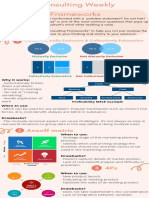
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharma Industry
Pharma Industry
Uploaded by
darshita bhuwalkaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dr. Karen's Stress Relief Brain Balancing ProtocolDocument4 pagesDr. Karen's Stress Relief Brain Balancing ProtocolKaren Kan, MD100% (2)
- LPL - PSC Rajouri Garden Home Visit: Patientreportscsuperpanel - SP - General - Template01 - SC (Version: 7)Document2 pagesLPL - PSC Rajouri Garden Home Visit: Patientreportscsuperpanel - SP - General - Template01 - SC (Version: 7)Rabinder BakhshiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Essential TremorDocument17 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Essential TremorМилица Милошевић100% (1)
- Week 1 PDFDocument41 pagesWeek 1 PDFRaghul BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis of Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument25 pagesCompetitive Analysis of Pharmaceutical IndustryAmaneet Singh Brar0% (3)
- Part 2 Nclex Question and Answer 2020Document5 pagesPart 2 Nclex Question and Answer 2020Joyce Corpuz100% (1)
- Pharmacy As A CareerDocument24 pagesPharmacy As A CareerGayatri JoshiNo ratings yet
- Indian Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented By: Dhruv Seth Kushal Shah Urvi ShahDocument23 pagesIndian Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented By: Dhruv Seth Kushal Shah Urvi ShahSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Economics of PharmaceuticalDocument12 pagesEconomics of PharmaceuticalTarandeepNo ratings yet
- Competitive StragetyDocument19 pagesCompetitive StragetyBashudev BhandariNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutical Industry: Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument27 pagesBiopharmaceutical Industry: Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryTommy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Analytical Testing ServicesDocument34 pagesHealthcare Analytical Testing ServicesAaryan AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain - PharmaceuticalsDocument17 pagesSupply Chain - Pharmaceuticalsabdullah2020No ratings yet
- Epidemic Response Covid 19 Issue 2Document7 pagesEpidemic Response Covid 19 Issue 2Trinh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain OperationsDocument19 pagesSupply Chain OperationsSana’ Jabber YaseenNo ratings yet
- Business Sector - Analysis - PharmaceuticalsDocument16 pagesBusiness Sector - Analysis - PharmaceuticalsAmlan JenaNo ratings yet
- MBT-204 - PM - Module IDocument61 pagesMBT-204 - PM - Module ISavya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PLI Schemes Final Updated 1 Feb 22 Lyst6824Document32 pagesPLI Schemes Final Updated 1 Feb 22 Lyst6824Nitesh kumawatNo ratings yet
- B2B Project ReportDocument9 pagesB2B Project ReportAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented byDocument16 pagesEthics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented bysiddheshsonawaneNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sector UnderstandingDocument6 pagesPharma Sector UnderstandingSrinivas NandikantiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Presented byDocument11 pagesStrategic Management: Presented byNeha SmritiNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument37 pagesPharmaSnehal Wanjari100% (1)
- Reshaping India Into A Life Sciences Innovation Hub: March 2020Document24 pagesReshaping India Into A Life Sciences Innovation Hub: March 2020KaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Project Planning-1Document32 pagesAssignment For Project Planning-1gunjan19834uNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile: 1.1.1 Overview of Pharmaceutical SectorDocument52 pagesIndustry Profile: 1.1.1 Overview of Pharmaceutical Sectormuruges88100% (1)
- Pharma Sector AnalysisDocument11 pagesPharma Sector AnalysisKritika TNo ratings yet
- A Review of MarketingDocument9 pagesA Review of Marketingrahuly12No ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals Executive Summary PDFDocument10 pagesPharmaceuticals Executive Summary PDFPaes C. MarceloNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument41 pagesPharmaBalajiNo ratings yet
