Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(8 F5 Notes) Kinematics
(8 F5 Notes) Kinematics
Uploaded by
Hui Jing0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
(8 F5 notes) kinematics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 page(8 F5 Notes) Kinematics
(8 F5 Notes) Kinematics
Uploaded by
Hui JingCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
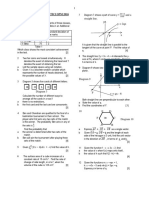
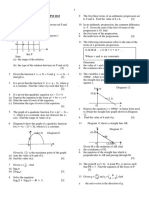
8.
0 KINEMATIC : MOTION ALONG A direction or the particle decreases its
STRAIGHT LINE velocity in the negative direction.
(1) A particles moves along a straight line and
(5) 3 cases can occur
its displacement, s metre from a fixed
(i) Given s = f (t)
point O can be expressed as a function of
t
❑ s=f (t) (ii) Given v = g(t)
⇒
(2) - Distance is a scalar quantity that
measures the distance apart between the
particle and the fixed point. (iii) Given a = h(t)
- Displacement is a vector quantity and it
represents the position of the particle
from a fixed point O. It has both
(6) Important remarks:
magnitude and direction.
(a) If the particle stopped instantaneously
- positive displacement ❑
⇒ the particle is
❑❑
⇒ ⇒
on the right side of the fixed point O.
(b) If the particle returns to O
- negative displacement ❑
⇒ the particle is ❑
⇒
on the left side of the fixed point O.
(c) If the particles moves in the opposite
- zero displacement ❑
⇒ the particle is at O
direction, ❑
⇒
(d) If the velocity of the particle increases in
(3) Instantaneous velocity, v, is the rate of the positive direction.
change of ……….. ❑ the particle experiences ………………..
⇒
❑ ❑
⇒ ⇒
(e) Maximum displacement occurs when
- Velocity is a vector quantity. It has
both magnitude and direction.
- Positive velocity ❑
⇒ the particle is (f) Maximum velocity occurs when
moving towards the …………
- negative velocity ❑
⇒ the particle is
moving towards the ………… *(g) Distance travelled during the nth
- when v = 0, ❑the particle stops
⇒
second
instantaneously / momentarily so as =
to reverse its direction of motion.
*(h) Distance travelled in the first n second
(4) Instantaneous Acceleration, a ,is the =
rate of change of ………………..❑
⇒
*(i) Average velocity in the first n second
=
- positive acceleration ❑
⇒ the particle
increases its velocity in the positive
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) April 2018 Paper 1Document16 pagesSecondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) April 2018 Paper 1Liz Kuan67% (3)
- Physics 2Document464 pagesPhysics 2Ronnith Nandy100% (1)
- Project: Vijayawada Thermal Power Station, Stage-IV Unit#7 (500 MW) Subject: Conveyor Design Calculation As Per 5th Edition of CEMADocument7 pagesProject: Vijayawada Thermal Power Station, Stage-IV Unit#7 (500 MW) Subject: Conveyor Design Calculation As Per 5th Edition of CEMASara Lopez100% (8)
- SPM 2019Document6 pagesSPM 2019Hui JingNo ratings yet
- (7 F5) Linear ProgrammingDocument5 pages(7 F5) Linear ProgrammingHui JingNo ratings yet
- SPM 2018Document6 pagesSPM 2018Hui JingNo ratings yet
- SPM 2017Document6 pagesSPM 2017Hui JingNo ratings yet
- SPM 2016Document5 pagesSPM 2016Hui JingNo ratings yet
- SPM 2015Document6 pagesSPM 2015Hui JingNo ratings yet
- SPM 2012Document5 pagesSPM 2012Hui JingNo ratings yet
- SPM 2013 (Edited)Document5 pagesSPM 2013 (Edited)Hui JingNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics SPM 2014 Paper 1Document5 pagesAdditional Mathematics SPM 2014 Paper 1Hui JingNo ratings yet
- Phy Chapter 4Document77 pagesPhy Chapter 4Hui JingNo ratings yet
- Callaghan Luminous MomentsDocument7 pagesCallaghan Luminous MomentsHelen HeathNo ratings yet
- 3.1 MatterDocument17 pages3.1 Mattercyberbat2008No ratings yet
- Solution Sample Paper 2Document8 pagesSolution Sample Paper 2h1320968No ratings yet
- Bushong: Radiologic Science For Technologists, 10th Edition: Laboratory ExperimentsDocument3 pagesBushong: Radiologic Science For Technologists, 10th Edition: Laboratory Experimentsmoussa medjahedNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMAnushka ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Bio WorkbookDocument6 pagesBio WorkbookZaina NasserNo ratings yet
- Soil PropertiesDocument34 pagesSoil PropertiesKaizer DAn100% (2)
- Solids and Fluids Turbulent Flow Turbulence ModellingDocument357 pagesSolids and Fluids Turbulent Flow Turbulence ModellingJNo ratings yet
- Section 7 6 Coupled Line Directional Couplers PackageDocument24 pagesSection 7 6 Coupled Line Directional Couplers PackagePablo Escobedo AraqueNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Laboratory ManualDocument46 pagesHydraulics Laboratory ManualMikaela LorescaNo ratings yet
- Main Group Chemistry NotesDocument15 pagesMain Group Chemistry NotesSurender MalikNo ratings yet
- 1999 Aipmt Pre English 13660Document16 pages1999 Aipmt Pre English 13660Neeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Shear Area of Reinforced Circular Concrete MembersDocument7 pagesShear Area of Reinforced Circular Concrete MemberstrabajosicNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Light Scattering Understanding The BasicsDocument13 pagesDynamic Light Scattering Understanding The BasicsTrương ThiênNo ratings yet
- Numerical Prediction of Characteristics of Ash Deposition in Heavy Fuel Oil Heat Recovery Steam GeneratorDocument12 pagesNumerical Prediction of Characteristics of Ash Deposition in Heavy Fuel Oil Heat Recovery Steam Generatorsattar aljabairNo ratings yet
- Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output ProcessesDocument38 pagesControl of Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output ProcessesdhineshpNo ratings yet
- Foosterer SummaryDocument2 pagesFoosterer SummaryRobert Machuca RamirezNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument18 pagesHydraulicsJeff MagliaNo ratings yet
- Forces, Moments and PressureDocument12 pagesForces, Moments and PressureDyna MoNo ratings yet
- N HTRZ 42 WQzo Koe AWDocument8 pagesN HTRZ 42 WQzo Koe AWRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter.5 MethodologyDocument14 pagesChapter.5 MethodologyUmesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Entropy: Entropy (S) Clausius Inequality Increase of Entropy Principle WhichDocument6 pagesEntropy: Entropy (S) Clausius Inequality Increase of Entropy Principle WhichEmad BassemNo ratings yet
- The Investigation of Simple PendulumDocument6 pagesThe Investigation of Simple PendulumUgne KupryteNo ratings yet
- Angular MomentumDocument9 pagesAngular MomentumSambid parajuli2002No ratings yet
- Brilliant: Exclusive Set of Previous Questions and Answers 2013-2020Document267 pagesBrilliant: Exclusive Set of Previous Questions and Answers 2013-2020Akshay S MNo ratings yet
- Tabel Pendingin Excel JalaDocument4 pagesTabel Pendingin Excel JalaBianda DeviNo ratings yet
- 9A01402 Hydraulics & Hydraulic MachineryDocument4 pages9A01402 Hydraulics & Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet