Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document
Document
Uploaded by
Nica OmpocOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document
Document
Uploaded by
Nica OmpocCopyright:
Available Formats
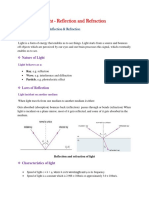
Reflection - A phenomenon in which a wave bounces off a surface and returns to the direction it has come from with
the
same wavelength and frequency
types of reflection based on the characteristics of the reflected image.
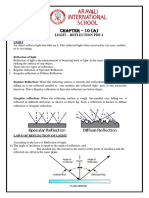
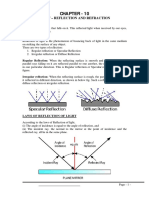
Specular reflection - Is observed when light hits a smooth, flat surface and reflects an image that is almost identical to
the object itself.
Diffused reflection - Occurs when reflected light rays scatter in different directions. This is observed when light strikes a
rough surface or any surface with an irregular density.
LAW OF REFLECTION - A law explaining that the angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
Incident ray - the ray of light approaching the mirror.
Reflected ray - the ray that bounces from the mirror.
Normal - vertical line that is perpendicular to the surface is drawn between the two rays.
Angle of incidence (θi) - refers to the angle formed by the incident ray and the normal.
Angle of reflection (θr) - refers to the angle formed by the reflected ray and the normal.(θi)=(θr)
Two major types of mirrors
PLANE MIRRORS - Made up of flat, reflective surfaces that produce a specular reflection either of an object or a person
in front of it.
The formation of images on mirrors
Line of sight - is the process of directing your sight towards a certain point in space.
Virtual image - is an image that forms when the light rays bouncing from an illuminated object appear to be meeting or
converging with each other at a definite point but do not actually meet.
Curved mirrors - Refers to crescent-shaped mirror that is part of a reflective sphere.
The spherical curved mirror is classified into two:
Concave mirror - A curved mirror with a reflective surface that curves inward.
Convex mirror - A curved mirror with a reflective surface that curves outward.
different parts of the concave and convex mirror
1.Center of Curvature- Point C in the illustration above is the center of the curvature and the center of the sphere itself.
2. Principal Axis- This is the line in the middle that intersects point A, F, and C and divides the sphere into two
hemisphere.
3.Vertex- This is denoted by point A where the principal axis meets the edge of the sphere or the surface of the curved
mirror.
4. Focal Point- This is represented by point F, which marks the midpoint between the center of the curvature and the
vertex.
5.Focal length- This refers to The distance between the focal point and the mirror’s vertex.the focal length is one half
the radius of the curvature..
6. Radius of curvature-Letter R is the sphere’s radius, marking the distance between the vertex and the center of
curvature.
Real image - An image that appears when light rays meet at a particular point once an object is reflected in the mirror.
The ray diagram method - Is a tool that determines the location of images formed in curved mirrors by tracing the path
of light rays passing through an object and bouncing on the surface of a mirror.
