL ENERGY INCREASES
16. Explain the difference between conductor and insulators. Give at least 3 examples of each.
CONDUCTOR-ALLOWS THERMAL ENERGY TO PASS THROUGH IT EASILY (COPPER,
GOLD, IRON)
INSULATOR-RESISTS THERMAL ENRGY GOING THROUGH IT (WOOD, RUBBER, AIR)
17. Define Thermal energy
THE ENERGY OF AN OBJECT DUE TO THE KINETIC ENERGY OF ITS MOLECULES (HEAT)
18. Draw the beaker from the colored ice cube lab and fully explain what happened and why.
MELTWATER SANK BECAUSE IT IS COLDER AND MORE DENSE THAN THE OTHER WATER. AFTER
MELTING IS DONE, THE WATER IS WARMER AT THE TOP AND COOLER AT THE BOTTOM BECAUSE WARM IS
LESS DENSE AND IT RISES. THIS IS CALLED A CONVECTION CURRENT.
19. What is the difference between thermal energy and temperature?
A. Temperature is the average kinetic energy while thermal energy is the average potential energy
B. Temperature is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy while thermal energy in the average kinetic energy
C. Temperature is the average potential energy while Thermal energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential
energy
D. Temperature is the average kinetic energy while thermal energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy
24. How does the average velocity of molecules in a high-temperature gas compare to the average velocity of
molecules of the same gas with a lower temperature?
A. It is lower
B. It is higher
C. They are the same
D. It can't be determined until we know the mass of each
25. _THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM__ occurs when 2 objects are in contact and have the same temperature.
26. Explain the 2 heat transfers during the astronaut suit experiment.
RADIATION FROM THE LIGHT TO THE OUTER LAYER OF THE SUIT.
CONDUCTION FROM THE OUTER LAYER OF THE SUIT TO THE WATER IN THE BOTTLE.
***Graph answers***
C Wood #1 & #2 104/116 Copper/Plastic A/C
You might also like
- POGIL - Heat TransferDocument4 pagesPOGIL - Heat TransferDon SekarNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesMeteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions Manualsaturnagamivphdh100% (20)
- Exercises - Sheet - Lesson-11 Heat and Temperature PDFDocument5 pagesExercises - Sheet - Lesson-11 Heat and Temperature PDFMaría Esperanza Velázquez CastilloNo ratings yet
- En - 13384 2 EnglishDocument61 pagesEn - 13384 2 Englishbadmike71No ratings yet
- Astm d2216 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm d2216 PDFemmanuel0% (1)
- Major Project PPT GGBSDocument20 pagesMajor Project PPT GGBSNaReN KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseDocument5 pagesPhysics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseRB100% (1)
- Transfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesTransfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersUsman babarNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesTransfer of Heat: Long Questions & AnswersUsman babarNo ratings yet
- Loiweza Abaga Beed 2A QuizDocument5 pagesLoiweza Abaga Beed 2A QuizLoiweza AbagaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter NotesDocument9 pagesHeat Chapter NotesMaanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Science TestDocument2 pagesScience TestJeist HideNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Conduction, Convection, and Radiation ConductionDocument16 pagesDefinitions of Conduction, Convection, and Radiation ConductionAnita MeghaniNo ratings yet
- 699908fe-9802-4080-ae15-004131ad3c25Document10 pages699908fe-9802-4080-ae15-004131ad3c25Herton FotsingNo ratings yet
- Radiation ProcessesDocument20 pagesRadiation ProcessesAnmol MalgotraNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument32 pagesHeatAndreiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 4 Heat PDF DownloadDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 7th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 4 Heat PDF Downloadpravin161079No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer 2Document24 pagesHeat Transfer 2AshMere MontesinesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-1 - Heat ConductionDocument51 pagesLecture 1-1 - Heat ConductionBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics: Class 9th (KPK)Document13 pagesPhysics: Class 9th (KPK)Jawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Heat End of Unit TestDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Heat End of Unit TestJayNo ratings yet
- Module Thermodynamics 1-4: Colorado State UniversityDocument28 pagesModule Thermodynamics 1-4: Colorado State UniversityAsyifa Rizqi UtamiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2019 C Captainstryouts-Enloe TestDocument4 pagesThermodynamics 2019 C Captainstryouts-Enloe Testjeetchoudhary7890No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Meteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Meteorology Today 11th Edition Ahrens Solutions Manual PDFtaylorloganptglt100% (13)
