Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
Uploaded by
pranithOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
Uploaded by
pranithCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty of Engineering
School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering
B. Tech (Automobile Engineering)
III Semester End Term Examination: 2019-20
AU1305 – Strength of Materials
(CLOSED BOOK)
Duration: 3 Hour Max. Marks: 80
Instructions:
• Answer any Five full questions.
• Missing data, if any, may be assumed suitably.
• Scientific calculator is permitted.
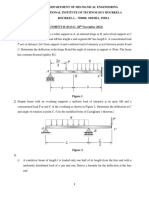
1. a A steel circular bar has three segments as shown in figure. Determine: [08]
i. total elongation of the bar;
ii. length of the middle segment to have zero elongation of the bar; and
iii. diameter of the last segment to have zero elongation of the bar.
Take Young’s modulus of elasticity (E) = 205 GPa.
b A steel rod of 30 mm diameter is enclosed in a brass [08]
tube of 42 mm external diameter and 32 mm internal
diameter. Each is 360 mm long and the assembly is
rigidly held between two stops 360 mm apart. The
temperature of the assembly is then raised by 50°C.
Determine:
i. stresses in the tube and the rod
ii. stresses in the tube and rod if the stops yield by 0.15 mm
iii. yield of the stops if the force at the stops is limited to 60 kN.
Take Es = 205 GPa; Eb = 90 GPa; αs = 11x106 per °C; αb = 19x106 per °C
2. a What are the different types of loads acting on a beam? Differentiate between a point load and a [04]
uniformly distributed load.
b A simply supported beam of 7 m span with overhangs rests on supports which are 4 m apart. The [12]
left end overhanging is 2 m. The beam carries loads of 30 kN and 20 kN on the left and the right
ends respectively apart from a uniformly distributed load of 25 kN/m between the supporting
points. Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams.
3. a A beam of rectangular section is to support a load of 20 kN over a span of 4 m. If the depth of the [08]
section is to be twice the breadth, and the stress in the beam is not to exceed 60 N/mm 2, find the
dimensions of the cross-section.
How would you modify the cross-section of the beam if it were a concentrated load placed at the
centre with the same ratio of breadth to depth?
b A 100 mm x 40 mm I-beam is subjected to a shear force of 15 kN. Find the transverse shear stress [08]
at the neutral axis and at the top of the web. Compare it with mean stress on the assumption of
uniform distribution over the web. What is the percentage of shear force carried by the web?
Moment of inertia of the section is 1.1 x 10 6 mm4, web thickness is 3 mm and flange thickness is
4 mm.
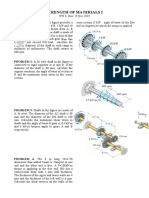
4. a Enumerate the assumptions made in pure torsion. Derive the relation for a circular shaft when [08]
T G
subjected to torsion as = = .
J R L
b Figure shows a hollow shaft. Determine the maximum power transmitted by the shaft at 200 rpm [08]
if the shear stress in the shaft is not to exceed 70 MPa. Also find the lengths of the two portions if
the twist produced in the two portions of the shaft are equal.
5. a A simply supported beam of I-section as shown in figure, deflects [08]
12 mm when subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 50 kN/m
length. Determine the safe load if the beam is used as a column with
both ends fixed. Use Euler’s formula with a factor of safety 5.
E = 205 GPa.
b A machine component is subjected to the [08]
stresses as shown in figure.
Find the normal and shearing stresses on the
section AB inclined at an angle of 60⁰ with
x-x axis. Also find the resultant stress on the
section.
6. A simply supported beam has its support 8 m apart at A and B. It carries a uniformly distributed [16]
load of 6 kN/m between A and B starting from 1 m and ending at 5 m from A. The end B of the
beam has an overhang of 1 m and at the free end a concentrated load of 8 kN is applied. Determine
deflection of the free end and the maximum deflection between A and B. Take E = 210 GPa and
I = 20 x 106 mm4.
