Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Session 2 ANAPHY Lec
Session 2 ANAPHY Lec
Uploaded by
Maria Jub MangrubanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Maturana Varela Tree of KnowledgeDocument231 pagesMaturana Varela Tree of KnowledgeFedor Volyanskiy100% (17)
- Apologia Biology Class Module 6 NotesDocument4 pagesApologia Biology Class Module 6 Noteschickfilamom100% (2)
- DLL Science Grade 7 2nd GradingDocument28 pagesDLL Science Grade 7 2nd GradingCharline A. Radislao91% (23)
- Ha Sas Lec #6-23 Answer Key PDFDocument66 pagesHa Sas Lec #6-23 Answer Key PDFMaria Jub Mangruban50% (2)
- Primary 3 To 6 Science Syllabus SingaporeDocument13 pagesPrimary 3 To 6 Science Syllabus SingaporeJohn KWNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 - 1.4 Kingdoms and DomainsDocument4 pagesBiology 11 - 1.4 Kingdoms and DomainsMinNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document8 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SASDocument8 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SASFherry Mae UsmanNo ratings yet
- Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument5 pagesSeeley's Essentials of Anatomy & PhysiologyZylith NanaseNo ratings yet
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument25 pagesL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsKurnish KhawolNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument20 pagesChapter IvLaila Abdullah AmparoNo ratings yet
- Cytology Student Notes PDFDocument70 pagesCytology Student Notes PDFElla BoyceNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane & Membra 1442Document48 pagesCell Membrane & Membra 1442Fady FadyNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure - A 2019Document88 pages2 Cell Structure - A 2019Isworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument7 pagesCELLSopingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- 4 Cytology PDFDocument32 pages4 Cytology PDFdaisysintszwaiNo ratings yet
- Membrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesDocument25 pagesMembrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesAshlee Venice CebuNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellhkrybmzxfbxbwnpfhnNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsCiara PanenNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument63 pagesCell Organellessyafi zulNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Bio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Document6 pagesBio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Mia NavarroNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument71 pagesPhysiologysalah.shashoraNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CellsDocument93 pagesStructure and Function of CellsRonald BakangNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument30 pagesCell BiologyHila Jagdish bhaiNo ratings yet
- Cells: General ZoologyDocument71 pagesCells: General ZoologyAzaleaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Biology NotesDocument16 pagesModule 1 Biology NotesPahulbir ThindNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary: Module 1 - Cells As The Basis of LifeDocument28 pagesBiology Summary: Module 1 - Cells As The Basis of LifeAbdullah AliNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsJade Lagada PagariganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- Session #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document5 pagesSession #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- Class NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Document28 pagesClass NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Cyril Josh MaisogNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesCell and Tissuesalvin jr ayugatNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesDocument37 pagesBiology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Principles of ZoologyDocument41 pagesIntegrated Principles of ZoologyEstherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityDocument15 pagesLecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityElleNo ratings yet
- Cells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Document59 pagesCells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Trevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument180 pagesTOPIC 2 Cellular Level of OrganizationAdlyn ShaheeraNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesrickyNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument18 pagesBiology Projecthana fathimaNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellDocument18 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- PHY LE 1 Finals ReviewerDocument14 pagesPHY LE 1 Finals Reviewerroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - CellsDocument32 pagesGen Bio - Cellsjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- AnaPhyLab The CellDocument3 pagesAnaPhyLab The CellCarren SabioNo ratings yet
- The CELL (I) : Physiology of For Pre-Medic Mesir (July 2013)Document65 pagesThe CELL (I) : Physiology of For Pre-Medic Mesir (July 2013)nasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument56 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Functionazrixone54No ratings yet
- Module 1 CellsDocument17 pagesModule 1 CellsLara C.No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology202370092No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYunie KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologykernelkobieNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument12 pages3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsPrince TeodocioNo ratings yet