- Presentation On Heat and Temperature: Our MembersDocument19 pagesPresentation On Heat and Temperature: Our Membersdavid jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat TransferDocument7 pagesTemperature and Heat TransferAhmed HashkarNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument27 pagesHeat TransferOmar EzzatNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Montalban San Jose, Rodriguez, Rizal: Institute of EducationDocument4 pagesColegio de Montalban San Jose, Rodriguez, Rizal: Institute of EducationVOLANTE, EDLYN JOYCENo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat Transfer: OjectiveDocument7 pagesMethods of Heat Transfer: OjectiveNadine BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiationnavketsharma6280100% (1)
- Energy and Heat CentersDocument4 pagesEnergy and Heat CentersmceldowneaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: ENERGY: Stop Monkey-N-ing Around and Go Green Already! P.S. I'm Mookie The MonkeyDocument167 pagesUnit 1: ENERGY: Stop Monkey-N-ing Around and Go Green Already! P.S. I'm Mookie The MonkeyhemajanarthananNo ratings yet
- ThermoelectricDocument8 pagesThermoelectricChandan MulherkarNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument78 pagesThermodynamicsHarold Jan R. TeranoNo ratings yet
- 2 Conduction Convection RadiationDocument24 pages2 Conduction Convection RadiationSyed Inam UllahNo ratings yet
- REVALIDAAAADocument4 pagesREVALIDAAAAmeccabryjoreyNo ratings yet
- 7 Heat SolutionsDocument7 pages7 Heat Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Science Script: Scene 1Document4 pagesScience Script: Scene 1Mikaela MercadoNo ratings yet
- HEAT ActivityDocument20 pagesHEAT ActivityFernan SibugNo ratings yet
- EEKJADocument16 pagesEEKJABrianna LedgisterNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter HeatDocument10 pagesClass 7 Chapter HeatBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Document20 pagesThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MaterialsDocument11 pagesThermal Properties of Materialsjacklog600No ratings yet
- Olp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Document17 pagesOlp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Shabbir H. KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HeatDocument32 pagesChapter 5 HeatbcggNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I: Introduction To Heat Transfer Methods of Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument83 pagesCHAPTER I: Introduction To Heat Transfer Methods of Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and RadiationSruthi ChallapalliNo ratings yet
- HSPTA - QP - Chapter 11-HssreporterDocument9 pagesHSPTA - QP - Chapter 11-HssreportersumeeshkNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - AssignmentDocument17 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - 2nd Law of Thermodynamics - AssignmentAhmad Ali MirNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics 6: Last TimeDocument6 pagesThermal Physics 6: Last TimekewancamNo ratings yet
- Basics of Heat Transfer: 1.1 Difference Between Heat and TemperatureDocument179 pagesBasics of Heat Transfer: 1.1 Difference Between Heat and TemperatureJam Arun Kumar100% (2)
- Physics Notes (Heat Part - 2)Document5 pagesPhysics Notes (Heat Part - 2)mitaliNo ratings yet
- 5 Lesson Plan On HeatDocument4 pages5 Lesson Plan On HeatJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The RelationshipsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Is The Branch of Physics That Deals With The Relationshipslarison09No ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Solutions Manual 1Document5 pagesIntroduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Solutions Manual 1bill100% (57)
- Water in The AirDocument5 pagesWater in The AirAlDellovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Jonathan Jay-r RestOr100% (1)
- General Instructions:: G10 Chemistry 2, Introduction To Organic Chemistry/General Inorganic Chemistry IIDocument3 pagesGeneral Instructions:: G10 Chemistry 2, Introduction To Organic Chemistry/General Inorganic Chemistry IIHernan Acut ChavezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Y 10 Thermal Energy NotesR4iDNo ratings yet
- Homework Will Be Posted at The Phys5D Website: Course Schedule Date Topic ReadingsDocument49 pagesHomework Will Be Posted at The Phys5D Website: Course Schedule Date Topic ReadingsMissChristianaNo ratings yet
- Igcse 42 ThermalenergyDocument43 pagesIgcse 42 ThermalenergyHany ElGezawy75% (4)
- ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesThermodynamicsSabyasachiNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS to Chem B Final exam 56Document13 pagesANSWERS to Chem B Final exam 56jr.zamora1380No ratings yet