You might also like
- Forensic Science Fundamentals and Investigations 2nd Edition by Bertino ISBN Test BankDocument7 pagesForensic Science Fundamentals and Investigations 2nd Edition by Bertino ISBN Test Bankmark100% (33)
- The Rich Get Richer and The Poor Get PrisonDocument1 pageThe Rich Get Richer and The Poor Get PrisonGunasundaryChandramohanNo ratings yet
- Prophecies in Islam & Prophet Muhammad - A.aliDocument82 pagesProphecies in Islam & Prophet Muhammad - A.aliZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- The Occult Origins of The Bank of EnglandDocument7 pagesThe Occult Origins of The Bank of EnglandMarbleManNo ratings yet
- The Generation of Postmemory: Writing and Visual Culture After The HolocaustDocument13 pagesThe Generation of Postmemory: Writing and Visual Culture After The HolocaustColumbia University Press100% (2)
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameavinashNo ratings yet
- JNTUH Usedpapers March 2022: (Common To ME, MCT, MIE)Document2 pagesJNTUH Usedpapers March 2022: (Common To ME, MCT, MIE)AshokNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNDocument12 pagesFoundation of Solid Mechanics: C D 50 KNLata SharmaNo ratings yet
- CE8301-Strength of Materials IDocument4 pagesCE8301-Strength of Materials Isyed1188No ratings yet
- Btech Me 3 Sem Strength of Materials Eme302 2020Document3 pagesBtech Me 3 Sem Strength of Materials Eme302 2020fahad chishtiNo ratings yet
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 28SupplementaryCE201CE201 I Ktu Qbankprasidh msNo ratings yet
- QB114462Document8 pagesQB114462ILAYAPERUMAL KNo ratings yet
- CE527 Correlation Course Structural Engi PDFDocument2 pagesCE527 Correlation Course Structural Engi PDFjunNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics Question BankDocument10 pagesSolid Mechanics Question BankMugilan VinsNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NameDocument10 pagesAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 Marks: Reg No.: - NamegalehNo ratings yet
- BE Civil III SOMDocument4 pagesBE Civil III SOMMohit BhagatNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat Noopwigs444No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Feb Mar 2022Document3 pagesMechanics of Solids Feb Mar 2022SabareeshNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Paper With AnswersDocument108 pagesPrevious Year Question Paper With AnswersTejasPatilNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids March 2021Document8 pagesMechanics of Solids March 2021LuckyNo ratings yet
- WWW Manaresults Co inDocument2 pagesWWW Manaresults Co inmahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- MOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23Document6 pagesMOS Assignment II Autumn 2022-23PankajNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoMadao111No ratings yet
- Ahmedabad Center-12Document2 pagesAhmedabad Center-12RenieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AssignmentsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 AssignmentsbattuarunNo ratings yet
- Ahmedabad Center-10Document2 pagesAhmedabad Center-10RenieNo ratings yet
- Som-Mos-I 205Document4 pagesSom-Mos-I 205Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. EXAMINATION, 2020: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Document5 pagesB. Tech. EXAMINATION, 2020: No. of Printed Pages: 05 Roll No. ......................Gopu KumarNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials-I: Inst Ruct Ions To Candidat EsDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials-I: Inst Ruct Ions To Candidat EsJaskaran SinghNo ratings yet
- L and L With Cross-Sections A and A - It Is Subjected To An Axial Pull FDocument3 pagesL and L With Cross-Sections A and A - It Is Subjected To An Axial Pull FAnonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument4 pagesSOMrrameshsmit0% (1)
- Diploma Quasion PapersDocument4 pagesDiploma Quasion PapersSundarasetty HarishbabuNo ratings yet
- A1101Document6 pagesA1101Khaja BashaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials I: PROBLEM 1. Gear C in The Figure Provides ADocument2 pagesStrength of Materials I: PROBLEM 1. Gear C in The Figure Provides AzıptıNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument4 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksMadan PanditNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument9 pagesMechanics of SolidsSrikanth GogineniNo ratings yet
- Aat 1Document4 pagesAat 1HARNITH EVILLNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2022 SMDocument4 pagesPrelim 2022 SMARJUNANo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials QB 2015Document10 pagesStrength of Materials QB 2015smg26thmayNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: R15 R15 R15 R15Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: R15 R15 R15 R15mahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- ME1101 Lecture3-Bending StressDocument47 pagesME1101 Lecture3-Bending StressNADULA RUSIRUNo ratings yet
- Queastion Bank MOM 22 26Document5 pagesQueastion Bank MOM 22 26karvaminNo ratings yet
- Used Papers SEP 2021: (Civil Engineering)Document3 pagesUsed Papers SEP 2021: (Civil Engineering)AYRUSNo ratings yet
- As Ad Supply 2017Document2 pagesAs Ad Supply 2017Manasa PanthaganiNo ratings yet
