Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus
Syllabus
Uploaded by
Diksha NasaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 18CSC304J - Compiler DesignDocument2 pages18CSC304J - Compiler Designthreee.six.five.365No ratings yet
- Syllabus 21CSS101J PpsDocument3 pagesSyllabus 21CSS101J PpsGhoulNo ratings yet
- 19PEEO65T - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing SyllabusDocument2 pages19PEEO65T - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing SyllabusSanthosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- 18CEO302J Modern Civil Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pages18CEO302J Modern Civil Engineering EconomicsmekalaNo ratings yet
- 18CEC304L Construction Engineering and Management LaboratoryDocument2 pages18CEC304L Construction Engineering and Management LaboratorymekalaNo ratings yet
- 18cse392t SyllabusDocument2 pages18cse392t SyllabusKavipriya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Programming For Problem Solving SyllabusDocument2 pagesProgramming For Problem Solving SyllabusSaurabh RajNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument4 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - Controlsateesh shivhareNo ratings yet
- Nil Nil Faculty of ManagementDocument19 pagesNil Nil Faculty of ManagementDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- 18MEC208T - Mechanical Engineering Design SyllabusDocument5 pages18MEC208T - Mechanical Engineering Design SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - 18CSC203J - Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument4 pagesSyllabus - 18CSC203J - Computer Organization and ArchitectureVaijayanthiNo ratings yet
- 18CSS202J CC Lab Manual 2022 2023 EvenDocument77 pages18CSS202J CC Lab Manual 2022 2023 EvenVAMSI TIYYAGURA (RA2111026010205)No ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ElectronicsDocument2 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronicsravi gokaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusDurga Devi PNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlsuchiNo ratings yet
- Automotive Control EngineeringDocument2 pagesAutomotive Control EngineeringChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- 18CSC303J - Database Management SystemsDocument2 pages18CSC303J - Database Management Systemsthreee.six.five.365No ratings yet
- NDM SyllabusDocument2 pagesNDM Syllabuskrisha vasuNo ratings yet
- Vehicle DynamicsDocument2 pagesVehicle DynamicsChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- ITSM&O Syllabus - SRMDocument2 pagesITSM&O Syllabus - SRMSanthosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabussaranya_subakaranNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - 18CSS202J - Computer CommunicationsDocument3 pagesSyllabus - 18CSS202J - Computer CommunicationsAakash PayalaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy LogicDocument2 pagesArtificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy LogicChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- 18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusDocument3 pages18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- PT CSE 2019 Curriculum and SyllabusDocument2 pagesPT CSE 2019 Curriculum and Syllabusneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Sample - Syllabus Template Revised - 13.07.2022Document3 pagesSample - Syllabus Template Revised - 13.07.2022Sowmmiya UNo ratings yet
- Pps SyllabusDocument4 pagesPps SyllabusØmÊn GamingNo ratings yet
- SylabusDocument3 pagesSylabusveeramatNo ratings yet
- 18CSC204J - DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS SyllabusDocument3 pages18CSC204J - DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS SyllabusMeenakshi AryaNo ratings yet
- 18CSS202J CC LAB MANUAL 2021 2022 EVEN 7bDocument77 pages18CSS202J CC LAB MANUAL 2021 2022 EVEN 7bSAI ANDALAM (RA2111003011353)No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Automotive EnginesDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Automotive EnginesChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- App SyllabusDocument2 pagesApp SyllabusMohammed JavidhNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlEric LonewolfNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For All Professional Electives Btech Programmes School of Computing 18 RegDocument241 pagesSyllabus For All Professional Electives Btech Programmes School of Computing 18 RegMonica Bhavani MNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument3 pagesOperating SystemsSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- Solid State Device SyllabusDocument2 pagesSolid State Device Syllabusnikunj sharmaNo ratings yet
