Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part 2 - w4
Part 2 - w4
Uploaded by
Linh ChiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Tecnotion Linear Motors: A Primer ofDocument27 pagesTecnotion Linear Motors: A Primer ofmatadorisheNo ratings yet
- Machine Lesson Final1Document94 pagesMachine Lesson Final1anon_156286001100% (8)
- Part 2 - w2Document2 pagesPart 2 - w2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - w4Document13 pagesPart 2 - w4Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Asynchronous (Or Induction) MachinesDocument40 pagesUnit 4. Asynchronous (Or Induction) MachinesAgustinBenedictoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Final Practical Exam: Pamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Computing and EngineeringDocument3 pagesLaboratory Final Practical Exam: Pamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Computing and EngineeringKrizalene ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJECT DC MotorDocument20 pagesPHY PROJECT DC Motorneelbhan23No ratings yet
- EM-2-PAPER-FINALDocument10 pagesEM-2-PAPER-FINALJose Miguel RuizNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ElectricalmotorsDocument7 pagesLab 6 Electricalmotorsapi-257558550No ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction in an AC Generator.pdf_20240620_010408_0000Document17 pagesMagnetic Induction in an AC Generator.pdf_20240620_010408_0000as2631234No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab March 16 UpdateDocument53 pagesElectrical Machines Lab March 16 Updatepeter vanderNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument7 pagesDC Machinesprakharsrivastava936No ratings yet
- BEEE Module 2 DC MachinesDocument313 pagesBEEE Module 2 DC Machinesmanohar kintaliNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAngelica VersolaNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 MagnetismDocument36 pagesSec 3 MagnetismA. Rahman AliNo ratings yet
- 3 Working Principle and Characteristic of DC Motor(1)Document81 pages3 Working Principle and Characteristic of DC Motor(1)usamaNo ratings yet
- Axial FluxDocument5 pagesAxial FluxsamuelNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJECT DC GeneratorDocument18 pagesPHY PROJECT DC Generatorelfbaba476No ratings yet
- TF Motores InglesDocument37 pagesTF Motores Inglesjdgarciag1No ratings yet
- 1.3 Electrical MachinesDocument31 pages1.3 Electrical MachinesMuhammad Adli Amin Mohd AmzukiNo ratings yet
- CPE400 Lab9 Fermin Gagabi Lim ZurbanoDocument12 pagesCPE400 Lab9 Fermin Gagabi Lim ZurbanoClyde FerminNo ratings yet
- Simple Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument17 pagesSimple Electric Motor and GeneratorAyla BonitaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 1 TA-AY MEE31Document5 pagesLaboratory Experiment 1 TA-AY MEE31JayNo ratings yet
- Adel LabDocument20 pagesAdel LabKendall BirjueNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENTS WITH SPIRAL AND WANKEL MOTORS, With Ted Loder, Ph.D.Document46 pagesEXPERIMENTS WITH SPIRAL AND WANKEL MOTORS, With Ted Loder, Ph.D.Tedd St Rain100% (1)
- Chapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SDocument112 pagesChapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SLim Kai XuanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Solar Motor?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Solar Motor?D K SHARMANo ratings yet
- DC Generators Jkuat 2024Document10 pagesDC Generators Jkuat 2024sikolia.wanjalaNo ratings yet
- EEC 123 Practical PDFDocument91 pagesEEC 123 Practical PDFEdwinEtuk50% (2)
- P3.21 Study of Industrial MotorsDocument3 pagesP3.21 Study of Industrial MotorsXingfang91No ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument79 pagesDC Machines231052560No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Simple MotorDocument6 pagesExperiment 4 Simple MotorKim HarlyNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - Construction and Operation of A DC GeneratorDocument11 pagesPart 2 - Construction and Operation of A DC GeneratorKevin Lester LoboNo ratings yet
- Observation of Force and Torque On A Current Loop Using A Simplified Electric MotorDocument3 pagesObservation of Force and Torque On A Current Loop Using A Simplified Electric Motorfrances leana capellan100% (2)
- AC Induction Motors - How AC Motors WorkDocument10 pagesAC Induction Motors - How AC Motors WorkBraulio IrrutiaNo ratings yet
- 3rd-4th Semester Detailed Syllabus - EEDocument30 pages3rd-4th Semester Detailed Syllabus - EESAUMYAJIT SABUINo ratings yet