- The Cell StudentDocument90 pagesThe Cell Studentmaricar basilanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEDocument3 pagesAnatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CellsDocument6 pagesAnatomy CellsChelsea SebastianNo ratings yet
- 5 - A&P The CellDocument23 pages5 - A&P The CellsabrinaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsRIVERA, BRENNAN L.No ratings yet
- 1 - Histology Lecture - Structure of Cell Membrane and Membranous OrganellesDocument40 pages1 - Histology Lecture - Structure of Cell Membrane and Membranous OrganellesAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE - Cell Structures and Functions - UY-OCODocument4 pagesWEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE - Cell Structures and Functions - UY-OCOBianca LouiseNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 13 PDFDocument8 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 13 PDFMaria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 18Document6 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 18Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 20Document6 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 20Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 15Document8 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 15Maria Jub Mangruban100% (1)
- Health Assessment SAS Session 14Document9 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 14Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Session 1 ANAPHY LecDocument8 pagesSession 1 ANAPHY LecMaria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (LEC)Document10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (LEC)Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Genetic TerminologyDocument6 pagesGenetic TerminologyMuthu KaruppanNo ratings yet
- 9th Science PBQ Chapter 1 To 15Document31 pages9th Science PBQ Chapter 1 To 15YogithaNo ratings yet
- Biology DefinitionDocument9 pagesBiology DefinitionMRhines GadgetBasketNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes in English PDFDocument21 pagesBiology Notes in English PDFAkshay PawarNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 9Document53 pagesBiology Ch. 9Juliet HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ScienceDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates ScienceJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Ylp Remove 2018Document5 pagesYlp Remove 2018mexfloziaNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 1 - The CellDocument4 pagesExercise # 1 - The CellMJMadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of ProkaryoteDocument3 pagesUltra Structure of ProkaryoteselvasrijaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Microbiology (TMCL) Lecture 1Document21 pagesCell and Microbiology (TMCL) Lecture 1Komi KaayNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MoleculessanaullahNo ratings yet
- MEDBIO KROK-1 English 2019-2020Document65 pagesMEDBIO KROK-1 English 2019-2020Катерина КабишNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Cell Structure Function & OrganellesDocument35 pages6.3 Cell Structure Function & OrganellesMarvin De Jonggoy100% (1)
- Eukariot Dan ProkariotDocument37 pagesEukariot Dan ProkariottidaniadevNo ratings yet
- CH - 40 - Introduction To The Cell CycleDocument15 pagesCH - 40 - Introduction To The Cell Cycleerichaas100% (1)
- Microbiology Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Final Exam ReviewJohn NinoNo ratings yet
- Endotoxin and Disease in Food AnimalsDocument8 pagesEndotoxin and Disease in Food Animalstaner_soysuren100% (1)
- DNA Translation J Muqaddas MukhtarDocument33 pagesDNA Translation J Muqaddas MukhtarSafia DurraniNo ratings yet
- Tissue EngineeringDocument17 pagesTissue EngineeringAntonio LoureiroNo ratings yet
- Catalogo General Microscopios OpticosDocument22 pagesCatalogo General Microscopios OpticosValentina HerreraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Fluid Mosaic Model & Transport Across Membranes My NotesDocument24 pagesTopic 1 Fluid Mosaic Model & Transport Across Membranes My NotesTinotenda J TamaiNo ratings yet
- 1 Da S63 M 1 A5 Ycv Pce MF TD CJZ 8 FHMYqs NViDocument12 pages1 Da S63 M 1 A5 Ycv Pce MF TD CJZ 8 FHMYqs NViYaziNo ratings yet
- Bio and HealthDocument5 pagesBio and HealthKissha TayagNo ratings yet
- Introduction of BacteriaDocument15 pagesIntroduction of BacteriaAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- DPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Document16 pagesDPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Savitri HegdeNo ratings yet
Session 2 ANAPHY Lec
Session 2 ANAPHY Lec
Uploaded by
Maria Jub MangrubanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Session 2 ANAPHY Lec
Session 2 ANAPHY Lec
Uploaded by
Maria Jub MangrubanCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy & Physiology - Lecture
STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEET BS NURSING / FIRST YEAR
Session # 2
LESSON TITLE: CELL STRUCTURES AND THEIR Materials:
FUNCTIONS
Book, pen and notebook
LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Upon completion of this lesson, you can:
1. Describe the cells involving human body and its main Reference: functions; VanPutte, C.,
Regan, J., & Russo, A. (2019).