- 18CSC205J OS Syllabus UpdatedDocument3 pages18CSC205J OS Syllabus UpdatedHarsh DeepNo ratings yet
- Third & Final Year SyllabusDocument80 pagesThird & Final Year SyllabusMerlin Linda GNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Solids PDFSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- MCA-SYLLABUS I SemesterDocument19 pagesMCA-SYLLABUS I SemesterMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)No ratings yet
- Curriculum and Syllabus Btech Mathematics Reg 2020 21Document24 pagesCurriculum and Syllabus Btech Mathematics Reg 2020 21Surya NathanNo ratings yet
- 18MEC108T 120 Zoomed Syllabus-Rotated PDFDocument2 pages18MEC108T 120 Zoomed Syllabus-Rotated PDFChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument3 pagesOperating SystemSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- Cn-18cse379t - Internet of ThingsDocument2 pagesCn-18cse379t - Internet of Thingsnagamalleswari2010No ratings yet
- 18BTC106J-Immunology SyllabusDocument2 pages18BTC106J-Immunology SyllabusChris PenielNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For All Open Electives Btech Programmes Faculty of E&t 18 RegDocument181 pagesSyllabus For All Open Electives Btech Programmes Faculty of E&t 18 RegSAPTARSHI BHATTACHARYA (RA2011003010182)No ratings yet
- SRM Cse - 2Document113 pagesSRM Cse - 2Yemen PurposeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- NSSE CT1 NotesDocument9 pagesNSSE CT1 NotesROHITM RA1811002040067No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUSSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- CT050-3-2 Web Applications (VD1) 6 January 2020Document2 pagesCT050-3-2 Web Applications (VD1) 6 January 2020makkarjsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus PDFNARESH SRIRAM G (RA2111038010004)No ratings yet
- Community ConnectDocument2 pagesCommunity ConnectgeethikarevanooriNo ratings yet
- Oops Syllabus - Jan 2024Document3 pagesOops Syllabus - Jan 2024Abishek DevNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusmm8805No ratings yet
- Syllabus 18EES101JDocument2 pagesSyllabus 18EES101JANKUSH SAHOO (RA2011003010531)No ratings yet
- Aut0motive Fault DiagnosticsDocument2 pagesAut0motive Fault DiagnosticsChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlpavanNo ratings yet
- Oodp Syllabus in DetailDocument3 pagesOodp Syllabus in Detailvasudevn1No ratings yet
- IOT Proj - Report 1Document31 pagesIOT Proj - Report 1Diksha NasaNo ratings yet
- IOT Proj - ReportDocument17 pagesIOT Proj - ReportDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- ASTW RA03 PracticalManualDocument18 pagesASTW RA03 PracticalManualDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Final Record Analog Consists of All The Materials That U Can Get Full MarksDocument171 pagesFinal Record Analog Consists of All The Materials That U Can Get Full MarksDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- IJSRP Paper Submission Format Single ColumnDocument3 pagesIJSRP Paper Submission Format Single ColumnDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- MC250 International Preselection Kit 2023 (Updated Oct 22)Document31 pagesMC250 International Preselection Kit 2023 (Updated Oct 22)Diksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Online Food Delivery App FoodieDocument12 pagesOnline Food Delivery App FoodieDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- SRM University BrochureDocument58 pagesSRM University Brochuresridhar ramanaNo ratings yet
- CGI Shortlist For Further ProcessDocument4 pagesCGI Shortlist For Further Processhari sriNo ratings yet
- Research Opportunities in "Semiconductor Materials and Devices" ROSMD-2020Document2 pagesResearch Opportunities in "Semiconductor Materials and Devices" ROSMD-2020Jayden Andrik V MNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument5 pagesLetterpushpakNo ratings yet
- Yoga For Modern Age - 1Document181 pagesYoga For Modern Age - 1GayathriNo ratings yet
- Technologies in Disaster ManagementDocument1 pageTechnologies in Disaster ManagementPablo GBNo ratings yet
- The Campus Newspaper of SRM University: Volume 2 Number 5Document24 pagesThe Campus Newspaper of SRM University: Volume 2 Number 5sonirocksNo ratings yet
