Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sailing Boat Description Transcript
Sailing Boat Description Transcript
Uploaded by
Yannick Paka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views4 pagesThis document provides an overview of sailing terminology and parts of a sailboat. It defines key terms like port, starboard, bow, stern, beam, ahead, astern, and discusses sailing maneuvers like tacking, jibing, beating, and reaching. It then describes the main parts of a sailboat including the deck, cabin, cockpit, companionway, hatch, helm, traveler, standing and running rigging, sails, boom, mast, rudder, and other hardware. The document aims to establish a foundational understanding of sailing language and boat components.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of sailing terminology and parts of a sailboat. It defines key terms like port, starboard, bow, stern, beam, ahead, astern, and discusses sailing maneuvers like tacking, jibing, beating, and reaching. It then describes the main parts of a sailboat including the deck, cabin, cockpit, companionway, hatch, helm, traveler, standing and running rigging, sails, boom, mast, rudder, and other hardware. The document aims to establish a foundational understanding of sailing language and boat components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views4 pagesSailing Boat Description Transcript
Sailing Boat Description Transcript
Uploaded by
Yannick PakaThis document provides an overview of sailing terminology and parts of a sailboat. It defines key terms like port, starboard, bow, stern, beam, ahead, astern, and discusses sailing maneuvers like tacking, jibing, beating, and reaching. It then describes the main parts of a sailboat including the deck, cabin, cockpit, companionway, hatch, helm, traveler, standing and running rigging, sails, boom, mast, rudder, and other hardware. The document aims to establish a foundational understanding of sailing language and boat components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
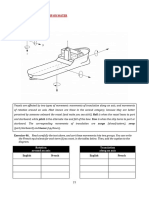
SAILING BOAT DESCRIPTION the wind upwind is called windward
TRANSCRIPT while
Ep 4: Learn to Sail: Part 1: downwind is leeward coming above or
tacking means to turn the boat with the
Parts of the Boat and Sailing bow passing through the eye of the
Terminology wind
while under sail
https://www.youtube.com/watch? driving is to turn the boat with the
v=67e5N2BsQfE stern passing through the eye of the
i everyone welcome to carpe diem
sailing my name is Marco I'm a sail wind while under sail
Canada cruising instructor and in since the sailboat cannot sail straight
today's video I'll be covering parts of into the wind we have to sail at an
the boat and some sailing terminology angle to it while coming about or
tacking at intervals in order to gain
in my 25 plus years of teaching I have ground upwind this is called a beat or
found that learning the language of beating to weather whenever a boat is
sailing often represents a bigger sailing upwind the pressure in the sails
challenge than actually learning to sail forces the boat to go sideways
learning the terms and parts of the sailboats
boat carry center boards or keels to create
is fundamental to establishing a lateral resistance all boats will drift
foundation and a logical place to start sideways to varying degrees
so we will do that here some of the depending on
terms will be self-explanatory like many factors this sideways drift while
cabin or deck but others like topping sailing upwind is referred to as leeway
lift or fairlead will not and will we can however sail directly before the
require some explanation to make sure wind and that is referred to as a run or
nothing is left out and to maximize your running the sails are generally set on
understanding of the terms I will be opposite sides of the boat and this is
covering them all methodically so let's called sailing wing on wing if not
get past all this and onto the pure trying to reach an upwind destination
unabated joy that sailing can be for by
free downloads of the diagrams used beating or running downwind we can
in essentially sail across the wind at
this video as well as notes and various angles this is what we call
checklists please visit our website at reaching is further divided
wwlp.com and now let's get started the into types of reaches based on the
left side of the boat is port the right angle
starboard the front of the boat is the of the wind but more on that in our
bow and the back the stern the widest video on the points of sail and finally
part of the boat is called a beam in a major safety point we have no doubt
front of the boat or moving forward is all heard horror stories of the boom
