Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MRI - Part3
MRI - Part3
Uploaded by
Reza A0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesThis document discusses various common knee injuries seen on MRI imaging. It describes iliotibial band friction syndrome seen in runners and cyclists. It also discusses quadriceps rupture appearing as a balled up retracted tendon edge with surrounding edema. Jumper's knee is described as an overuse injury of the proximal patellar tendon seen in basketball and volleyball players. Osgood Schlatter disease involves degeneration of the distal patellar tendon seen as ossification. Lateral patellar dislocation results in bruising of the patella and tear of the medial retinaculum. Baker's cyst appears as a fluid collection in the semimembranosus bursa extending between tendons. Stress
Original Description:
Original Title
MRI- part3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various common knee injuries seen on MRI imaging. It describes iliotibial band friction syndrome seen in runners and cyclists. It also discusses quadriceps rupture appearing as a balled up retracted tendon edge with surrounding edema. Jumper's knee is described as an overuse injury of the proximal patellar tendon seen in basketball and volleyball players. Osgood Schlatter disease involves degeneration of the distal patellar tendon seen as ossification. Lateral patellar dislocation results in bruising of the patella and tear of the medial retinaculum. Baker's cyst appears as a fluid collection in the semimembranosus bursa extending between tendons. Stress
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views24 pagesMRI - Part3
MRI - Part3
Uploaded by
Reza AThis document discusses various common knee injuries seen on MRI imaging. It describes iliotibial band friction syndrome seen in runners and cyclists. It also discusses quadriceps rupture appearing as a balled up retracted tendon edge with surrounding edema. Jumper's knee is described as an overuse injury of the proximal patellar tendon seen in basketball and volleyball players. Osgood Schlatter disease involves degeneration of the distal patellar tendon seen as ossification. Lateral patellar dislocation results in bruising of the patella and tear of the medial retinaculum. Baker's cyst appears as a fluid collection in the semimembranosus bursa extending between tendons. Stress
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 24
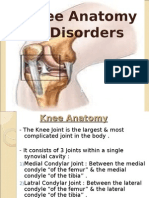
Iliotibial Band Injury
■ Overuse injury usually seen in runners
and bicyclists
■ Iliotibial band Friction syndrome- Due to
rubbing of ITB against lateral femoral
condyle
Quadriceps rupture
Appears as balled up and mildly retracted
tendon edge with edema in surrounding
soft tissue and tendon gap.
Patellar Tendon Rupture
Jumper knee/Patellar tendinitis
■ Overuse injury to proximal aspect of patellar
tendon.
■ Usually seen in basket/volleyball players.
■ Misnomer, mucoid degeneration of collagen
fibers of tendon.
■ MRI- Swelling of proximal aspect of tendon
with internal high signal intensity.
Jumper’s Knee
Osgood Schlatter disease
Degeneration of distal aspect of patellar
tendon.
Triad- Pain, soft tissue swelling, ossification
in distal aspect of patellar tendon.
MRI- Enlarged distal tendon with low signal
intensity foci of heterotopic ossification.
Osgood’s Schlatter Disease
Lateral dislocation of patella
Bony bruise in medial aspect of patella
and lateral aspect of lateral femoral
condyle.
Tear of medial retinaculum appears as
thickening and internal high signal
intensity on T2 weighed image.
Tear of vastus medialis oblique muscle
appear as high signal intensity on T2
weighed image.
Baker cyst
Fluid collection in semimembranosus
medial gastrocnemius bursa
Axial MRI- comma shaped with neck
extending between tendon of medial
gastrocnemius and semimembranosus
tendon
Baker cyst
Baker cyst
Pre patellar bursitis
Pes Anserinus Bursitis
Pes anserinus bursa is located
between tendon of pes anserinus and
medial collateral ligament.
MRI- High signal intensity fluid filled
bursa with low signal intensity
internal debris.
Pes anserinus bursitis
Superficial infrapatellar bursitis/Preacher’s knee
Present anterior to tibia tubercle and distal
aspect of patellar tendon
Named so because it gets compressed
between tibia tubercle and wooden bench
on which a preacher sit
MRI- Low signal intensity on T1 sequence
and high intensity on T2 sequence
Osteochonderal injury
■ Can be a focal cartilage contusion or loose osteochondral fragment.