- Bba SRMDocument10 pagesBba SRMLorance ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Handbook 2017 18Document266 pagesHandbook 2017 18sakthivel vedachalamNo ratings yet
- M.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering) : With Additional Specialization in Data Science and Machine LearningDocument15 pagesM.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering) : With Additional Specialization in Data Science and Machine Learningguru_maheshNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument4 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - Controlsateesh shivhareNo ratings yet
- SRMIST Scholarship InfoDocument14 pagesSRMIST Scholarship InfoGokulNo ratings yet
- Lab Front Sheet - MergedDocument112 pagesLab Front Sheet - MergedBennetNo ratings yet
- SRM University SRM FeekartDocument1 pageSRM University SRM FeekartJosé FranciscoNo ratings yet
- SRM Ist-Brochure - Iceabm2023Document6 pagesSRM Ist-Brochure - Iceabm2023Mahendra Singh DhoniNo ratings yet
- List of State Nursing Council Recognised Institutions Offering Post Basic Diploma Programme Inspected Under Section 13 and 14 of INC Act For The Academic Year 2020-2021Document16 pagesList of State Nursing Council Recognised Institutions Offering Post Basic Diploma Programme Inspected Under Section 13 and 14 of INC Act For The Academic Year 2020-2021Anmol GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mci Status of Medical Colleges For Admission For The Academic Year 2009-2010Document31 pagesMci Status of Medical Colleges For Admission For The Academic Year 2009-2010Aimhigh_PPMNo ratings yet
- Alankrrit Bali: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesAlankrrit Bali: Career ObjectivearupNo ratings yet
- Compare SRM IST Chennai Vs MSRIT Bangalore Vs University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering Vs VIT VDocument4 pagesCompare SRM IST Chennai Vs MSRIT Bangalore Vs University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering Vs VIT VRakshith NNo ratings yet
- Front Page, BONOFIDE & IndexDocument3 pagesFront Page, BONOFIDE & IndexVijay SudarsanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Guide To Entrance ExamDocument40 pagesDokumen - Tips Guide To Entrance ExamGlynicka joyce GarciaNo ratings yet
- SRM Brochure 2016 PDFDocument20 pagesSRM Brochure 2016 PDFsriniefsNo ratings yet
- Civil SRMIST Workshop Jan 2023Document1 pageCivil SRMIST Workshop Jan 2023Dinesh RamoNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Application FORM 2020Document2 pagesB.Tech Application FORM 2020uthaya uthranNo ratings yet
- Sensors SyllabusDocument2 pagesSensors Syllabusdirector.sportssrmistNo ratings yet
- SRM MbaDocument13 pagesSRM MbaSasidharan GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- Final Brochure FDocument8 pagesFinal Brochure FpritiNo ratings yet
- 5-14 NewDocument9 pages5-14 NewVASUDEVAN N (RC2113003011006)No ratings yet
- DR - Dillibabu - 5.4.23Document2 pagesDR - Dillibabu - 5.4.23TechnetNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology: (Deemed To Be University U/s 3 of UGC Act, 1956)Document2 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology: (Deemed To Be University U/s 3 of UGC Act, 1956)Girijashankar KhuntiaNo ratings yet
Syllabus
Syllabus
Uploaded by
Diksha NasaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus
Syllabus
Uploaded by
Diksha NasaCopyright:
Available Formats
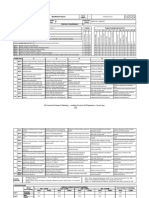
SEMESTER - VII
Course Course Course L T P C
18MBH463J SERVICES SCIENCE AND SERVICE OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT C Humanities & Social Sciences
Code Name Category 3 0 2 4
Pre-requisite Co-requisite Progressive
Nil Nil Nil
Courses Courses Courses
Course Offering Department College of Management Data Book / Codes/Standards Nil
Course Learning Rationale (CLR): The purpose of learning this course is to: Learning Program Learning Outcomes (PLO)
CLR-1 : Define the differences between goods and services 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
CLR-2 : Discuss characteristics of services
Level of Thinking (Bloom)
Expected Proficiency (%)
Expected Attainment (%)
Individual & Team Work
Engineering Knowledge
Design & Development
Project Mgt. & Finance
CLR-3 : Analyse services design concepts and evaluate them
Modern Tool Usage
CLR-4 : Discuss methods to manage Service business
Life Long Learning
Society & Culture
Problem Analysis
Analysis, Design,
CLR-5 : Plan innovation in Service
Communication
Environment &
Sustainability
