Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math1 q1 Week1 Day4
Math1 q1 Week1 Day4
Uploaded by
Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bruer 1993 Schools For ThoughtDocument360 pagesBruer 1993 Schools For ThoughtDaniel LopezNo ratings yet
- Sanford MeisnerDocument4 pagesSanford MeisnerPepa Delasandía86% (7)
- MTB Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMTB Lesson PlanVia Mae VirtousaNo ratings yet
- COT1 DLP - English 2 - 1st RatingDocument5 pagesCOT1 DLP - English 2 - 1st RatingKaren Apa-DañoNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 DLL MTB Q4 Week 9Document6 pagesGrade 1 DLL MTB Q4 Week 9Chat DivineNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 DLL English 2 q4 Week 8Document14 pagesGrade 2 DLL English 2 q4 Week 8Evan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Science 3 - Q2-Quiz # 1 (Week 1-2)Document4 pagesScience 3 - Q2-Quiz # 1 (Week 1-2)Ferdinand James PascuaNo ratings yet
- 1st Performance Task in English Grade 2 Quarter 1Document2 pages1st Performance Task in English Grade 2 Quarter 1Revilyn NimoNo ratings yet
- LP For Cot Math Q2Document5 pagesLP For Cot Math Q2Karjed PiamonteNo ratings yet
- Note Important DetailsDocument3 pagesNote Important DetailsAngel AndersonNo ratings yet
- Dll-Week 2Document3 pagesDll-Week 2LV BENDANA100% (1)
- English DLPDocument5 pagesEnglish DLPTin Plagata Revelo-RanisNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG School: Matindeg Elementary School Grade Level: FOUR Teacher: WARREN M. SINCO English Teaching Dates/Time: Week 3 Quarter: 2NDDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG School: Matindeg Elementary School Grade Level: FOUR Teacher: WARREN M. SINCO English Teaching Dates/Time: Week 3 Quarter: 2NDWarren Millo SincoNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Joel Segubience Lucita Armecin Rosalinda GuicoDocument9 pagesGroup 3: Joel Segubience Lucita Armecin Rosalinda GuicoJoel SegubienceNo ratings yet
- English Week 2 Day 1Document4 pagesEnglish Week 2 Day 1meanNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 4 q2 w9Document6 pagesDLL Mathematics 4 q2 w9RyannDeLeonNo ratings yet
- Division - Initiated Contextualized Kindergarten Learning Resources Teacher's GuideDocument4 pagesDivision - Initiated Contextualized Kindergarten Learning Resources Teacher's GuideAira Castillano CuevasNo ratings yet
- Basa Pilipinas QTR 2Document254 pagesBasa Pilipinas QTR 2Michelle DanielaNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q4 English 3 Melc BasedDocument8 pagesPeriodical Test Q4 English 3 Melc Basedaileen godoyNo ratings yet
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 8 MTB 3Document9 pagesDLL Quarter 2 Week 8 MTB 3Arvin TocinoNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: JUNE 4-8, 2018 (WEEK 1)Document4 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: JUNE 4-8, 2018 (WEEK 1)Aletheia Vivien Ablona0% (1)
- PIVOT 4A Lesson Exemplar in English 3-Quarter 2-Week 8Document9 pagesPIVOT 4A Lesson Exemplar in English 3-Quarter 2-Week 8CES MAIN REIGNSNo ratings yet
- 3rd COT in English Lesson PlanDocument6 pages3rd COT in English Lesson PlanLeceil Oril PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- English 3 TG Quarter 3Document111 pagesEnglish 3 TG Quarter 3carmela guinevereNo ratings yet
- For Grade 2 - Psychosocial DLL (August 22-26, 2022)Document8 pagesFor Grade 2 - Psychosocial DLL (August 22-26, 2022)Evelyn DEL ROSARIO100% (1)
- DLL Mathematics-2 Q2 W6Document3 pagesDLL Mathematics-2 Q2 W6Marites James - Lomibao100% (1)
- DLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Feb 9Document10 pagesDLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Feb 9jeraldine endenoNo ratings yet
- G3 DLL Q2 W5 EnglishDocument3 pagesG3 DLL Q2 W5 EnglishAnonymous NZjEDgKRNo ratings yet
- List of KSADocument35 pagesList of KSAMa Estrella Zinampan MesaNo ratings yet
- Math1 Q1 Week4 Day4Document10 pagesMath1 Q1 Week4 Day4Mariel Jane IgnaligNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 5Document6 pagesDLP Week 5一人で ユーリ100% (1)
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W7Document6 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W7Joshua Romano RicoNo ratings yet