ahead while behind a boat or moving crashing across the boat indeed
backwards is a stern right angles to the people
boat is called a beam and forward and have been seriously injured so it's
aft are turns relative to being on the important to understand how this
boat much of sailing is in reference to happens
as the boat sails downwind the only
thing holding the mainsail forward is mast through an articulating joint
the wind pressure should the wind shift called the gooseneck the standing
or the boat change direction so that the rigging which consists of the four stay
wind gets in behind the mainsail it will the backstay and the shrouds holds the
come crashing over in what is called mast up the stays and shrouds are
an connected to the mast by tanks and to
accidental or flying jibe when the wind the hull in deck by chain plates the
shifts to the same side of the boat that standing rigging is tensioned with
the mainsail is on we run the risk of an turnbuckles the running rigging is
accidental jibe this is referred to as made
sailing by the lis now that we've up of all the working lines on the boat
covered some terms let's move on to the main sheet is the main line that
the controls the angle and shape of the
parts of the boat the deck and cabin mainsail the boom bang along with the
are traveller help to fine-tune the shape of
self-explanatory the sail the topping lift holds the end
the cockpit is the main working center of the boom up when the mainsail is
of a sailboat the companionway is the not
main staircase down into the cabin the in use the heavy loads on keel boats
main hatch covers the companionway are
while managed by winches the windlass is
the secondary midships and forward an
hatches provide ventilation and electrical anchor winch found on larger
emergency exits boats the push bit is the safety railing
the helm is the steering station and can at the stern of the boat
be a traditional tiller or more popular while the pulpit is at the bow they are
on newer boats a wheel the traveler is connected by lifelines which are
connected to the mainsheet which supported along their length by steel
incidentally is a line which controls posts called stanchions spreaders
the mainsail fairleads redirect the load of the shrouds to the
direct jib or Genoa sheets once again top of the mast the transom is the very
these are lines to the cockpit clutches back of the boat and traditionally
or jammers are line managing tools rudders were hung here the gudgeon
that is a
usually lead to a winch cleats are used tube which receives the pintle to create
to make lines fast they can be found on a hinge shackles in their various
the mast or the boom as well as on configurations connect lines to
deck hardware
looking at the boat in profile we have and sails now that we've seen the parts
the hull which includes the keel as on a diagram I'd like to go through our
mentioned the keel provides lateral teaching boat and just go over the
resistance which allows the boat to sail parts
upwind on a keel boat once again just to give you an idea of
it also provides ballast which helps how they're laid out on an actual boat
keep the boat upright the rudder steers so starting at the very back of the boat
the boat the mast holds the sails up at the stern we have our boarding
while the boom works at the mainsheet ladder
to and then just for to the boarding ladder
control the shape and angle of the we have this hard railing here which is
mainsail the boom is connected to the called the push bit for to the push bit
we have the backstay the backstay is are the lines that actually control the
part of the standing rigging the sails since we only have the two
standing rigging is the rigging that winches
supports the mast from falling side to and we have eight different lines
side and fore and aft leading forward coming
from the push bit are these lifelines through here we also have these
the lifelines lead all the way forward things
to the pulpit and on the way they're here called clutches you can also have
supported by stainless steel posts jammers different types of rope line
called stanchions another piece of managing tools so that when these
deck lines
hardware down here which is very are not on the winches they can be
common held
on boats is called cleat cleats are used fast by these clutches four of the
to make lines fast in this case dock dogger we have this which is called the
lines moving into the middle of the traveler the mainsheet is connected to
cockpit which is the main working area the traveler and the mainsheet is also
of a sail boat we have the helm in this connected to the boom which is
case the helm is a wheel you can also ultimately connected to the mainsail