2. Identify the structure of cell membrane; and, Seeley’s essentials of anatomy & physiology
3. Describe the structure and functions of different (10th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill
Education.
organelles.
4. Identify the major organelles contained in generalized cells;
5. Define the two types of movement through the cell membrane;
6. Define diffusion and concentration gradient;
7. Explain the role of osmosis;
8. Compare hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solutions;
9. Describe the various carrier-mediated transport mechanisms;
10. Differentiate endocytosis and exocytosis;
11. Describe the cytoskeleton and whole activity of a cell;
12. Identify the process in gene expression;
13. Define cell cycle and its phases;
14. Enumerate the process occurring during mitosis;
15. Define differentiation and apoptosis; and,
16. List down the cellular aspects of aging.
LESSON REVIEW/PREVIEW
Before we start the new chapter, let us take a review first from the previous chapter. Kindly answer the
following items on your own, without looking at your notes. Enjoy!
Identification
1. This is the study of the processes and functions of the body. Answer: Physiology
2. The study of the structures of the body. Answer: Anatomy
3. The condition in which body functions, body fluids, and other factors of the internal environment
are maintained within a range of values suitable to support life. Answer: Homeostasis
4. Enumerate the 11 organ systems of the human body.
▪ Integumentary System
▪ Skeletal System
▪ Muscular System
▪ Nervous System
▪ Endocrine System
▪ Cardiovascular System
▪ Lymphatic System
▪ Respiratory System
▪ Digestive System
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 1
▪ Urinary System
▪ Reproductive System
of 5
MAIN LESSON
You must read & study the concepts and refer to figures/tables in Chapter 3 of the book.
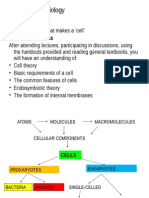
Cells – the basic living unit of all organisms; each cell is a highly organized unit.
Organelles – specialized structures in cells that perform specific functions.
Cytoplasm – jelly-like substance that holds organelles and is enclosed by cell membrane (aka plasma
membrane).
Functions of the Cell:
1. Cell metabolism and energy use
2. Synthesis of molecules
3. Communication
4. Reproduction and inheritance
Cell Membrane / Plasma Membrane
▪ It is the outermost component of the cell that forms a selective barrier between intracellular
(materials inside the cell) and extracellular substances (materials outside the cells).
Molecular Structure:
Major Molecules Definition / Function(s)
Form a double layer that contains 2 regions:
Phospholipids 1. Polar Region – “heads”, exposed to H2O (hydrophilic)
2. Nonpolar Region – “tails”, away from H2O (hydrophobic)
▪ Float among the phospholipid molecules and in some, extend from inner to the
outer surface of cell membrane
Protein
▪ Function as membrane channels, carrier molecules, receptor molecules,
enzymes, or structural supports in membrane
Other Components Definition / Function(s)
▪ Provide added strength & stability by limiting the amount of movement of
Cholesterol
phospholipids.
Carbohydrates ▪ May be bound to some CHON molecules, modifying their functions.
