Professional Documents
Culture Documents
25 31 - 34 00 Ley
25 31 - 34 00 Ley
Uploaded by
Salo PhilippinesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Burt Word Recognition TestDocument8 pagesBurt Word Recognition TestYiwen Wu100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanShiela Marvic Hassan100% (4)
- Chapter I Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument42 pagesChapter I Random Variables and Probability DistributionMinel Constantino Estevez33% (3)
- DLP Deferred StatDocument8 pagesDLP Deferred StatVal Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- Illustrating A Random Variable (Discrete and Continuous)Document47 pagesIllustrating A Random Variable (Discrete and Continuous)Clariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Q3 Statistics and Probability Week 3 - 4Document21 pagesQ3 Statistics and Probability Week 3 - 4AngeleehNo ratings yet
- A Review of What We Did Last Time: Empirical Rule Outliers, Normality and Decision MakingDocument19 pagesA Review of What We Did Last Time: Empirical Rule Outliers, Normality and Decision Makinglance WuNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument18 pagesCH 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistryhamzaansari2728No ratings yet
- Sap (Modules 3)Document7 pagesSap (Modules 3)chrishelyn.dacsilNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument44 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyClaudette TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Villas DLP (Discrete and Continuous)Document7 pagesVillas DLP (Discrete and Continuous)Glory Mae Ferrials Villas100% (1)
- Module 7 Week 8Document37 pagesModule 7 Week 8Maureen D. FloresNo ratings yet
- SP Iii-11Document4 pagesSP Iii-11Antonio SearesNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument5 pagesMeasures of VariabilityGemine Ailna Panganiban NuevoNo ratings yet
- The T TEST An IntroductionDocument5 pagesThe T TEST An IntroductionthishaniNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: in Class AssignmentDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: in Class AssignmentAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Measures of Variation and Skewness: 9.0 ObjectivesDocument24 pagesUnit 9 Measures of Variation and Skewness: 9.0 ObjectivesTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Variability - Leary Fall 2015Document18 pagesBehavioral Variability - Leary Fall 2015Joicelyn BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Math 11 Stat Q1 M1 W1 V2Document13 pagesHybrid Math 11 Stat Q1 M1 W1 V2L AlcosabaNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics HandoutsDocument108 pagesBiostatistics HandoutsSalah SaeedNo ratings yet
- PSM 2 Variabel AcakDocument27 pagesPSM 2 Variabel AcakIzza AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Intro To Political Analysis and Research - Measures of Variablity and Normal DistriDocument5 pagesIntro To Political Analysis and Research - Measures of Variablity and Normal Distribyun baek hyunNo ratings yet
- 1.1 StatDocument20 pages1.1 StatEs AmNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob. Q3W3 Video Lesson ScriptDocument16 pagesStat and Prob. Q3W3 Video Lesson ScriptSanchez EdwinNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log School Time: 2:30-3:30 Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson Log School Time: 2:30-3:30 Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayJerrylyn AnonteNo ratings yet
- Research IV - QTR 3 - Week 3Document7 pagesResearch IV - QTR 3 - Week 3andrei bercadezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ProbabilityDocument35 pagesModule 2 ProbabilityRobert Angelo TulaganNo ratings yet
- Myopia ReportDocument16 pagesMyopia ReportgeorgiospapNo ratings yet
- Pit and Pendulum JournalDocument6 pagesPit and Pendulum Journalsoadquake981No ratings yet
- 4th QTR - Feb 27, 2019 - Day 2 - Measures of Spread - Outlier and Box PlotDocument5 pages4th QTR - Feb 27, 2019 - Day 2 - Measures of Spread - Outlier and Box PlotLen AnastacioNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and DispersionDocument7 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and DispersionLaren Kaye100% (1)
- ResumoDocument13 pagesResumoluanamdonascimentoNo ratings yet
- Moments, Skewness and KurtosisDocument7 pagesMoments, Skewness and KurtosisAfework KetemaNo ratings yet
- L2-Stat. Prob - Distinguishing Between Discrete and Continuous Random VariableDocument7 pagesL2-Stat. Prob - Distinguishing Between Discrete and Continuous Random VariableRene Mulleta DueñasNo ratings yet
- Morgenthaler (2003) - John W. Tukey As TeacherDocument4 pagesMorgenthaler (2003) - John W. Tukey As TeacherLinden JavaScriptNo ratings yet
- Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocument33 pagesInductive and Deductive ReasoningBelinda LapsitNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department: Practical Research 2Document5 pagesSenior High School Department: Practical Research 2Mayaka SyNo ratings yet
- Statistics For BiologyDocument18 pagesStatistics For Biologyidawayu100% (1)
- Q3-Week 7 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument32 pagesQ3-Week 7 - Statistics and ProbabilityJose LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Range, Variance, Standard DeviationDocument31 pagesModule 5 - Range, Variance, Standard DeviationKenneth tejamNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesLesson Plannaze grace dulnuanNo ratings yet
- S2 Chp1 BinomialDocument42 pagesS2 Chp1 BinomialRamón PalaciosNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Economics Statistics Chapter 3 Organisation of DataDocument9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Economics Statistics Chapter 3 Organisation of DataAvijit RoyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument27 pagesCH 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistryanurag raiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13: Describing Variability Using The Interquartile Range (IQR)Document10 pagesLesson 13: Describing Variability Using The Interquartile Range (IQR)Hiền TTTNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Significance of The Difference of Frequency: Chi-SquareDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Significance of The Difference of Frequency: Chi-SquareSara RituNo ratings yet
- CO - Discrete and Continuous VariablesDocument9 pagesCO - Discrete and Continuous VariablesRolly FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Biostats Research WorkDocument4 pagesBiostats Research WorkReimond VinceNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module For Grade 11Document21 pagesSelf-Learning Module For Grade 11Puthuyaveetil SoorajNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document28 pagesUnit 2Muhammed Mikhdad K G 21177No ratings yet
- Test of Hypothesis - T and Z Tests. Chi-Square Test. F Test.Document15 pagesTest of Hypothesis - T and Z Tests. Chi-Square Test. F Test.Barath RajNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesLesson PlanJhon Lerry MedinNo ratings yet
- SLM4 Q2 Research 1 FinalDocument11 pagesSLM4 Q2 Research 1 FinalSarah PepitoNo ratings yet
- BIOEPIDocument2 pagesBIOEPIThea GailNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Analysis With An Introduction To Proof PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Analysis With An Introduction To Proof PDFmary.sales786100% (31)
- 003 Measures of DispersionDocument6 pages003 Measures of DispersionVaishnavi AnandNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 4-3Document18 pagesNotes Unit 4-3kulkarni.himani19940809No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MMWDocument27 pagesChapter 3 MMWANHIBEY, JEZREEL ACE S.No ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Emotional Well-Being ScriptDocument11 pagesEmotional Well-Being ScriptSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 30 01 - 45 00 LeyDocument2 pages30 01 - 45 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 20 00 - 30 00 LeytDocument2 pages20 00 - 30 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 20 00 - 25 00 LeytDocument2 pages20 00 - 25 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Dna ReplicationDocument1 pageEnzymes Dna ReplicationSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Activation of TrnaDocument3 pagesActivation of TrnaSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 10 01 - 15 00 KeyDocument2 pages10 01 - 15 00 KeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 18 01 - 24 00 LeytDocument2 pages18 01 - 24 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 8 01 - 12 00 LaysDocument2 pages8 01 - 12 00 LaysSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Assumptions For Qualitative Research 1Document7 pagesPhilosophical Assumptions For Qualitative Research 1Salo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 25 31 - 34 00 LeyDocument3 pages25 31 - 34 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 6 01-9 00 LateDocument2 pages6 01-9 00 LateSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 8 01 - 12 00 KeyDocument2 pages8 01 - 12 00 KeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 15 01 - 20 00 LeyDocument1 page15 01 - 20 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 25 31 - 34 00 LeytDocument2 pages25 31 - 34 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Mercadal Sanico Cabuslay Thesis TurnitinDocument19 pagesMercadal Sanico Cabuslay Thesis TurnitinLucy CabuslayNo ratings yet