- Naveen KumarDocument2 pagesNaveen KumarNave2n adventurism & art works.No ratings yet
- Indian Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument9 pagesIndian Pharmaceutical IndustryAshish GondaneNo ratings yet
- Essential MedicineDocument35 pagesEssential MedicinePavan SahitNo ratings yet
- MBA Summer Training Report On Marketing of Pharmaceutical ProductsDocument49 pagesMBA Summer Training Report On Marketing of Pharmaceutical Productsneha satish pawarNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Puratchikody: Problems and Prospectus of Pharmaceutical Industries in IndiaDocument14 pagesDr. A. Puratchikody: Problems and Prospectus of Pharmaceutical Industries in IndiairfanNo ratings yet
- Pfizer and The Challenges of The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument36 pagesPfizer and The Challenges of The Pharmaceutical IndustryRizki KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Business PPT Template High EndDocument32 pagesBusiness PPT Template High EndMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Dynamics and IntelligenceDocument9 pagesPharmaceutical Supply Chain Dynamics and IntelligenceBeroe Inc.100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Industry in Ghana-2022Document45 pagesPharmaceutical Industry in Ghana-2022listodartNo ratings yet
- Analysing Market OpportunitiesDocument44 pagesAnalysing Market Opportunitiespoisoned54545No ratings yet
- Analysis of Pharmaceutical Industry: by Vlss ConsultanciesDocument25 pagesAnalysis of Pharmaceutical Industry: by Vlss ConsultanciessagardextorNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis - Pharma SectorDocument25 pagesIndustry Analysis - Pharma SectorLini Susan JohnNo ratings yet
- (3.2) WHO Prequalification Project - Status 2006Document21 pages(3.2) WHO Prequalification Project - Status 2006Jose PerezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pharmaceutical Value Chain PDFDocument40 pagesUnderstanding Pharmaceutical Value Chain PDFsantosh kumar pandaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Industry: A Close LookDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Industry: A Close LookVikramSubramanianNo ratings yet
- Crams - 1Document28 pagesCrams - 1Janam AroraNo ratings yet
- Quality Circle For GenericsDocument38 pagesQuality Circle For GenericsAngelica BolosNo ratings yet
- Competitive StragetyDocument28 pagesCompetitive StragetyBashudev BhandariNo ratings yet
- P.E.S.T. AnalysisDocument9 pagesP.E.S.T. AnalysisaaravaroraNo ratings yet
- 2018 US Medicine Spending Outlook To 2022Document60 pages2018 US Medicine Spending Outlook To 2022syedNo ratings yet
- PHARMA Industry Overview PresentationDocument27 pagesPHARMA Industry Overview PresentationdishaNo ratings yet
- USFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewDocument100 pagesUSFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: 1. IndroductionDocument48 pagesChapter - 1: 1. IndroductionFarin TabassumNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2402590Document5 pagesIJCRT2402590syyedadnan638875No ratings yet
- Generic Drugs 26th Feb 2021 LatestDocument60 pagesGeneric Drugs 26th Feb 2021 LatestDr.Athira K RNo ratings yet
- Pharma Industry AnalysisDocument8 pagesPharma Industry AnalysisVenkataramanan VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Generics Life and Money Saving A ReviewDocument5 pagesGenerics Life and Money Saving A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- STW ReportDocument12 pagesSTW ReportShradhanjali BeheraNo ratings yet
- Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) for Pharmaceutical ProductsFrom EverandCurrent Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) for Pharmaceutical ProductsNo ratings yet
- The FDA and Worldwide Current Good Manufacturing Practices and Quality System Requirements Guidebook for Finished PharmaceuticalsFrom EverandThe FDA and Worldwide Current Good Manufacturing Practices and Quality System Requirements Guidebook for Finished PharmaceuticalsNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Reform: A Guide to Improving Performance and EquityFrom EverandPharmaceutical Reform: A Guide to Improving Performance and EquityNo ratings yet