- DLL Q3 WK9 EnglishDocument12 pagesDLL Q3 WK9 EnglishjeninaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Unpacking of Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)Document1 pageDepartment of Education: Unpacking of Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)SARAH FABIAN67% (3)
- Week 6 - New KTG DLLDocument5 pagesWeek 6 - New KTG DLLCesar VidadNo ratings yet
- DLL All Subjects 2 q3 w4 d2Document9 pagesDLL All Subjects 2 q3 w4 d2Gyle Contawe GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kra 1Document7 pagesKra 1Peter Priya Aporever100% (1)
- ENGLISH - Lesson-Exemplar-WEEK5Document5 pagesENGLISH - Lesson-Exemplar-WEEK5Iza AlunanNo ratings yet
- Subject Area - Grade Level - Quarter No. - GADGET - 2022 Revised v.2Document84 pagesSubject Area - Grade Level - Quarter No. - GADGET - 2022 Revised v.2Lav ZurcNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lessonplan in Mathematics 2Document9 pagesDetailed Lessonplan in Mathematics 2jewel jumonongNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Lesson Exemplar WEEK7Document5 pagesENGLISH Lesson Exemplar WEEK7Iza Mae AlunanNo ratings yet
- DLP - Subject PronounsDocument3 pagesDLP - Subject PronounsKirk Andrade100% (1)
- Bersamin Elementary School Name of Teacher Section Leaning Area Time Grade Level DateDocument2 pagesBersamin Elementary School Name of Teacher Section Leaning Area Time Grade Level DateCecille Cabrera CariagaNo ratings yet
- DemoDocument5 pagesDemoJoelyn PredicalaNo ratings yet
- MTB-2-diagnostic - TOSDocument2 pagesMTB-2-diagnostic - TOSDonalyn Taaca Orpiano100% (1)
- Minutes of The Meeting (Wipes) 2Document3 pagesMinutes of The Meeting (Wipes) 2Meramae Arreglo VargasNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 DLL ENGLISH 3 Q2 Week 3Document3 pagesGrade 3 DLL ENGLISH 3 Q2 Week 3Jessa Versoza CalisteNo ratings yet
- Dll-English-Q1-Week 4Document6 pagesDll-English-Q1-Week 4Allyn MadeloNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 3 - Q1 - W8Document3 pagesDLL - English 3 - Q1 - W8Rose Dagdag-LaguitaoNo ratings yet
- BOW English 2 Q1Document57 pagesBOW English 2 Q1Rheinjohn Aucasa SampangNo ratings yet
- RM No. NCR 185 S. 2021 Learning Assurance For Monitoring and Progress Mid Year and Year Exit AssessmentDocument26 pagesRM No. NCR 185 S. 2021 Learning Assurance For Monitoring and Progress Mid Year and Year Exit AssessmentNickBlaireNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report EditedDocument6 pagesAccomplishment Report EditedMetchi Ann MelgarNo ratings yet
- Inventory of Available Learning Resources: ST THDocument9 pagesInventory of Available Learning Resources: ST THArnold C ZenarosaNo ratings yet
- What Time Is ItDocument3 pagesWhat Time Is ItsillyaiNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W2Document6 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W2ArvinMantesNo ratings yet
- New DLL-Week-20Document6 pagesNew DLL-Week-20Irene Alavanza SolayaoNo ratings yet
- DLL English-4 Q2 W2Document8 pagesDLL English-4 Q2 W2fe purificacionNo ratings yet
- MTB Storya Ug LetraDocument32 pagesMTB Storya Ug LetraRosalie AlposNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 5 - PPT - WEEK 6 - Quarter 4Document76 pagesENGLISH 5 - PPT - WEEK 6 - Quarter 4ruvel.albino04100% (1)
- FILIPINO 1 - Quarter 3 - Week 8 (COT)Document9 pagesFILIPINO 1 - Quarter 3 - Week 8 (COT)Actions Avon100% (1)
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q1 - W7Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q1 - W7Frelen Lequinan100% (1)
- Math1 q1 Week1 Day3Document10 pagesMath1 q1 Week1 Day3Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Math1 q1 Week1 Day5Document10 pagesMath1 q1 Week1 Day5Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Math1 q1 Week1 Day2Document11 pagesMath1 q1 Week1 Day2Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Math1 q1 Week2 Day5Document11 pagesMath1 q1 Week2 Day5Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Pelatihan Teknik Pengajaran Vocabulary Berbasis Media RealiaDocument9 pagesPelatihan Teknik Pengajaran Vocabulary Berbasis Media RealiaSyariNo ratings yet
- Pred 141 - Lesson 2Document17 pagesPred 141 - Lesson 2JudemilNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2012Document16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2012Yiannis PapamichaelNo ratings yet
- Co1 LorraineDocument6 pagesCo1 LorraineAngelie Cyrile SorinoNo ratings yet
- 2013 PHD Webster Thomas PDFDocument229 pages2013 PHD Webster Thomas PDFLiudmyla HarmashNo ratings yet
- 1 2020 General Prospectus With CoverDocument271 pages1 2020 General Prospectus With CoverChris WebbNo ratings yet
- CAE Writing MemoDocument12 pagesCAE Writing MemoValery100% (5)
- Admit CardDocument2 pagesAdmit CardVishnu thakurNo ratings yet
- V1 - FRIENDS: Do I Look Fat: Part 1 - Topic Speaking: Dating Part 3 - Script & VideoDocument4 pagesV1 - FRIENDS: Do I Look Fat: Part 1 - Topic Speaking: Dating Part 3 - Script & VideoEvelyn Méndez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Internship Final TemplateDocument5 pagesInternship Final TemplateSupraja ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode: at The End of This Activity, I Will Be Able ToDocument7 pagesLearning Episode: at The End of This Activity, I Will Be Able Toedward mirandilla miranda jr.100% (1)
- Why Science Need PhilosophyDocument4 pagesWhy Science Need PhilosophyRhain TabigneNo ratings yet
- Basic Fresher Resume For Students TemplateDocument2 pagesBasic Fresher Resume For Students TemplateAthi YanNo ratings yet
- Sudlanan in English - Google SearchDocument1 pageSudlanan in English - Google SearchMitz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Script Breakdown 7 Petala CintaDocument59 pagesScript Breakdown 7 Petala CintaKASIH ADINDA DAMIA AHMAD SURADINo ratings yet
- Review - Text and Act - Essays On Music and Performance by Richard TaruskinDocument4 pagesReview - Text and Act - Essays On Music and Performance by Richard TaruskinCarlos Montes de Oca GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Table of Specification: Science-Grade 7 1 Quarter ExaminationDocument3 pagesComprehensive Table of Specification: Science-Grade 7 1 Quarter ExaminationAnnie Bagalacsa Cepe-TeodoroNo ratings yet
- The Feedback Matrix: Developed by Cam Brooks Based On Hattie and Timperley's Model of Feedback (2007)Document1 pageThe Feedback Matrix: Developed by Cam Brooks Based On Hattie and Timperley's Model of Feedback (2007)รณกฤต ไชยทองNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Educational Psychology Developing Learners 9th Edition Ormrod Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Educational Psychology Developing Learners 9th Edition Ormrod Test Bank PDFphelandieuz7n100% (15)
- Comsats Institute Information Technology Department of Management Sciences Islamabad CampusDocument3 pagesComsats Institute Information Technology Department of Management Sciences Islamabad CampusOra gooNo ratings yet
- Specification of Content Beyond SyllabusDocument1 pageSpecification of Content Beyond SyllabusDr. Shailendra Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Rectangular Dielectric Resonator AntennaDocument4 pagesAn Integrated Rectangular Dielectric Resonator AntennaThiripurasundari DNo ratings yet
- Unit/Lesson Plan For 5th Grade - Multiplying Whole Numbers by FractionsDocument11 pagesUnit/Lesson Plan For 5th Grade - Multiplying Whole Numbers by Fractionsapi-578964781No ratings yet
- Nios Study Center-List-TelanganaDocument9 pagesNios Study Center-List-TelanganaarakeelNo ratings yet
- Banksy WecompressDocument7 pagesBanksy WecompressMariane CostaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Theory and Associated TherapiesDocument3 pagesCognitive Theory and Associated TherapiesEfren RJ PongaseNo ratings yet
- Legal OlympiadDocument6 pagesLegal OlympiadAbby AroraNo ratings yet
- English 3sci20 2trim d2Document2 pagesEnglish 3sci20 2trim d2Męawy MįlkshãkeNo ratings yet
Math1 q1 Week1 Day4
Math1 q1 Week1 Day4
Uploaded by
Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math1 q1 Week1 Day4
Math1 q1 Week1 Day4
Uploaded by
Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaCopyright:
Available Formats
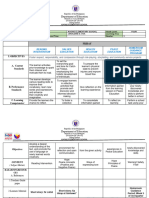
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
QUARTER II
Week 1 – Day 4
Subject: MATH Grade Level: 1
Date: __________________ Day: 4
The Learner demonstrates understanding of whole
Content Standard numbers up to 100, ordinal numbers up to 10th, money
up to PhP100 and fractions ½ and 1/4.