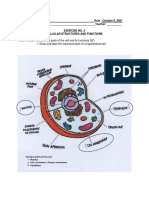
Organelles and Their Functions:
Organelles Function(s)
▪ Contains genetic material of cell (DNA) and nucleoli
Nucleus
▪ Site of RNA synthesis & ribosomal subunit assembly
Ribosomes ▪ Site of protein synthesis
Rough Endoplasmic ▪ Has may ribosomes attached
Reticulum ▪ Site of protein synthesis
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 2 of 6
Smooth Endoplasmic ▪ Site of lipid synthesis
Reticulum ▪ Participates in detoxification
Golgi Apparatus ▪ Modifies CHON structure & packages CHON in secretory vesicles
▪ Contains materials produced in cell
Secretory Vesicle ▪ Formed by the Golgi Apparatus
▪ Secreted by exocytosis
Lysosome ▪ Contains enzymes that digest material taken into the cell
Peroxisome ▪ Breaks down fatty acids, amino acids, and hydrogen peroxide
Mitochondria ▪ Site of aerobic respiration and the major site of ATP synthesis
▪ Supports cytoplasm
Microtubule
▪ Assists in cell division and forms components of cilia & flagella
Centrioles ▪ Facilitate the movement of chromosomes during cell division
Cilia ▪ Located on cell surface that move substances over surfaces of certain cells
Flagella ▪ Proper sperm cells
Microvilli ▪ Increase surface area of certain cells
You must read & study the concepts and refer to figures/tables in Chapter 3 of the book. Generalized
Cell (Refer to Figure 3.1, page 43)
Movement through the cell membrane may be passive or active.
▪ Passive Membrane Transport – does not require the cell to expend energy. This includes
diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion.
▪ Active Membrane Transport – does require the cell to expend energy, usually in the form of ATP.
This includes active transport, secondary active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis.
Diffusion is the movement of a solute from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower
concentration within a solvent. At equilibrium, the distribution of molecules is uniform.
Concentration gradient is the concentration of a solute at one point in a solvent minus the concentration
of that solute at another point in the solvent divided by the distance between the points.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Osmotic pressure is the
force required to prevent movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane. (Refer to Figure
3.7, page 49)
Facilitated Diffusion – this moves substances from a higher to lower concentration and does not require
energy in the form of ATP.
Carrier-Mediated Transport – the movement of a substance across a membrane by means of a carrier
molecule. The substances transported tend to be large, water-soluble molecules or ions.
Active Transport – moves substances from a lower to a higher concentration and requires ATP.
Secondary Active Transport uses the energy of one substance moving down its concentration gradient
to move another substance across the cell membrane. In co-transport, both substances move in the same
direction; in counter-transport, they move in opposite directions.
Endocytosis - movement of materials into cells by the formation of a vesicle.
▪ Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis – involves cell receptors attaching to molecules
▪ Phagocytosis – movement of solid material into cells (cell-eating)
▪ Pinocytosis – the materials ingested is much smaller and is in solution (cell-drinking)
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 3 of 6
Exocytosis – the secretion of materials from cells by vesicle formation.
Cytoskeleton is a cell’s framework. This is vital for providing support, holding organelles in place and
enabling the cell to change shape.
Types of Cytoskeleton:
1. Microtubules – largest diameter; provide structural support, assist in cell division, forming
essential components of certain organelles (cilia and flagella)
2. Intermediate Filaments – medium diameter; maintain cell shape
3. Microfilaments – smallest diameter; determine cell shape and involved in cell movement
Whole-Cell Activity
A cell’s characteristics are ultimately determined by the type of proteins produced, which are determined
by the genetic information in the nucleus. Information in DNA provides the cell with a code for its cellular
processes.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) – a double helix nucleus, composed of nucleotides, and contains five
carbon sugars (deoxyribose), nitrogen base, & phosphate. ▪ !"#$%&’()*)+,-’&’( Nucleotide Pairs
▪ ./"0&’()*)12(’&’(
Gene Expression: A process in which the information in DNA directs protein synthesis. This has two
stages:
1. Transcription – process by which DNA is “read”
The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA; the
mRNA moves through the nuclear pores to ribosomes.
ex: thymine of DNA to adenine of RNA
2. Translation – process by mRNA is converted into amino acids (polypeptides)
The sequence of codons in mRNA is used at ribosomes to produce proteins. Anticodons of tRNA
bind to the codons of mRNA, and the amino acids carried by tRNA are joined to form protein. ex: UUU
codon of mRNA binds to AAA anticodon of tRNA.