CLR-6 : Incorporate the different types of services and management strategy
Research
PSO – 3
PSO - 1
PSO - 2
Ethics
Course Learning Outcomes (CLO): At the end of this course, learners will be able to:
CLO-1 : Analyse concepts about Services and distinguish it from Goods 3 80 70 M M M M M M - - M M L M - - -
CLO-2 : Identify characteristics and nature of Services 3 85 75 M H L M L - - - M L - H - - -
CLO-3 : Comprehend ways to design Services and evaluate them using Service qualities 3 75 70 M H M H L - - - M L - H - - -
CLO-4 : Apply how various methods can be used to operate and manage Service businesses 3 85 80 M H M H L - - - M L - H - - -
CLO-5 : Explain how innovation can be approached from Services point of view 3 85 75 H H M H L - - - M L - H - - -
CLO-6 : Construct the different types of services and management strategy for them 3 80 70 L H - H L - - - L L - H - - -
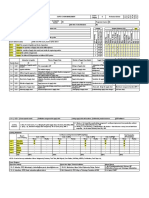
Duration
15 15 15 15 15
(hour)
SLO-1 Introduction-Basic Terminology Strategic Service Vision Technology in Service Capacity Planning Management of Service Project
S-1
SLO-2 Service Economy Competitive environment for Services Emergence of Service Encounter Leveling Capacity Service Product Development
SLO-1 Role of Services Competitive Service Strategies Service Encounter Triad Demand Management Project Management
S-2 Encounter Dominated by the Service
SLO-2 Evolution of Economy Strategic Analysis Demand Management Strategies Principles of Project Management
Organization
SLO-1 Nature of Service Sector Service Benchmarking Contact Personnel–Dominated Encounter Customer-Induced Variability Project Management Process
S-3
SLO-2 Differences between Goods and Services Service Innovation Customer-Dominated Encounter Segmenting Demand Triple Objectives
S SLO-1 Experience Economy Offering Price Incentives/ Promoting Off-
New Service Development. Service Organization Elements Project Team/ Project Leadership
4-5 SLO-2 Service Dominant Logic Peak Demand
SLO-1 Characteristics of Service Operations Service System Design Service Control Systems Developing Complementary Services Project Management Techniques
S-6
SLO-2 Complexity – Customer Participation Approaches for Service Design Contact Personnel management Reservation Systems and Overbooking Objectives of Project Management
SLO-1 Simultaneity and its consequences Service Quality Customer Expectations Strategies for Managing Capacity Gantt Charts
S-7
SLO-2 Perishability SERVQUAL Creating Customer Orientation Defining Service Capacity Pros and Cons of Gantt charts
S-8 SLO-1 Intangibility Walk Through Audits Service Profit chain Daily Workshift Scheduling Project network
SRM Institute of Science & Technology – Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations)
134
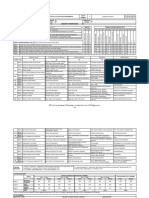
Duration
15 15 15 15 15
(hour)
SLO-2 Heterogeneity Quality by Design Facility Design Daily Workshift with constraints Critical Path Method
S SLO-1 Non Transference of Ownership
Strategic Positioning Process Analysis Increasing Customer Participation Resource Constraints
9-10 SLO-2 Outcomes of complexity
SLO-1 Pre-industrial Economy Service Blueprint Facility layout Creating Adjustable Capacity Activity Crashing
S-11
SLO-2 Industrial Economy Taxonomy of Service Process Environment Orientation Sharing Capacity Activity Crashing tools
SLO-1 Post-Industrial Economy Degree of Divergence Process Improvement Yield Management Uncertainty in Activity duration
S-12
SLO-2 Evolution and Innovation Object of Service Process Queue analysis Productivity/ Part time Employees PERT
SLO-1 Value co-creation Customer Contact types Queue Applications Waiting Line Management Issues in CPM
S-13
SLO-2 Service Encounters Information Empowerment Service Productivity Service Level Issues in PERT
S SLO-1 Service Package
Customer Centric approaches Quality Tools Demand Forecasting Project Monitoring techniques
14-15 SLO-2 Grouping by Delivery Processes
1. Fitzsimmons & Fitzsimmons, Service Management: Operations, Strategy, Information
4. Reason, Ben, and Lovlie, Lavrans, (2016) Service Design for Business: A Practical Guide to Optimizing the
Technology, McGraw Hill publications (9th edition), 2019
Learning Customer Experience, Pan Macmillan India
2. Wilson, A., Zeithaml, V. A., Bitner, M. J., & Gremler, D. D. (2012). Services marketing:
Resources 5. Chesbrough, H. (2010). Open services innovation: Rethinking your business to grow and compete in a new
Integrating customer focus across the firm. McGraw Hill.