The learner is able to recognize, represent, and order
Performance Standard whole numbers up to 100 and money up to PhP100 in
various forms and contexts.
Competency
I. OBJECTIVES
Knowledge: Define
Skills: visualizes and represents numbers from 31 to 50
using a variety of materials.
reads and writes numbers from 31 to 50 in
symbols and in words.
Affective: Find pleasure in doing classroom activities.
II. CONTENT Numbers and Number Sense
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide Teacher’s Guide (TG) in Mathematics 1, pp. 18-21
Pages
2. Learner’s Learner’s Module (LM) in Math 1, pp. 22-25
Materials Pages
3. Textbook Pages
4. Additional
Materials
5. Learning Resources
(LR) portal
B. Other Learning Retrieved from www.google.ph.com
Resources (counters, pictures, charts)
IV. PROCEDURES
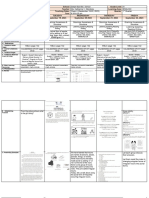
A. Reviewing or Let pupils recite the rhyme one, two tie my shoe three,
presenting the new four shut the door, five ,six pickup sticks,…
lesson
B. Establishing a Direct pupils attention to the banderitas hanging inside
purpose for the lesson their classroom.
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
Ask pupils
1. Where did they see these things? (During fiestas.)
C. Presenting examples ACTIVITY
of the new lesson
1. Teacher count the flaglets.1up to 50.
2. Let pupils repeat the counting.
3. Introduce the number symbols shown in the
number chart with the number word.
4. Give individual practice in reading the numbers.
5. Let pupils count their sticks from 1 to 50.
6. Emphasize that 30 means 3 tens and 0 ones.40 4
tens and 0 ones,50 5 tens and 0 ones.
7. Repeat the process on illustrating ones and tens.
D. Discussing new Show a number chart with missing numbers . Have
concepts and pupils write the missing numbers.
practicing new skills
#1
E. Discussing new ACTIVITY:
concepts and
practicing new skills Write the missing number.
#2
1.
2. ,5 ,6__ 7
3. 25,26,27,__
4. 10,__11,12, 13
F. Developing Mastery Workingby two,’s
1. Distribute number cards.
2. Each pair will arrange the numbers.
3. The first pair to finish the activity will
have a prize.
G. Finding practical Work individualy.
applications of Connect the dots from 31 to 50.
concepts and skills in
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
daily living What shape is form?
H. Making 1. What did you do with the objects and the
Generalizations and numbers? (We counted them.)
abstractions about 2. What can you do now? (We count from 0 to
the lesson 50.)
I. Evaluating learning Write the missing number.
J. Additional Practice counting number from 0 to 50 using counters.
Activities for
application or
remediation
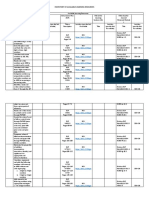
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who __ of learners who earned 80% above
earned 80% in the
evaluation
B. No. of learners who ___ of Learners who require additional activities for remediation
require additional
activities for remediation
C. Did the remedial ___Yes ___No
lessons work? No. of ____ of Learners who caught up the lesson
learners who have
caught up the lesson
D. No. of learners who ___ of Learners who continue to require remediation
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
continue to require
remediation
E. Which of my teaching Strategies used that work well:
strategies worked well? ___ Group collaboration
___ Games
Why did these work? ___ Solving Puzzles/Jigsaw
___ Answering preliminary
activities/exercises
___ Carousel
___ Diads
___ Think-Pair-Share (TPS)
___ Rereading of Paragraphs/
Poems/Stories
___ Differentiated Instruction
___ Role Playing/Drama
___ Discovery Method
___ Lecture Method
Why?
___ Complete IMs
___ Availability of Materials
___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn
___ Group member’s Cooperation in
doing their tasks
F. What difficulties did I __ Bullying among pupils
encounter which my __ Pupils’ behavior/attitude
__ Colorful IMs
principal and supervisor __ Unavailable Technology
help me solve? Equipment (AVR/LCD)
__ Science/ Computer/
Internet Lab
__ Additional Clerical works
Planned Innovations:
__ Localized Videos
__ Making big books from
views of the locality
__ Recycling of plastics to be used as Instructional Materials
__ local poetical composition
G. What innovation or
localized I used/discover The lesson have successfully delivered due to:
___ pupils’ eagerness to learn
which I wish to share
___ complete/varied IMs
with other teacher? ___ uncomplicated lesson
___ worksheets
___ varied activity sheets
Strategies used that work well:
___ Group collaboration
___ Games
___ Solving Puzzles/Jigsaw
___ Answering preliminary
activities/exercises
___ Carousel
___ Diads
___ Think-Pair-Share (TPS)
___ Rereading of Paragraphs/
Poems/Stories
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
___ Differentiated Instruction
___ Role Playing/Drama
___ Discovery Method
___ Lecture Method
Why?
___ Complete IMs
___ Availability of Materials
___ Pupils’ eagerness to learn
___ Group member’s Cooperation in
doing their tasks
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
ATTACHMENT
Session: 1 (1 day)
Content: Direct Variation
DISCUSSIONS:
A variable y varies directly as variable x if and only if ¿ kx . The
constant is called the variation constant or the constant of
proportionality. If we know one pair of values that varies directly, then
we can find k. Once k is known, we can write the equation of variation
and use it to determine other values.
In the same manner, that a variable y varies directly as the square
of x is expressed as .
Direct variation is also related to proportion. Let (x1,y1) and (x2,
y2) be any two solutions for , then or . Similarly
you have or . Since we can equate and to , it
follows that .
SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES
Note: The activities included here will be used only when needed.
DIRECTION: Which of the following situations show direct variation?
1. Water pressure on a submarine depends on the depth.
2. The area of the face of a cube is related to its volume.
3. The cost of life insurance depends on the age of the insured person.
4. The age of a used car is related to its resale value.
5. The distance an airplane fly depends on its time of travel.
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
DIRECTION: Which of the equations is of the form y=kx and shows
direct relationship?
1. 3 x−2
2. y = 5x
3. y=x
4. y= x2 + 1
5. y = 3x2
DIRECTION: Write an equation for the following statements:
1. The length L of a person’s shadow at a given time varies directly as the height h of that
person.
2. The cost of electricity C varies directly as the number of kilowatt-hour consumption I.
3. The volume V of a cylinder varies directly as its height h.
4. The weight W of an object is directly proportional to its mass m
5.The area A of a triangle is proportional to its height h.
DIRECTION: Write an equation to describe these situations.
1. varies directly as .
2. varies directly as the fourth root of
3. The surface area of a sphere varies directly as the square of the radius .
DIRECTION: Read the phrases below. Tell whether each of the phrases
below represents a direct variation. If they do, write the equation to
describe the situation:
1. The time spent in walking to the rate at which a person walks.
2. The cost of life insurance to the age of the insured person.
3. The age of a used car to its resale value.
4. The amount of money raised in a concert to the number of tickets sold.
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
5. The distance an airplane flies to the time travelling.
DIRECTION: Read the following situation then answer the question that
follow:
1. Your distance from lightning varies directly with the time it takes you to hear thunder.
If you hear thunder 10 seconds after you see the lighting, you are about 2 miles from
the lightning.
Question: Write a direct variation equation for the relationship between time and
distance?
2. A recipe for 2 dozen corn muffins calls for 3 cups of flour. The number of muffins
varies directly with the amount of flour you use.
Question: Write a direct variation equation for the relationship between the
number of cups of flour and the number of muffins.
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
MATHEMATICS RESOURCE PACKAGE
REFERENCES
A. DepEd INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS:
EASE Modules Year 2, Module 1: Variation
Bryant, M., & et. al. (2014). Mathematics-Grade 9 Learner’s Module (1st Ed.).
Pasig City: DepEd-IMCS
B. BOOKS AND OTHER REFERENCES
Mendoza, M. and Oronce, O. (2007). e-Math Intermediate Algebra. Quezon City,
Philippines: Rex Book Store.
Bernabe, J. and Soledad, J. (2009) Intermediate Algebra Textbook for Second
Year, Rev. Ed. Quezon City: SD Publications, Inc.
