Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emst Midterm Lessons
Emst Midterm Lessons
Uploaded by
Maden betoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Emst Midterm Lessons
Emst Midterm Lessons
Uploaded by
Maden betoCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2
COMPUTER SYSTEMS AND ITS
ELEMENTS
USES OF I.T.
THE INTERNET AND THE WORLD WIDE
WEB
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 1
Lesson 6: THE COMPUTER SYSTEM AND ITS ELEMENTS
(Week 7 & 8)
Objectives:
1. Define Computing System;
2. Define Computer;
3. Name and describe the different parts of Computer;
4. Explain & identify the importance of Computing System Elements and
how they work;
5. Identify the function of the four basic components of Hardware;
6. Appreciate the importance of the Computer Hardware.
7. Differentiate the Application and operating software
8. Organize the different parts of Computer according to their uses and
arrange its basic components
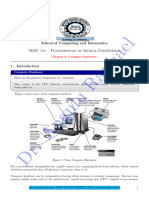
THE COMPUTER SYSTEM AND ITS ELEMENTS
COMPUTER
• What is Computer: Computer is an electronic device that is designed to
work with Information.
• The term computer is derived from the Latin term ‘computare’, this
means to calculate or programmable machine. Computer cannot do
anything without a Program. It represents the decimal numbers through
a string of binary digits. The Word 'Computer' usually refers to
the Center Processor Unit plus Internal memory.
• Is an electronic device for storing and processing data, typically in
binary form, according to instructions given to it in a variable program.
• It is an electronic device capable of interpreting and performing
programmed instructions.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 2
• It is also a device that accepts processes, stores and outputs data at
high speed.
• Charles Babbage is called the "Grand Father" of the computer. The First
mechanical computer designed by Charles Babbage was called
Analytical Engine. It uses read-only memory in the form of punch cards.
• Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as
input from the user and processes these data under the control of set of
instructions (called program) and gives the result (output) and saves
output for the future use. It can process both numerical and non-
numerical (arithmetic and logical) calculations.
The basic components of a modern digital computer are: Input
Device, Output Device, Central Processor Unit (CPU), mass storage device and
memory. A Typical modern computer uses LSI Chips. Large-scale
integration (LSI) is the process of integrating or embedding thousands of
transistors on a single silicon semiconductor microchip.
• Four Functions about computer are:
accepts data Input
processes data Processing
produces output Output
stores results Storage
Input (Data):
• Input is the raw information entered into a computer from the input
devices. It is the collection of letters, numbers, images etc.
• The process of entering data and instructions into the computer system
Process:
• Process is the operation of data as per given instruction. It is totally
internal process of the computer system.
• Performing arithmetic, and logical operations on data in order to
convert them into useful information.
Output:
• Output is the processed data given by computer after data
processing. Output is also called as Result. We can save these results in
the storage devices for the future use.
• The process of producing useful information or results for the user, such
as a printed report or visual display.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 3
Storage
• Saving data and instructions so that they are available for processing
as and when required.
• Storage is the device use in storing all the result being done in the input,
process and output.
A system is a collection of elements or components that are organized for a
common purpose. The word sometimes describes the organization or plan itself
(and is similar in meaning to method, as in "I have my own little system") and
sometimes describes the parts in the system (as in "computer system").
A computer system consists of hardware components that have been carefully
chosen so that they work well together and software components or programs
that run in the computer.
COMPUTING SYSTEM ELEMENTS:
I. Hardware
II. Software
III. People ware
It represents the physical and tangible
components of a computer i.e. the
components that can be seen and
touched.
Examples of Hardware are following:
• Input devices -- keyboard, mouse
etc.
• Output devices -- printer, monitor
etc.
• Secondary storage devices -- Hard
disk, CD, DVD etc.
• Internal components -- CPU, motherboard, RAM etc.
Relationship between Hardware and Software
• Hardware and software are mutually dependent on each other. Both
of them must work together to make a computer produce a useful
output.
• Software cannot be utilized without supporting hardware.
• Hardware without set of programs to operate upon cannot be utilized
and is useless.
• To get a particular job done on the computer, relevant software should
be loaded into the hardware
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 4
• Hardware is a one-time expense.
• Software development is very expensive and is a continuing expense.
• Different software applications can be loaded on hardware to run
different jobs.
• Software acts as an interface between the user and the hardware.
• If hardware is the 'heart' of a computer system, then software is its 'soul'.
Both are complimentary to each other.
The Four Main Components of Hardware
1. INPUT DEVICES
2. PROCESSING DEVICES
3. STORAGE DEVICES
4. OUTPUT DEVICES
1. INPUT
Following are few of the important input devices which are used in a
computer:
• Keyboard
• Mouse
• Joy Stick
• Light pen
• Track Ball
• Scanner
• Graphic Tablet
• Microphone
• Magnetic Ink Card Reader(MICR)
• Optical Character Reader(OCR)
Keys Description
Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and
digit keys (0-9) which generally give same
layout as that of typewriters.
Numeric Keypad It is used to enter numeric data or cursor
movement. Generally, it consists of a set of
17 keys that are laid out in the same
configuration used by most adding
machines and calculators.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 5
Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the
keyboards which are arranged in a row at
the top of the keyboard. Each function key
has unique meaning and is used for some
specific purpose.
Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen
control. It includes four directional arrow
keys. Control keys also include Home, End,
Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down,
Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc).
Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special
purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock,
Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen.
• Bar Code Reader
• Optical Mark Reader(OMR)
Keyboard
Keyboard is the most common
and very popular input device
which helps in inputting data to
the computer. The layout of the
keyboard is like that of traditional
typewriter, although there are
some additional keys provided for
performing additional functions.
Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102 keys, but now keyboards with
104 keys or 108 keys are also available for Windows and Internet.
The keys on the keyboard are as follows:
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 6
Mouse
Mouse is most popular pointing
device. It is a very famous
cursor-control device having a
small palm size box with a round
ball at its base which senses the
movement of mouse and sends
corresponding signals to CPU
when the mouse buttons are
pressed.
Generally it has two buttons called left and right button and a wheel is present
between the buttons. Mouse can be used to control the position of cursor on
screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer.
Advantages
• Easy to use
• Not very expensive
• Moves the cursor faster than the arrow keys of keyboard.
Joystick
Joystick is also a pointing device which is used to
move cursor position on a monitor screen. It is a stick
having a spherical ball at its both lower and upper
ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket.
The joystick can be moved in all four directions.
The function of joystick is similar to that of a mouse.
It is mainly used in Computer Aided Designing
(CAD) and playing computer games.
Light Pen
Light pen is a pointing device which is similar to a
pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or
draw pictures on the monitor screen. It consists of a
photocell and an optical system placed in a small
tube. When the tip of a light pen is moved over the
monitor screen and pen button is pressed, its
photocell sensing element detects the screen location and sends the
corresponding signal to the CPU.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 7
Track Ball
Track ball is an input device that is mostly
used in notebook or laptop computer,
instead of a mouse. This is a ball which is half
inserted and by moving fingers on ball,
pointer can be moved. Since the whole
device is not moved, a track ball requires
less space than a mouse. A track ball comes
in various shapes like a ball, a button and a
square.
Scanner
Scanner is an input device which works
more like a photocopy machine. It is used
when some information is available on a
paper and it is to be transferred to the
hard disc of the computer for further
manipulation. Scanner captures images
from the source which are then
converted into the digital form that can
be stored on the disc. These images can
be edited before they are printed.
Digitizer
Digitizer is an input device
which converts analog
information into digital form.
Digitizer can convert a signal
from the television or camera
into a series of numbers that
could be stored in a
computer. They can be used
by the computer to create a
picture of whatever the
camera had been pointed at. Digitizer is also known as Tablet or Graphics
Tablet because it converts graphics and pictorial data into binary inputs. A
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 8
graphic tablet as digitizer is used for doing fine works of drawing and image
manipulation applications.
Microphone
Microphone is an input device to input sound
that is then stored in digital form. The
microphone is used for various applications
like adding sound to a multimedia
presentation or for mixing music.