- Marpower Week 5 To 8Document8 pagesMarpower Week 5 To 8Haeisy SimsuangcoNo ratings yet
- Slides EM ch1Document124 pagesSlides EM ch1Saman RubabNo ratings yet
- Period 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and GeneratorsDocument5 pagesPeriod 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and GeneratorsCharlene DinawanaoNo ratings yet
- Uniaxial Shaking Machine of Ground Motion SimulationDocument5 pagesUniaxial Shaking Machine of Ground Motion SimulationSumit TarachandaniNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVESDocument3 pagesOBJECTIVESJulius BoitizonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Chapter 8 Basic Electric Motors Flashcards - QuizletDocument7 pagesElectrical Chapter 8 Basic Electric Motors Flashcards - QuizletAli UzairNo ratings yet
- Long Examination 214Document4 pagesLong Examination 214Kobe Alcantara ReyesNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument20 pagesDC MachinesELON MUSKNo ratings yet
- Generato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueDocument33 pagesGenerato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueChamain MarreroNo ratings yet
- Transformers Generators and Protection Theory 68Document1 pageTransformers Generators and Protection Theory 68Satyasrinivas PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electricity Using Fan PDFDocument4 pagesGeneration of Electricity Using Fan PDFAmruta KageNo ratings yet
- Ac and DC ModuleDocument123 pagesAc and DC ModuleRaymark Flores EllamilNo ratings yet
- Cut-Out SectionsDocument3 pagesCut-Out SectionsSwaroop MallickNo ratings yet
- Phsyics Revision Notes PhyDocument16 pagesPhsyics Revision Notes PhyAiza ImranNo ratings yet
- IJRTI2304240Document10 pagesIJRTI2304240Xavier BrownNo ratings yet
- Topic 16Document1 pageTopic 16valek02No ratings yet
- Unit 6. Direct Current MachinesDocument37 pagesUnit 6. Direct Current MachinesAgustinBenedictoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document20 pagesModule 1zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Searl TechnologyDocument21 pagesSearl TechnologyMelanie MartinssonNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- motion in 2D - thầy KhánhDocument2 pagesmotion in 2D - thầy KhánhLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- History of Quantum MechanicsDocument22 pagesHistory of Quantum MechanicsLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- Hello TeacherDocument3 pagesHello TeacherLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- W5 Part2Document8 pagesW5 Part2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- TT Co5Document2 pagesTT Co5Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- TT Co5Document7 pagesTT Co5Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - w2Document2 pagesPart 2 - w2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part2 w5Document8 pagesPart2 w5Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - w4Document13 pagesPart 2 - w4Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document5 pagesPart 2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
Part 2 - w4
Part 2 - w4
Uploaded by
Linh ChiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part 2 - w4
Part 2 - w4
Uploaded by
Linh ChiCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Purpose
- Learn the structure and working principle of 2 types of generators: 1
phase and 3 phase
- Understand the method of pairing a generator with a computer to
overcome some difficulties in the experiment.
- Survey and study some characteristic curves of generators
2+3+4. Drawing layout, assembling experimental equipment (not allowed
to take pictures of real experiments nor take videos of experiments. You
can draw with drawing software or draw pictures on paper and take
drawn pictures). Briefly describe the main function of the main
equipment in the experiment.
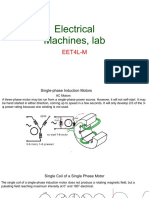
a) Test set: 1 phase generator
1
Tuabin
2
6
4
3
- Turbine: rotates the coil
- 1) Magnet (stator): stand still, attract magnetic field, support motor to
operate. When current is passed through coils placed inside the steel
core, it generates an electromagnetic induction force to convert
electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- 2) Coil (roto): rotates around the magnetic field so that the magnetic
field changes through the coil. The force of interaction between the
coils and the charged magnetic fields creates a torque around the
rotor's axis of rotation.