have a more traditional tiller we have a and
compass we have engine controls we you'll see later on in our videos on how
have a boat sails that the mainsheet and the
instruments there's a line back here traveler are used to shape the mainsail
which is called a furling line that that's all I'm gonna say about that for
furling line leads forward and actually now
rolls and unrolls but it's nice to know what exactly the
are John Genoa or head sail a little bit traveler is the traveler lines do run
more in the video coming up later on through the dogger windows and back
that a lot of these loads are quite into
heavy so we use winches for the cockpit so I can control everything
mechanical from the cockpit as I mentioned earlier
advantage we're gonna have another all of these lines are part of the
video running rigging so these are halyards
coming up later on the different types and reefing lines the blue one is the
of winches and how to safely use these mainsheet this one right here is the
winches moving forward into the boom vang these here are Genoa or jib
companionway sheets or head sail sheets so any of
the companionway is the main the
staircase sails that we mount up forward or
down into the boat we have the main college called head sails the Genoa is
hatch which closes the top of the the big one jibs tend to be smaller
companionway and then these little we have handrails here and this part is
boards called wash boards or drop called a lifeline the lifelines are held
boards up by stanchions and the lifelines
will slide in here to seal this area off connect the pulpit and the push bit now
in this area here under this canopy more of the standing rigging these
called the Dodger we have two more ones
winches and we have in this case eight are called shrouds the shrouds are
lines these lines are all part of the connected to the boat at the bottom
running rigging so the running rigging through chain plates the top of the
shroud where it's connected to the
mast
is called the tang
and tanks traditionally were just plates
through bolted on the mast and I'll
have
a picture of that we have the mast the
boom is connected to the mast through
the gooseneck the topping lift is a line
that actually goes from the top of the
mast to the aft end of the boom to hold
the boom up when the mainsail is
actually lowered holding our mainsail in
place our our sail ties and you'll
notice that the sail is nice and neatly
flaked on the boom which is how a sail
should be stowed moving forward to
the fore deck we have our forward
hatch and
we have our pulpit we have the anchor
Locker with our anchor Road we have
another dock or a deck cleat with our
bow breast line and our spring line we
have an anchor up forward we have a
furling system so the furling system is
a way of stowing a head sail on the
boat
without having to put it up and down if
you had to put it up and down you
would
actually be clipping the sail on to the
four-state the force stays the standing
rigging that holds the mast up from the
front of the boat and you have these
clips called Hanks and the Hanks
would
actually clip the fail on to the force
day in this case with our throwing line
we simply roll and unroll the sail
without having to lower in and raise it
every time we want to use it and that
brings us to the end of this video
You might also like
- Boat Ed Unit 1 and 2Document71 pagesBoat Ed Unit 1 and 2Esper SorianoNo ratings yet
- Notes of a Seaplane Instructor: An Instructional Guide to Seaplane FlyingFrom EverandNotes of a Seaplane Instructor: An Instructional Guide to Seaplane FlyingNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Nautical Terms and Ship Part PDFDocument5 pagesDefinitions of Nautical Terms and Ship Part PDFmcdaleNo ratings yet
- The Land Lubbers ChapterDocument7 pagesThe Land Lubbers ChapterJan BooysenNo ratings yet
- Sailing ManualDocument113 pagesSailing ManualTomislav PavicicNo ratings yet
- Important Guidelines To Carry Out Anchoring Procedure Safety and SmoothlyDocument7 pagesImportant Guidelines To Carry Out Anchoring Procedure Safety and SmoothlyyeimiNo ratings yet
- Different Parts Of A Ship ExplainedDocument28 pagesDifferent Parts Of A Ship ExplainedJohn Anthony DanaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Boats and ShipsDocument11 pagesParts of Boats and ShipsCarlos GuarataNo ratings yet
- Ship's TermsDocument11 pagesShip's TermsНаталья ЛандикNo ratings yet
- Nautical TermsDocument11 pagesNautical TermsMitanshu ChadhaNo ratings yet
- ANCGUENG003Document2 pagesANCGUENG003Tom MoritzNo ratings yet
- 2Document22 pages2luisNo ratings yet
- Parts of A ShipDocument16 pagesParts of A ShipTebureiwa BontemanNo ratings yet