Magnetic Ink Card Reader (MICR)
MICR input device is generally used in banks because of a large number of
cheques to be processed every day. The bank's
code number and cheque number are printed on
the cheques with a special type of ink that contains
particles of magnetic material that are machine
readable. This reading process is called Magnetic Ink
Character Recognition (MICR). The main
advantages of MICR are that it is fast and less error
prone.
Optical Character Reader (OCR)
OCR is an input device used to read a printed text. OCR scans text optically
character by character, converts them into a machine readable code and
stores the text on the system memory.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 9
Bar Code Readers
Bar Code Reader is a device used
for reading bar coded data (data in
form of light and dark lines). Bar
coded data is generally used in
labelling goods, numbering the
books etc. It may be a hand held
scanner or may be embedded in a
stationary scanner. Bar Code
Reader scans a bar code image,
converts it into an alphanumeric
value which is then fed to the computer to which bar code reader is
connected.
Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
OMR is a special type of
optical scanner used to
recognize the type of
mark made by pen or
pencil. It is used where
one out of a few
alternatives is to be
selected and marked. It
is specially used for checking the answer sheets of examinations having
multiple choice questions.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 10
2. PROCESSING DEVICES
CPU consists of the following features:
• CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
• CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
• It stores data, intermediate results and instructions (program).
• It controls the operation of all parts of computer.
CPU itself has following three components.
• Memory or Storage Unit
• Control Unit
• ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Memory or Storage Unit
This unit can store instructions, data
and intermediate results. This unit
supplies information to the other
units of the computer when
needed. It is also known as internal
storage unit or main memory or
primary storage or Random access
memory (RAM).
Its size affects speed, power and capability. Primary memory and secondary
memory are two types of memories in the computer. Functions of memory unit
are:
• It stores all the data and the instructions required for processing.
• It stores intermediate results of processing.
• It stores final results of processing before these results are released to an
output device.
• All inputs and outputs are transmitted through main memory.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 11
Control Unit
This unit controls the operations of all parts of computer but does not carry out
any actual data processing operations.
Functions of this unit are:
• It is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions
among other units of a computer.
• It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
• It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them, and directs
the operation of the computer.
• It communicates with Input/output devices for transfer of data or results
from storage.
• It does not process or store data.
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
This unit consists of two subsections namely
• Arithmetic section
• Logic Section
Arithmetic Section
Function of arithmetic section is to perform arithmetic operations like addition,
subtraction, multiplication and division. All complex operations are done by
making repetitive use of above operations.
Logic Section
Function of logic section is to perform logic operations such as comparing,
selecting, matching and merging of data.
3. STORAGE DEVICES
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions.
Computer memory is the storage space in computer where data is to be
processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is
divided into large number of small parts called cells. Each location or cell has
a unique address which varies from zero to memory size minus one. For
example if computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024=65536
memory locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.
Memory is primarily of three types
• Cache Memory
• Primary Memory/Main Memory
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 12
• Secondary Memory
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a very high speed semiconductor memory which can
speed up CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and main memory. It is
used to hold those parts of data and program which are most frequently used
by CPU. The parts of data and programs are transferred from disk to cache
memory by operating system, from where CPU can access them.
Advantages
The advantages of cache memory are as follows:
• Cache memory is faster than main memory.
• It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
• It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of
time.
• It stores data for temporary use.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cache memory
are as follows:
• Cache memory has limited
capacity.
• It is very expensive.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and
instructions on which computer is currently
working. It has limited capacity and data is lost
when power is switched off. It is generally made
up of semiconductor device. These memories are
not as fast as registers. The data and instruction
required to be processed reside in main memory.
It is divided into two subcategories RAM and
ROM.
Characteristics of Main Memory
• These are semiconductor memories
• It is known as main memory.
• Usually volatile memory.
• Data is lost in case power is switched off.
• It is working memory of the computer.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 13
• Faster than secondary memories.
• A computer cannot run without primary memory.
Secondary Memory
This type of memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is
slower than main memory. These are used for storing data/Information
permanently. CPU directly does not access these memories instead they are
accessed via input-output routines. Contents of secondary memories are first
transferred to main memory, and then CPU can access it. For example: disk,
CD-ROM, DVD etc.
Characteristic of Secondary Memory
• These are magnetic and optical memories
• It is known as backup memory.
• It is non-volatile memory.
• Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
• It is used for storage of data in a computer.
• Computer may run without secondary
memory.
• Slower than primary memories.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 14
4. OUTPUT DEVICES
Following are few of the important output devices which are used in a
computer.
• Monitors
• Graphic Plotter
• Printer
Monitors
Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output
device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are
arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon
the number of pixels.
There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors.
• Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)
• Flat- Panel Display
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller
the pixels, the better the image clarity, or resolution. It takes more than one
illuminated pixel to form whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word
help.
A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The
screen can be divided into a series of character boxes - fixed location on the
screen where a standard character can
be placed. Most screens are capable of
displaying 80 characters of data
horizontally and 25 lines vertically. There
are some disadvantages of CRT:
• Large in Size
• High power consumption
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 15
Flat-Panel Display Monitor
The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced
volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can
hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel
displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer,
graphics display.
The flat-panel display is divided into two categories:
• Emissive Displays - The emissive displays are devices that convert
electrical energy into light. Example are plasma panel and LED(Light-
Emitting Diodes).
• Non-Emissive Displays - The Non-emissive displays use optical effects to
convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns.
Example is LCD(Liquid-Crystal Device)
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 16
Speakers
An output device that produce sound.
Printers
Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper.
There are two types of printers:
• Impact Printers
• Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
The impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon which
is then pressed on the paper.
Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following:
• Very low consumable costs
• Very noisy
• Useful for bulk printing due to low cost
• There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image
These printers are of two types
• Character printers
• Line printers
Character Printers
Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time.
These are further divided into two types:
• Dot Matrix Printer(DMP)
• Daisy Wheel
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 17
DOT MATRIX PRINTER
In the market one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These
printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price.
Each character printed is in form of pattern of dots and head consists of a
Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which comes out to form a character
that is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer.
Advantages
• Inexpensive
• Widely Used
• Other language characters can be
printed
Disadvantages
• Slow Speed
• Poor Quality
DAISY WHEEL
Head is lying on a wheel
and pins corresponding to characters are like petals of Daisy (flower name)
that is why it is called Daisy Wheel Printer. These printers are generally used for
word-processing in offices which require a few letters to be sent here and
there with very nice quality.
Advantages
• More reliable than DMP
• Better quality
• The fonts of character can be easily changed
Disadvantages
• Slower than DMP
• Noisy
• More expensive than DMP
Line Printers
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 18
Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time.
These are of further two types
• Drum Printer
• Chain Printer
DRUM PRINTER
This printer is like a drum in shape so it is called drum printer. The surface of
drum is divided into number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to size of paper
i.e. for a paper width of 132 characters, drum will have 132 tracks. A character
set is embossed on track. The different character sets available in the market
are 48 character set, 64 and 96 characters set. One rotation of drum prints
one line. Drum printers are fast in speed and can print 300 to 2000 lines per
minute.
Advantages
• Very high speed
Disadvantages
• Very expensive
• Characters fonts cannot be changed
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 19
CHAIN PRINTER
In this printer, chain of character sets is used so it is called Chain Printer. A
standard character set may have 48, 64, or 96 characters.
Advantages
• Character fonts can easily be changed.
• Different languages can be used with the same printer.
Disadvantages
• Noisy
NON-IMPACT PRINTERS
Non-impact printers print the characters without using ribbon. These printers
print a complete page at a time so they are also called as Page Printers.
Two Types of Non-impact
• Laser Printers
• Inkjet Printers
Characteristics of Non-impact Printers
• Faster than impact printers.
• They are not noisy.
• High quality.
• Support many fonts and different
character size.
Laser Printers
These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots
needed to form the characters to be printed on a page.
ADVANTAGES
• Very high speed
• Very high quality output
• Give good graphics quality
• Support many fonts and different character size
DISADVANTAGES
• Expensive.