■ Instability- On T2 weighed image fluid signal intensity in the interface
between fragment and donor pit and cystic change adjacent to donor pit.
Osteochondral injury
High signal at interface Cyst
Osteochondritis dissecans
Occur due to blood deprivation.
Cracks forms in cartilage and
subchondral bone.
Fragmentation of cartilage and bone in
the joint.
Complete medial plica
Plicae are remnants of fetal synovial tissue.
Symptomatic only if complete.
Forms a shelf from medial side of joint
capsule to infrapatellar fat pad.
Overuse injury in sports like running, bicycling.
MRI- Thickened low signal intensity on T2
weighed image.
Complete medial plica
Stress Fracture
You might also like
- MRI Sample ReportsDocument10 pagesMRI Sample Reportssaber shaikhNo ratings yet
- Knee DisordersDocument63 pagesKnee Disordersmeto100% (1)
- UW ObjectivesDocument220 pagesUW ObjectivesRaymond Bernatowicz100% (2)
- AnatomyDocument29 pagesAnatomyazeemNo ratings yet
- Knee Injury: By: Haspreet GillDocument18 pagesKnee Injury: By: Haspreet GillRoshandiep GillNo ratings yet
- Ankle Ligament MriDocument4 pagesAnkle Ligament Mrifrubetto_06No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis KneeDocument12 pagesTuberculosis KneePrasanna ChandiralingamNo ratings yet
- TMJ CompleteDocument54 pagesTMJ CompleteNeal Torwane100% (3)
- Lateral & Medial Knee Pain 2Document31 pagesLateral & Medial Knee Pain 2Muhammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant Shoulder - Rotator Cuff InjuryDocument1 pageThe Radiology Assistant Shoulder - Rotator Cuff InjuryKhalid Al maneiNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Kelainan PeriartikulerDocument20 pagesKuliah Kelainan PeriartikulerRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Knee AnatomyDocument44 pagesKnee AnatomyYanti WijayaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis and OsteoporosispptDocument92 pagesOsteoarthritis and OsteoporosispptDian Puspa0% (1)
- 7 - Knee Joint - D3Document28 pages7 - Knee Joint - D3aslooclt100% (1)
- Radiological Signs in Orthopaedic Part 1-1Document167 pagesRadiological Signs in Orthopaedic Part 1-1andrehrNo ratings yet
- Introduction of MSK ImagingDocument63 pagesIntroduction of MSK ImagingyeabsraNo ratings yet
- ANKLE JOINT &joints of FootDocument35 pagesANKLE JOINT &joints of Foothhaanniiss3870No ratings yet
- Cubital Fossa and Elbow JointDocument31 pagesCubital Fossa and Elbow Jointbravestone974No ratings yet
- The Femur - Proximal - Distal - Shaft - TeachMeAnatomyDocument9 pagesThe Femur - Proximal - Distal - Shaft - TeachMeAnatomyitsvaibhavpathak1710No ratings yet
- Retinacula Around The AnkleDocument17 pagesRetinacula Around The AnkleShobhit GargNo ratings yet
- 03 Soft TissueDocument21 pages03 Soft TissueMajid Khan0% (1)
- Imaging in Arthritis: DR ArchanaDocument98 pagesImaging in Arthritis: DR ArchanadrprasadpsalunkheNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Chronic Non-Traumatic Shoulder Pain: Dr. Naveed Ahmed Fcps FRCRDocument70 pagesImaging of Chronic Non-Traumatic Shoulder Pain: Dr. Naveed Ahmed Fcps FRCRNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mri KneeDocument159 pagesMri KneeNoura Rose100% (2)
- USG - Hip & Knee-Dr - NarayanDocument92 pagesUSG - Hip & Knee-Dr - NarayancmonmanNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular Joint: DR Bhaumik Thakkar MDS-Part 1. Dept. of Periodontology and ImplantologyDocument60 pagesTemporomandibular Joint: DR Bhaumik Thakkar MDS-Part 1. Dept. of Periodontology and ImplantologyJoseph Eduardo Villar CordovaNo ratings yet
- Nerve Injury - Lower LimbDocument4 pagesNerve Injury - Lower LimbstuffNo ratings yet
- JOINTS2Document61 pagesJOINTS2api-19916399No ratings yet
- DDX Backpain & Lumbar Spine DisorderDocument97 pagesDDX Backpain & Lumbar Spine Disorderilabella315No ratings yet