- Frameworks 2Document1 pageFrameworks 2darshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- ICON Profitability CasesDocument14 pagesICON Profitability Casesdarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- FMCG IndustryDocument2 pagesFMCG Industrydarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce IndustryDocument2 pagesE-Commerce Industrydarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- Pest Control Risk Assessment Indoor and OutdoorDocument72 pagesPest Control Risk Assessment Indoor and Outdoorarmkarthick0% (1)
- Ex 2 PSMDocument2 pagesEx 2 PSMRachel Dominique EstrellaNo ratings yet
- HSS2305 Fall2016 Course Syllabus FinalDocument9 pagesHSS2305 Fall2016 Course Syllabus FinalzozoNo ratings yet
- Basic B.SC Nursing - 060620Document6 pagesBasic B.SC Nursing - 060620shubham rathodNo ratings yet
- CBDR Handouts V2Document49 pagesCBDR Handouts V2Ariane Villanueva100% (2)
- ScriptDocument27 pagesScriptIqrarNo ratings yet
- Anywhere Cashless - Process and Feature BriefDocument9 pagesAnywhere Cashless - Process and Feature BriefMadhu SweetieNo ratings yet
- Sdgs Vaibhav Bisaria VIII-B (Roll No.28)Document11 pagesSdgs Vaibhav Bisaria VIII-B (Roll No.28)Rishi BisariaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument29 pagesHypertensionمبدر حامدNo ratings yet
- Mapeh (Health 10) Healthcare Providers and Healthcare PlanDocument7 pagesMapeh (Health 10) Healthcare Providers and Healthcare PlanKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Anzcor Guideline 13 6 Apr 2021Document6 pagesAnzcor Guideline 13 6 Apr 2021Essam HassanNo ratings yet
- Risk Benefit FinalDocument7 pagesRisk Benefit FinalgoaltechNo ratings yet
- NON Communicable DiseasesDocument45 pagesNON Communicable DiseaseshemihemaNo ratings yet
- Varicose Vein Exercise and CareDocument8 pagesVaricose Vein Exercise and CareAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Women and Mental HealthDocument15 pagesWomen and Mental HealthMAMTA SANODIYA100% (1)
- V 6 Module 5 Level 1 I PLAN MY MEALS PDFDocument38 pagesV 6 Module 5 Level 1 I PLAN MY MEALS PDFBanupriyaNo ratings yet
- Sylvia PlathDocument12 pagesSylvia Plathapi-534201968No ratings yet
- Non-Hodgkin's Malignant Lymphomas of The Palatine Tonsils: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesNon-Hodgkin's Malignant Lymphomas of The Palatine Tonsils: A Case ReportWorld Journal of Case Reports and Clinical Images (ISSN: 2835-1568) CODEN:USANo ratings yet
- Working With The Capacity For Connection in Healing Developmental Trauma (Better Copy)Document16 pagesWorking With The Capacity For Connection in Healing Developmental Trauma (Better Copy)William Harryman100% (1)
- Sistem Klasifikasi Internasional WhoDocument9 pagesSistem Klasifikasi Internasional WhoMona Meidya100% (1)
- JunioryearataglanceDocument22 pagesJunioryearataglanceapi-197663945No ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To First AidDocument12 pagesModule 1 Introduction To First Aidmarieta bandiala100% (6)
- Tiklos (Also Called "Pintakasi") Is The Waray Equivalent To The "Bayanihan". Groups ofDocument2 pagesTiklos (Also Called "Pintakasi") Is The Waray Equivalent To The "Bayanihan". Groups ofJanine Ginog FerrerNo ratings yet
- Uterovesical FistulaDocument42 pagesUterovesical Fistulakhadzx100% (2)
- Water For All Reading Text 2Document1 pageWater For All Reading Text 2milenepioNo ratings yet
- Italy and FoodDocument40 pagesItaly and FoodCorina VasiuNo ratings yet
Pharma Industry
Pharma Industry
Uploaded by
darshita bhuwalkaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharma Industry
Pharma Industry
Uploaded by
darshita bhuwalkaCopyright:
Available Formats
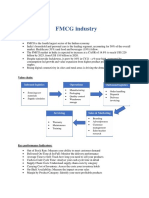
Pharmaceutical industry
Overview and trends:
• India is the 3rd largest pharmaceutical market in the world by value and 14th by value. It is also the
largest producer of vaccines accounting for 60% of all vaccines.