• Cannot be used to produce multiple copies of a document in a single
printing.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 20
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new
technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper.
Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.
They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many
styles of printing modes available. Color printing is also possible. Some models
of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also.
ADVANTAGES
• High quality printing
• More reliable
DISADVANTAGES
• Expensive as cost per page is high
• Slow as compared to laser printer
Plotter
• A type of printer than can produce
larger printouts like blueprint or plan of
a buildings etc.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 21
Software is a set of programs, which is designed to perform a well-defined
function. A program is a sequence of instructions written to solve a particular
problem.
There are two types of software
• System Software
• Application Software
System Software
The system software is collection of programs designed to operate, control,
and extend the processing capabilities of the computer itself. System software
are generally prepared by computer manufactures. These software products
comprise of programs written in low-level languages which interact with the
hardware at a very basic level. System software serves as the interface
between hardware and the end users.
Some examples of system software are Operating System, Compilers,
Interpreter, and Assemblers etc.
Features of system software are as follows:
• Close to system
• Fast in speed
• Difficult to design
• Difficult to understand
• Less interactive
• Smaller in size
• Difficult to manipulate
• Generally written in low-level language
Application Software
Application software products are designed to satisfy a particular need of a
particular environment. All software applications prepared in the computer
lab can come under the category of Application software.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 22
Application software may consist of a single program, such as a Microsoft's
notepad for writing and editing simple text. It may also consist of a collection
of programs, often called a software package, which work together to
accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet package.
Examples of Application software are following:
• Payroll Software
• Student Record Software
• Inventory Management Software
• Income Tax Software
• Railways Reservation Software
• Microsoft Office Suite Software
• Microsoft Word
• Microsoft Excel
• Microsoft Powerpoint
Features of application software are as follows:
• Close to user
• Easy to design
• More interactive
• Slow in speed
• Generally written in high-level language
• Easy to understand
• Easy to manipulate and use
• Bigger in size and requires large storage space
It is a program with following features:
• An operating system is a program that acts as an interface between
the software and the computer hardware.
• It is an integrated set of specialized programs that are used to manage
overall resources and operations of the computer.
• It is specialized software that controls and monitors the execution of all
other programs that reside in the computer, including application
programs and other system software.
Objectives of Operating System
• To make a computer system convenient to use in an efficient manner
• To hide the details of the hardware resources from the users
• To provide users a convenient interface to use the computer system
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 23
• To act as an intermediary between the hardware and its users and
making it easier for the users to access and use other resources
• To manage the resources of a computer system
• To keep track of who is using which resource, granting resource
requests, according for resource using and mediating conflicting
requests from different programs and users
• To provide efficient and fair sharing of resources among users and
programs
Characteristics of Operating System
• Memory Management -- keeps tracks of primary
memory i.e. what part of it is in use by whom, what part
is not in use etc. and allocates the memory when a
process or program requests it.
• Processor Management -- allocates the processor
(CPU) to a process and deallocates processor when it is
no longer required.
• Device Management -- keeps track of all devices. This
is also called I/O controller that decides which process
gets the device, when, and for how much time.
• File Management -- allocates and de-allocates the
resources and decides who gets the resources.
• Security -- prevents unauthorized access to programs
and data by means of passwords and similar other
techniques.
• Job accounting -- keeps track of time and resources
used by various jobs and/or users.
• Control over system performance -- records delays
between request for a service and from the system.
• Interaction with the operators -- The interaction may
take place via the console of the computer in the form of instructions.
Operating System acknowledges the same, does the corresponding
action and informs the operation by a display screen.
• Error-detecting aids -- Production of dumps, traces, error messages and
other debugging and error-detecting methods.
• Coordination between other software and users -- Coordination and
assignment of compilers, interpreters, assemblers and other software to
the various users of the computer systems.
People ware can refer to anything that has to do with the role of people in the
development or use of computer software and hardware systems, including
such issues as developer productivity, teamwork, group dynamics, the
psychology of programming, project management, organizational factors,
human interface design, and human-machine-interaction
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 24
The most important element of a computer system is its users. They are also
called live-ware of the computer system.
The following types of people interact with a computer system:
(a) System Analysts:
• People who design the operation and processing of the system.
(b) System Programmers:
• People who write codes and programs to implement the working
of the system
(c) System Operators:
• People who operate the system and use it for different purposes.
Also called the end users.
User – friendly - refers to a gadget that is easy and convenient to use.
Friendly – user - refers to a person that handles a gadget with an extra care.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 25
A. Name the parts of the computer based on the number indicated on the
exploded image.
B. Group the parts of the computer on their respective components.
Write it on the box.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 26
Lesson 7: VARIOUS USE OF INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY IN TODAY’S ARENA
(Week 9)
Objectives:
1. Discuss and explain the impact of IT in our daily life;
2. Explain and identify the various applications of computers in today's it
era that we use in our daily life.
COMPUTERS IN OUR DAILY LIFE
Computers are very essential in our daily life nowadays. Almost anyone
rely on computers whether you are students, government employees,
company employees working from home, and even just communicating from
friends, relatives or love ones. We can’t deny that we are now in the computer
age generation. According to Rappler 2019, Philippines tops the world in using
social media. Philippines average time online is 10 hours and 2 minutes in a day,
not covering those who are not online. Did you ask yourself, how computers
affect your life? What are the benefits of computers in our daily life? For better
understanding, in this chapter we will discuss Applications, their relevance to
day-to-day activities, and the basic computer network.
Mobile applications or apps have become an essential part of our life
that helps us achieve our daily activities with an ease. Now that we are in the
technical computer age with smartphones on our side every day, the proper
use of our smartphones is depending on how we use it. We can maximize the
use of the apps in our daily life if we use the technology in what and how are
they design to.
VARIOUS APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS IN TODAY'S IT ERA THAT WE USE IN OUR
DAILY LIFE
BUSINESS
• A computer has high speed of
calculation, diligence, accuracy,
reliability, or versatility which made it an
integrated part in all business
organizations.
Computer is used in business organizations for:
• Payroll calculations
• Budgeting
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 27
• Sales analysis
• Financial forecasting
• Managing employees database
• Maintenance of stocks etc.
BANKING
Today banking is almost totally
dependent on computer.
Banks provide following facilities:
• Banks provide online
accounting facility, which
includes current balances,
deposits, overdrafts, interest
charges, shares, and trustee
records.
• ATM machines are making it
even easier for customers to
deal with banks.
• Different banks made their own banking apps, to accommodate more
customer in a day, not crowding in the bank. In these apps, you can
invest, fund transfer, pay bills, and withdraw cash from your hand at
home. Also there are lots of application introducing of e-money. As easy
as scanning a QR code, you can pay bills.
TRANSPORTATION
Out of the
bright minds of the programmers of
transportation apps, searching transportation is
made easy through this app. From booking
international flights to booking a car to be your
service to hiring a motorcycle to be your rides to
work. This will help us save time rather than
waiting outside for a public utility vehicle to pass
by.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 28
INSURANCE
Insurance companies are keeping all records
up-to-date with the help of computers. The
insurance companies, finance houses and
stock broking firms are widely using
computers for their concerns.
Insurance companies are maintaining a
database of all clients with information
showing
• procedure to continue with policies
• starting date of the policies
• next due installment of a policy
• maturity date
• interests due
• survival benefits
• bonus
EDUCATION
The computer has provided a lot of facilities in the education system.
• The computer provides a tool in the education system known as CBE
(Computer Based Education).
• CBE involves control, delivery, and evaluation of learning.
• The computer education is rapidly increasing the graph of number of
computer students.
• There are number of methods in which educational institutions can use
computer to educate the students.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 29
• It is used to prepare a database about performance of a student and
analysis is carried out on this basis.
• Apps like Google Classroom, Edmodo, and some university LMS, are used in
Education to still continue educating students while at home. Taking
advantage of some platforms in communication and entertainment types
can be used to get the attention of the students and meet them at their
convenience. Studying at home is not a problem anymore, thanks to
Applications
MARKETING
In marketing, uses of computer
are following:
Advertising - With computers,
advertising professionals
create art and graphics, write
and revise copy, and print and
disseminate ads with the goal
of selling more products.