- Piotr Blumczyński - Experiencing Translationality - Material and Metaphorical Journeys-Routledge (2023)Document223 pagesPiotr Blumczyński - Experiencing Translationality - Material and Metaphorical Journeys-Routledge (2023)Ambreen AbbasNo ratings yet
- 7TCA083670R0648 lk243 10tDocument3 pages7TCA083670R0648 lk243 10tGeorge TheodosiouNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ling. Module 7 BSITDocument9 pagesIntro To Ling. Module 7 BSITReyan BallasoNo ratings yet
- Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filter: Dr. Dur-e-Shahwar Kundi Lec-7Document37 pagesFinite Impulse Response (FIR) Filter: Dr. Dur-e-Shahwar Kundi Lec-7UsamaKhalidNo ratings yet
- Smart Buildings: John Smiciklas Director, BOMA Canada Jsmiciklas@bomacanada - CaDocument24 pagesSmart Buildings: John Smiciklas Director, BOMA Canada Jsmiciklas@bomacanada - Catest testNo ratings yet
- CE3040 Water Treatment Assignment 2Document1 pageCE3040 Water Treatment Assignment 2Anonymous Vx9KTkM8nNo ratings yet
- 4 Gauss Forward Formula2Document10 pages4 Gauss Forward Formula2Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Final GEUDP Waesano ESIA Document - Bahasa PDFDocument317 pagesFinal GEUDP Waesano ESIA Document - Bahasa PDFVenan HaryantoNo ratings yet
- All Purpose Paint Remover - Dipping Grade: PRODUCT CODE: RRA 200-SeriesDocument2 pagesAll Purpose Paint Remover - Dipping Grade: PRODUCT CODE: RRA 200-SeriesPieter FourieNo ratings yet
- PDF 1Document302 pagesPDF 1LuckyNo ratings yet
- A Sample U1 Physics Mock ExamDocument14 pagesA Sample U1 Physics Mock ExamSham JaggernauthNo ratings yet
- AHFE 2021 Congreso ErgonomiaDocument2 pagesAHFE 2021 Congreso ErgonomiavillarroyaNo ratings yet
- Technology in The Ancient WorldDocument66 pagesTechnology in The Ancient WorldAngela Danielle Tan100% (1)
- MTESI004 Shaking Things Up PDFDocument56 pagesMTESI004 Shaking Things Up PDFAndre OuimetNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Dog Training Stop Your Dog's Behavior ProblemsDocument3 pagesSecrets To Dog Training Stop Your Dog's Behavior ProblemsfennarioNo ratings yet
- 1998 - (Advances in Archaeological and Museum Science 3) M. Steven Shackley (Auth.), M. Steven Shackley (Eds.) - Archaeological Obsidian Studies - Method and Theory-Springer US (1998)Document257 pages1998 - (Advances in Archaeological and Museum Science 3) M. Steven Shackley (Auth.), M. Steven Shackley (Eds.) - Archaeological Obsidian Studies - Method and Theory-Springer US (1998)Luis VelderrainNo ratings yet
- Tuning of PID Controller: What Is A PID Control?Document4 pagesTuning of PID Controller: What Is A PID Control?Mohammad HussnainNo ratings yet
- ME 308 Machine Elements Ii: Spring Design - 1Document66 pagesME 308 Machine Elements Ii: Spring Design - 1xxxNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope LubricatorDocument8 pagesWire Rope LubricatorvlmiltonNo ratings yet
- Sample Weekly Planner 1Document8 pagesSample Weekly Planner 1api-662941487No ratings yet
- ChangelogDocument45 pagesChangeloggodcapuzNo ratings yet
- Tender Recommendation Report ContentDocument2 pagesTender Recommendation Report ContentIslam HamdyNo ratings yet
- Arenstorf OriginalDocument18 pagesArenstorf OriginalMister DumbledoreNo ratings yet
- C, PNP 8 Foundation InitiativesDocument1 pageC, PNP 8 Foundation InitiativesLakan DulaNo ratings yet
- Crack Width Cal-T Beam-Euro CodeDocument10 pagesCrack Width Cal-T Beam-Euro CodeGautham AllimuthuNo ratings yet
- Design of Electrical Wiring Harness For EV and Charging of Battery by Wind Energy Ijariie20194Document6 pagesDesign of Electrical Wiring Harness For EV and Charging of Battery by Wind Energy Ijariie20194arun.nagarkarNo ratings yet
- A Workshop On Using Your Superpower of InfluenceDocument71 pagesA Workshop On Using Your Superpower of InfluenceChandra HaasNo ratings yet
- Earning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)Document7 pagesEarning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)Renalyn ManzanoNo ratings yet
25 31 - 34 00 Ley
25 31 - 34 00 Ley
Uploaded by
Salo PhilippinesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
25 31 - 34 00 Ley
25 31 - 34 00 Ley
Uploaded by
Salo PhilippinesCopyright:
Available Formats
25:31 - 34:00 ley o It because in the determination
of the median value, we are
Properties of Median
looking for the middle value. If
- Unique and simple. we arrange our values in an
o Similar to mean which means array even though there are
there is only 1 median per data extreme values on both ends we
set and simple meaning will only make use of the
interpretation is easy. It’s the middle value.