era. John Wiley & Sons
3. Lovelock, C. (2011). Services Marketing, 7/e. Pearson Education India
Learning Assessment
Continuous Learning Assessment (50% weightage)
Bloom’s Final Examination (50% weightage)
CLA – 1 (10%) CLA – 2 (15%) CLA – 3 (15%) CLA – 4 (10%)#
Level of Thinking
Theory Practice Theory Practice Theory Practice Theory Practice Theory Practice
Remember
Level 1 20% 20% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15%
Understand
Apply
Level 2 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20%
Analyze
Evaluate
Level 3 10% 10% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 15%
Create
Total 100 % 100 % 100 % 100 % 100%
# CLA – 4 can be from any combination of these: Assignments, Seminars, Tech Talks, Mini-Projects, Case-Studies, Self-Study, MOOCs, Certifications, Conf. Paper etc.,
Course Designers
Experts from Industry Experts from Higher Technical Institutions Internal Experts
Dr. S.K. Manivannan, SRMIST
Expert Member from TCS -
Dr.K.Sadasivan, SRMIST
SRM Institute of Science & Technology – Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations)
135
You might also like
- 18CSC304J - Compiler DesignDocument2 pages18CSC304J - Compiler Designthreee.six.five.365No ratings yet
- Syllabus 21CSS101J PpsDocument3 pagesSyllabus 21CSS101J PpsGhoulNo ratings yet
- 19PEEO65T - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing SyllabusDocument2 pages19PEEO65T - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing SyllabusSanthosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- 18CEO302J Modern Civil Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pages18CEO302J Modern Civil Engineering EconomicsmekalaNo ratings yet
- 18CEC304L Construction Engineering and Management LaboratoryDocument2 pages18CEC304L Construction Engineering and Management LaboratorymekalaNo ratings yet
- 18cse392t SyllabusDocument2 pages18cse392t SyllabusKavipriya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Programming For Problem Solving SyllabusDocument2 pagesProgramming For Problem Solving SyllabusSaurabh RajNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument4 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - Controlsateesh shivhareNo ratings yet
- Nil Nil Faculty of ManagementDocument19 pagesNil Nil Faculty of ManagementDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- 18MEC208T - Mechanical Engineering Design SyllabusDocument5 pages18MEC208T - Mechanical Engineering Design SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - 18CSC203J - Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument4 pagesSyllabus - 18CSC203J - Computer Organization and ArchitectureVaijayanthiNo ratings yet
- 18CSS202J CC Lab Manual 2022 2023 EvenDocument77 pages18CSS202J CC Lab Manual 2022 2023 EvenVAMSI TIYYAGURA (RA2111026010205)No ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ElectronicsDocument2 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronicsravi gokaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusDurga Devi PNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlsuchiNo ratings yet
- Automotive Control EngineeringDocument2 pagesAutomotive Control EngineeringChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- 18CSC303J - Database Management SystemsDocument2 pages18CSC303J - Database Management Systemsthreee.six.five.365No ratings yet
- NDM SyllabusDocument2 pagesNDM Syllabuskrisha vasuNo ratings yet
- Vehicle DynamicsDocument2 pagesVehicle DynamicsChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- ITSM&O Syllabus - SRMDocument2 pagesITSM&O Syllabus - SRMSanthosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabussaranya_subakaranNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - 18CSS202J - Computer CommunicationsDocument3 pagesSyllabus - 18CSS202J - Computer CommunicationsAakash PayalaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy LogicDocument2 pagesArtificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy LogicChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- 18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusDocument3 pages18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- PT CSE 2019 Curriculum and SyllabusDocument2 pagesPT CSE 2019 Curriculum and Syllabusneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Sample - Syllabus Template Revised - 13.07.2022Document3 pagesSample - Syllabus Template Revised - 13.07.2022Sowmmiya UNo ratings yet