At Home Shopping - Home
shopping has been made
possible through use of computerised catalogues that provide access to
product information and permit direct entry of orders to be filled by the
customers.
Famous Shopping Apps in the Philippines are the Shopee, Lazada, Facebook Market,
etc. These mobile apps made it easy for shoppers buying their want and needs at
their hands without going out of their home. These apps provide the seller different
choices from different variety of stores.
HEALTH CARE
Computers have
become important
part in hospitals, labs,
and dispensaries. The
computers are being
used in hospitals to
keep the record of
patients and
medicines. It is also
used in scanning and
diagnosing different
diseases. ECG, EEG,
Ultrasounds and CT Scans etc., are also done by computerized machines.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 30
Some major fields of health care in which computers are used are:
• Diagnostic System - Computers are used to collect data and identify
cause of illness.
• Lab-diagnostic System - All tests can be done and reports are
prepared by computer.
• Patient Monitoring System - These are used to check patient's signs for
abnormality such as in Cardiac Arrest, ECG etc.
• Pharma Information System - Computer checks Drug-Labels, Expiry
dates, harmful drug’s side effects etc.
• Surgery: Nowadays, computers are also used in performing surgery.
ENGINEERING DESIGN
Computers are widely used in
engineering purpose.
One of major areas is CAD
(Computer aided design). That
provides creation and modification
of images. Some fields are:
• Structural Engineering
- Requires stress and strain
analysis for design of Ships,
Buildings, Budgets, Airplanes
etc.
• Industrial Engineering - Computers deal with design, implementation
and improvement of integrated systems of people, materials and
equipment.
• Architectural Engineering - Computers help in planning towns,
designing buildings, determining a range of
buildings on a site using both 2D and 3D
drawings.
MILITARY
Computers are largely used in defense. Modern
tanks, missiles, weapons etc. Military also employs
computerized control systems. Some military areas
where a computer has been used are:
• Missile Control
• Military Communication
• Military Operation and Planning
• Smart Weapons
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 31
COMMUNICATION
Communication means to convey a message, an idea, a picture or speech
that is received and understood clearly and correctly by the person for whom
it is meant for. Some main areas in this category are:
• E-mail
• Chatting
• Usenet
• FTP
• Telnet
• Video-conferencing
Communication or some called it
as Social Media applications like
Facebook, Twitter, Intagram,
WhatsApp, Facetime, Skype Zoom, Google Meet etc. that everyone uses in
order to connect to their friends and love ones from apart. Even in education,
we use these platforms a lot of time during the pandemic to have a
communication between students and teachers even at home. Also for those
who are working from home, businesses use Social Media Apps to run
businesses even at home. These apps provide us a feature of video and
audio calling other than texting, that makes the user feel more connected to
someone.
GOVERNMENT
Computers play an important role in government. Some major fields in this
category are:
• Budgets
• Sales tax department
• Income tax department
• Male/Female ratio
• Computerization of voters lists
• Computerization of driving licensing system
• Computerization of PAN card
• Weather forecasting
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 32
ENTERTAINMENT.
Majority of the user of the computer
choose application for their own
entertainment to released them in
stress and frustrations. There are lots of
apps for entertainment like games,
music, videos, clips, movies, TV series,
live streaming and others. Some of the
user make these application to earn
money as they entertain others.
FOOD DELIVERY
Even food deliveries are now made easy. You don’t need to call their hotline
anymore, you just need to tap on their app, click product you want, then
order out. Other food delivery
app, that are outside the delivery
system of the company alone,
are introduced. In this app, you
can order food in different
companies at once
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 33
Exercise 1. Identify the following statement.
1. ________________Provides creation and modification of images.
2. ________________deal with design, implementation and improvement of
integrated systems of people, materials and equipment.
3. ________________help in planning towns, designing buildings, determining
a range of buildings on a site using both 2D and 3D drawings.
4. ________________tests can be done and reports are prepared by
computer.
5. ________________checks Drug-Labels, Expiry dates harmful drug’s side
effects etc.
6. ________________used to collect data and identify cause of illness.
7. ________________It reduces the need of people and increases unemployment
in society.
8. ________________Many people use computers without positive purpose
9. ________________Computer cannot take any decision of its own
10. ________________The data stored on a computer can be accessed by
unauthorized persons through networks
11. ________________is a method to reduce the electricity consumed and
environmental waste generated when using a computer.
12. ________________The improper and prolonged use of computer can results in
injuries or disorders of hands, wrists, elbows, eyes, necks and back.
13. ________________The privacy of a person can be violated if the personal and
confidential records are not protected properly.
14. ________________means to convey a message, an idea, a picture or speech
that is received and understood clearly and correctly by the person for whom
it is meant for.
Exercise 2. Enumerate the following.
Various Applications of Computers in:
A. Military
B. Business
C. Communication
D. Healthcare
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 34
Lesson 8
(Week 10)
UNDERSTANDING THE INTERNET AND ITS SERVICES
Objectives:
1. Discuss the history of the Internet;
2. Name the pioneers of the internet
3. Define and understand the World Wide Web;
4. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using the Internet/WWW;
How Did the Internet Get Started?
Fifty (50) years ago, the concept of an Internet was just
an idea shared by a few scientists. There were no
computer networks anywhere. People at that time
used computers as calculators, not to communicate.
Scientists who needed to share their ideas began to explore ways to expand
the computer's role. Those who owned expensive supercomputers also wanted
to make it possible for more researchers to use their amazing machines.
It is commonly said, "necessity is the mother of all inventions," and today's
Internet is a prime example.
In the late 1960s, researchers and supercomputer users wanted to share
information. Funding came from a number of sources, including the U.S.
government. The government realized that a network of computers would be
valuable in allowing researchers, educators and others to share information
and help each other. It also believed that a computer network capable of
sending messages along multiple paths would enhance national security. If
one part of the network didn't work or was destroyed, the network could still
continue to operate. Thus, the President could stay in touch with his advisors
even in the event of a nuclear attack.
The grandfather of today's Internet was called the "ARPANET," named after the
Department of Defense's Advanced Research Projects Agency that developed
it in the late 1970s and early 1980s.
President Dwight D. Eisenhower saw the need for the Advanced Research Projects
Agency(ARPA) after the Soviet Union’s 1957 launch of Sputnik.
The organization united some of America’s most brilliant people, who developed the
United States’ first successful satellite in 18 months. Several years later ARPA began to
focus on computer networking and communications technology.
In August 1962, Dr. J.C.R. Licklider was chosen to head ARPA’s research in
improving the military’s use of computer technology. Licklider was a visionary
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 35
who sought to make the government’s use of computers more interactive. The
quickly expand technology, Licklider saw the need to move ARPA’s contracts
from private sector to universities and laid the foundations for what would
become the ARPANET.
He envisioned a globally interconnected set of computers through which
everyone could quickly access data and programs from any site. In spirit, the
concept was very much like the Internet of today.
Licklider was the first head of the computer research program at DARPA, starting in
October 1962.
ARPANET was currently using the Network Control Protocol or NCP to transfer data.
NCP – this allowed communications between hosts running on the same network.
1n 1972, the First E-mail program was created by Raymond “Ray” S. Tomlinson
of Bolt Beranek and Newman (BBN).
In 1973, Development began on the protocol to be called TCP/IP (Transmission
Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol)
TCP/IP – so called Internet Formats.
- This are set of rules that allow for inter – machine communication.
- A rules that allows clients and servers use to talk to each other.
TCP/IP was developed by a group headed by Vinton G. Cerf from Stanford and
Robert E. Kahn from DARPA.
Vinton Cerf – manager of the Internet Program of DARPA.
In 1983, Internet Activities Board was created
IAB - focused on a particular area of the technology (e.g. routers, end-to-end
protocols, etc.