• Indian pharma will reach US$ 130 billion by 2030, growing at a 22% CAGR
• Indian drug & pharma exports stood at US$ 24.60 billion in FY22 and US$ 24.44 billion in FY21.
• Medical device market is expected to grow to US$ 25 billion by 2025
• India is the second-largest contributor of global biotech and pharmaceutical workforce.
• Indian healthcare sector, one of the fastest growing, is expected to cross US$372 billion by end of 2022
• The Indian biotechnology industry was valued at US$ 70.2 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach
US$ 150 billion by 2025.
Value chain:
R&D Active ingredients Manufacturing
• Identify disease • Based on R&D, figure • Milling
• Select the target cells out the active • Granulation
• Administration mode ingredient formulation • Drug Blending
• Drug development • Sourcing API from • Drug coating
and clinical research suppliers • Tablet pressing
Final dispensing Distribution
• Providing correct form • Transportation
and dosage to the right and handling of
patient in a timely medicines from
manner manufacturer to
• Inform about potential retailer/ hospital/
interactions doctor
Costs incurred and value added in components of value chain:
Key performance Indicators:
• R&D cost on drug development → Total expense that a company invests in its R&D sector as
compared to the total number of drug discoveries during that period
• Lead, takt and cycle time → Measure the efficiency of pharma operations
o Cycle time: average time taken to complete production of 1 unit (optimal time of delivery)
o Takt time: average time taken between starting production of 1 unit and the next unit (rate at
which drugs should be produced to meet customer demands)
o Lead time: average time taken between receiving and delivering an order
• Product quality complaint rate → measures the number of customer complaints regarding product
quality with respect to the total number of products distributed within a fixed period
• Sales growth and health/ safety KPIs as regulated by governments
Risks in the industry:
• Pharmaceutical fraud:
Pharmaceutical fraud remains a major challenge for the industry — and it was possibly even worse
during COVID-19. Industry observers have predicted that misconduct during the pandemic will lead to
higher-than-average health care fraud recoveries this year.
• Supply chain disruptions:
The pandemic revealed significant weaknesses in the pharmaceutical logistics. The lean supply chains
cultivated by the industry are not resilient to sudden shocks or issues with production. As a result, long
manufacturing lead times and unpredictable demand are likely to cause problems. The supply chain
may also be vulnerable to intentional disruption by cybercriminals. Moreover, poor visibility and
transparency in the supply chain make a number of these challenges worse.
• Rising consumer expectations and difficulties managing brand health:
Pharmaceutical companies are under major scrutiny from customers, meaning brand management is
more important than usual. At the same time, consumers are expecting more from the pharmaceutical
industry, and it is becoming increasingly common for customers to carefully consider the dollar value a
medicine provides and shop around when buying medicine. Pharmaceutical companies will need to
manage growing consumer expectations and be prepared to respond to brand crises throughout the year
— like issues that may arise as supply chains continue to be disrupted by COVID-19.
Opportunities:
• Cost efficiency:
Low cost of production and R&D boosts efficiency of Indian pharma companies, leading to
competitive exports. India’s cost of production is 1/3rd that of US firms. Hence, the ability to produce
high-quality, low-priced medicines presents a huge opportunity for domestic businesses.
• Policy support:
In February 2021, the government approved a production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme for the
pharmaceuticals sector valid till FY 2029. This is predicted to increase investments and sales in the
sector, with enhanced exports. Additional outlay of $26.6B was announced in June 2021, to be utilised
over 5 years for the PLI scheme in 13 key sectors like active pharmaceutical ingredients, drug
intermediaries and key starting materials.
• Launch of patented drugs:
Following the introduction of product patents, several multinational companies are expected to launch
patented drugs in India. Growth in the number of lifestyle diseases in India could boost the sale of
drugs in this segment. Permission to import patent drugs from foreign players in the Indian market.