middle most point in an array of
MODE
values.
o Does not make use of all - The values which occurs most
observations in computation. frequently in a set of observations or
Compared to arithmetic values.
mean we will get the o Meaning this is the most
sum of all the frequent seen number.
observations and we o It can be absent or multiple. We
will divide it to the no. can have only 1 mode that is
of observations. In common or multiple modes,
median, it is odd meaning there are many
numbers we will only different common observations.
get the one on the value - Computation is generally not needed
without concerning o Because what we need to do
other values. If the here is we need to tally the
number of observations answers on how many values
is even, we will only get are common to each other.
the mean of the 2 - May be determined for any type of
middle most position. variable or scale of measurement.
- Can be computed for quantitative o It has a more general application
variables and variables in the ordinal because even in the nominal
scale. scale we can determine the
o Since in the ordinal scale it is modes. There is no calculation.
qualitative, since it has ranking
system, we can get the median Example:
value of the ordinal. Example Eleven (11) students were asked about their
we have survey questionnaire favourite street food. The results were as
and the manner of answering is follows:
in a likert scale (1-5), if we
summarize those values the Student Street food
most appropriate is the median 1. Fish ball
to see the middle most 2. Kwek kwek
observation. It can be 50% of 3. Kikiam
the respondents answered 2 and 4. Kwek kwek
below and then the others more 5. Cheese sticks
than 2. 6. Kwek kwek
- The median is not as drastically affected 7. Fish ball
by extreme values unlike the mean. 8. Kwek kwek
9. Kikiam
10. Cheese sticks data set. Because if the data set
11. Kikiam have same values, for example
in a class of 40 students an
examination is conducted and
This are nominal scale date because the
all of the students got 30/40,
categories under street food are just labels or
there are no variation. But if
descriptors.
there are different scores such as
In order to determine the most frequent or mode 20, 15, 10, 40 so there will be
we just have to determine the street food with variability or variation.
the most response.
Arranged version by mode:
Street food
Cheese sticks
Cheese sticks
Fish ball
Fish ball
Kikiam
Kikiam
Kikiam
Kwek kwek
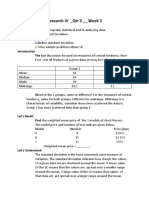
In the study of dispersion or variation, there
Kwek kwek
three frequency distributions with equal means
Kwek kwek
but different amount of dispersion. The graph
Kwek kwek
Therefore, by just looking by this arranged above that there are 3 frequency distributions
values we can see there are two (2) respondents that olds different colors. We have curve I, curve
that answered cheese sticks, two (2) for fish ball, II, and curve III. As we can see their central
three (3) for kikiam, and four (4) for kwek kwek. tendency is only one because their peaks are at
one place. However, their spread or width is
Kwek kwek is the mode of our data sets different where curve I has a narrow spread,
becauseit has the most observations. curve II has a wider spread than curve 1, and the
widest is curve III.
Interpretation:
What does this graph means?
The most common (or most usual) street food
favourite of students is kwek kwek (4/11). Meaning curve I has a smallest dispersion or
variation, where its data sets has nearer values to
That is all for central tendency. Again the central
the central tendency compared to curve II and
tendencies are the best representation our data
curve III. The widest curve is curve III meaning
sets. Usual value in the center.
its values has larger gap from the central
Measures of Dispresion tendency or far from each other. Curve I has
values near to each other within the data set.