In 1984, the ARPANET was divided into two networks: MILNET and ARPANET
MILNET – to serve the need of the military
ARPANET – to support the advance research component, the Department of Defense
Continued to support both networks.
Thus, by 1985, Internet was already well established as a technology supporting a
broad community of researchers and developers, and was beginning to be used by
other communities for daily computer communications. Electronic mail was being
used broadly across several communities, often with different systems, but
interconnection between different mail systems was demonstrating the utility of broad
based electronic communications between people.
In 1986, the Internet Engineering Task Force or IETF was created to serve as a forum for
technical coordination by contractors for DARPA working on ARPANET, US Defense
Data Network(DDN) and the Internet Core Gateway System( ICGS).
In 1990, the ARPANET was decommissioned, leaving only the vast network – of –
networks called the Internet. The number of hosts exceeded 300,000
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 36
The Internet doesn't have a birthday like you do because it wasn't "born" on a
single day. There were many, many steps needed to make the Internet.
Probably the most important step was to get all of these computers to send
and receive messages from each other. That happened in 1982, when the
standards for sending and receiving messages were adapted by the ARPANET.
Who Governs the Internet?
The Internet is truly democratic. It has no owner or executive who says how it
should run. Everyone who uses the Internet can voice an opinion on how it
should work. Volunteers groups, such as the Internet Society set standards and
manage the use of limited resources, such as domain names and e-mail
addresses.
If you would like to get involved, you can volunteer for the Internet Society. Or,
if you think you have a great idea for improving the Internet, you might consider
going to the public meetings of the Society's Internet Engineering Task Force
(IETF). The IETF handles technical issues, such as computer languages and
connections on the Internet. If you want to be heard at these meetings, come
prepared to demonstrate your new idea in action. (If they agreed to listen to
everyone with a good idea, the meetings might never end.)
Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. (DARPA)
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network. (ARPANET)
Federal Networking Council (FNC)
National Science Foundation (NSF)
Corporation for National Research Initiatives (CNRI)
(W3C)World Wide Web Consortium
(WG)Working Group
Internet Activities Board (IAB)
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
Internet Research Group (IRG)
International Cooperation Board (ICB)
Task Forces (TF’s)
Coordinating Committee on Inter-continental Research Networking (CCIRN
Who Pays for the Internet?
Everyone. Individuals who dial in through an "Internet Service Provider" (ISP) pay
a fee to use the Internet. Large companies with thousands of employees using
the Internet also pay an ISP to connect the company's computer to the
Internet.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 37
INTERNET TIMELINE
Internet
✓ It is a worldwide system which has the following characteristics:
• Internet is a world-wide / global system of interconnected computer networks.
• Internet uses the standard Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
• Every computer in internet is identified by a unique IP address.
• IP Address is a unique set of numbers (such as 110.22.33.114) which identifies a
computer’s location.
• A special computer DNS (Domain Name Server) is used to give name to the IP
Address so that user can locate a computer by a name.
• For example, a DNS server will resolve a name
http://www.tutorialspoint.com to a particular IP address to uniquely identify
the computer on which this website is hosted.
• Internet is accessible to every user all over the world.
Intranet
• Intranet is system in which multiple PCs are connected to each other.
• PCs in intranet are not available to the world outside the intranet.
• Usually each company or organization has their own Intranet network and
members/employees of that company can access the computers in their
intranet.
• Each computer in Intranet is also identified by an IP Address which is unique
among the computers in that Intranet.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 38
Exercise 1. Identify the following terms.
1. __________Is system in which multiple PCs are connected to each other.
2. __________Is a world-wide / global system of interconnected computer
networks.
3. __________The year ARPANET was decommissioned, leaving only the vast
network – of – networks called the Internet
4. __________to support the advance research component, the Department of
Defense Continued to support both networks
5. __________The year ARPANET was divided into two networks: MILNET and
ARPANET.
6. __________Focused on a particular area of the technology (e.g. routers, end-
to-end protocols, etc.
7. __________manager of the Internet Program of DARPA
8. __________This are set of rules that allow for inter – machine communication
9. __________The First E-mail program was created by___________________.
10. __________This allowed communications between hosts running on the same
network.
Exercise 2. (Venn diagram)
Differentiate Intranet and Internet…
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 39
Lesson 9: THE SERVICES OF THE INTERNET
(Week 11)
Objectives:
1. Discuss and explain the services of the Net;
2. Identify and use the services of the net;
3. Create an E-mail account;
4. Attach a file in e-mail and send e-mail;
The services available on the Internet are the following:
1. E- mail
2. Telnet
3. FTP
4. E-mail Discussion Group
5. Usenet News
6. Chat and Instant Messaging
7. MUD
8. World Wide Web
What is E-Mail?
E-mail: (Electronic Mail)
- Use to describe an Internet service, which allows computer users
locally and world widely exchange messages.
Email Account - is an access in the service of an email provider.
Email is in some ways similar to postal services. The only difference is the speed in which
delivered.
A powerful feature of E-mail/s is the option to send electronic files. These E-files are
referred to as MIME (Multimedia Internet Mail Extension) attachments.
The First E-mail program was created by Raymond “Ray” S. Tomlinson of Bolt Beranek
and Newman (BBN) in 1972. He uses the @ sign to distinguished between the sender’s
name and network name in the e-mail address.
Presidential candidate Jimmy Carter and running mate Walter Mondale use email to
plan campaign events. Queen Elizabeth sends her first email. She’s the first state
leader to do so.
Parts of Electronic Mail Work Area:
1. To – refers to the address you wish to send the mail.
2. CC – refers to Carbon Copy where you place the address of the person you
want tp send a duplicate
3. Main Body – it is where you type your message
4. Subject – contains the topic of your letter or the reason why you wrote the
letter.
5. Attach Files – this tab is used to attach images, documents or videos.
6. Toolbar – display icons used to enhance the letter.
7. Send – this tab is use to send your letter by clicking it.
8. Save as Draft – your created letter will go to drafts folder once you click it.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 40
9. Cancel – to escape from the work area.
Improving your Letter
• You can improved and enhance the layout of your letter. And you can add
personality to a letter by using emoticons and acronyms.
Emoticons and Acronyms
• Emoticons – are the ones that indicate humor.
• Acronyms – are letters that form group of words.
Some kinds of Emoticons:
:-) Happy :-( Sad :-o Surprised :-@Screaming :-| Indifferent :-<
Mad :-e Disappointed :-D Laughing ;-) Winking
The Standard Acronyms used both in e-mail and chatting
FOFL – Fall on the floor laughing
LOL – Laugh Out Loud
ROTFL – Roll on the floor laughing
TTFN – Ta Ta for now
Grin – grin, Joking
VBG – Very Big Grin
TIA – Thanks in Advance
IMNSHO – In my not so humble opinion
IRL – in real life
YMMW – your mileage may vary
ITRW – in the real world
BTW – by the way
BG – Big grin
RTFM – read the flaming manual
IMHO – in my humble opinion
IOW – in other words
NASL –name, age, sex, location
ASAP – as soon as possible
DM – Direct Message
PM – Private Message
E-MAIL ETIQUETTE – to observe certain rules and behavior in using mail.
1. Clearly summarize the contents of your message in the subject line.
2. Don’t use CC to copy your message to everyone.
3. Use BCCs (Blind Carbon Copies) when addressing a message that will go to
large group of people who don’t necessarily know each other.
4. Keep your message short and focused.
5. Avoid using all capital letters.
6. Don’t write anything you wouldn’t say in public.
7. Use a smiley to make sure that a statement is not misunderstood.
8. Avoid sending emails to large numbers of people unless you have serious
reason to do it.
9. Nasty emails should also be avoided
10. As a courtesy to your recipient, include your name at the bottom of the
message.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 41
What is TELNET?
Telnet (Teletype network) is a network protocol used on the Internet or local area
networks to provide a bidirectional interactive communications facility
Telnet is now a feature available on the WWW. Program must be installed on
your local computer and configured to your web browser in order to work.
is a program that allows you to log onto computers linked to the internet. Once
logged on you can look at online databases, library catalogs, chat services
and more.