K to 12 Curriculum Guide Mathematics. (2012). Department of Education,
Philippines;
C. INTERNET SOURCES:
www.google.ph.com
Direct Variation. E-math Ii Tm' 2007 Ed.(intermediate Algebra). Retrieved on
October 10, 2017 from https://books.google.com.ph/books
Direct variation Worksheet(pdf). Retrieved on October 10, 2017 from
https://www.anderson5.net
Prepared by: Gemma Urciada
You might also like
- Bruer 1993 Schools For ThoughtDocument360 pagesBruer 1993 Schools For ThoughtDaniel LopezNo ratings yet
- Sanford MeisnerDocument4 pagesSanford MeisnerPepa Delasandía86% (7)
- MTB Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesMTB Lesson PlanVia Mae VirtousaNo ratings yet
- COT1 DLP - English 2 - 1st RatingDocument5 pagesCOT1 DLP - English 2 - 1st RatingKaren Apa-DañoNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 DLL MTB Q4 Week 9Document6 pagesGrade 1 DLL MTB Q4 Week 9Chat DivineNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 DLL English 2 q4 Week 8Document14 pagesGrade 2 DLL English 2 q4 Week 8Evan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Science 3 - Q2-Quiz # 1 (Week 1-2)Document4 pagesScience 3 - Q2-Quiz # 1 (Week 1-2)Ferdinand James PascuaNo ratings yet
- 1st Performance Task in English Grade 2 Quarter 1Document2 pages1st Performance Task in English Grade 2 Quarter 1Revilyn NimoNo ratings yet
- LP For Cot Math Q2Document5 pagesLP For Cot Math Q2Karjed PiamonteNo ratings yet
- Note Important DetailsDocument3 pagesNote Important DetailsAngel AndersonNo ratings yet
- Dll-Week 2Document3 pagesDll-Week 2LV BENDANA100% (1)
- English DLPDocument5 pagesEnglish DLPTin Plagata Revelo-RanisNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG School: Matindeg Elementary School Grade Level: FOUR Teacher: WARREN M. SINCO English Teaching Dates/Time: Week 3 Quarter: 2NDDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG School: Matindeg Elementary School Grade Level: FOUR Teacher: WARREN M. SINCO English Teaching Dates/Time: Week 3 Quarter: 2NDWarren Millo SincoNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Joel Segubience Lucita Armecin Rosalinda GuicoDocument9 pagesGroup 3: Joel Segubience Lucita Armecin Rosalinda GuicoJoel SegubienceNo ratings yet
- English Week 2 Day 1Document4 pagesEnglish Week 2 Day 1meanNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 4 q2 w9Document6 pagesDLL Mathematics 4 q2 w9RyannDeLeonNo ratings yet
- Division - Initiated Contextualized Kindergarten Learning Resources Teacher's GuideDocument4 pagesDivision - Initiated Contextualized Kindergarten Learning Resources Teacher's GuideAira Castillano CuevasNo ratings yet
- Basa Pilipinas QTR 2Document254 pagesBasa Pilipinas QTR 2Michelle DanielaNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test Q4 English 3 Melc BasedDocument8 pagesPeriodical Test Q4 English 3 Melc Basedaileen godoyNo ratings yet
- DLL Quarter 2 Week 8 MTB 3Document9 pagesDLL Quarter 2 Week 8 MTB 3Arvin TocinoNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: JUNE 4-8, 2018 (WEEK 1)Document4 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log: JUNE 4-8, 2018 (WEEK 1)Aletheia Vivien Ablona0% (1)
- PIVOT 4A Lesson Exemplar in English 3-Quarter 2-Week 8Document9 pagesPIVOT 4A Lesson Exemplar in English 3-Quarter 2-Week 8CES MAIN REIGNSNo ratings yet
- 3rd COT in English Lesson PlanDocument6 pages3rd COT in English Lesson PlanLeceil Oril PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- English 3 TG Quarter 3Document111 pagesEnglish 3 TG Quarter 3carmela guinevereNo ratings yet
- For Grade 2 - Psychosocial DLL (August 22-26, 2022)Document8 pagesFor Grade 2 - Psychosocial DLL (August 22-26, 2022)Evelyn DEL ROSARIO100% (1)
- DLL Mathematics-2 Q2 W6Document3 pagesDLL Mathematics-2 Q2 W6Marites James - Lomibao100% (1)
- DLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Feb 9Document10 pagesDLL Catch Up Friday Grade 4 Feb 9jeraldine endenoNo ratings yet
- G3 DLL Q2 W5 EnglishDocument3 pagesG3 DLL Q2 W5 EnglishAnonymous NZjEDgKRNo ratings yet
- List of KSADocument35 pagesList of KSAMa Estrella Zinampan MesaNo ratings yet