Dispersion / Variation
- Refers to the variety or spread exhibited
by a set of observations.
o Dispersion or variation happens
if the data set is different or the
values are not the same within a
You might also like
- Burt Word Recognition TestDocument8 pagesBurt Word Recognition TestYiwen Wu100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanShiela Marvic Hassan100% (4)
- Chapter I Random Variables and Probability DistributionDocument42 pagesChapter I Random Variables and Probability DistributionMinel Constantino Estevez33% (3)
- DLP Deferred StatDocument8 pagesDLP Deferred StatVal Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- Illustrating A Random Variable (Discrete and Continuous)Document47 pagesIllustrating A Random Variable (Discrete and Continuous)Clariza Jane MetroNo ratings yet
- Q3 Statistics and Probability Week 3 - 4Document21 pagesQ3 Statistics and Probability Week 3 - 4AngeleehNo ratings yet
- A Review of What We Did Last Time: Empirical Rule Outliers, Normality and Decision MakingDocument19 pagesA Review of What We Did Last Time: Empirical Rule Outliers, Normality and Decision Makinglance WuNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument18 pagesCH 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistryhamzaansari2728No ratings yet
- Sap (Modules 3)Document7 pagesSap (Modules 3)chrishelyn.dacsilNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument44 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyClaudette TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Villas DLP (Discrete and Continuous)Document7 pagesVillas DLP (Discrete and Continuous)Glory Mae Ferrials Villas100% (1)
- Module 7 Week 8Document37 pagesModule 7 Week 8Maureen D. FloresNo ratings yet
- SP Iii-11Document4 pagesSP Iii-11Antonio SearesNo ratings yet
- Measures of VariabilityDocument5 pagesMeasures of VariabilityGemine Ailna Panganiban NuevoNo ratings yet
- The T TEST An IntroductionDocument5 pagesThe T TEST An IntroductionthishaniNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: in Class AssignmentDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: in Class AssignmentAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Measures of Variation and Skewness: 9.0 ObjectivesDocument24 pagesUnit 9 Measures of Variation and Skewness: 9.0 ObjectivesTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Variability - Leary Fall 2015Document18 pagesBehavioral Variability - Leary Fall 2015Joicelyn BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Math 11 Stat Q1 M1 W1 V2Document13 pagesHybrid Math 11 Stat Q1 M1 W1 V2L AlcosabaNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics HandoutsDocument108 pagesBiostatistics HandoutsSalah SaeedNo ratings yet
- PSM 2 Variabel AcakDocument27 pagesPSM 2 Variabel AcakIzza AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Intro To Political Analysis and Research - Measures of Variablity and Normal DistriDocument5 pagesIntro To Political Analysis and Research - Measures of Variablity and Normal Distribyun baek hyunNo ratings yet
- 1.1 StatDocument20 pages1.1 StatEs AmNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob. Q3W3 Video Lesson ScriptDocument16 pagesStat and Prob. Q3W3 Video Lesson ScriptSanchez EdwinNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log School Time: 2:30-3:30 Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson Log School Time: 2:30-3:30 Teacher Grade Level Learning Area Quarter Week DayJerrylyn AnonteNo ratings yet
- Research IV - QTR 3 - Week 3Document7 pagesResearch IV - QTR 3 - Week 3andrei bercadezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ProbabilityDocument35 pagesModule 2 ProbabilityRobert Angelo TulaganNo ratings yet
- Myopia ReportDocument16 pagesMyopia ReportgeorgiospapNo ratings yet
- Pit and Pendulum JournalDocument6 pagesPit and Pendulum Journalsoadquake981No ratings yet
- 4th QTR - Feb 27, 2019 - Day 2 - Measures of Spread - Outlier and Box PlotDocument5 pages4th QTR - Feb 27, 2019 - Day 2 - Measures of Spread - Outlier and Box PlotLen AnastacioNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and DispersionDocument7 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and DispersionLaren Kaye100% (1)
- ResumoDocument13 pagesResumoluanamdonascimentoNo ratings yet
- Moments, Skewness and KurtosisDocument7 pagesMoments, Skewness and KurtosisAfework KetemaNo ratings yet
- L2-Stat. Prob - Distinguishing Between Discrete and Continuous Random VariableDocument7 pagesL2-Stat. Prob - Distinguishing Between Discrete and Continuous Random VariableRene Mulleta DueñasNo ratings yet