Cell Cycle: This consists of a series of events that produce new cells for growth & tissue repair. This has
two phases:
1. Interphase – the non-dividing phase in which the DNA replicates.
2. Cell Division – the formation of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. Each cell contains 46
chromosomes (diploid), except sperm & egg cells which contain 23 chromosomes.
This process occurs through mitosis, which is divided into four stages: (PMAT)
a. Prophase: Each chromosome consists of two chromatids joined at the centromere.
b. Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
c. Anaphase: Chromatids separate at the centromere and migrate to opposite poles.
d. Telophase: The two nuclei assume their normal structure, and cell division is completed,
producing two new daughter cells.
Differentiation – the process by which cells develop specialized structures and functions, results from the
selective activation and inactivation of DNA sections. Ex: the functioning of bone cells is different from the
muscle cells
Apoptosis – also known as programmed cell death, is a normal process by which cell numbers within
various tissues are adjusted and controlled.
Cellular Aspects of Aging: It is estimated that at least 35% of the factors affecting aging are genetic.
1. Cellular clock
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 4 of 6
2. Death genes
3. DNA damage
4. Free radicals
Mitochondrial damage
CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING
You will answer and rationalize this by yourself. This will be recorded as your quiz. One (1) point will be
given to the correct answer and another one (1) point for the correct ratio. Superimpositions or erasures in
your answer/ratio is not allowed. You are given 20 minutes for this activity.
Multiple Choice
1. Which of the following organelles are incorrectly paired with their location within the cell?
a. nucleolus - within the nucleus d. microtubules - within the cytoplasm
b. cilia - on the cell surface e. smooth endoplasmic reticulum - within the
c. Golgi apparatus - on the cell surface cytoplasm of the cell
ANSWER: C.
RATIO: Golgi apparatus isn’t located on the cell surface, it is located/found close to the ER and
near the cell nucleus.
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 5 of 6
2. The nucleolus:
a. is located in the cytoplasm.
b. Is the location for production of large and small ribosomal subunits.
c. Has its own distinct membrane.
d. Is important for the formation of Golgi apparatus.
e. has all of these characteristics
ANSWER: B.
RATIO: The nucleolus is a ribosome production factory, designed to fulfill the need for large-scale
production of rRNAs and assembly of the ribosomal subunits.
3. A cell that was producing large amounts of lipoproteins (proteins combined with lipids) for secretion
from the cell would have large numbers of:
a. Lysosomes. d. Membrane transporters.
b. Golgi apparatus. e. All of these structures.
c. Centrioles.
ANSWER: B.
RATIO: The Golgi apparatus, functions as a factory in which proteins received from the ER are
further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations : lysosomes, the plasma
membrane, or secretion.
4. Which of these cells would most likely have the largest number of mitochondria?
a. bone cells d. blood cells
b. muscle cells e. skin cells c. fat cells
ANSWER: B.
RATIO: Muscle cells are associated with a large number of mitochondria as they require more ATP
(energy) to function than other cells.
5. Substances outside the cell membrane are called:
a. Intracellular substances.
b. Extracellular substances.
c. Intercellular substances.
d. Both extracellular material and intercellular material are correct names.
e. All of these are correct names.
ANSWER: B.
RATIO: Substance outside the cell membrane are called extracellular substance that are responsible for the
cohesion of microorganisms and adhesion of biofilms to surfaces, influencing spatial organization, allowing
interactions among microorganisms, and acting as adhesives between cells.