You might also like
- Training Plan 10k Advanced v2Document4 pagesTraining Plan 10k Advanced v2BrooksRunning100% (1)
- E111 - AgustinDocument20 pagesE111 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light 1Document28 pagesReflection of Light 1Anne MalobagoNo ratings yet
- Optics 10-PhysicsDocument6 pagesOptics 10-PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - LightDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - LightMadhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 1 PDFHarshil SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision NotesDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notesprateeksahu1111No ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Images by Convex Concave R ExplainedDocument11 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Images by Convex Concave R ExplainedSeetha SenthilNo ratings yet
- Physics - Light Reflection N Refraction Class 10Document11 pagesPhysics - Light Reflection N Refraction Class 10M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of Light Chapter 10 NOTESDocument4 pagesReflection and Refraction of Light Chapter 10 NOTESTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Class 10 LightDocument23 pagesClass 10 LightMathew AbrahamNo ratings yet
- CH 1 PhysicsDocument18 pagesCH 1 Physicsraj chopdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteJay Maki100% (1)
- Light Reflection & RefractionDocument29 pagesLight Reflection & Refractionmacff217No ratings yet
- Reflection Mirrors 2022 2023Document92 pagesReflection Mirrors 2022 2023Jeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsDocument59 pagesClass 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsRamya L NNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2-Lesson - Light and MirrorsDocument72 pagesQuarter 2-Lesson - Light and MirrorsTrendi Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument11 pagesScienceMark Laurence RiraoNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Sci+Document19 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Sci+Sahil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction - CBSE - XDocument7 pagesReflection and Refraction - CBSE - Xvidyamane23100% (1)
- Reflection of LightDocument17 pagesReflection of LightNishant SinghNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument11 pagesReflection of Lightlohitha charyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument48 pagesChapter 9 - Light - Reflection and Refractionsekhsayan0102No ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument10 pagesReflection of Lightaryayu0123No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument2 pagesLight - Reflection and Refractionanilpatel39No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction 10th Phy PDFDocument10 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction 10th Phy PDFManeeshAkhandJyoyi100% (1)
- Chapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktDocument17 pagesChapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktSarveshyaNo ratings yet
- Light: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesLight: Light - Reflection and RefractionShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Science Notes6Document37 pagesScience Notes6abhyudai.edwardsNo ratings yet
- Light and Reflection NotesDocument2 pagesLight and Reflection NotesRakesh palNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesDocument51 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notesved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Light Physics Class 10 Part 1Document12 pagesLight Physics Class 10 Part 1Kishwar SachanNo ratings yet
- 3prep - FirstTerm-UnitTwoDocument18 pages3prep - FirstTerm-UnitTwoKamal NaserNo ratings yet
- Light Mirror and LensesDocument11 pagesLight Mirror and LensesDanbert TaopaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience Reviewerarieannie katlyNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Revised Grade 10 ScienceDocument32 pagesReflection of Light Revised Grade 10 ScienceFurr JoyNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection NotesDocument8 pagesLight Reflection NotesSuperParthz GAMING100% (2)
- ScienceDocument10 pagesScienceStopnaplsNo ratings yet
- Reflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesReflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionmathclubNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionDocument12 pagesChapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi Bhatia100% (1)
- Support material, X, Chapter- LightDocument12 pagesSupport material, X, Chapter- Lightaestheticmax23No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Subject-Science CHAPTER - 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 pagesGrade 10 Subject-Science CHAPTER - 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Notesluv manotNo ratings yet