- Morgenthaler (2003) - John W. Tukey As TeacherDocument4 pagesMorgenthaler (2003) - John W. Tukey As TeacherLinden JavaScriptNo ratings yet
- Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocument33 pagesInductive and Deductive ReasoningBelinda LapsitNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Department: Practical Research 2Document5 pagesSenior High School Department: Practical Research 2Mayaka SyNo ratings yet
- Statistics For BiologyDocument18 pagesStatistics For Biologyidawayu100% (1)
- Q3-Week 7 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument32 pagesQ3-Week 7 - Statistics and ProbabilityJose LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Descriptives StatisticsKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Range, Variance, Standard DeviationDocument31 pagesModule 5 - Range, Variance, Standard DeviationKenneth tejamNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesLesson Plannaze grace dulnuanNo ratings yet
- S2 Chp1 BinomialDocument42 pagesS2 Chp1 BinomialRamón PalaciosNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Economics Statistics Chapter 3 Organisation of DataDocument9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Economics Statistics Chapter 3 Organisation of DataAvijit RoyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument27 pagesCH 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistryanurag raiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13: Describing Variability Using The Interquartile Range (IQR)Document10 pagesLesson 13: Describing Variability Using The Interquartile Range (IQR)Hiền TTTNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Significance of The Difference of Frequency: Chi-SquareDocument13 pagesUnit 1 Significance of The Difference of Frequency: Chi-SquareSara RituNo ratings yet
- CO - Discrete and Continuous VariablesDocument9 pagesCO - Discrete and Continuous VariablesRolly FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Biostats Research WorkDocument4 pagesBiostats Research WorkReimond VinceNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module For Grade 11Document21 pagesSelf-Learning Module For Grade 11Puthuyaveetil SoorajNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document28 pagesUnit 2Muhammed Mikhdad K G 21177No ratings yet
- Test of Hypothesis - T and Z Tests. Chi-Square Test. F Test.Document15 pagesTest of Hypothesis - T and Z Tests. Chi-Square Test. F Test.Barath RajNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesLesson PlanJhon Lerry MedinNo ratings yet
- SLM4 Q2 Research 1 FinalDocument11 pagesSLM4 Q2 Research 1 FinalSarah PepitoNo ratings yet
- BIOEPIDocument2 pagesBIOEPIThea GailNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Analysis With An Introduction To Proof PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Analysis With An Introduction To Proof PDFmary.sales786100% (31)
- 003 Measures of DispersionDocument6 pages003 Measures of DispersionVaishnavi AnandNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 4-3Document18 pagesNotes Unit 4-3kulkarni.himani19940809No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MMWDocument27 pagesChapter 3 MMWANHIBEY, JEZREEL ACE S.No ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Probability and Statistics, Revised EditionNo ratings yet
- Emotional Well-Being ScriptDocument11 pagesEmotional Well-Being ScriptSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 30 01 - 45 00 LeyDocument2 pages30 01 - 45 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 20 00 - 30 00 LeytDocument2 pages20 00 - 30 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 20 00 - 25 00 LeytDocument2 pages20 00 - 25 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Dna ReplicationDocument1 pageEnzymes Dna ReplicationSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Activation of TrnaDocument3 pagesActivation of TrnaSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 10 01 - 15 00 KeyDocument2 pages10 01 - 15 00 KeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 18 01 - 24 00 LeytDocument2 pages18 01 - 24 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 8 01 - 12 00 LaysDocument2 pages8 01 - 12 00 LaysSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Assumptions For Qualitative Research 1Document7 pagesPhilosophical Assumptions For Qualitative Research 1Salo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 25 31 - 34 00 LeyDocument3 pages25 31 - 34 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 6 01-9 00 LateDocument2 pages6 01-9 00 LateSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 8 01 - 12 00 KeyDocument2 pages8 01 - 12 00 KeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 15 01 - 20 00 LeyDocument1 page15 01 - 20 00 LeySalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- 25 31 - 34 00 LeytDocument2 pages25 31 - 34 00 LeytSalo PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Mercadal Sanico Cabuslay Thesis TurnitinDocument19 pagesMercadal Sanico Cabuslay Thesis TurnitinLucy CabuslayNo ratings yet