- BursitisDocument21 pagesBursitisJigisha ChavdaNo ratings yet
- MRI of Knee - Part2Document62 pagesMRI of Knee - Part2Reza ANo ratings yet
- Elbow and Antebrachium NotesDocument8 pagesElbow and Antebrachium NoteschadNo ratings yet
- Vivek ShindeDocument2 pagesVivek ShindeSubham deyNo ratings yet
- Kirstie Lower LimbDocument79 pagesKirstie Lower LimbVasile OnigaNo ratings yet
- Injuries of The Shoulder and KneeDocument77 pagesInjuries of The Shoulder and KneeDefaNo ratings yet
- Meniscal TearDocument6 pagesMeniscal TearAdrian Diago TevesNo ratings yet
- TM JointDocument22 pagesTM Jointapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Anterior Shin Splint ProjectDocument59 pagesAnterior Shin Splint ProjectK sai sufhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Bone, Joint, Tendon, and Soft Tissue Injury in Lower Limb (Knee)Document143 pagesLecture 13 Bone, Joint, Tendon, and Soft Tissue Injury in Lower Limb (Knee)Wilson HalimNo ratings yet
- Arthritis RadiologyDocument36 pagesArthritis RadiologyMariam NadeemNo ratings yet
- Imaging of ArthritisDocument99 pagesImaging of ArthritisMd.AlauddinNo ratings yet
- New Biomechanics of Elbow - Wrist JointDocument33 pagesNew Biomechanics of Elbow - Wrist JointFatima AnjumNo ratings yet
- Presentation 6Document18 pagesPresentation 6136 Sandra A PNo ratings yet
- Presented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KDocument81 pagesPresented By: DR Venkatesh V Moderator: DR Harish KPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic: General PrinciplesDocument3 pagesOrthopedic: General PrinciplesJohn Christopher LucesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of KneeDocument47 pagesAnatomy of Kneehanuman kannaNo ratings yet
- Sinding Larsen Johansson SyndromeDocument3 pagesSinding Larsen Johansson SyndromeLuis Miguel MartinsNo ratings yet
- Bimbingan NEURORADIOLOGY - SPINE-YOGYADocument42 pagesBimbingan NEURORADIOLOGY - SPINE-YOGYARizki Khoirun HafidahNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower LimbDocument55 pagesJoints of Lower LimbHanis ZahirahNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Cps 2019 02 006Document9 pages10 1016@j Cps 2019 02 006Deborah SalinasNo ratings yet
- Temporo: MandibularDocument38 pagesTemporo: MandibularyomanNo ratings yet
- Lec 14 THE KNEE JOINTDocument17 pagesLec 14 THE KNEE JOINTMaheen IrfanNo ratings yet
- Ankle Fractures: Dr. T. VikramDocument35 pagesAnkle Fractures: Dr. T. VikramVicky VikramNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument53 pagesLower LimbRupesh M DasNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ajit K VarmaDocument36 pagesDr. Ajit K VarmaDevana MaelissaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis of The Bones and JointsDocument26 pagesTuberculosis of The Bones and JointsLynn TakwadaNo ratings yet
- Median NerveDocument40 pagesMedian Nervehumera100% (2)
- Screenshot 2024-04-03 at 6.35.50 PMDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2024-04-03 at 6.35.50 PMkshweta2605No ratings yet
- P 147 JQ 8293Document2 pagesP 147 JQ 8293Reza ANo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument17 pagesAnswer KeyReza ANo ratings yet
- Assessment 1401Document44 pagesAssessment 1401Reza ANo ratings yet
- MRI of Knee - Part2Document62 pagesMRI of Knee - Part2Reza ANo ratings yet
- MRI - Part1Document50 pagesMRI - Part1Reza A100% (1)
- PREBOARD Gen Ed 1Document16 pagesPREBOARD Gen Ed 1Janice Mayola Alcorin100% (1)
- Reparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Microemulsion For Topical Delivery of ItraconazoleDocument10 pagesReparation, Characterization, and Optimization of Microemulsion For Topical Delivery of ItraconazoleVeni UNNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 March30 Biology Question Paper Solutions 2023Document16 pagesICSE Class 10 March30 Biology Question Paper Solutions 2023Kresha PariharNo ratings yet