To telnet to a computer, you must know the its IP address. This address consists
of words. (E.g. deped.gov.ph)
What is FTP?
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to exchange and
manipulate files over an Internet Protocol computer network, such as the Internet. FTP
is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data
connections between the client and server applications..
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol – this is a both program and the method
used to transfer files between computers
Is an option that allows user to transfer files from thousands of host computers
on the internet to their personal computer account.
FTP sites contain books, articles, software, games, images, sounds, multimedia,
course work, data sets and also use by school to set up their own FTP sites to
allow their students to access specific school related information such as
students handouts, course outlines, and even sample examination.
FTP transfer should be done in WWW using WS_FTP for windows to conduct a file
transfer.
“Whenever you download software from a website to your local computer, you
are actually using FTP.”
What is E-mail Discussion Group?
E-mail Discussion Group – provide an opportunity to exchange ideas worldwide via e-
mail.
These are administered by software program such as listserv.
Listserv – the most common discussion group
Majordomo and Listproc – another two programs that administer e-mail
discussion group.
The commands for subscribing is simply type “subscribe” as the message title to
join, “unsubscribe” to stop receiving the message.
All messages will go to your mail box.
A program that handles subscription.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 42
What is Usenet News?
USENET NEWS – is a global electronic bulletin board
system in which millions of computers users exchange
information on a vast range of topics.
a portmanteau of "user" and "network", is a
worldwide distributed Internet discussion
system. It evolved from the general purpose
UUCP(Unix-to-Unix Copy Program) architecture
of the same name.(portmanteau- is used
broadly to mean a blend of two (or more)
words,)
Is a set of machines that exchanges messages
or articles from Usenet discussion forums
There are thousands of Usenet newsgroup in existence, many are academic in
nature and recreational and sports topics.
What is Chat and Instant Messaging?
A virtual community where people from all over the world can communicate
on – line by exchanging text data at almost real time.
Chat – allows user on the internet to communicate with each other in real time.
Instant Messaging – Variations of chat where a user on the web can contact another
user currently logged on and type a conversation.
Chat Programs:
YM (Yahoo Messenger) is an advertisement-supported instant
messaging client and associated protocol provided by Yahoo!.
Yahoo! Messenger was originally launched under the name Yahoo!
Pager on March 9, 1998
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a form of real-time Internet text messaging (chat) or
synchronous conferencing. It is mainly designed for group communication in
discussion forums, called channels, but also allows one-to-one communication
via private message as well as chat and data transfers via Direct Client-to-
Client.
synchronous conferencing- is the formal term used in science, in particular in
computer-mediated communication, collaboration and learning, to describe
online chat technologies
America Online ICQ (I Seek You) s a popular
instant messaging computer program, which was
first developed by the Israeli company Mirabilis,
now owned by Time Warner's AOL subsidiary, was
released in November 1996 and ICQ became one
of the first Internet-wide instant messaging services.
SKYPE - is a software application that allows users to make telephone calls over
the Internet. Calls to other users of the service, and in some countries to free-of-
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 43
charge numbers are free, while calls to other landlines and mobile phones can
be made for a fee. Additional features include instant messaging, file transfer
and video conferencing.
Initial release: August 2003 and stable release on June 04, 2009
Facebook Messenger
Release in August 20111, it is the official Facebook app that
lets you have text conversations with all of your friends on the
popular social network. This app, enable to send and
receive text messages in conversations which you can later
continue on your computer.
As with other instant messaging
apps, Facebook Messenger lets you share images, or your
location, in the text messages; you can even add several
recipients and open chat windows with several people at
the same time. Each conversation is then kept in a bubble which you can
conveniently move around on your device’s screen.
What is MUD?
MUD (Multi User Dungeon) – are multi user virtual reality games based on simulated
worlds.
Pronounced /mʌd/ is a multi-user real-time virtual world described entirely in
text. It combines elements of role-playing games, hack and slash, interactive
fiction, and online chat. Players can read descriptions of rooms, objects, other
players, non-player characters, and actions performed in the virtual world.
Players interact with each other and the world by typing commands that
resemble a natural language.
This component of the Internet allows you to play popular network games as
such counter strike, RAN on line and others.
There are MUDs of all kinds on the Internet, and many can be joined free of
charge.
A role-playing game (RPG; often roleplaying game) is a game in which the
participants assume the roles of fictional characters. Participants determine the
actions of their characters based on their characterization,[1] and the actions
succeed or fail according to a formal system of rules and guidelines.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 44
What Is the World Wide Web?
The World Wide Web was born in the 1990s. Because the Web allows people
to view text and graphics on the Internet, it has made the Internet very popular.
Tim Berners-Lee at the Physics Laboratory in Cern, Switzerland founded the
World Wide Web.
His goal was to:
Make sure that information could be reused once it was created. Because
books printed on paper get fragile with time, and are hard to update when
new information is available, he saw computers as the best way to share
knowledge.
Before the Web was introduced, it was very difficult for someone on one
computer system to look at anything (except text) that was produced on a
different system. The creation of the Web allows Internet users to display
information in a simple way so that anyone can read it. This is true whether
you're using a Mac, a Microsoft Windows-compatible computer, or any other
type of computer.
World Wide Web
is a system of Internet servers that supports hypertext to access several Internet
protocols on a single interface.
• Hypertext – is a document containing words that connect to other
documents so called “Links”
The fastest growing component of the Internet
It was developed in 1989 by Tim Berners – Lee, a British computer scientist. And
began to incorporate
graphics, sounds and
videos in 1993.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 45
Exercise 1. Give the meaning of the following ACRONYMS.
1. MUD➔_________________________________________________
2. WWW➔_________________________________________________
3. CERN➔_________________________________________________
4. RPG➔_________________________________________________
5. ICQ➔_________________________________________________
6. UUCP➔_________________________________________________
7. IRC➔_________________________________________________
8. FTP➔_________________________________________________
9. HTTP➔_________________________________________________
10. TELNET➔_________________________________________________
Exercise 2. Identify the following terms.
1. ____________is an access in the service of an email provider
2. ____________The First E-mail program was created by
3. ____________allows computer users locally and world widely exchange
messages
4. ____________Contains the topic of your letter or the reason why you wrote the
letter.
5. ____________Are the ones that indicate humor.
6. ____________to observe certain rules and behavior in using mail
7. ____________is a network protocol used on the Internet or local area networks
to provide a bidirectional interactive communications facility
8. ____________is a standard network protocol used to exchange and manipulate
files over an Internet Protocol computer network, such as the Internet
9. ____________Provide an opportunity to exchange ideas worldwide via e-mail.
10. ____________is a global electronic bulletin board system in which millions of
computers users exchange information on a vast range of topics
11. ____________is a global electronic bulletin board system in which millions of
computers users exchange information on a vast range of topics
12. ____________Variations of chat where a user on the web can contact another
user currently logged on and type a conversation
13. ____________Allows user on the internet to communicate with each other in real
time.
14. ____________Is an advertisement-supported instant messaging client and
associated protocol provided by Yahoo!.
15. ____________is the official Facebook app that lets you have text conversations
with all of your friends on the popular social network.
ACTIVITY: LAB
➔Use the Internet to start creating an e-mail account using Gmail or
yahoo.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 46
Lesson 10: THE COMPUTER NETWORK
(Week 11)
Objectives:
1. Discuss and explain Computer Network;
2. Explain the characteristic of Computer
Network.
3. Identify and enumerate the tools in setting up computer network.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a system in which multiple computers are connected
to each other to share information and resources.
Characteristics of a computer network
• Share Resources from one computer to another
• Create files and store them in one computer, access those files from the
other computer(s) connected over the network
• Connect a printer, scanner, or a fax machine to one computer within
the network and let other computers of the network use the machines
available over network.
Following is the list of hardware's required to setup a computer network.
• Network Cables
• Distributors
• Routers
• Internal Network Cards
• External Network Cards
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 47
Network Cables
Network cables are used to connect computers. The most commonly used
cable is Category 5 cable RJ-45.