- MosDocument10 pagesMosalagar krishna kumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Document51 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Joshua DariaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Unit 1,2Document7 pagesImportant Questions Unit 1,2rajeswariNo ratings yet
- PartDocument9 pagesPartMahendranath Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- Ahmedabad Center-11Document2 pagesAhmedabad Center-11RenieNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological Universityharnishtanna21285No ratings yet
- 2020 10 28SupplementaryME201ME201 I Ktu QbankDocument3 pages2020 10 28SupplementaryME201ME201 I Ktu Qbankred18ggmuNo ratings yet
- MosDocument20 pagesMosutsav_koshtiNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.karthikeyankv.mech DscetNo ratings yet
- Sa I PDFDocument2 pagesSa I PDFbhartuhari pargiNo ratings yet
- Assignment04 (2:11:14)Document2 pagesAssignment04 (2:11:14)Gabriel SmithNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument2 pagesFinalpranithNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of SolidsDocument15 pagesMechanics of Solidsselva1975No ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument6 pagesStrength of Materialsgayatri_vyas1No ratings yet
- 075 - CE8301, CE6306 Strength of Materials I - Question BankDocument10 pages075 - CE8301, CE6306 Strength of Materials I - Question BankGERARD HAULENo ratings yet
- Notes Ch.3-Es205Document4 pagesNotes Ch.3-Es205indayieee.12No ratings yet
- ES 13 1920A Problem Set 2Document5 pagesES 13 1920A Problem Set 2Charmaine ColetaNo ratings yet
- 12043-Strength of MaterialsDocument4 pages12043-Strength of MaterialsManiVijayNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & MechatronicsDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & MechatronicspranithNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument2 pagesFinalpranithNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & MechatronicsDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & MechatronicspranithNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithNo ratings yet
- Brightpancar Catalog PDFDocument125 pagesBrightpancar Catalog PDFBobby RajNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: Power ElectronicsDocument13 pagesElectrical Engineering: Power ElectronicsSaif UddinNo ratings yet
- The Emoji Factor: Humanizing The Emerging Law of Digital SpeechDocument33 pagesThe Emoji Factor: Humanizing The Emerging Law of Digital SpeechCityNewsTorontoNo ratings yet
- Facilities and Design Midterm Exam Part 2 2ND Sem 2023-24Document2 pagesFacilities and Design Midterm Exam Part 2 2ND Sem 2023-24bertjohnvillavert14No ratings yet
- Ake PH3 00 Par DWG SW 55002Document1 pageAke PH3 00 Par DWG SW 55002JericFuentesNo ratings yet
- TEM ManualDocument6 pagesTEM ManualmcsteiNo ratings yet
- Major Fractures of The Pilon The Talus and The Calcaneus Current Concepts of TreatmentDocument241 pagesMajor Fractures of The Pilon The Talus and The Calcaneus Current Concepts of TreatmentPaul Radulescu - FizioterapeutNo ratings yet
- Towards An Absolute Chronology For The Aegean Iron Age: New Radiocarbon Dates From Lefkandi, Kalapodi and CorinthDocument11 pagesTowards An Absolute Chronology For The Aegean Iron Age: New Radiocarbon Dates From Lefkandi, Kalapodi and CorinthZorana DimkovićNo ratings yet
- CHP 15 MULTIDIMENSIONAL SCALING FOR BRAND POSITIONING Group 1 & 2Document16 pagesCHP 15 MULTIDIMENSIONAL SCALING FOR BRAND POSITIONING Group 1 & 2alfin luanmasaNo ratings yet
- ISO 22301 Lead Implementer - Two Page BrochureDocument2 pagesISO 22301 Lead Implementer - Two Page BrochurePECBCERTIFICATIONNo ratings yet
- Body Repairs General Body RepairsDocument87 pagesBody Repairs General Body RepairsergdegNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 (Autosomes & Sex Chromosome)Document2 pagesWorksheet 9 (Autosomes & Sex Chromosome)HalaNo ratings yet
- No Smoking in The TriangleDocument60 pagesNo Smoking in The TriangleThomas L HaydenNo ratings yet
- English Literature AnthologyDocument25 pagesEnglish Literature AnthologyShrean RafiqNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Honeywell Dolphin 70e BlackDocument2 pagesDatasheet Honeywell Dolphin 70e Blackblue 1234No ratings yet
- 02 Surface Production Material Movement V70Document49 pages02 Surface Production Material Movement V70Jobs Mathan100% (1)
- E.M Year 10 Term 2 NotesDocument25 pagesE.M Year 10 Term 2 NotesNANCYNo ratings yet
- Flow ControlDocument87 pagesFlow Controlibrahim_nfsNo ratings yet
- Lva1 App6892Document146 pagesLva1 App6892Adam Shahabuddin Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PBLDocument21 pagesIntroduction To PBLChipego NyirendaNo ratings yet
- ARTH 103 Introduction To Architecture: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument7 pagesARTH 103 Introduction To Architecture: Course Description and ObjectivesWall Street News AgencyNo ratings yet
- 01 Lord Krishna-VrindavanDocument304 pages01 Lord Krishna-VrindavanJey AnandNo ratings yet
- Prolink ShareHub Device ServerDocument33 pagesProlink ShareHub Device Serverswordmy2523No ratings yet
- Monash UniversityDocument17 pagesMonash Universityimmanuel nauk elokpereNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Static EquilibriumDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Static Equilibriumshahrul100% (1)