Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is The Heart
What Is The Heart
Uploaded by
HR JobsfinderOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is The Heart
What Is The Heart
Uploaded by
HR JobsfinderCopyright:
Available Formats
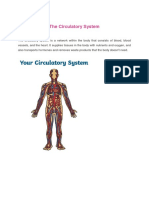
What is the heart?
The heart is a fist-sized organ that pumps blood throughout your body.
It's the primary organ of your circulatory system.
Your heart contains four main sections (chambers) made of muscle
and powered by electrical impulses. Your brain and nervous
system direct your heart’s function.
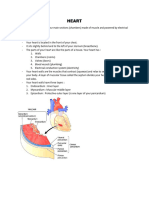
What does a heart diagram look like?
The inside and outside of your heart contain components that direct
blood flow:
Inside of the Heart
Outside of the Heart
FUNCTION
What is the heart’s function?
Your heart’s main function is to move blood throughout your body.
Your heart also:
Controls the rhythm and speed of your heart rate.
Maintains your blood pressure.
How does your heart work with other organs?
Your heart works with other body systems to control your heart rate
and other body functions. The primary systems are:
Nervous system: Your nervous system helps control your heart
rate. It sends signals that tell your heart to beat slower during
rest and faster during stress.
Endocrine system: Your endocrine system sends out
hormones. These hormones tell your blood vessels to constrict
or relax, which affects your blood pressure. Hormones from your
thyroid gland can also tell your heart to beat faster or slower.
ANATOMY
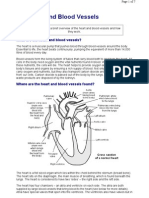
Where is your heart located?
Your heart is located in the front of your chest. It sits slightly behind
and to the left of your sternum (breastbone). Your ribcage protects
your heart.
What side is your heart on?
Your heart is slightly on the left side of your body. It sits between your
right and left lungs. The left lung is slightly smaller to make room for
the heart in your left chest.
How big is your heart?
Everyone’s heart is a slightly different size. Generally, adult hearts are
about the same size as two clenched fists, and children’s hearts are
about the same size as one clenched fist.
How much does your heart weigh?
On average, an adult’s heart weighs about 10 ounces. Your heart may
weigh a little more or a little less, depending on your body size and
sex.
What are the parts of the heart’s anatomy?
The parts of your heart are like the parts of a house. Your heart has:
Walls.
Chambers (rooms).
Valves (doors).
Blood vessels (plumbing).
Electrical conduction system (electricity).
Heart walls
Your heart walls are the muscles that contract (squeeze) and relax to
send blood throughout your body. A layer of muscular tissue called the
septum divides your heart walls into the left and right sides.
Your heart walls have three layers:
Endocardium: Inner layer.
Myocardium: Muscular middle layer.
Epicardium: Protective outer layer.
The epicardium is one layer of your pericardium. The pericardium is a
protective sac that covers your entire heart. It produces fluid to
lubricate your heart and keep it from rubbing against other organs.
Heart chambers
Your heart is divided into four chambers. You have two chambers on
the top (atrium, plural atria) and two on the bottom (ventricles), one on
each side of the heart.
Right atrium: Two large veins deliver oxygen-poor blood to your
right atrium. The superior vena cava carries blood from your
upper body. The inferior vena cava brings blood from the lower
body. Then the right atrium pumps the blood to your right
ventricle.
Right ventricle: The lower right chamber pumps the oxygen-
poor blood to your lungs through the pulmonary artery. The lungs
reload blood with oxygen.
Left atrium: After the lungs fill blood with oxygen, the pulmonary
veins carry the blood to the left atrium. This upper chamber
pumps the blood to your left ventricle.
Left ventricle: The left ventricle is slightly larger than the right. It
pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of your body.
You might also like
- Autopsy of Baby WyllowDocument10 pagesAutopsy of Baby WyllowKOLD News 13100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument93 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJack Keurig100% (6)
- Carpio - Learning Objective StratMedDocument29 pagesCarpio - Learning Objective StratMedaemancarpioNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument3 pagesHeartchewyahkisserNo ratings yet
- Blue Orange Creative Diabetes Presentation - 20231108 - 194927 - 0000Document10 pagesBlue Orange Creative Diabetes Presentation - 20231108 - 194927 - 0000thea ramosNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy and FunctionDocument1 pageHeart Anatomy and FunctionanushkaisaproNo ratings yet
- Heart - XIDocument4 pagesHeart - XIVighneshNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument3 pagesHEARTShan ShanNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow and TransportDocument7 pagesBlood Flow and Transporttarekegn balangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Heart The Heart (Heading)Document9 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Heart The Heart (Heading)Arbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- What Makes Up The Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesWhat Makes Up The Cardiovascular SystemRenieze EllaNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument16 pagesHuman HeartDelfin Jr UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument3 pagesHeart Anatomymuskaan.kukrejaNo ratings yet
- Prevention: Blood Pressure Body Weight Here BMIDocument4 pagesPrevention: Blood Pressure Body Weight Here BMIdwi krismaNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument7 pagesHuman HeartAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- What Are The Heart and Blood Vessels?Document7 pagesWhat Are The Heart and Blood Vessels?phbnaiduNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Heart and Blood Vessels - PatientDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The Heart and Blood Vessels - Patientaasuman123No ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument8 pagesCirculatoryKristel Faye DioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Biology Unit 5Document10 pagesBiology Unit 5Aaditya MenonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemWild RiftNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Heart PhysiologyDocument11 pagesHeart Physiologyzzahraadam80No ratings yet
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Overview of The HeartDocument3 pagesOverview of The HeartSamanthaKhallanNo ratings yet
- The Mammalian HeartDocument14 pagesThe Mammalian HeartAkili ArmaniNo ratings yet
- P.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2ADocument29 pagesP.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2AAlea Jane AranjuezNo ratings yet
- Heart and Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesHeart and Circulatory SystemBryent GawNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemAnkit PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o oDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o okayaldrNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesThe Circulatory SystemTrung Ngô Lê BảoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemMr. Christian ParabuacNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Your Heart FunctionsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding How Your Heart FunctionsthenameisvijayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1Document22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1adedayodavid860No ratings yet
- The Heart Is A Muscle: BloodDocument8 pagesThe Heart Is A Muscle: BloodJhoewil QuintuaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Systemleah rualesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Notes On HEARTDocument2 pagesNotes On HEARThk royNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 5: Reading About of "The Cardiovascular System."Document4 pagesTOPIC 5: Reading About of "The Cardiovascular System."Hans Rojas MedinaNo ratings yet
- Our Heart BeatsDocument7 pagesOur Heart BeatsferyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory SystemGO BIGNo ratings yet
- The Human HeartDocument19 pagesThe Human HeartbeshlyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemEzequiel ManluluNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Document10 pagesLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebDocument4 pagesBasic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebMay Larkspur TadeoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology The HeartDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology The Heartkheng100% (4)
- The Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9Document17 pagesThe Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9hareem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemChekaina Rain BaldomarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Circulatory Systemmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SummaryDocument6 pagesCirculatory System Summaryvictor fdezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDaniel PancuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Human Heart ScienceDocument7 pagesHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-01 at 5.39.08 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2022-09-01 at 5.39.08 PMTrishia EspejaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologydammenoelNo ratings yet
- Cardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDocument13 pagesCardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDavid GoliathNo ratings yet
- The Heart Weighs Between 7 and 15 OuncesDocument2 pagesThe Heart Weighs Between 7 and 15 OunceshengkyhengkyNo ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Cardiac Tamponade Whyra Pratama SaidDocument10 pagesCardiac Tamponade Whyra Pratama SaidWhira pratama saidNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument43 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseaseVickeeNo ratings yet
- Perfusion BookDocument127 pagesPerfusion Bookreader100% (1)
- 2.02 Gross Anatomy Trans - HeartDocument15 pages2.02 Gross Anatomy Trans - HeartElma Gonzales100% (1)
- Anatomical Descriptive Source - Integumentary Skin, Tissue, and CellsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Descriptive Source - Integumentary Skin, Tissue, and CellsGURPARABJOT KAURNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Cardiovascular SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- Year One Anatomy and Physiology Study NotesDocument94 pagesYear One Anatomy and Physiology Study Notescoolpinkgurl100% (8)
- Basic Cardiac Structure and FunctionDocument13 pagesBasic Cardiac Structure and FunctiondeaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic SystemsDocument9 pagesAssessing The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic SystemsYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- PDF Catatan Kuliah Kardiologi CompressDocument99 pagesPDF Catatan Kuliah Kardiologi CompressYohanes BagusNo ratings yet
- Frog ALL SYSTEMS-1Document85 pagesFrog ALL SYSTEMS-1Ranjeet PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyElvin MoletaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pakai 6 (Patofisiologi, Diagnosis, Gejala)Document13 pagesJurnal Pakai 6 (Patofisiologi, Diagnosis, Gejala)Satrya DitaNo ratings yet
- 10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument140 pages10 General Anatomy of The Cardiovascular SystemSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Pericardial Diseases: Dr. Abazie, Ugochi CDocument63 pagesPericardial Diseases: Dr. Abazie, Ugochi CUgochi AbazieNo ratings yet
- Assessing Heart and Neck Vessel Heart Heart Chambers: (Tricuspid & Bicuspid)Document7 pagesAssessing Heart and Neck Vessel Heart Heart Chambers: (Tricuspid & Bicuspid)Dan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 (Anph - B5)Document21 pagesWeek 2 (Anph - B5)Elleine Jade TinidoNo ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmo NotesDocument12 pagesCardio Pulmo NotesCherrie MaeNo ratings yet
- TB Child ExtrapulmonaryDocument9 pagesTB Child Extrapulmonarygiant nitaNo ratings yet
- SirkulasiDocument17 pagesSirkulasiJessica VanyaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Cardiovascular-SystemDocument113 pagesCH 11 Cardiovascular-SystemHazel Banday100% (1)
- Lab Report #6 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMDocument4 pagesLab Report #6 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMJamaica M DanguecanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Marian Diamond)Document34 pagesAnatomy (Marian Diamond)NHZANo ratings yet
- Tumores CardiacosDocument16 pagesTumores CardiacosAlejandro Estrada RiosNo ratings yet
- Module Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesModule Cardiovascular SystemVynz Morales CosepNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument42 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyancillaagraynNo ratings yet
- M2F Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesM2F Cardiovascular SystemMeteor 858No ratings yet
- !!!!!!!!subiecteDocument33 pages!!!!!!!!subiecteAura ConstantinNo ratings yet