Distributors
A computer can be connected to another one via a serial port but if we
need to connect many computers to produce a network, this serial
connection will not work. The solution is to use a central body to which other
computers, printers, scanners etc. can be connected and then this body will
manage or distribute network traffic
Router
A router is a type of device which acts as the central
point among computers and other devices that are part
of a network. A router is equipped with holes called ports
and computers and other devices are connected to a
router using network cables. Now-a-days router comes in wireless modes using
which computers can be connected without any physical cable.
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 48
Network Card
Network card is a necessary component of a computer without which a
computer cannot be connected over a network. It is also known as network
adapter or Network Interface Card (NIC). Most branded computers have
network card pre-installed. Network cards are of two types: Internal and
External Network Cards.
INTERNAL NETWORK CARDS
Motherboard has a slot for internal network card where it is to be inserted.
Internal network cards are of two types in which first type uses Peripheral
Component Interconnect (PCI) connection while the second type uses
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA). Network cables are required to provide
network access.
EXTERNAL NETWORK CARDS
External network cards come in two flavors: Wireless and USB based. Wireless
network card need to be inserted into the motherboard but no network cable
is required to connect to network
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 49
Universal Serial Bus (USB)
USB card are easy to use and connect via USB
port. Computers automatically detect USB
card and can install the drivers required to
support the USB network card automatically
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 50
A. What are the requirements to set up a computer Network?
A. Crimp Cable to Connect Computers to Network…
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 51
REFERENCES:
Books: Computing for Life, FNB Educational, Inc., Ma. Melizza D. Tan, Anthony
Joseph C. Ocampo, Ma. Estermin B. Saroca, Pablo R. Malastas, Ph.D., Ma.
Angela A. Coralejo, Enrique F. Coralejo, Ph.D.
Online Resources:
https://www.scribd.com/doc/7076390/Basic-Concepts-of-Computer
http://www.slideshare.net/AnaTan1/introduction-to-basic-computer-
concepts-presentation?from_action=save
The Int. Review of Res. in Open and Distributed Learning Vol 14 no 1 pp 167-85
Baker, K.(2021). The 11 Most Common Types of Malware.
https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/malware/types-of-malware/
Depusoy, J. L., Romuar, F. B. & Nartea, M. A. (2020). e-Banking Facility Services
in the Philippines. International Journal of Disaster Recovery and Business
Continuity
Vol.11, No. 2, pp. 166–178 Fasttrack IT Academy (n.d.). The future of mobile
app development in the Philippines.
https://fitacademy.ph/mobile-app-development-in-the-philippines/. Galeon,
H., Garcia, P. G. Jr., & dela Cruz, J. (2019) E-learning roadmap for open
distance learning in Cordillera Administrative Region. The International
Conference on Information Technology
Hubspot (2022) A Brief Timeline of the History of Blogging retrieved from
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/history-of-blogging
visme (2022) How to Start a Vlog: Guide for Beginners to YouTube for 2022
retrieved from https://visme.co/blog/how-to-start-a-vlog/#create-your-
youtube-channel
EMST 1 ------------ by: MISS MARY GRACE L. SADANG, MIT Page 52
You might also like
- Basic Computer Skills PPT Lecture NotesDocument88 pagesBasic Computer Skills PPT Lecture Noteszemedu abebe75% (8)
- Product Visio Icon0900aecd800940d9Document264 pagesProduct Visio Icon0900aecd800940d9Fede VarelaNo ratings yet
- Information Communication Technology: National Youth Service-Engineering InstituteDocument31 pagesInformation Communication Technology: National Youth Service-Engineering InstituteEmile TygaNo ratings yet
- Component of ComputerDocument27 pagesComponent of ComputerHuleshwar Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- DC 102 Module 1 Lesson 1Document12 pagesDC 102 Module 1 Lesson 1jerome paulinesNo ratings yet
- ... DesignedComputer Fundamentals TutorialDocument85 pages... DesignedComputer Fundamentals TutorialFredrick OringoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Components of ComputerDocument42 pagesWeek 2 Components of Computerayesha ambreenNo ratings yet
- Input Devices OF ComputerDocument12 pagesInput Devices OF ComputerAjoyNo ratings yet
- My NotesDocument4 pagesMy Notescossykin19No ratings yet
- Keyboard Is The Most Common and Very Popular Input Device Which Helps To Input Data To The ComputerDocument4 pagesKeyboard Is The Most Common and Very Popular Input Device Which Helps To Input Data To The ComputerDivina Labuguen TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Basics of Information TechnologyDocument126 pagesUnit-1: Basics of Information TechnologyKritika KapoorNo ratings yet
- Copa HardwareDocument25 pagesCopa HardwareRasik PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CompleteDocument17 pagesChapter 2 CompleteappawashNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and Software UcuDocument58 pagesComputer Hardware and Software UcuvianneloroNo ratings yet
- Mcrocomputer SystemDocument7 pagesMcrocomputer SystemVICTOR OCHIENGNo ratings yet
- Lec 5&6Document24 pagesLec 5&6UnknownNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ComputerDocument11 pagesFundamentals of ComputerMwanahamisi MniachiNo ratings yet
- Parts of Computer and Input and Output DevicesDocument27 pagesParts of Computer and Input and Output Devicesdua tanveerNo ratings yet
- Operate Personal ComputerDocument92 pagesOperate Personal ComputerAmanuel KassaNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument29 pagesCentral Processing Unitsaurav gautam singhNo ratings yet
- 175 16cacca1b 2020052204230029Document119 pages175 16cacca1b 2020052204230029shrivastavabhoomi46No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 The Basic Function of A Computer2Document21 pagesLesson 3 The Basic Function of A Computer2Jenry EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of C 1Document20 pagesFundamentals of C 1yzNo ratings yet
- Form 5 & 6 Notes PDFDocument264 pagesForm 5 & 6 Notes PDFYuyun FrancisNo ratings yet
- C Programming Unit-I - IntroduntionDocument44 pagesC Programming Unit-I - IntroduntionPathivadaSantoshNaiduNo ratings yet
- 1) Introduction To ComputerDocument50 pages1) Introduction To ComputerSajalNo ratings yet
- BayehDocument11 pagesBayehTEWODROS TADDESENo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Document32 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)poo235No ratings yet
- Week 1Document61 pagesWeek 1Maria FazalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of It and ProgrammingDocument6 pagesFundamentals of It and ProgrammingRavi Mohan BhattNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Computer System MICTCSDocument61 pagesWeek 2 Computer System MICTCSBloodmoon Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1 Basic Concepts of Information Technology: XI Computer Science Page 1 of 28Document28 pagesChapter # 1 Basic Concepts of Information Technology: XI Computer Science Page 1 of 28sqamar68No ratings yet
- CpfdfileDocument27 pagesCpfdfileSukhpal KaurNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems & Programs Ejaz Mahmood Shahid Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering M.SC (Mech. Engg.) MCSDocument26 pagesComputer Systems & Programs Ejaz Mahmood Shahid Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering M.SC (Mech. Engg.) MCSM Hamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Document32 pagesBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)abhi_txt90No ratings yet
- Chapter#1Document67 pagesChapter#1Wasif QaziNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1nd2Document16 pagesChapter 1nd2Yabex Ye àĺèmlijNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Computer System: Lecture OneDocument35 pagesAn Overview of The Computer System: Lecture OneSaabir Sheekh Muuse MoalimNo ratings yet
- MS Office and Computer ApplicationDocument12 pagesMS Office and Computer ApplicationAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- COM111 Prractical Manual - 2016Document151 pagesCOM111 Prractical Manual - 2016PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Programming in C Mccs 2022Document218 pagesProgramming in C Mccs 2022224akiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Lighting and ShadowsDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Lighting and Shadowsnickmcklin7No ratings yet