6. According to the fluid-mosaic model of the cell membrane:
a. Protein molecules that perform important cellular functions float in a lipid bilayer.
b. There is a double protein layer in the plasma membrane.
c. There are fats floating in the protein layer.
d. Carbohydrates function as membrane channels.
e. nonpolar ends of phospholipids are exposed to water inside and outside the cell
ANSWER: A.
RATIO: It states that proteins float in the lipid bilayer, some anchored, and others floating freely. Occasional
cholesterol molecules add extra fluidity. Because it is fluid, the membrane's shape may be altered.
7. _____________ is an example of a molecule that can directly pass through the phospholipid bilayer of
the plasma membrane.
a. Carbon dioxide d. Glucose
b. Potassium e. Calcium
c. Sodium
ANSWER: A.
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 6 of 9
RATIO: Small gasses such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can easily pass through the
membrane. Lipid soluble substances can also pass through the phospholipids. Water soluble
(hydrophilic) substances such as glucose and charged molecules such as ions, however, are
unable to pass through the lipid bilayer.
8. Cell membranes are said to be selectively permeable because they:
a. Allow the free passage of some materials and restrict the passage of others.
b. Allow the passage of materials in one direction but not the other.
c. Permit the passage of most materials but not of water.
d. Cell membranes are NOT normally selectively permeable
ANSWER: A.
RATIO: The cell membrane is said to be selectively permeable because it lets certain substances
pass through while restricting the passage of others.
9. Which of the following statements is TRUE concerning the cell membrane? (Select all that apply)
a. Cholesterol within the membrane gives it added strength and flexibility.
b. Receptor molecules are embedded in the membrane for intercellular communication.
c. Carbohydrates bind to protein molecules thereby modifying the proteins function as a
membrane channel.
d. Receptor molecules embedded in the membrane are involved in cellular recognition.
ANSWER: A, B, C, and D.
RATIO: All of the choices are true concerning the cell membrane.
10. Which of the following would occur if all cell membranes were no longer selectively permeable? (Select
all that apply)
a. Action potentials would no longer be generated.
b. Cells would be hypertonic to their environment.
c. You would be subject to a higher rate of illness and disease.
d. Cells would not be able to get and keep enough glucose to function.
ANSWER: A, B, C, and D.
RATIO: All of the choices occurs if all cell membrane were no longer selectively permeable.
RATIONALIZATION ACTIVITY (THIS WILL BE DONE DURING THE FACE TO FACE INTERACTION)
The instructor will now rationalize the answers. You can now ask questions and debate among yourselves.
Write the correct answer and correct/additional ratio in the space provided.
1. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
2. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
3. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
4. ANSWER: ________
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 7 of 9
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
5. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
6. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
7. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
8. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
9. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
10. ANSWER: ________
RATIO: ___________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
____________
LESSON WRAP-UP
You will now mark (encircle) the session you have finished today in the tracker below. This is simply a
visual to help you track how much work you have accomplished and how much work there is left to do.
You are done with the session! Let’s track your progress.
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 8 of 9
AL Activity: CAT: 3-2-1
This strategy provides a structure for you to record your own comprehension and summarize your learning.
Let us see your progress in this chapter!
Three things you learned:
1. I learned all about the structures and functions shared by all cells.
2. I learned and have understood that the activity of an organism depends on the collective activities of its
cells.
3. I learned that activities of cells are dictated by their structure which determines functions.
Two things that you’d like to learn more about:
1. I’d like to learn more about the functions of each cells, and get a thorough explanation about how it
functions.
2. I’d like to learn more about the cell membrane and how to identify the hydrophilic and the hydrophobic.
One question you still have:
1. Why do phospholipids organize into a bilayer, tail to tail, in a watery environment?
This document and the information thereon is the property of
PHINMA Education (Department of Nursing) 9 of 9
You might also like
- Maturana Varela Tree of KnowledgeDocument231 pagesMaturana Varela Tree of KnowledgeFedor Volyanskiy100% (17)
- Apologia Biology Class Module 6 NotesDocument4 pagesApologia Biology Class Module 6 Noteschickfilamom100% (2)
- DLL Science Grade 7 2nd GradingDocument28 pagesDLL Science Grade 7 2nd GradingCharline A. Radislao91% (23)
- Ha Sas Lec #6-23 Answer Key PDFDocument66 pagesHa Sas Lec #6-23 Answer Key PDFMaria Jub Mangruban50% (2)
- Primary 3 To 6 Science Syllabus SingaporeDocument13 pagesPrimary 3 To 6 Science Syllabus SingaporeJohn KWNo ratings yet
- Biology 11 - 1.4 Kingdoms and DomainsDocument4 pagesBiology 11 - 1.4 Kingdoms and DomainsMinNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document8 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SASDocument8 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #2 - SASFherry Mae UsmanNo ratings yet
- Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument5 pagesSeeley's Essentials of Anatomy & PhysiologyZylith NanaseNo ratings yet
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument25 pagesL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsKurnish KhawolNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument20 pagesChapter IvLaila Abdullah AmparoNo ratings yet
- Cytology Student Notes PDFDocument70 pagesCytology Student Notes PDFElla BoyceNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane & Membra 1442Document48 pagesCell Membrane & Membra 1442Fady FadyNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure - A 2019Document88 pages2 Cell Structure - A 2019Isworo RukmiNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument7 pagesCELLSopingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- 4 Cytology PDFDocument32 pages4 Cytology PDFdaisysintszwaiNo ratings yet
- Membrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesDocument25 pagesMembrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesAshlee Venice CebuNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellhkrybmzxfbxbwnpfhnNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsCiara PanenNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument63 pagesCell Organellessyafi zulNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Bio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Document6 pagesBio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Mia NavarroNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument71 pagesPhysiologysalah.shashoraNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CellsDocument93 pagesStructure and Function of CellsRonald BakangNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument30 pagesCell BiologyHila Jagdish bhaiNo ratings yet
- Cells: General ZoologyDocument71 pagesCells: General ZoologyAzaleaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Biology NotesDocument16 pagesModule 1 Biology NotesPahulbir ThindNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary: Module 1 - Cells As The Basis of LifeDocument28 pagesBiology Summary: Module 1 - Cells As The Basis of LifeAbdullah AliNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsJade Lagada PagariganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- Session #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document5 pagesSession #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- Class NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Document28 pagesClass NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Cyril Josh MaisogNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesCell and Tissuesalvin jr ayugatNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesDocument37 pagesBiology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Principles of ZoologyDocument41 pagesIntegrated Principles of ZoologyEstherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityDocument15 pagesLecture 2ALevels of Organization in Animal ComplexityElleNo ratings yet
- Cells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Document59 pagesCells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Trevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument180 pagesTOPIC 2 Cellular Level of OrganizationAdlyn ShaheeraNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesrickyNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument18 pagesBiology Projecthana fathimaNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellDocument18 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- PHY LE 1 Finals ReviewerDocument14 pagesPHY LE 1 Finals Reviewerroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - CellsDocument32 pagesGen Bio - Cellsjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- AnaPhyLab The CellDocument3 pagesAnaPhyLab The CellCarren SabioNo ratings yet
- The CELL (I) : Physiology of For Pre-Medic Mesir (July 2013)Document65 pagesThe CELL (I) : Physiology of For Pre-Medic Mesir (July 2013)nasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument56 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Functionazrixone54No ratings yet