- Math1 Q1 Week4 Day4Document10 pagesMath1 Q1 Week4 Day4Mariel Jane IgnaligNo ratings yet
- DLP Week 5Document6 pagesDLP Week 5一人で ユーリ100% (1)
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W7Document6 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W7Joshua Romano RicoNo ratings yet
- DLL Q3 WK9 EnglishDocument12 pagesDLL Q3 WK9 EnglishjeninaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Unpacking of Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)Document1 pageDepartment of Education: Unpacking of Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs)SARAH FABIAN67% (3)
- Week 6 - New KTG DLLDocument5 pagesWeek 6 - New KTG DLLCesar VidadNo ratings yet
- DLL All Subjects 2 q3 w4 d2Document9 pagesDLL All Subjects 2 q3 w4 d2Gyle Contawe GarciaNo ratings yet
- Kra 1Document7 pagesKra 1Peter Priya Aporever100% (1)
- ENGLISH - Lesson-Exemplar-WEEK5Document5 pagesENGLISH - Lesson-Exemplar-WEEK5Iza AlunanNo ratings yet
- Subject Area - Grade Level - Quarter No. - GADGET - 2022 Revised v.2Document84 pagesSubject Area - Grade Level - Quarter No. - GADGET - 2022 Revised v.2Lav ZurcNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lessonplan in Mathematics 2Document9 pagesDetailed Lessonplan in Mathematics 2jewel jumonongNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH Lesson Exemplar WEEK7Document5 pagesENGLISH Lesson Exemplar WEEK7Iza Mae AlunanNo ratings yet
- DLP - Subject PronounsDocument3 pagesDLP - Subject PronounsKirk Andrade100% (1)
- Bersamin Elementary School Name of Teacher Section Leaning Area Time Grade Level DateDocument2 pagesBersamin Elementary School Name of Teacher Section Leaning Area Time Grade Level DateCecille Cabrera CariagaNo ratings yet
- DemoDocument5 pagesDemoJoelyn PredicalaNo ratings yet
- MTB-2-diagnostic - TOSDocument2 pagesMTB-2-diagnostic - TOSDonalyn Taaca Orpiano100% (1)
- Minutes of The Meeting (Wipes) 2Document3 pagesMinutes of The Meeting (Wipes) 2Meramae Arreglo VargasNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 DLL ENGLISH 3 Q2 Week 3Document3 pagesGrade 3 DLL ENGLISH 3 Q2 Week 3Jessa Versoza CalisteNo ratings yet
- Dll-English-Q1-Week 4Document6 pagesDll-English-Q1-Week 4Allyn MadeloNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 3 - Q1 - W8Document3 pagesDLL - English 3 - Q1 - W8Rose Dagdag-LaguitaoNo ratings yet
- BOW English 2 Q1Document57 pagesBOW English 2 Q1Rheinjohn Aucasa SampangNo ratings yet
- RM No. NCR 185 S. 2021 Learning Assurance For Monitoring and Progress Mid Year and Year Exit AssessmentDocument26 pagesRM No. NCR 185 S. 2021 Learning Assurance For Monitoring and Progress Mid Year and Year Exit AssessmentNickBlaireNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report EditedDocument6 pagesAccomplishment Report EditedMetchi Ann MelgarNo ratings yet
- Inventory of Available Learning Resources: ST THDocument9 pagesInventory of Available Learning Resources: ST THArnold C ZenarosaNo ratings yet
- What Time Is ItDocument3 pagesWhat Time Is ItsillyaiNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 1 - Q4 - W2Document6 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q4 - W2ArvinMantesNo ratings yet
- New DLL-Week-20Document6 pagesNew DLL-Week-20Irene Alavanza SolayaoNo ratings yet
- DLL English-4 Q2 W2Document8 pagesDLL English-4 Q2 W2fe purificacionNo ratings yet
- MTB Storya Ug LetraDocument32 pagesMTB Storya Ug LetraRosalie AlposNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 5 - PPT - WEEK 6 - Quarter 4Document76 pagesENGLISH 5 - PPT - WEEK 6 - Quarter 4ruvel.albino04100% (1)
- FILIPINO 1 - Quarter 3 - Week 8 (COT)Document9 pagesFILIPINO 1 - Quarter 3 - Week 8 (COT)Actions Avon100% (1)
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q1 - W7Document7 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q1 - W7Frelen Lequinan100% (1)
- Math1 q1 Week1 Day3Document10 pagesMath1 q1 Week1 Day3Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Math1 q1 Week1 Day5Document10 pagesMath1 q1 Week1 Day5Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Math1 q1 Week1 Day2Document11 pagesMath1 q1 Week1 Day2Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Math1 q1 Week2 Day5Document11 pagesMath1 q1 Week2 Day5Loudeth Guelas BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Pelatihan Teknik Pengajaran Vocabulary Berbasis Media RealiaDocument9 pagesPelatihan Teknik Pengajaran Vocabulary Berbasis Media RealiaSyariNo ratings yet