- AMPK in Skeletal Muscle Function and Metabolism 2018Document38 pagesAMPK in Skeletal Muscle Function and Metabolism 2018Rita De Cassia Marqueti DuriganNo ratings yet
- DR Tourkey Note New Edition MRCSDocument468 pagesDR Tourkey Note New Edition MRCSchenghui maNo ratings yet
- Biological Diversity of GujaratDocument289 pagesBiological Diversity of GujaratSidat AzazNo ratings yet
- Science (A Progressive Approach) STDocument9 pagesScience (A Progressive Approach) STAbi ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues Class 9thDocument1 pagePlant Tissues Class 9thSantoshPathakNo ratings yet
- VERTICAL GARDEN - Srishti Dokras PDFDocument15 pagesVERTICAL GARDEN - Srishti Dokras PDFKIINSXX Music100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 21: Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceDocument235 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 21: Evolving Concept of Life Based On Emerging Pieces of EvidenceArenz CudalNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam Preperation WorksheetDocument12 pagesAnnual Exam Preperation WorksheetKyakhur IrfanNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord Blood Gas AnalysisDocument2 pagesUmbilical Cord Blood Gas AnalysisqisthiaufaNo ratings yet
- Pentraxin-3 in Chronic Heart Failure: The CORONA and GISSI-HF TrialsDocument8 pagesPentraxin-3 in Chronic Heart Failure: The CORONA and GISSI-HF TrialscamiloNo ratings yet
- Q4 Genetic Diseases Week6Document8 pagesQ4 Genetic Diseases Week6Cold CoockiesNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: M.Bilal BSN, Rn. MSN UhsDocument52 pagesPrepared By: M.Bilal BSN, Rn. MSN UhsXweet AdilNo ratings yet
- DNA Barcode Dan Molekuler Filogeni Turbo Sp. Di Perairan Manokwari Papua BaratDocument12 pagesDNA Barcode Dan Molekuler Filogeni Turbo Sp. Di Perairan Manokwari Papua BaratWelco KarembangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Growing MediaDocument45 pagesLesson 1: Growing Mediakeeth azarconNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal - Physiotherapy - Amy WashbrookDocument35 pagesMusculoskeletal - Physiotherapy - Amy WashbrookRaluca Andreea100% (1)
- Short Story PDF - Short Stories PDF - Bedtime Stories PDF - Moral Story PDFDocument16 pagesShort Story PDF - Short Stories PDF - Bedtime Stories PDF - Moral Story PDFExecutive SecretaryNo ratings yet
- Nouradini PDFDocument15 pagesNouradini PDFDavi AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 GenomicsDocument43 pagesChapter 20 GenomicsNicholasNo ratings yet
- KarbohidratDocument55 pagesKarbohidratAhmad FirmanNo ratings yet
- Sisal Review - Sarkar and Jha - 2017Document11 pagesSisal Review - Sarkar and Jha - 2017smudge740610No ratings yet
- Exemplary Local Governance Practices in Agriculture and Fishery DevelopmentDocument32 pagesExemplary Local Governance Practices in Agriculture and Fishery DevelopmentepraNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Circulatory System Study Questions WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Circulatory System Study Questions WorksheetEshrat TushyNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Engineering QuestionsDocument13 pagesBioprocess Engineering QuestionsPalanisamy Selvamani100% (1)
- Nutrients in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrients in PlantsYesha Shah CherubsNo ratings yet
- Sthapatya Veda Effect On Crime and Mental HealthDocument12 pagesSthapatya Veda Effect On Crime and Mental HealthGO Exclusive TrainingNo ratings yet
- Meyer Et Al-2017-Biotechnology ProgressDocument40 pagesMeyer Et Al-2017-Biotechnology ProgressDNav14No ratings yet
- (PROJECT) RHINO - Rhinoceros Facts For Kids - StudyDocument15 pages(PROJECT) RHINO - Rhinoceros Facts For Kids - StudyIan FlackNo ratings yet