Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practice 10302 Ans
Practice 10302 Ans
Uploaded by
Pak Yu Chau0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 page1. When we get out of a swimming pool, water on our skin absorbs energy from our bodies and evaporates, causing us to lose energy and feel cold. If it is windy, the evaporation and cooling rates will be higher.
2. When water vapor meets a cool surface, it will condense and release energy. Water vapor condenses on cold glasses after getting out of a car or steamy bathroom.
3. Glass A has half its surface covered by plastic, trapping some evaporating water vapor and lowering the evaporation rate. Condensed water drips back in, slowing the drop in water level compared to Glass B.
Original Description:
Original Title
Practice_10302_ans
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. When we get out of a swimming pool, water on our skin absorbs energy from our bodies and evaporates, causing us to lose energy and feel cold. If it is windy, the evaporation and cooling rates will be higher.
2. When water vapor meets a cool surface, it will condense and release energy. Water vapor condenses on cold glasses after getting out of a car or steamy bathroom.
3. Glass A has half its surface covered by plastic, trapping some evaporating water vapor and lowering the evaporation rate. Condensed water drips back in, slowing the drop in water level compared to Glass B.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pagePractice 10302 Ans
Practice 10302 Ans
Uploaded by
Pak Yu Chau1. When we get out of a swimming pool, water on our skin absorbs energy from our bodies and evaporates, causing us to lose energy and feel cold. If it is windy, the evaporation and cooling rates will be higher.
2. When water vapor meets a cool surface, it will condense and release energy. Water vapor condenses on cold glasses after getting out of a car or steamy bathroom.
3. Glass A has half its surface covered by plastic, trapping some evaporating water vapor and lowering the evaporation rate. Condensed water drips back in, slowing the drop in water level compared to Glass B.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
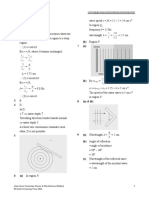
1 Heat and Gases Chapter 3 Change of State
Practice 3.2 (p.86) =
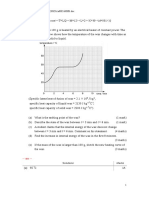
1 A
2 C = 314 W
3 C (c) Any two of the following:
4 Energy loss Temperature of the liquid
= mlv = 1.5 2.26 10 = 3.39 10 J
6 6 Surface area of the liquid
5 When we get out of a swimming pool, water Density of vapour
on our skin absorbs energy from our bodies 8 (a) Energy taken away = mlv
and evaporates. Therefore, we lose energy and = 0.2 2.26 106
feel cold. = 4.52 105 J
If it is windy, the evaporation rate, and (b) By Q = mcT,
therefore the rate at which our bodies lose decrease in temperature =
energy, will be higher. We would feel much
cooler. =
6 When water vapour meets a cool surface, it
= 2.58 C
will condense on the surface and release
9 Water vapour condenses to droplets on cold
energy.
surfaces.
(a) The glasses are cooler than the
Since the temperature is lower than the
surroundings when the person has just
freezing point, the droplets solidify to form
got out of the car. Therefore, water
frost.
vapour condenses on them.
10 As glass A is half covered by a plastic sheet,
(b) The reason is similar to (a). The water
some water vapour that evaporates from the
vapour in the steamy bathroom is at a
hot water is trapped in the glass and the
higher temperature than the glasses.
density of vapour increases. Therefore, the
Also, the large amount of vapour
rate of evaporation is lower in glass A. Also,
enhances the condensation.
water vapour condenses on the plastic sheet
7 (a) Assume that the latent heat of
and drips back into the glass. As a result, the
vaporization is solely obtained from his
water level in glass A drops more slowly than
body.
that of glass B.
Q = mlv = 0.5 2.26 106 = 1.13 106 J
The maximum amount of energy
removed is 1.13 106 J.
(b) Rate of cooling by sweating
=
New Senior Secondary Physics at Work (Second Edition) 1
Oxford University Press 2015
You might also like
- Chemistry SL - ANSWERS - Third Edition - Pearson 2023Document55 pagesChemistry SL - ANSWERS - Third Edition - Pearson 2023Kelvin ChoyNo ratings yet
- SG Unit8ProgressCheckMCQDocument20 pagesSG Unit8ProgressCheckMCQAzfar MohamedNo ratings yet
- 02 07 Transpiration Lab ReportDocument6 pages02 07 Transpiration Lab ReportIsland VitalNo ratings yet
- Physics 03 - Exercise - Solutions - e PDFDocument12 pagesPhysics 03 - Exercise - Solutions - e PDFNg Ho Wang吳皓弘No ratings yet
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-9 Latent Heat PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-9 Latent Heat PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- On Site Water Tightness Testing For Curtain WallingDocument4 pagesOn Site Water Tightness Testing For Curtain WallingManojkumar kondaveetiNo ratings yet
- Scicent AB TE U2 eDocument28 pagesScicent AB TE U2 erayckng2No ratings yet
- Assignment AC U2 Final eDocument28 pagesAssignment AC U2 Final eYuenHei KwokNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Part 2Document10 pagesChemistry - Part 2BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Phy Ch3 Long QuestionDocument11 pagesPhy Ch3 Long Question黃家熙No ratings yet
- Ap 10 Ps em Qa 01 Heat 5Document3 pagesAp 10 Ps em Qa 01 Heat 5VikashNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chem CH 1 2ND HalfDocument1 pageWorksheet Chem CH 1 2ND Halfanushri sinhaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings - Practice SheetDocument3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings - Practice Sheetsifivar867No ratings yet
- HL AnswersDocument33 pagesHL AnswersabidmothishamNo ratings yet
- Section 6 - General Physics 2 With SolutionsDocument15 pagesSection 6 - General Physics 2 With SolutionspaimoNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers For Lecture 2: Molecular Weight, G/moleDocument7 pagesQuestions and Answers For Lecture 2: Molecular Weight, G/moleAndrew SetiadiNo ratings yet
- AK_Assignment_2_Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument7 pagesAK_Assignment_2_Matter in Our SurroundingsSharayu KalibhatNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings Practice Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings Practice Sheet PDF2medhajainNo ratings yet
- Kids Solutions Pvt. LTD.: Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument5 pagesKids Solutions Pvt. LTD.: Matter in Our Surroundingsbashu gamersNo ratings yet
- Thermal and Marine Pollution NewDocument6 pagesThermal and Marine Pollution NewGourav YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document7 pagesChapter 03api-3826695100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDocument20 pagesMechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenjjNo ratings yet
- Test Chapter 17Document18 pagesTest Chapter 17damonchooNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDebroop MajumderNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Answers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument62 pagesHapter: Answers Multiple Choice QuestionsRajatNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Exemplar Chapter 1 AnswerDocument3 pages9 Science Exemplar Chapter 1 Answeratul kumarNo ratings yet
- 3412EM-Physics Study Material Chap-1-7Document85 pages3412EM-Physics Study Material Chap-1-7Karnati Siva rama Swetha ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2021 P5 Science Weighted Assessment 1 AiTongDocument26 pages2021 P5 Science Weighted Assessment 1 AiTongအင္တာေနရွင္နယ္ေက်ာင္းမ်ား၏ ေမးခြန္လႊာဘာသာစံုျဖန္႕ခ်ီေရးNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Workbook ANSWERDocument39 pagesUnit 2 Workbook ANSWERTang Hing Yiu, SamuelNo ratings yet
- Class 10 p1 Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pagesClass 10 p1 Thermal PhysicsSameer Abu MunsharNo ratings yet
- ch1 1Document9 pagesch1 1vrndrnirmalkar11No ratings yet