• Scope in generics market:
India’s generic drugs account for 20% of global exports in terms of volume, making it the largest
provider of generic medicines globally. The generics drug market accounts for around 70% of the
pharmaceutical industry. India supplies >40% generics to the US market
You might also like
- Dr. Karen's Stress Relief Brain Balancing ProtocolDocument4 pagesDr. Karen's Stress Relief Brain Balancing ProtocolKaren Kan, MD100% (2)
- LPL - PSC Rajouri Garden Home Visit: Patientreportscsuperpanel - SP - General - Template01 - SC (Version: 7)Document2 pagesLPL - PSC Rajouri Garden Home Visit: Patientreportscsuperpanel - SP - General - Template01 - SC (Version: 7)Rabinder BakhshiNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Essential TremorDocument17 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Essential TremorМилица Милошевић100% (1)
- Week 1 PDFDocument41 pagesWeek 1 PDFRaghul BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis of Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument25 pagesCompetitive Analysis of Pharmaceutical IndustryAmaneet Singh Brar0% (3)
- Part 2 Nclex Question and Answer 2020Document5 pagesPart 2 Nclex Question and Answer 2020Joyce Corpuz100% (1)
- Pharmacy As A CareerDocument24 pagesPharmacy As A CareerGayatri JoshiNo ratings yet
- Indian Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented By: Dhruv Seth Kushal Shah Urvi ShahDocument23 pagesIndian Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented By: Dhruv Seth Kushal Shah Urvi ShahSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Economics of PharmaceuticalDocument12 pagesEconomics of PharmaceuticalTarandeepNo ratings yet
- Competitive StragetyDocument19 pagesCompetitive StragetyBashudev BhandariNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutical Industry: Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument27 pagesBiopharmaceutical Industry: Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical IndustryTommy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Analytical Testing ServicesDocument34 pagesHealthcare Analytical Testing ServicesAaryan AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain - PharmaceuticalsDocument17 pagesSupply Chain - Pharmaceuticalsabdullah2020No ratings yet
- Epidemic Response Covid 19 Issue 2Document7 pagesEpidemic Response Covid 19 Issue 2Trinh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain OperationsDocument19 pagesSupply Chain OperationsSana’ Jabber YaseenNo ratings yet
- Business Sector - Analysis - PharmaceuticalsDocument16 pagesBusiness Sector - Analysis - PharmaceuticalsAmlan JenaNo ratings yet
- MBT-204 - PM - Module IDocument61 pagesMBT-204 - PM - Module ISavya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PLI Schemes Final Updated 1 Feb 22 Lyst6824Document32 pagesPLI Schemes Final Updated 1 Feb 22 Lyst6824Nitesh kumawatNo ratings yet
- B2B Project ReportDocument9 pagesB2B Project ReportAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented byDocument16 pagesEthics in Pharmaceutical Industry: Presented bysiddheshsonawaneNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sector UnderstandingDocument6 pagesPharma Sector UnderstandingSrinivas NandikantiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Presented byDocument11 pagesStrategic Management: Presented byNeha SmritiNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument37 pagesPharmaSnehal Wanjari100% (1)
- Reshaping India Into A Life Sciences Innovation Hub: March 2020Document24 pagesReshaping India Into A Life Sciences Innovation Hub: March 2020KaraNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Project Planning-1Document32 pagesAssignment For Project Planning-1gunjan19834uNo ratings yet
- Industry Profile: 1.1.1 Overview of Pharmaceutical SectorDocument52 pagesIndustry Profile: 1.1.1 Overview of Pharmaceutical Sectormuruges88100% (1)
- Pharma Sector AnalysisDocument11 pagesPharma Sector AnalysisKritika TNo ratings yet