- 3) LED: glows when current passes through it in a certain direction,
detects direct current or alternating current
- 4) Incandescent lamp: current is detected
- 5) Sensor + adapter: is the connection wire to connect the
experimental device to the computer.
- 6) Computer: describe the current emitted by the generator
b)
Experiment set: 3 phase generator
- Coil (stator): generates induced current.
- Magnet (roto): rotates a magnetic field around a fixed coil, creating a
magnetic field and flux variation in each coil.
- LED: detects current flowing through the coil
- The terminals + electrical circuits in star and triangle shape: plug in
the connecting wires between the devices.
You might also like
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationFrom EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Tecnotion Linear Motors: A Primer ofDocument27 pagesTecnotion Linear Motors: A Primer ofmatadorisheNo ratings yet
- Machine Lesson Final1Document94 pagesMachine Lesson Final1anon_156286001100% (8)
- Part 2 - w2Document2 pagesPart 2 - w2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - w4Document13 pagesPart 2 - w4Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Asynchronous (Or Induction) MachinesDocument40 pagesUnit 4. Asynchronous (Or Induction) MachinesAgustinBenedictoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Final Practical Exam: Pamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Computing and EngineeringDocument3 pagesLaboratory Final Practical Exam: Pamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Computing and EngineeringKrizalene ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJECT DC MotorDocument20 pagesPHY PROJECT DC Motorneelbhan23No ratings yet
- EM-2-PAPER-FINALDocument10 pagesEM-2-PAPER-FINALJose Miguel RuizNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ElectricalmotorsDocument7 pagesLab 6 Electricalmotorsapi-257558550No ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction in an AC Generator.pdf_20240620_010408_0000Document17 pagesMagnetic Induction in an AC Generator.pdf_20240620_010408_0000as2631234No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab March 16 UpdateDocument53 pagesElectrical Machines Lab March 16 Updatepeter vanderNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument7 pagesDC Machinesprakharsrivastava936No ratings yet
- BEEE Module 2 DC MachinesDocument313 pagesBEEE Module 2 DC Machinesmanohar kintaliNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAngelica VersolaNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 MagnetismDocument36 pagesSec 3 MagnetismA. Rahman AliNo ratings yet
- 3 Working Principle and Characteristic of DC Motor(1)Document81 pages3 Working Principle and Characteristic of DC Motor(1)usamaNo ratings yet
- Axial FluxDocument5 pagesAxial FluxsamuelNo ratings yet
- PHY PROJECT DC GeneratorDocument18 pagesPHY PROJECT DC Generatorelfbaba476No ratings yet
- TF Motores InglesDocument37 pagesTF Motores Inglesjdgarciag1No ratings yet
- 1.3 Electrical MachinesDocument31 pages1.3 Electrical MachinesMuhammad Adli Amin Mohd AmzukiNo ratings yet
- CPE400 Lab9 Fermin Gagabi Lim ZurbanoDocument12 pagesCPE400 Lab9 Fermin Gagabi Lim ZurbanoClyde FerminNo ratings yet
- Simple Electric Motor and GeneratorDocument17 pagesSimple Electric Motor and GeneratorAyla BonitaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment 1 TA-AY MEE31Document5 pagesLaboratory Experiment 1 TA-AY MEE31JayNo ratings yet
- Adel LabDocument20 pagesAdel LabKendall BirjueNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENTS WITH SPIRAL AND WANKEL MOTORS, With Ted Loder, Ph.D.Document46 pagesEXPERIMENTS WITH SPIRAL AND WANKEL MOTORS, With Ted Loder, Ph.D.Tedd St Rain100% (1)
- Chapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SDocument112 pagesChapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SLim Kai XuanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Solar Motor?Document11 pagesWhat Is A Solar Motor?D K SHARMANo ratings yet
- DC Generators Jkuat 2024Document10 pagesDC Generators Jkuat 2024sikolia.wanjalaNo ratings yet