- Elasticity - Thermal Expansion - Calorimetry - Heat - CC - WADocument12 pagesElasticity - Thermal Expansion - Calorimetry - Heat - CC - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- Practice 10402 AnsDocument1 pagePractice 10402 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Elixir Chemistry Tuition Center, Ramnagar-3, Agartala, Tripura-799002, PH: 8794052358Document19 pagesElixir Chemistry Tuition Center, Ramnagar-3, Agartala, Tripura-799002, PH: 8794052358Elixir ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Important Questions Before Half Yearly ExamDocument14 pagesChemistry: Important Questions Before Half Yearly ExamSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Thermal Physics, Home Work Sheet-3Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Thermal Physics, Home Work Sheet-3bhadrabijumohan2007No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics PartDocument17 pagesThermal Physics PartSammyJayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 (Done)Document6 pagesWorksheet 1 (Done)samyak jainNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up: Wet Floor Is Left To Dry Up. Are These Examples of Evaporation?Document33 pagesWarm-Up: Wet Floor Is Left To Dry Up. Are These Examples of Evaporation?Fauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- Part2 ch03Document4 pagesPart2 ch03api-3705610No ratings yet
- PhyChem2 FinalsDocument2 pagesPhyChem2 FinalsKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- Assignment On CH-1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesAssignment On CH-1 Matter in Our Surroundingsabc100% (1)
- Item 0 20181223050211203Document10 pagesItem 0 20181223050211203DeepNo ratings yet
- 4 Transfer Processes: Practice 4.1 (p.109)Document6 pages4 Transfer Processes: Practice 4.1 (p.109)Oscar TSANGNo ratings yet
- Exercise - I: Objective ProblemsDocument6 pagesExercise - I: Objective ProblemsRishabhNo ratings yet
- Exercise - I: Objective ProblemsDocument6 pagesExercise - I: Objective Problemsashu mishraNo ratings yet
- 9th Quiz Chap 11Document3 pages9th Quiz Chap 11Sherry DkNo ratings yet
- The Specific Heat of The Metal Object Was Determined: 5. ConclusionDocument3 pagesThe Specific Heat of The Metal Object Was Determined: 5. ConclusionElishae SamonteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesDocument24 pagesChapter 12 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase ChangesGregNo ratings yet
- CH - 6 Heat and EnergyDocument2 pagesCH - 6 Heat and Energyalonesuvam.123No ratings yet
- Physics em PDFDocument79 pagesPhysics em PDFD SiddaiahNo ratings yet
- Specific and Latent Heat: MarkschemeDocument6 pagesSpecific and Latent Heat: MarkschememNo ratings yet
- Physics Exercise 5Document26 pagesPhysics Exercise 5Law Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surrounding QuestionDocument2 pagesMatter in Our Surrounding QuestionMachhindra DahifaleNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Pre C.T 2020-2021 Subject: Physics Duration: 30 Min. Date: Name: Grade:-VIII Sec:-RollDocument5 pages4th Quarter Pre C.T 2020-2021 Subject: Physics Duration: 30 Min. Date: Name: Grade:-VIII Sec:-RollWakif Khan PrantoNo ratings yet
- Sol - Test - No7 Iit-Jee XiDocument5 pagesSol - Test - No7 Iit-Jee XiPriyansh AnandNo ratings yet
- Episode 608 - Latent Heat - 1 - 0Document16 pagesEpisode 608 - Latent Heat - 1 - 0revetalkNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 1Document12 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 1vaishnavisingh 8BNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 8 Physics Sample Paper 2Document5 pagesICSE Class 8 Physics Sample Paper 2madhumitra mohantyNo ratings yet
- P6 Water Cycle Revision 2 Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesP6 Water Cycle Revision 2 Worksheet AnswersAnanth GanigaNo ratings yet
- Simulating Weather Experiments for Kids - Science Book of Experiments | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandSimulating Weather Experiments for Kids - Science Book of Experiments | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Simple Experiments in Static Electricity - A Series of Instructive and Entertaining Experiments in Static Electricity for Students and AmateursFrom EverandSimple Experiments in Static Electricity - A Series of Instructive and Entertaining Experiments in Static Electricity for Students and AmateursNo ratings yet
- Practice 3B0402 AnsDocument2 pagesPractice 3B0402 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Practice 3B0603 AnsDocument1 pagePractice 3B0603 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Practice 3B0502 AnsDocument2 pagesPractice 3B0502 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Practice 10401 AnsDocument1 pagePractice 10401 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Practice 3B0704 AnsDocument1 pagePractice 3B0704 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Practice 10402 AnsDocument1 pagePractice 10402 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- RevEx 101 AnsDocument3 pagesRevEx 101 AnsPak Yu ChauNo ratings yet
- Health6 q1 Module2Document23 pagesHealth6 q1 Module2Precious Marga BaldeoNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Integrated Strategies For The Control and Mitigation of Plastic and Microplastic PollutionDocument19 pagesSolutions and Integrated Strategies For The Control and Mitigation of Plastic and Microplastic Pollutionashadi asriNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan Geography English (2023)Document169 pagesRajasthan Geography English (2023)manvendrasingh618No ratings yet
- 03-730003-4800000507-CH2-MEC-DBR-000003 - A v11Document30 pages03-730003-4800000507-CH2-MEC-DBR-000003 - A v11WuillNo ratings yet
- Wall Mounted Gas Boiler - AristonDocument13 pagesWall Mounted Gas Boiler - Aristononga yaaNo ratings yet
- Forest DepartmentDocument20 pagesForest Departmentstella nNo ratings yet
- GRP Sectional Tanks BrochureDocument16 pagesGRP Sectional Tanks BrochurepipecogroupNo ratings yet
- Final Vertical Green Habitat DissertationDocument53 pagesFinal Vertical Green Habitat DissertationEkansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- + + 5 10 (5 × 2 ) + (5 × ) 10 18 (Maximum Ultimate BOD) Maximum 5-Day BOD (1 ) 18 × (1 )Document3 pages+ + 5 10 (5 × 2 ) + (5 × ) 10 18 (Maximum Ultimate BOD) Maximum 5-Day BOD (1 ) 18 × (1 )JaneNo ratings yet
- Piping Considerations - Maximum Fluid VelocityDocument1 pagePiping Considerations - Maximum Fluid VelocityTran Ngoc HaNo ratings yet
- Mcdowall & Taylor. - Enviromental Indicators of Habitat Quality in A Migratory Freshwater FDocument18 pagesMcdowall & Taylor. - Enviromental Indicators of Habitat Quality in A Migratory Freshwater FLuisCarlosVillarrealDíazNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions of This NOCDocument9 pagesTerms and Conditions of This NOCARUL SANKARANNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions (91 To 105) : SSC-JE, AE (PSC), RRB EtcDocument33 pagesObjective Questions (91 To 105) : SSC-JE, AE (PSC), RRB EtcSuvendu ParidaNo ratings yet
- Wamser HydropowerDocument14 pagesWamser HydropowerWing MacNo ratings yet
- Sierra Air Flow (Compatibility Mode)Document19 pagesSierra Air Flow (Compatibility Mode)DangolNo ratings yet
- GAD Report 2016Document18 pagesGAD Report 2016Pa Rian Rho DoraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties and Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesMechanical Properties and Physical Propertiesimran shakirNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project: Biology 2022-2023Document11 pagesInvestigatory Project: Biology 2022-2023EVAN GERSHONNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Multi Influence Factor, Weight of Evidence and Frequency Ratio Techniques To Evaluate Groundwater Potential Zones of Basaltic Aquifer SystemsDocument31 pagesComparison of Multi Influence Factor, Weight of Evidence and Frequency Ratio Techniques To Evaluate Groundwater Potential Zones of Basaltic Aquifer SystemsnitinNo ratings yet
- Rosendal, Hardangerfjord: Historic Village by The FjordDocument1 pageRosendal, Hardangerfjord: Historic Village by The FjordGrazyella YoshidaNo ratings yet
- Shvila 1943 - Correlation of The Habitats of Amphibians With Their Ability To Survive The Loss ofDocument9 pagesShvila 1943 - Correlation of The Habitats of Amphibians With Their Ability To Survive The Loss ofFrancisco IribasNo ratings yet
- HPL-Pipe Manifold Drg-ModelDocument1 pageHPL-Pipe Manifold Drg-ModelSandhyaRamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Dimtu - Blate Military Borro Pit (M' 1+00 RHS)Document48 pagesDimtu - Blate Military Borro Pit (M' 1+00 RHS)AshebirNo ratings yet
- Oil Spills in Marine EnvironmentDocument13 pagesOil Spills in Marine EnvironmentDesy NofellahNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Engr. Usman Muhammad B.Sc. Civil Engineering (UET Taxila) M.Sc. Structural Engineering (UET Taxila)Document56 pagesInstructor: Engr. Usman Muhammad B.Sc. Civil Engineering (UET Taxila) M.Sc. Structural Engineering (UET Taxila)nauman100% (1)
- JSAbrochureDocument44 pagesJSAbrochureShuja ShowkatNo ratings yet
- Master Plumbing 4Document23 pagesMaster Plumbing 4Roland CepedaNo ratings yet