Professional Documents
Culture Documents
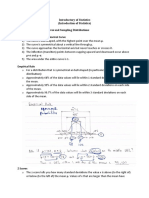
Normal Curve Notes
Normal Curve Notes
Uploaded by
RAISHAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Curve Notes
Normal Curve Notes
Uploaded by
RAISHACopyright:
Available Formats
The Normal Distribution
The Empirical Rule: 65%-95%-99.7%
The Normal Distribution is defined by the density function:
1 (𝑥−𝜇)2
−
𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑒 2𝜎2
𝜎 √2𝜋
The Normal Curve possesses the following properties:
1. The curve is bell-shaped and symmetric about the vertical axis through mean
(population).
2. The total area under the curve is 1.
3. The Mean, Median, and Mode are equal.
4. The curve extends from the mean in both directions toward infinity.
5. The curve has a single peak
6. The mean (average) lies at the center of the distribution.
Compiled by: Robert Jay N. Angco
The following diagram illustrates three various normal curves for different means and
standard deviation.
a. Normal curves with equal standard deviations but with different means.
b. Normal curves with unequal standard deviations but with equal means.
c. Normal curves with unequal standard deviations and unequal means.
The Z-score
Here, the X-score is transformed into a Z-score. Z is called the standard normal
random variable with mean equals 0 and standard deviation equals 1.
Z score tells us the number of standard deviations a score lies above or below its
mean. A positive Z-score is located above the mean and a negative Z-score is below the mean.
It is given by:
𝑥−𝜇
𝑧=
𝜎
Example 1.
A student got a grade of 58 in Psychology and 49 in Statistics. In his Psychology class, the
mean grade was 55 with a standard deviation of 6. On the other hand, the mean grade of his
Compiled by: Robert Jay N. Angco
Statistics class was 45 with a standard deviation of 4. In which of the two subjects did the
student perform better?
Solution:
Computing the Z-scores for each subject:
Graphically,
Thus, the student performs better in Statistics than in Psychology.
There are instances when X lies between two values X1 and X2. In this case, the random
variable Z will fall between the corresponding values.
Compiled by: Robert Jay N. Angco
Note:
In the X curve, the mean and standard deviation values are base from the raw scores given,
while in the Z curve, X values are converted to Z. Also, the value of the mean in the Z curve is
always zero.
Example 2, find:
2.1 P(Z<1.65)
2.2 P(-1.23<Z<1.54)
2.3 P(Z>2.46)
Solution:
Since the values are already converted to Z, we shall locate the values in the Z table right
away.
2.1 P(Z<1.65) = 0.9505
Compiled by: Robert Jay N. Angco
Graphically using the z-curve
Therefore, the area to the left of Z= 1.65 is about 95.05% of the total area under the curve.
2.2 P(-1.23<Z<1.54)
Compiled by: Robert Jay N. Angco
Graphically,
Therefore, the area of the standard normal curve between Z=-1.23 and Z=1.54 is about
82.89% of the total area under the curve.
2.3 P(Z>2.46)
Here, since the total area under the curve is 1 already, then
Exercise (Do it Yourself)
The IQ of 100 college students in CTU are found to be normally distributed with mean 105
and a standard deviation of 8.
a. If a student’s IQ score is 90, what is the probability that another student randomly
selected has an IQ score less than 90?
b. How many students have IQ scores below 90?
c. How many students have IQ scores between 80 and 110?
d. What is the probability that a student selected at random will have an IQ score
greater than 100?
Show the x-curve and the z-curve.
Compiled by: Robert Jay N. Angco
You might also like
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Stat. & Prob 11Document7 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Stat. & Prob 11Marinella Mauro100% (4)
- MATH 10 - Q4 - WEEK 1 - MODULE 1 - Illustrating-The-Measures-Of-Position-Quartiles-Deciles-And-PercentilesDocument23 pagesMATH 10 - Q4 - WEEK 1 - MODULE 1 - Illustrating-The-Measures-Of-Position-Quartiles-Deciles-And-PercentilesLyle Isaac L. Illaga67% (27)
- Probability and Statistics: Progress Test 2Document4 pagesProbability and Statistics: Progress Test 2Duy QuangNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12: Continuous Distributions: Prepared By: Mashfiqul Huq Chowdhury September 18, 2020Document5 pagesLecture-12: Continuous Distributions: Prepared By: Mashfiqul Huq Chowdhury September 18, 2020Monir HossainNo ratings yet
- Normal Random VariableDocument8 pagesNormal Random VariableLoraine Buen FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 4.-Normal-Distribution - LECTUREDocument34 pages4.-Normal-Distribution - LECTURERoyce GomezNo ratings yet
- StatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFDocument9 pagesStatProb LAS Week2 Normal Distribution PDFMark Cidric Roquero IINo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module For Grade 11: Chapter Ii: Normal DistributionDocument38 pagesSelf-Learning Module For Grade 11: Chapter Ii: Normal DistributionAldrin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Prob and Stats, Nov 5: The Normal Probability Distribution Book Sections: N/ADocument22 pagesProb and Stats, Nov 5: The Normal Probability Distribution Book Sections: N/AShanna Mae TarusanNo ratings yet
- PO 1-09 Normal Distribution PDFDocument4 pagesPO 1-09 Normal Distribution PDFshynaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Normal DistributionDocument39 pagesChapter II Normal DistributionMaricris Jagto-calixtoNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument32 pagesNormal Distributionmariannchello123No ratings yet