- Piotr Blumczyński - Experiencing Translationality - Material and Metaphorical Journeys-Routledge (2023)Document223 pagesPiotr Blumczyński - Experiencing Translationality - Material and Metaphorical Journeys-Routledge (2023)Ambreen AbbasNo ratings yet
- 7TCA083670R0648 lk243 10tDocument3 pages7TCA083670R0648 lk243 10tGeorge TheodosiouNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ling. Module 7 BSITDocument9 pagesIntro To Ling. Module 7 BSITReyan BallasoNo ratings yet
- Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filter: Dr. Dur-e-Shahwar Kundi Lec-7Document37 pagesFinite Impulse Response (FIR) Filter: Dr. Dur-e-Shahwar Kundi Lec-7UsamaKhalidNo ratings yet
- Smart Buildings: John Smiciklas Director, BOMA Canada Jsmiciklas@bomacanada - CaDocument24 pagesSmart Buildings: John Smiciklas Director, BOMA Canada Jsmiciklas@bomacanada - Catest testNo ratings yet
- CE3040 Water Treatment Assignment 2Document1 pageCE3040 Water Treatment Assignment 2Anonymous Vx9KTkM8nNo ratings yet
- 4 Gauss Forward Formula2Document10 pages4 Gauss Forward Formula2Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Final GEUDP Waesano ESIA Document - Bahasa PDFDocument317 pagesFinal GEUDP Waesano ESIA Document - Bahasa PDFVenan HaryantoNo ratings yet
- All Purpose Paint Remover - Dipping Grade: PRODUCT CODE: RRA 200-SeriesDocument2 pagesAll Purpose Paint Remover - Dipping Grade: PRODUCT CODE: RRA 200-SeriesPieter FourieNo ratings yet
- PDF 1Document302 pagesPDF 1LuckyNo ratings yet
- A Sample U1 Physics Mock ExamDocument14 pagesA Sample U1 Physics Mock ExamSham JaggernauthNo ratings yet
- AHFE 2021 Congreso ErgonomiaDocument2 pagesAHFE 2021 Congreso ErgonomiavillarroyaNo ratings yet
- Technology in The Ancient WorldDocument66 pagesTechnology in The Ancient WorldAngela Danielle Tan100% (1)
- MTESI004 Shaking Things Up PDFDocument56 pagesMTESI004 Shaking Things Up PDFAndre OuimetNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Dog Training Stop Your Dog's Behavior ProblemsDocument3 pagesSecrets To Dog Training Stop Your Dog's Behavior ProblemsfennarioNo ratings yet
- 1998 - (Advances in Archaeological and Museum Science 3) M. Steven Shackley (Auth.), M. Steven Shackley (Eds.) - Archaeological Obsidian Studies - Method and Theory-Springer US (1998)Document257 pages1998 - (Advances in Archaeological and Museum Science 3) M. Steven Shackley (Auth.), M. Steven Shackley (Eds.) - Archaeological Obsidian Studies - Method and Theory-Springer US (1998)Luis VelderrainNo ratings yet
- Tuning of PID Controller: What Is A PID Control?Document4 pagesTuning of PID Controller: What Is A PID Control?Mohammad HussnainNo ratings yet
- ME 308 Machine Elements Ii: Spring Design - 1Document66 pagesME 308 Machine Elements Ii: Spring Design - 1xxxNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope LubricatorDocument8 pagesWire Rope LubricatorvlmiltonNo ratings yet
- Sample Weekly Planner 1Document8 pagesSample Weekly Planner 1api-662941487No ratings yet
- ChangelogDocument45 pagesChangeloggodcapuzNo ratings yet
- Tender Recommendation Report ContentDocument2 pagesTender Recommendation Report ContentIslam HamdyNo ratings yet
- Arenstorf OriginalDocument18 pagesArenstorf OriginalMister DumbledoreNo ratings yet
- C, PNP 8 Foundation InitiativesDocument1 pageC, PNP 8 Foundation InitiativesLakan DulaNo ratings yet
- Crack Width Cal-T Beam-Euro CodeDocument10 pagesCrack Width Cal-T Beam-Euro CodeGautham AllimuthuNo ratings yet
- Design of Electrical Wiring Harness For EV and Charging of Battery by Wind Energy Ijariie20194Document6 pagesDesign of Electrical Wiring Harness For EV and Charging of Battery by Wind Energy Ijariie20194arun.nagarkarNo ratings yet
- A Workshop On Using Your Superpower of InfluenceDocument71 pagesA Workshop On Using Your Superpower of InfluenceChandra HaasNo ratings yet
- Earning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)Document7 pagesEarning Outcomes: LSPU Self-Paced Learning Module (SLM)Renalyn ManzanoNo ratings yet