- A Review of MarketingDocument9 pagesA Review of Marketingrahuly12No ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals Executive Summary PDFDocument10 pagesPharmaceuticals Executive Summary PDFPaes C. MarceloNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument41 pagesPharmaBalajiNo ratings yet
- Naveen KumarDocument2 pagesNaveen KumarNave2n adventurism & art works.No ratings yet
- Indian Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument9 pagesIndian Pharmaceutical IndustryAshish GondaneNo ratings yet
- Essential MedicineDocument35 pagesEssential MedicinePavan SahitNo ratings yet
- MBA Summer Training Report On Marketing of Pharmaceutical ProductsDocument49 pagesMBA Summer Training Report On Marketing of Pharmaceutical Productsneha satish pawarNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Puratchikody: Problems and Prospectus of Pharmaceutical Industries in IndiaDocument14 pagesDr. A. Puratchikody: Problems and Prospectus of Pharmaceutical Industries in IndiairfanNo ratings yet
- Pfizer and The Challenges of The Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument36 pagesPfizer and The Challenges of The Pharmaceutical IndustryRizki KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Business PPT Template High EndDocument32 pagesBusiness PPT Template High EndMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Dynamics and IntelligenceDocument9 pagesPharmaceutical Supply Chain Dynamics and IntelligenceBeroe Inc.100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Industry in Ghana-2022Document45 pagesPharmaceutical Industry in Ghana-2022listodartNo ratings yet
- Analysing Market OpportunitiesDocument44 pagesAnalysing Market Opportunitiespoisoned54545No ratings yet
- Analysis of Pharmaceutical Industry: by Vlss ConsultanciesDocument25 pagesAnalysis of Pharmaceutical Industry: by Vlss ConsultanciessagardextorNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis - Pharma SectorDocument25 pagesIndustry Analysis - Pharma SectorLini Susan JohnNo ratings yet
- (3.2) WHO Prequalification Project - Status 2006Document21 pages(3.2) WHO Prequalification Project - Status 2006Jose PerezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pharmaceutical Value Chain PDFDocument40 pagesUnderstanding Pharmaceutical Value Chain PDFsantosh kumar pandaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Industry: A Close LookDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Industry: A Close LookVikramSubramanianNo ratings yet
- Crams - 1Document28 pagesCrams - 1Janam AroraNo ratings yet
- Quality Circle For GenericsDocument38 pagesQuality Circle For GenericsAngelica BolosNo ratings yet
- Competitive StragetyDocument28 pagesCompetitive StragetyBashudev BhandariNo ratings yet
- P.E.S.T. AnalysisDocument9 pagesP.E.S.T. AnalysisaaravaroraNo ratings yet
- 2018 US Medicine Spending Outlook To 2022Document60 pages2018 US Medicine Spending Outlook To 2022syedNo ratings yet
- PHARMA Industry Overview PresentationDocument27 pagesPHARMA Industry Overview PresentationdishaNo ratings yet
- USFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewDocument100 pagesUSFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewHarsh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: 1. IndroductionDocument48 pagesChapter - 1: 1. IndroductionFarin TabassumNo ratings yet
- IJCRT2402590Document5 pagesIJCRT2402590syyedadnan638875No ratings yet
- Generic Drugs 26th Feb 2021 LatestDocument60 pagesGeneric Drugs 26th Feb 2021 LatestDr.Athira K RNo ratings yet
- Pharma Industry AnalysisDocument8 pagesPharma Industry AnalysisVenkataramanan VaidyanathanNo ratings yet
- Generics Life and Money Saving A ReviewDocument5 pagesGenerics Life and Money Saving A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- STW ReportDocument12 pagesSTW ReportShradhanjali BeheraNo ratings yet
- Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) for Pharmaceutical ProductsFrom EverandCurrent Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) for Pharmaceutical ProductsNo ratings yet