- MS104 March 2 DiscussionDocument36 pagesMS104 March 2 DiscussionEminNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document34 pagesLecture 6Luna eukharisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3B - SPECIAL: Probability DistributionDocument28 pagesChapter 3B - SPECIAL: Probability DistributionAhmad AiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Z ScoreDocument32 pagesLesson 5 Z ScoreLala CkeeNo ratings yet
- 1 Normal DistributionDocument34 pages1 Normal DistributionDANELYN PINGKIANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03-Normal DistributionsDocument28 pagesChapter 03-Normal DistributionsamandaluvsanimalsNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument11 pagesNormal DistributionJema SantillanNo ratings yet
- 04 NormalDistributionDocument43 pages04 NormalDistributionShane Olen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument63 pagesNormal DistributionSafi Sheikh100% (1)
- The Unit Normal CurveDocument9 pagesThe Unit Normal CurveGrace GuiebNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Lecture 2Document26 pagesUnit 5 Lecture 2kousar parveenNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Normal DistributionDocument60 pagesLESSON 4 Normal DistributionCarbon CopyNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 5) Normal DistributionDocument55 pages(Lecture 5) Normal DistributionSabaNo ratings yet
- P&S 6Document69 pagesP&S 6muhyadin20husseinNo ratings yet
- Probab Stat 5 8 1Document29 pagesProbab Stat 5 8 1Roan CaluagNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability 11Document12 pagesStatistics and Probability 11joshcaleboliverosNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesDocument11 pagesSaint Joseph College Senior High School Department Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte 6600 PhilippinesJimkenneth RanesNo ratings yet
- Converting Z ScoresDocument14 pagesConverting Z ScoresMary Jane Duma-ogNo ratings yet
- Review 2 PDFDocument10 pagesReview 2 PDFParminder SinghNo ratings yet
- WIN SEM (2020-21) CSE4029 ETH AP2020215000156 Reference Material I 27-Jan-2021 DistibutionDocument7 pagesWIN SEM (2020-21) CSE4029 ETH AP2020215000156 Reference Material I 27-Jan-2021 DistibutionmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- Week11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)Document59 pagesWeek11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)düşünennurNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument29 pagesNormal DistributionGuard'z SmieyeleNo ratings yet
- Topic IVDocument28 pagesTopic IVluciagabriela.theoktisto01No ratings yet
- Las Statistics&probability Week4Document27 pagesLas Statistics&probability Week4Jemar AlipioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Normal DistributionDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Normal DistributionJustin BorjaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 M3 The Normal DistributionDocument44 pagesLESSON 3 M3 The Normal DistributionEunice M100% (1)
- Review 2Document10 pagesReview 2Anastasia Monica KhunniegalshottestNo ratings yet
- Day 02-Random Variable and Probability - Part (I)Document34 pagesDay 02-Random Variable and Probability - Part (I)Sparsh VijayvargiaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument60 pagesContinuous Probability DistributionJethro MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 1 Properties of Normal DistributionDocument36 pagesModule 5 Lesson 1 Properties of Normal DistributionShai MacapillarNo ratings yet
- Normaldistribution 160627092159 PDFDocument24 pagesNormaldistribution 160627092159 PDFGladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- Normaldistribution 160627092159Document24 pagesNormaldistribution 160627092159Bryan Jay dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument26 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityMarianne Pareja100% (1)
- Lesson 2: Normal DistributionDocument47 pagesLesson 2: Normal DistributionMARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- The Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesThe Normal DistributionDog VenturesNo ratings yet
- Gec004 - Module 4 - Normal Distribution and RegressionDocument84 pagesGec004 - Module 4 - Normal Distribution and RegressionDan TañoNo ratings yet
- AStat Module - Q4 W1 and W2 1 PDFDocument8 pagesAStat Module - Q4 W1 and W2 1 PDF7C-B05 de Guzman, Jaydee M.No ratings yet
- A. The Standard Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesA. The Standard Normal DistributionAlexa LeeNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionsDocument44 pagesProbability Distributionsjohn baptist ngolobeNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Part 1Document42 pagesCH 7 Part 1kavinbhatia777No ratings yet
- Chap4 ElsyDocument60 pagesChap4 ElsyKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions: by Dr. Ameer Kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community MedicineDocument37 pagesProbability Distributions: by Dr. Ameer Kadhim Hussein. M.B.Ch.B. FICMS (Community Medicinemedical.student.messiNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesModule 6 Normal Distributions.prosia.maviemhoniqueNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Probability and Normal DistributionDocument30 pagesWeek 2 - Probability and Normal DistributionAbrashiNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument27 pagesStatisticsBernice Mikaela IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Stats10 - Chapter 6Document51 pagesStats10 - Chapter 6poopypee6942021No ratings yet