- EEC 123 Practical PDFDocument91 pagesEEC 123 Practical PDFEdwinEtuk50% (2)
- P3.21 Study of Industrial MotorsDocument3 pagesP3.21 Study of Industrial MotorsXingfang91No ratings yet
- DC MachineDocument79 pagesDC Machines231052560No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Simple MotorDocument6 pagesExperiment 4 Simple MotorKim HarlyNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - Construction and Operation of A DC GeneratorDocument11 pagesPart 2 - Construction and Operation of A DC GeneratorKevin Lester LoboNo ratings yet
- Observation of Force and Torque On A Current Loop Using A Simplified Electric MotorDocument3 pagesObservation of Force and Torque On A Current Loop Using A Simplified Electric Motorfrances leana capellan100% (2)
- AC Induction Motors - How AC Motors WorkDocument10 pagesAC Induction Motors - How AC Motors WorkBraulio IrrutiaNo ratings yet
- 3rd-4th Semester Detailed Syllabus - EEDocument30 pages3rd-4th Semester Detailed Syllabus - EESAUMYAJIT SABUINo ratings yet
- Marpower Week 5 To 8Document8 pagesMarpower Week 5 To 8Haeisy SimsuangcoNo ratings yet
- Slides EM ch1Document124 pagesSlides EM ch1Saman RubabNo ratings yet
- Period 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and GeneratorsDocument5 pagesPeriod 16 Activity Sheet: Motors and GeneratorsCharlene DinawanaoNo ratings yet
- Uniaxial Shaking Machine of Ground Motion SimulationDocument5 pagesUniaxial Shaking Machine of Ground Motion SimulationSumit TarachandaniNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVESDocument3 pagesOBJECTIVESJulius BoitizonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Chapter 8 Basic Electric Motors Flashcards - QuizletDocument7 pagesElectrical Chapter 8 Basic Electric Motors Flashcards - QuizletAli UzairNo ratings yet
- Long Examination 214Document4 pagesLong Examination 214Kobe Alcantara ReyesNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument20 pagesDC MachinesELON MUSKNo ratings yet
- Generato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueDocument33 pagesGenerato RS: Prepared By: Ms. Clydine Jethna O. SigueChamain MarreroNo ratings yet
- Transformers Generators and Protection Theory 68Document1 pageTransformers Generators and Protection Theory 68Satyasrinivas PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electricity Using Fan PDFDocument4 pagesGeneration of Electricity Using Fan PDFAmruta KageNo ratings yet
- Ac and DC ModuleDocument123 pagesAc and DC ModuleRaymark Flores EllamilNo ratings yet
- Cut-Out SectionsDocument3 pagesCut-Out SectionsSwaroop MallickNo ratings yet
- Phsyics Revision Notes PhyDocument16 pagesPhsyics Revision Notes PhyAiza ImranNo ratings yet
- IJRTI2304240Document10 pagesIJRTI2304240Xavier BrownNo ratings yet
- Topic 16Document1 pageTopic 16valek02No ratings yet
- Unit 6. Direct Current MachinesDocument37 pagesUnit 6. Direct Current MachinesAgustinBenedictoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document20 pagesModule 1zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Searl TechnologyDocument21 pagesSearl TechnologyMelanie MartinssonNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- motion in 2D - thầy KhánhDocument2 pagesmotion in 2D - thầy KhánhLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- History of Quantum MechanicsDocument22 pagesHistory of Quantum MechanicsLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- Hello TeacherDocument3 pagesHello TeacherLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- W5 Part2Document8 pagesW5 Part2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- TT Co5Document2 pagesTT Co5Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- TT Co5Document7 pagesTT Co5Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - w2Document2 pagesPart 2 - w2Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part2 w5Document8 pagesPart2 w5Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - w4Document13 pagesPart 2 - w4Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document5 pagesPart 2Linh ChiNo ratings yet