- Dinghy Sailing Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Sailing SkillsFrom EverandDinghy Sailing Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Sailing SkillsNo ratings yet
- D.G Ov .Au: 1.0 PreparationDocument9 pagesD.G Ov .Au: 1.0 PreparationNgaire TaylorNo ratings yet
- Salin-1. Main Parts of Ships-Mareng II-trpk Meeting 1Document18 pagesSalin-1. Main Parts of Ships-Mareng II-trpk Meeting 1Nanang MaolanaNo ratings yet
- Yachting Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Yachting SkillsFrom EverandYachting Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Yachting SkillsNo ratings yet
- Voltejear (Web 3)Document4 pagesVoltejear (Web 3)jorgeduardo9219No ratings yet
- Basic SeamanshipDocument25 pagesBasic SeamanshipzahasherNo ratings yet
- AnchoringDocument12 pagesAnchoringDryanmNo ratings yet
- An Education On The Different Parts of An Oil TankerDocument54 pagesAn Education On The Different Parts of An Oil TankerOzgean Osman100% (3)
- Sailing Course Manual: Dome Marina Sailing CentreDocument17 pagesSailing Course Manual: Dome Marina Sailing CentreDave Kukla100% (5)
- Bow and Stern RegionDocument2 pagesBow and Stern RegionDaisy Diane TorresNo ratings yet
- ANCHORINGDocument11 pagesANCHORINGCorina SandNo ratings yet
- YCC Sailing Course For BeginnersDocument42 pagesYCC Sailing Course For BeginnersUrt Django AlessandroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2,3,4Document54 pagesChapter 1,2,3,4Alin Pie100% (1)
- Basic Seamanship: Deck Seamanship Learning Objective: When You Finish This Chapter, YouDocument16 pagesBasic Seamanship: Deck Seamanship Learning Objective: When You Finish This Chapter, YoufitzNo ratings yet
- Curs 10 Ship Manoeuvring and Directional Control Be, Have, Do 2.1. Ship Manoeuvring and Directional ControlDocument12 pagesCurs 10 Ship Manoeuvring and Directional Control Be, Have, Do 2.1. Ship Manoeuvring and Directional ControlJB ClarkNo ratings yet
- Main Parts of Ships-Mareng II-trpk Meeting 1Document18 pagesMain Parts of Ships-Mareng II-trpk Meeting 1Nanang MaolanaNo ratings yet
- Handling Characteristics Power Driven Craft: Comparison OF VariousDocument18 pagesHandling Characteristics Power Driven Craft: Comparison OF VariousMike CasdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Anchor and Cable WorkDocument5 pagesUnit 4 Anchor and Cable WorkRazvan RaduNo ratings yet
- Bulkheads. Bulkheads Are Vertical Steel Walls Which Go Across and Along TheDocument12 pagesBulkheads. Bulkheads Are Vertical Steel Walls Which Go Across and Along TheCarla GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Sailing and SeamanshipDocument55 pagesSailing and Seamanshipdrcriss0704No ratings yet
- Anch OringDocument5 pagesAnch Oringasdqwe123dsaNo ratings yet
- Seamanship Ch. 5Document52 pagesSeamanship Ch. 5Alonso Olaya RuizNo ratings yet
- 04 Mooring 2Document6 pages04 Mooring 2Eduard CristianNo ratings yet
- Ship Design and Construction: (General Introduction)Document13 pagesShip Design and Construction: (General Introduction)pirata927No ratings yet
- Materi Tambahan - Carriage Good by SeaDocument15 pagesMateri Tambahan - Carriage Good by Seaine fitriaNo ratings yet
- Curs Navigatie Anul IIDocument125 pagesCurs Navigatie Anul IIRobert UzumNo ratings yet
- En GlezaDocument113 pagesEn Glezaasdqwe123dsaNo ratings yet
- Basic Naval Architecture and Ship Dimensions ExplainedDocument4 pagesBasic Naval Architecture and Ship Dimensions ExplainedArdyas Wisnu BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Other Seakeeping PerformancesDocument4 pagesLesson 3-Other Seakeeping PerformancestrungNo ratings yet
- Material For Written Test XN 21Document5 pagesMaterial For Written Test XN 21Aurora LotreanuNo ratings yet
- ch04b StrokesmaneuversDocument15 pagesch04b StrokesmaneuverskotsofrodosNo ratings yet
- Anchoring 1.: Unit Read The Following Text and Try To Guess The Meaning of The New Words and Phrases From The ContextDocument3 pagesAnchoring 1.: Unit Read The Following Text and Try To Guess The Meaning of The New Words and Phrases From The Contextasdqwe123dsaNo ratings yet
- Boat NomenclatureDocument5 pagesBoat NomenclatureAshok KamathNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Anchoring PDFDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Anchoring PDFRazvan RaduNo ratings yet
- Your Sailing Handbook For BeginnersDocument26 pagesYour Sailing Handbook For BeginnersIgnacio Moratinos CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. General Description of A Ship: Skills: Getting To Know The Main Parts of The Ships, Their Types andDocument31 pagesUnit 1. General Description of A Ship: Skills: Getting To Know The Main Parts of The Ships, Their Types andMarina TsynovaNo ratings yet