- Statistics - Special Probability DistributionsDocument46 pagesStatistics - Special Probability DistributionsMariano Nino OlivaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Philippine Political Science Journal January 2008Document10 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Philippine Political Science Journal January 2008RAISHANo ratings yet
- Notes 109Document26 pagesNotes 109RAISHANo ratings yet
- Baselinenutritional Status 2019 2020Document20 pagesBaselinenutritional Status 2019 2020RAISHANo ratings yet
- Teaching Scienceinthe New NormalDocument18 pagesTeaching Scienceinthe New NormalRAISHANo ratings yet
- Stat - 7 Correlation and Regression AnalysisDocument9 pagesStat - 7 Correlation and Regression AnalysisRAISHANo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Materials AToolin Improving Students Academic PerformanceDocument23 pagesStrategic Intervention Materials AToolin Improving Students Academic PerformanceRAISHANo ratings yet
- ACTIONPLANSCIENCE2022Document3 pagesACTIONPLANSCIENCE2022RAISHANo ratings yet
- 3sectionsf To F Class ScheduleDocument5 pages3sectionsf To F Class ScheduleRAISHANo ratings yet
- Which Test Should I Use (Revised)Document1 pageWhich Test Should I Use (Revised)RAISHANo ratings yet
- Limiting Reagent Worksheet No AnswersDocument4 pagesLimiting Reagent Worksheet No AnswersRAISHANo ratings yet
- Form 14 by Teacher TechDocument4 pagesForm 14 by Teacher TechRAISHANo ratings yet
- Ijerph 15 01271 v2Document16 pagesIjerph 15 01271 v2RAISHANo ratings yet
- Averages: Mean, Median, And Mode (Group Data) : εf cf< fmDocument3 pagesAverages: Mean, Median, And Mode (Group Data) : εf cf< fmmichNo ratings yet
- CE 459 Statistics: Assistant Prof. Muhammet Vefa AKPINARDocument211 pagesCE 459 Statistics: Assistant Prof. Muhammet Vefa AKPINARGhulam ShabirNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions 10.1. Single Mean:: SolutionDocument15 pagesSampling Distributions 10.1. Single Mean:: SolutionTalha AzanNo ratings yet
- Other Chart Types HSC QuestionsDocument16 pagesOther Chart Types HSC QuestionsDania SharjeelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13: Describing Variability Using The Interquartile Range (IQR)Document10 pagesLesson 13: Describing Variability Using The Interquartile Range (IQR)Hiền TTTNo ratings yet
- Numerical Descriptive MeasuresDocument21 pagesNumerical Descriptive MeasuresANKUR ARYANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument34 pagesUntitledCherry Arcilla CanapiNo ratings yet
- MATM111Document8 pagesMATM111Maria Jenina CervantesNo ratings yet
- Case Solve Chapter 13Document4 pagesCase Solve Chapter 13Ashik Uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledkihembo pamelahNo ratings yet
- Measures of Location and VARIATION For 1 VariableDocument44 pagesMeasures of Location and VARIATION For 1 VariableRobert ManeaNo ratings yet
- Winters Model Excel For SPCDocument14 pagesWinters Model Excel For SPCNitin ShankarNo ratings yet
- Genetica CuantitativaDocument120 pagesGenetica CuantitativaAlexis Josue Vallecillo GodoyNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument41 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityMarjhane RañaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Sampling DistributionDocument4 pagesLecture 5 - Sampling Distributionhoangminhdung2209No ratings yet
- Engineering Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesEngineering Data AnalysisDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistic'S: Activity #2Document9 pagesApplied Statistic'S: Activity #2MUHAMMAD AMMAD ARSHADNo ratings yet
- C E R T I F I C A T I O N: Cultural Mission AcademyDocument12 pagesC E R T I F I C A T I O N: Cultural Mission AcademyKisha Faith Pulido ObinaNo ratings yet
- Ungrouped DataDocument3 pagesUngrouped DatazulheymeyNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document48 pagesClass 1MoamenNo ratings yet
- LAS Quarter-4-GRADE-7Document6 pagesLAS Quarter-4-GRADE-7Hazy Mae MonteroNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Symbols TableDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols TableChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Statistics: A Brach of Mathematics Which Deals With Collection, Classification andDocument12 pagesStatistics: Statistics: A Brach of Mathematics Which Deals With Collection, Classification andKomanduri Murali SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis - Chapter 4 - Model Adequacy Checking - Shalabh, IIT KanpurDocument36 pagesRegression Analysis - Chapter 4 - Model Adequacy Checking - Shalabh, IIT KanpurAbcNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Data ManagementPart 1 For SPOCDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Data ManagementPart 1 For SPOCRyan Cholo P. CarlosNo ratings yet
- 3 Dispersion Skewness Kurtosis PDFDocument42 pages3 Dispersion Skewness Kurtosis PDFKelvin Kayode OlukojuNo ratings yet
- Hydrology AssignmentDocument6 pagesHydrology AssignmentHopeson NazombeNo ratings yet
- Formulae For Mhrm510: Descriptive StatisticsDocument3 pagesFormulae For Mhrm510: Descriptive StatisticsDon Rayburn PilanNo ratings yet