- Software: IT WorkshopDocument12 pagesSoftware: IT WorkshopAnjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Computer Studies 2ND Term Lesson NoteDocument11 pagesComputer Studies 2ND Term Lesson NotelordsenoxNo ratings yet
- What Is An Operating SystemDocument9 pagesWhat Is An Operating Systemspiroo spirooNo ratings yet
- Pre Grade Computer Book 5 - 7 Introduction To Computers. Book Vol Ume - 1Document21 pagesPre Grade Computer Book 5 - 7 Introduction To Computers. Book Vol Ume - 1andsenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument73 pagesIntroduction To ComputerNaman SinghNo ratings yet
- PSC - Doc - 2017 - 12 PDFDocument119 pagesPSC - Doc - 2017 - 12 PDFSunil Kumar VemulaNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Introduction To Computer System and ProgrammingDocument21 pagesCH-1 Introduction To Computer System and ProgrammingpriyeshNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Class 11 Chapter 1Document26 pagesMultimedia Class 11 Chapter 1akshatsharma007100% (1)
- Introduction To Computer: Chapter OneDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Computer: Chapter OneYaregal ChalachewNo ratings yet
- IT ConceptsDocument11 pagesIT ConceptsMohammed Sumaila Sawadugu Action-90No ratings yet
- Computer Funda (2)Document30 pagesComputer Funda (2)nirbabuyNo ratings yet
- Unit I - CabDocument35 pagesUnit I - CabsathyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1Mr Sathesh Abraham Leo CSENo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalsDocument34 pagesComputer Fundamentalsvladimire ternateNo ratings yet
- Learn Computer ScienceDocument24 pagesLearn Computer Sciencefabiobonadia100% (1)
- Module-1 NewDocument20 pagesModule-1 Newbibekbasnet7800No ratings yet
- Lec 5 (NO NEED)Document113 pagesLec 5 (NO NEED)ShujaAmjadNo ratings yet
- Digital and Media Literacy of Science and Mathematics StudentsDocument18 pagesDigital and Media Literacy of Science and Mathematics StudentsMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Hahahh AhDocument3 pagesHahahh AhMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-3Document7 pagesLesson 1-3Maden betoNo ratings yet
- Gelacio 3b Mathematics Grade SheetDocument1 pageGelacio 3b Mathematics Grade SheetMaden betoNo ratings yet
- FS 1 AnswersDocument8 pagesFS 1 AnswersMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Scie Ee 2023Document3 pagesScie Ee 2023Maden betoNo ratings yet
- AC LinksDocument1 pageAC LinksMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Final Lab QuizDocument5 pagesFinal Lab QuizMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Parents ConsentInternshipDocument2 pagesParents ConsentInternshipMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Microbial Diversity The Eukaryotic Microbes - Chapter 4 - BSEDDocument5 pagesLecture - Microbial Diversity The Eukaryotic Microbes - Chapter 4 - BSEDMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4Maden betoNo ratings yet
- SCI 102 - Lesson 5Document3 pagesSCI 102 - Lesson 5Maden betoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Samples of Action PlanDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - Samples of Action PlanMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Diffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Document5 pagesDiffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Maden betoNo ratings yet
- SCI 102 SamplesDocument24 pagesSCI 102 SamplesMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document12 pagesLesson 2Maden betoNo ratings yet
- PHYS 105: Waves and OpticsDocument9 pagesPHYS 105: Waves and OpticsMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document13 pagesLesson 1Maden betoNo ratings yet
- Enrichment Activities 1Document2 pagesEnrichment Activities 1Maden betoNo ratings yet
- Elements of Computer SystemDocument39 pagesElements of Computer SystemMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Enrichment Activities 2Document1 pageEnrichment Activities 2Maden betoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 ContinuationDocument7 pagesLesson 3 ContinuationMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Electric PotentialDocument30 pagesElectric PotentialMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism - Oersted DiscoveryDocument4 pagesElectromagnetism - Oersted DiscoveryMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Light Absorption, Reflection, and TransmissionDocument9 pagesLight Absorption, Reflection, and TransmissionMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Midterm EmstDocument22 pagesMidterm EmstMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Intellectual Property RightsDocument4 pagesWeek 13 Intellectual Property RightsMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument20 pagesElectric FieldMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Reforms: IN DepedDocument19 pagesReforms: IN DepedMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain DictionaryDocument2 pagesBlockchain DictionaryVijay DinanathNo ratings yet
- Nikolli, Ramiz Berisha, Ferim Gashi, E.IsufiDocument66 pagesNikolli, Ramiz Berisha, Ferim Gashi, E.IsufiStudio Hapsira sh.p.kNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To The Internet and WebDocument8 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To The Internet and WebKelvin ChaulaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 WorkSheet 1Document5 pages1.1 WorkSheet 1Dewi Nila RositaNo ratings yet
- MDA Troubleshooting GuideDocument8 pagesMDA Troubleshooting GuideQasim HussainNo ratings yet
- AKU-EB SSC-II Computer Science Hacking and Computer SecurityDocument7 pagesAKU-EB SSC-II Computer Science Hacking and Computer SecurityMuhammad SaimNo ratings yet
- EDGE TechnologyDocument15 pagesEDGE TechnologyBhanu PartapNo ratings yet
- Clinical Database Metadata Quality Control With SAS® and PythonDocument16 pagesClinical Database Metadata Quality Control With SAS® and PythonSUMAN CHAUDHURINo ratings yet
- PFRODocument2 pagesPFROJefferson FrandiniNo ratings yet
- SD WAN WorkbookDocument150 pagesSD WAN WorkbookPhilip RichardNo ratings yet
- Subject Code AP-522 Office AutomationDocument6 pagesSubject Code AP-522 Office Automationmahira bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Skills Framework For Retail Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumentDocument2 pagesSkills Framework For Retail Technical Skills and Competencies (TSC) Reference DocumenthanaNo ratings yet
- 2021 11 01 Hackercool MagazineDocument58 pages2021 11 01 Hackercool MagazineMiljenko SimicNo ratings yet
- Kf-Sell Architecture and Design: Mission StatementDocument23 pagesKf-Sell Architecture and Design: Mission StatementLavanya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Symptom: LanguageDocument2 pagesSymptom: LanguageSenpaiThongamNo ratings yet
- Installing Virl On Vmware Esxi 5Document12 pagesInstalling Virl On Vmware Esxi 5baraboljaNo ratings yet
- Lab ISCW: Cau Hinh Load Balancing Tren 2 Line ADSL Dùng SAA. I. Sơ Đ LabDocument4 pagesLab ISCW: Cau Hinh Load Balancing Tren 2 Line ADSL Dùng SAA. I. Sơ Đ LabLe Ngoc KhoaNo ratings yet
- NSE 3 FortiADC CompleteCourse v3 WM 2019Q4Document42 pagesNSE 3 FortiADC CompleteCourse v3 WM 2019Q4Luis GarayNo ratings yet
- Customer Services Division: e-CAF Android TrainingDocument39 pagesCustomer Services Division: e-CAF Android TrainingJemal Yaya100% (1)
- Technical Professionals BrieflyDocument3 pagesTechnical Professionals BrieflyVikas ShahNo ratings yet
- Whatis Techtarget Mobile SecurityDocument3 pagesWhatis Techtarget Mobile Securitydevid mandefroNo ratings yet
- AZ-900 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals - 12Document8 pagesAZ-900 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals - 12nagendra reddy panyamNo ratings yet
- IDEA Installation GuideDocument23 pagesIDEA Installation GuidebayuschNo ratings yet
- Using AWS in The Context of New Zealand Privacy ConsiderationsDocument20 pagesUsing AWS in The Context of New Zealand Privacy ConsiderationsweeralalithNo ratings yet
- History of San Mateo County (1916)Document291 pagesHistory of San Mateo County (1916)peninsulastoryNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ESDocument5 pagesLesson Plan ESsureshvkumarNo ratings yet
- Dual Serial Ports User GuideDocument9 pagesDual Serial Ports User GuideVõ Thành LongNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Certified Azure Developer AssociateDocument8 pagesMicrosoft Certified Azure Developer AssociateDotNetTricksNo ratings yet
- VLSMDocument3 pagesVLSMEdwin Ancizar Vargas ZartaNo ratings yet