- 2 Out 2 PDFDocument426 pages2 Out 2 PDFSwapnil MaladkarNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesJohn Malig100% (1)
- NMAT Reviewer Geometrical OpticsDocument37 pagesNMAT Reviewer Geometrical Opticsmannypot83% (12)
- p8 LightDocument7 pagesp8 LightLeslie MasiyandimaNo ratings yet
- Light Chapter'sDocument24 pagesLight Chapter'sPratik ChavanNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument37 pagesPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X For 2017 18 5 42Document38 pagesPhysics Class X For 2017 18 5 42jatinder kohliNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Light MirrorsDocument57 pagesLight MirrorsPhylicia RamosNo ratings yet
- Folio Physics Chapter 5: Light: Name: Nor Nadia Mohd Azam Class: 4 Ibn Khaldun Teacher'S Name: en - Zai HousneyDocument16 pagesFolio Physics Chapter 5: Light: Name: Nor Nadia Mohd Azam Class: 4 Ibn Khaldun Teacher'S Name: en - Zai Housneynornadeeya_94No ratings yet
- Lecture On LightDocument4 pagesLecture On LightAshly DeniseNo ratings yet
- Image Formation in Lenses.Document5 pagesImage Formation in Lenses.Syed AkramNo ratings yet
- Light ShikshaDocument13 pagesLight Shikshabratajeet.ghosh.14No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction NotesRaviraj Desai100% (2)
- LIGHT - Light i-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesLIGHT - Light i-WPS OfficeUtsav BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Dictionary & Learners Phonetic Pronunciation Key ESL Project by RS MinerDocument3 pagesDictionary & Learners Phonetic Pronunciation Key ESL Project by RS MinerRich MinérNo ratings yet
- Bizourka and Freestyle Flemixh MazurkaDocument3 pagesBizourka and Freestyle Flemixh MazurkaPe VandeNo ratings yet
- NumbersDocument28 pagesNumberspayal.soniNo ratings yet
- Review 2 Mid Test SMT 2 FF5Document3 pagesReview 2 Mid Test SMT 2 FF5Zulfan FirdausiNo ratings yet
- LUNA enDocument2 pagesLUNA enAlex Burcea0% (1)
- 2006 - P. 31 Gordon Tucker's Speech The Genius of HeschelDocument95 pages2006 - P. 31 Gordon Tucker's Speech The Genius of HeschelYehudah DovBer ZirkindNo ratings yet
- Facing, Interfacings, Interlinings and Linings: Submitted By-Shruti Verma (FD-4) 2022183Document35 pagesFacing, Interfacings, Interlinings and Linings: Submitted By-Shruti Verma (FD-4) 2022183ShrutiNo ratings yet
- Doll Amigurumi Free Crochet PatternDocument7 pagesDoll Amigurumi Free Crochet Patterncastroanap67% (3)
- (EN) S104 - Signal Processing - Midterm Exam Study Guide STUDENTDocument13 pages(EN) S104 - Signal Processing - Midterm Exam Study Guide STUDENTJustinNo ratings yet
- What Really Wins MoneyDocument20 pagesWhat Really Wins Moneyjaren2100% (3)
- Beasts of Chaos RemindersDocument4 pagesBeasts of Chaos RemindersCarlos González LeónNo ratings yet
- Cornish Rugby and Cultural IndentityDocument17 pagesCornish Rugby and Cultural IndentityPhilip HoskingNo ratings yet
- Ohio Investigative Unit - Bars CitedDocument26 pagesOhio Investigative Unit - Bars CitedWBNS-TVNo ratings yet
- The Little GirlDocument2 pagesThe Little GirlBaibhab BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Panagbenga InfoDocument3 pagesPanagbenga InfoErica Mae PaladNo ratings yet
- 50 Chapter 1 - The Seers of StrokDocument14 pages50 Chapter 1 - The Seers of StrokALFREDNo ratings yet
- Doctor Who ScriptDocument53 pagesDoctor Who ScriptArthur PuttnerNo ratings yet
- Asessment 4Document2 pagesAsessment 4Marie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- 0-Ecolier CompressedDocument8 pages0-Ecolier CompressedIshaq HashmiNo ratings yet
- NF28132325493824 ETicketDocument3 pagesNF28132325493824 ETicketCS Labdhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Using The Words in ParenthesesDocument4 pagesUsing The Words in ParenthesesamataNo ratings yet
- Duergar The Undying Warlock 15Document3 pagesDuergar The Undying Warlock 15João PedroNo ratings yet
- Axis Bank Credit CardsDocument19 pagesAxis Bank Credit Cardsamit singhNo ratings yet
- Italy Now Abruzzo PDFDocument84 pagesItaly Now Abruzzo PDFSamuel DuarteNo ratings yet
- Asael Marquez Flores 2nd Partial HW 7Document17 pagesAsael Marquez Flores 2nd Partial HW 7Asael Flores0% (1)
- Aos Warscroll Chaos Marauders enDocument1 pageAos Warscroll Chaos Marauders enDiego PignatonNo ratings yet
- TASK Unit 11 (Regita)Document2 pagesTASK Unit 11 (Regita)Regita Elvia SesraNo ratings yet
- Raid On The Goblin Stronghold: A 2-Hour Adventure For 1st-4th Level CharactersDocument8 pagesRaid On The Goblin Stronghold: A 2-Hour Adventure For 1st-4th Level CharactersLucas FreireNo ratings yet