- Module 1 CellsDocument17 pagesModule 1 CellsLara C.No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology202370092No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument5 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYunie KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologykernelkobieNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument12 pages3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsPrince TeodocioNo ratings yet
- The Cell StudentDocument90 pagesThe Cell Studentmaricar basilanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEDocument3 pagesAnatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CellsDocument6 pagesAnatomy CellsChelsea SebastianNo ratings yet
- 5 - A&P The CellDocument23 pages5 - A&P The CellsabrinaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesActivity 1 Parts of Cell and Function Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsRIVERA, BRENNAN L.No ratings yet
- 1 - Histology Lecture - Structure of Cell Membrane and Membranous OrganellesDocument40 pages1 - Histology Lecture - Structure of Cell Membrane and Membranous OrganellesAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE - Cell Structures and Functions - UY-OCODocument4 pagesWEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE - Cell Structures and Functions - UY-OCOBianca LouiseNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 13 PDFDocument8 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 13 PDFMaria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 18Document6 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 18Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 20Document6 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 20Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment SAS Session 15Document8 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 15Maria Jub Mangruban100% (1)
- Health Assessment SAS Session 14Document9 pagesHealth Assessment SAS Session 14Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Session 1 ANAPHY LecDocument8 pagesSession 1 ANAPHY LecMaria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (LEC)Document10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (LEC)Maria Jub MangrubanNo ratings yet
- Genetic TerminologyDocument6 pagesGenetic TerminologyMuthu KaruppanNo ratings yet
- 9th Science PBQ Chapter 1 To 15Document31 pages9th Science PBQ Chapter 1 To 15YogithaNo ratings yet
- Biology DefinitionDocument9 pagesBiology DefinitionMRhines GadgetBasketNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes in English PDFDocument21 pagesBiology Notes in English PDFAkshay PawarNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 9Document53 pagesBiology Ch. 9Juliet HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ScienceDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates ScienceJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Ylp Remove 2018Document5 pagesYlp Remove 2018mexfloziaNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 1 - The CellDocument4 pagesExercise # 1 - The CellMJMadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Ultra Structure of ProkaryoteDocument3 pagesUltra Structure of ProkaryoteselvasrijaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Microbiology (TMCL) Lecture 1Document21 pagesCell and Microbiology (TMCL) Lecture 1Komi KaayNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MoleculessanaullahNo ratings yet
- MEDBIO KROK-1 English 2019-2020Document65 pagesMEDBIO KROK-1 English 2019-2020Катерина КабишNo ratings yet
- 6.3 Cell Structure Function & OrganellesDocument35 pages6.3 Cell Structure Function & OrganellesMarvin De Jonggoy100% (1)
- Eukariot Dan ProkariotDocument37 pagesEukariot Dan ProkariottidaniadevNo ratings yet
- CH - 40 - Introduction To The Cell CycleDocument15 pagesCH - 40 - Introduction To The Cell Cycleerichaas100% (1)
- Microbiology Final Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Final Exam ReviewJohn NinoNo ratings yet
- Endotoxin and Disease in Food AnimalsDocument8 pagesEndotoxin and Disease in Food Animalstaner_soysuren100% (1)
- DNA Translation J Muqaddas MukhtarDocument33 pagesDNA Translation J Muqaddas MukhtarSafia DurraniNo ratings yet
- Tissue EngineeringDocument17 pagesTissue EngineeringAntonio LoureiroNo ratings yet
- Catalogo General Microscopios OpticosDocument22 pagesCatalogo General Microscopios OpticosValentina HerreraNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Fluid Mosaic Model & Transport Across Membranes My NotesDocument24 pagesTopic 1 Fluid Mosaic Model & Transport Across Membranes My NotesTinotenda J TamaiNo ratings yet
- 1 Da S63 M 1 A5 Ycv Pce MF TD CJZ 8 FHMYqs NViDocument12 pages1 Da S63 M 1 A5 Ycv Pce MF TD CJZ 8 FHMYqs NViYaziNo ratings yet
- Bio and HealthDocument5 pagesBio and HealthKissha TayagNo ratings yet
- Introduction of BacteriaDocument15 pagesIntroduction of BacteriaAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- DPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Document16 pagesDPS Revision Offline Test - 1: Based On DPS 1 To DPS 30Savitri HegdeNo ratings yet