- ChemQuest 29Document4 pagesChemQuest 29Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- ACT Balancing Equations PhetDocument3 pagesACT Balancing Equations PhetJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 SG and Answers ChemDocument8 pagesCHP 3 SG and Answers ChemJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- Gizmos Ch. 2 Twostepeqse-2 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGizmos Ch. 2 Twostepeqse-2 Lesson 2Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Review Answer KeyDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter Review Answer KeyJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- ChemQuest 26Document4 pagesChemQuest 26Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Honors Final Review Answer KeyDocument2 pagesGeometry Honors Final Review Answer KeyJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- .Lab Beanium IsotopesDocument3 pages.Lab Beanium IsotopesJosie KileyNo ratings yet
- ChemQuest 28Document3 pagesChemQuest 28Josie KileyNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 in PpeDocument4 pagesActivity 1 in PpeJenny Mae Pomeda100% (1)
- MMO titanium anodes, cathodes, HHO Generator, Fuel Cell Kits, Dry Cell Kit , H2O statuary engines, fuel benefits pollution free exhaust, Water4gas, fuel saver, wate car, Hydrogen and Oxygen, Green Gas, Brown's Gas, Rhodes Gas, Bubbler, Hydrogen Generator, Water reservoir, dryer, Increase the Mileage, electrolyzer.Document24 pagesMMO titanium anodes, cathodes, HHO Generator, Fuel Cell Kits, Dry Cell Kit , H2O statuary engines, fuel benefits pollution free exhaust, Water4gas, fuel saver, wate car, Hydrogen and Oxygen, Green Gas, Brown's Gas, Rhodes Gas, Bubbler, Hydrogen Generator, Water reservoir, dryer, Increase the Mileage, electrolyzer.Mr. Velappan JeyakummarNo ratings yet
- BeeswaxDocument6 pagesBeeswaxmuahdib11No ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument11 pagesSteam TablesARNOUXNo ratings yet
- Slow Drips: Another FREE SAMPLE LAB From Tops Learning Systems!Document1 pageSlow Drips: Another FREE SAMPLE LAB From Tops Learning Systems!Ismah WinahNo ratings yet
- CH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelDocument21 pagesCH 21 Bridge Works - Super Structure - SteelSubhash SinhaNo ratings yet
- XI Science PDFDocument26 pagesXI Science PDFCreative GamingNo ratings yet
- The Corrosion Inhibitor Availability Model 51300 00034 SG PDFDocument13 pagesThe Corrosion Inhibitor Availability Model 51300 00034 SG PDFrachedNo ratings yet
- For Biology, Food & Cosmetics, Drug Discovery, Chemistry: Dolomite - A One-Stop Shop For Microfluidic SolutionsDocument11 pagesFor Biology, Food & Cosmetics, Drug Discovery, Chemistry: Dolomite - A One-Stop Shop For Microfluidic SolutionsWang CharlesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Power PointDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry Power PointTai PanNo ratings yet
- F 008 741 Blank Oral Troche (0.9 ML Mold)Document5 pagesF 008 741 Blank Oral Troche (0.9 ML Mold)J C Torres FormalabNo ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument19 pagesFracture Mechanics: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchReeverse MasterminddNo ratings yet
- FM IS Standard 3600Document14 pagesFM IS Standard 3600SureshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry Viva QuestionsShivamNo ratings yet
- Compressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockDocument10 pagesCompressive and Brazilian Test Tunel RockPalak ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Manual Visible Dye Penetrant PDFDocument16 pagesManual Visible Dye Penetrant PDFAndik SetyawanNo ratings yet
- A Plastic Solar Water Purifier With High Output: John WardDocument5 pagesA Plastic Solar Water Purifier With High Output: John WardDrEmadEl-SaidNo ratings yet
- Failures Analysis of E-Glass Fibre Reinforced PipeDocument11 pagesFailures Analysis of E-Glass Fibre Reinforced PipeScarllett Lalesca Santos LimaNo ratings yet
- Mining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowDocument3 pagesMining: Supercritical Flow Critical Flow Subcritical FlowBoonsita NammanaNo ratings yet
- Peka 1 (Activity 2.4)Document9 pagesPeka 1 (Activity 2.4)Zarina Idris50% (2)
- Science 9 Module 3Document3 pagesScience 9 Module 3cherish calachanNo ratings yet
- Floor Cleaner Making ClassesDocument8 pagesFloor Cleaner Making ClassesMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Biological MethodsDocument91 pagesBiological MethodsnahomNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshDocument27 pagesPpt-Sugarcane Bagasse AshHegdeVenugopalNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Viscocities 140hDocument8 pagesLubricant Viscocities 140hPablo Gaspar D'Agostini AmengualNo ratings yet
- FDA Stability TestingDocument114 pagesFDA Stability TestingAmalia Riska GNo ratings yet