- The FDA and Worldwide Current Good Manufacturing Practices and Quality System Requirements Guidebook for Finished PharmaceuticalsFrom EverandThe FDA and Worldwide Current Good Manufacturing Practices and Quality System Requirements Guidebook for Finished PharmaceuticalsNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Reform: A Guide to Improving Performance and EquityFrom EverandPharmaceutical Reform: A Guide to Improving Performance and EquityNo ratings yet
- Frameworks 2Document1 pageFrameworks 2darshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- ICON Profitability CasesDocument14 pagesICON Profitability Casesdarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- FMCG IndustryDocument2 pagesFMCG Industrydarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce IndustryDocument2 pagesE-Commerce Industrydarshita bhuwalkaNo ratings yet
- Pest Control Risk Assessment Indoor and OutdoorDocument72 pagesPest Control Risk Assessment Indoor and Outdoorarmkarthick0% (1)
- Ex 2 PSMDocument2 pagesEx 2 PSMRachel Dominique EstrellaNo ratings yet
- HSS2305 Fall2016 Course Syllabus FinalDocument9 pagesHSS2305 Fall2016 Course Syllabus FinalzozoNo ratings yet
- Basic B.SC Nursing - 060620Document6 pagesBasic B.SC Nursing - 060620shubham rathodNo ratings yet
- CBDR Handouts V2Document49 pagesCBDR Handouts V2Ariane Villanueva100% (2)
- ScriptDocument27 pagesScriptIqrarNo ratings yet
- Anywhere Cashless - Process and Feature BriefDocument9 pagesAnywhere Cashless - Process and Feature BriefMadhu SweetieNo ratings yet
- Sdgs Vaibhav Bisaria VIII-B (Roll No.28)Document11 pagesSdgs Vaibhav Bisaria VIII-B (Roll No.28)Rishi BisariaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument29 pagesHypertensionمبدر حامدNo ratings yet
- Mapeh (Health 10) Healthcare Providers and Healthcare PlanDocument7 pagesMapeh (Health 10) Healthcare Providers and Healthcare PlanKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Anzcor Guideline 13 6 Apr 2021Document6 pagesAnzcor Guideline 13 6 Apr 2021Essam HassanNo ratings yet
- Risk Benefit FinalDocument7 pagesRisk Benefit FinalgoaltechNo ratings yet
- NON Communicable DiseasesDocument45 pagesNON Communicable DiseaseshemihemaNo ratings yet
- Varicose Vein Exercise and CareDocument8 pagesVaricose Vein Exercise and CareAtu KaushalNo ratings yet
- Women and Mental HealthDocument15 pagesWomen and Mental HealthMAMTA SANODIYA100% (1)
- V 6 Module 5 Level 1 I PLAN MY MEALS PDFDocument38 pagesV 6 Module 5 Level 1 I PLAN MY MEALS PDFBanupriyaNo ratings yet
- Sylvia PlathDocument12 pagesSylvia Plathapi-534201968No ratings yet
- Non-Hodgkin's Malignant Lymphomas of The Palatine Tonsils: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesNon-Hodgkin's Malignant Lymphomas of The Palatine Tonsils: A Case ReportWorld Journal of Case Reports and Clinical Images (ISSN: 2835-1568) CODEN:USANo ratings yet
- Working With The Capacity For Connection in Healing Developmental Trauma (Better Copy)Document16 pagesWorking With The Capacity For Connection in Healing Developmental Trauma (Better Copy)William Harryman100% (1)
- Sistem Klasifikasi Internasional WhoDocument9 pagesSistem Klasifikasi Internasional WhoMona Meidya100% (1)
- JunioryearataglanceDocument22 pagesJunioryearataglanceapi-197663945No ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To First AidDocument12 pagesModule 1 Introduction To First Aidmarieta bandiala100% (6)
- Tiklos (Also Called "Pintakasi") Is The Waray Equivalent To The "Bayanihan". Groups ofDocument2 pagesTiklos (Also Called "Pintakasi") Is The Waray Equivalent To The "Bayanihan". Groups ofJanine Ginog FerrerNo ratings yet
- Uterovesical FistulaDocument42 pagesUterovesical Fistulakhadzx100% (2)
- Water For All Reading Text 2Document1 pageWater For All Reading Text 2milenepioNo ratings yet
- Italy and FoodDocument40 pagesItaly and FoodCorina VasiuNo ratings yet