- Joy of SharpiesDocument5 pagesJoy of SharpiesJohn M. Watkins50% (2)
- Berthing: A Master's Guide ToDocument40 pagesBerthing: A Master's Guide Tonguyen ngocleNo ratings yet
- Seamanship Ch. 5 Boat Handling: REFERENCES: Chapman's Chapter 6 and AUX Study GuideDocument37 pagesSeamanship Ch. 5 Boat Handling: REFERENCES: Chapman's Chapter 6 and AUX Study Guidebehzad parsiNo ratings yet
- Basic Seamanship - Basic Shipboard KnowledgeDocument21 pagesBasic Seamanship - Basic Shipboard Knowledgeselvithimmarajan@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Ship HandlingDocument43 pagesShip HandlingSyamesh SeaNo ratings yet
- Motorboating Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Motorboating SkillsFrom EverandMotorboating Start to Finish: From Beginner to Advanced: The Perfect Guide to Improving Your Motorboating SkillsNo ratings yet
- Marpol Convention ExplainedDocument57 pagesMarpol Convention ExplainedYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- List of Descriptive WordsDocument11 pagesList of Descriptive WordsYannick Paka100% (1)
- 10 Reasons You Must Thank SeafarersDocument6 pages10 Reasons You Must Thank SeafarersYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- 6 - MEP - Elementary - First AidDocument2 pages6 - MEP - Elementary - First AidYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- 9 - MEP - Elementary - Maritime SecurityDocument2 pages9 - MEP - Elementary - Maritime SecurityYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- 4 - MEP - Elementary - Radio CommunicationsDocument2 pages4 - MEP - Elementary - Radio CommunicationsYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- My Life Without MoneyDocument4 pagesMy Life Without MoneyYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Nautical Charts Navigational WarningsDocument9 pagesNautical Charts Navigational WarningsYannick Paka100% (1)
- Ecology and Environment VocabularyDocument6 pagesEcology and Environment VocabularyYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument34 pagesGrammarYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- FOR-DURING-WHILE Printable Exercise - Learn English TodayDocument1 pageFOR-DURING-WHILE Printable Exercise - Learn English TodayYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Leçons de Grammaire AnglaiseDocument35 pagesLeçons de Grammaire AnglaiseYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Sailing Vocabulary and ExpressionsDocument3 pagesSailing Vocabulary and ExpressionsYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- No Sleep Print Friendly Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesNo Sleep Print Friendly Lesson PlanYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- GP SyllabusDocument136 pagesGP SyllabusYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Oral Anglais TerminalesDocument4 pagesOral Anglais TerminalesYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Motions of ShipDocument3 pagesMotions of ShipYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Reading Day 2 - Grand CanyonDocument4 pagesReading Day 2 - Grand CanyonYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Basic Maritime LessonDocument45 pagesBasic Maritime LessonYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Catamaran Terminology: Identify and Describe The Functions of The Following Terms and Structural ComponentsDocument5 pagesCatamaran Terminology: Identify and Describe The Functions of The Following Terms and Structural ComponentsYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Vocab and SentencesDocument6 pagesVocab and SentencesYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Know Your Sailboats: Sailboat TypesDocument3 pagesKnow Your Sailboats: Sailboat TypesYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Multiple QuestionsDocument13 pagesMultiple QuestionsYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Impacts Associated To Off-Shore Wind Power ProjectsDocument7 pagesBiodiversity Impacts Associated To Off-Shore Wind Power ProjectsYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Test Number OneDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Test Number OneYannick PakaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulaire: Shipping Forecast - Prévisions Météo Marine Tableau Etat de La Mer Echelle de Beaufort Sea State Beaufort ScalesDocument3 pagesVocabulaire: Shipping Forecast - Prévisions Météo Marine Tableau Etat de La Mer Echelle de Beaufort Sea State Beaufort ScalesYannick PakaNo ratings yet
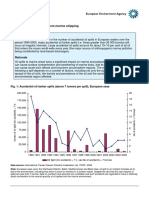
- EN15 Accidental Oil Spills From Marine Shipping: Key MessageDocument5 pagesEN15 Accidental Oil Spills From Marine Shipping: Key MessageYannick PakaNo ratings yet