- Pred 141 - Lesson 2Document17 pagesPred 141 - Lesson 2JudemilNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2012Document16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2012Yiannis PapamichaelNo ratings yet
- Co1 LorraineDocument6 pagesCo1 LorraineAngelie Cyrile SorinoNo ratings yet
- 2013 PHD Webster Thomas PDFDocument229 pages2013 PHD Webster Thomas PDFLiudmyla HarmashNo ratings yet
- 1 2020 General Prospectus With CoverDocument271 pages1 2020 General Prospectus With CoverChris WebbNo ratings yet
- CAE Writing MemoDocument12 pagesCAE Writing MemoValery100% (5)
- Admit CardDocument2 pagesAdmit CardVishnu thakurNo ratings yet
- V1 - FRIENDS: Do I Look Fat: Part 1 - Topic Speaking: Dating Part 3 - Script & VideoDocument4 pagesV1 - FRIENDS: Do I Look Fat: Part 1 - Topic Speaking: Dating Part 3 - Script & VideoEvelyn Méndez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Internship Final TemplateDocument5 pagesInternship Final TemplateSupraja ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode: at The End of This Activity, I Will Be Able ToDocument7 pagesLearning Episode: at The End of This Activity, I Will Be Able Toedward mirandilla miranda jr.100% (1)
- Why Science Need PhilosophyDocument4 pagesWhy Science Need PhilosophyRhain TabigneNo ratings yet
- Basic Fresher Resume For Students TemplateDocument2 pagesBasic Fresher Resume For Students TemplateAthi YanNo ratings yet
- Sudlanan in English - Google SearchDocument1 pageSudlanan in English - Google SearchMitz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Script Breakdown 7 Petala CintaDocument59 pagesScript Breakdown 7 Petala CintaKASIH ADINDA DAMIA AHMAD SURADINo ratings yet
- Review - Text and Act - Essays On Music and Performance by Richard TaruskinDocument4 pagesReview - Text and Act - Essays On Music and Performance by Richard TaruskinCarlos Montes de Oca GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Table of Specification: Science-Grade 7 1 Quarter ExaminationDocument3 pagesComprehensive Table of Specification: Science-Grade 7 1 Quarter ExaminationAnnie Bagalacsa Cepe-TeodoroNo ratings yet
- The Feedback Matrix: Developed by Cam Brooks Based On Hattie and Timperley's Model of Feedback (2007)Document1 pageThe Feedback Matrix: Developed by Cam Brooks Based On Hattie and Timperley's Model of Feedback (2007)รณกฤต ไชยทองNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Educational Psychology Developing Learners 9th Edition Ormrod Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Educational Psychology Developing Learners 9th Edition Ormrod Test Bank PDFphelandieuz7n100% (15)
- Comsats Institute Information Technology Department of Management Sciences Islamabad CampusDocument3 pagesComsats Institute Information Technology Department of Management Sciences Islamabad CampusOra gooNo ratings yet
- Specification of Content Beyond SyllabusDocument1 pageSpecification of Content Beyond SyllabusDr. Shailendra Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- An Integrated Rectangular Dielectric Resonator AntennaDocument4 pagesAn Integrated Rectangular Dielectric Resonator AntennaThiripurasundari DNo ratings yet
- Unit/Lesson Plan For 5th Grade - Multiplying Whole Numbers by FractionsDocument11 pagesUnit/Lesson Plan For 5th Grade - Multiplying Whole Numbers by Fractionsapi-578964781No ratings yet
- Nios Study Center-List-TelanganaDocument9 pagesNios Study Center-List-TelanganaarakeelNo ratings yet
- Banksy WecompressDocument7 pagesBanksy WecompressMariane CostaNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Theory and Associated TherapiesDocument3 pagesCognitive Theory and Associated TherapiesEfren RJ PongaseNo ratings yet
- Legal OlympiadDocument6 pagesLegal OlympiadAbby AroraNo ratings yet
- English 3sci20 2trim d2Document2 pagesEnglish 3sci20 2trim d2Męawy MįlkshãkeNo ratings yet