- Pps SyllabusDocument4 pagesPps SyllabusØmÊn GamingNo ratings yet
- SylabusDocument3 pagesSylabusveeramatNo ratings yet
- 18CSC204J - DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS SyllabusDocument3 pages18CSC204J - DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS SyllabusMeenakshi AryaNo ratings yet
- 18CSS202J CC LAB MANUAL 2021 2022 EVEN 7bDocument77 pages18CSS202J CC LAB MANUAL 2021 2022 EVEN 7bSAI ANDALAM (RA2111003011353)No ratings yet
- Syllabus - Automotive EnginesDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Automotive EnginesChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- App SyllabusDocument2 pagesApp SyllabusMohammed JavidhNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlEric LonewolfNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For All Professional Electives Btech Programmes School of Computing 18 RegDocument241 pagesSyllabus For All Professional Electives Btech Programmes School of Computing 18 RegMonica Bhavani MNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument3 pagesOperating SystemsSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- Solid State Device SyllabusDocument2 pagesSolid State Device Syllabusnikunj sharmaNo ratings yet
- 18CSC205J OS Syllabus UpdatedDocument3 pages18CSC205J OS Syllabus UpdatedHarsh DeepNo ratings yet
- Third & Final Year SyllabusDocument80 pagesThird & Final Year SyllabusMerlin Linda GNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Solids PDFSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- MCA-SYLLABUS I SemesterDocument19 pagesMCA-SYLLABUS I SemesterMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)No ratings yet
- Curriculum and Syllabus Btech Mathematics Reg 2020 21Document24 pagesCurriculum and Syllabus Btech Mathematics Reg 2020 21Surya NathanNo ratings yet
- 18MEC108T 120 Zoomed Syllabus-Rotated PDFDocument2 pages18MEC108T 120 Zoomed Syllabus-Rotated PDFChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument3 pagesOperating SystemSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- Cn-18cse379t - Internet of ThingsDocument2 pagesCn-18cse379t - Internet of Thingsnagamalleswari2010No ratings yet
- 18BTC106J-Immunology SyllabusDocument2 pages18BTC106J-Immunology SyllabusChris PenielNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For All Open Electives Btech Programmes Faculty of E&t 18 RegDocument181 pagesSyllabus For All Open Electives Btech Programmes Faculty of E&t 18 RegSAPTARSHI BHATTACHARYA (RA2011003010182)No ratings yet
- SRM Cse - 2Document113 pagesSRM Cse - 2Yemen PurposeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- NSSE CT1 NotesDocument9 pagesNSSE CT1 NotesROHITM RA1811002040067No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUSDocument2 pagesSupply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUSSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- CT050-3-2 Web Applications (VD1) 6 January 2020Document2 pagesCT050-3-2 Web Applications (VD1) 6 January 2020makkarjsNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus PDFNARESH SRIRAM G (RA2111038010004)No ratings yet
- Community ConnectDocument2 pagesCommunity ConnectgeethikarevanooriNo ratings yet
- Oops Syllabus - Jan 2024Document3 pagesOops Syllabus - Jan 2024Abishek DevNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusmm8805No ratings yet
- Syllabus 18EES101JDocument2 pagesSyllabus 18EES101JANKUSH SAHOO (RA2011003010531)No ratings yet
- Aut0motive Fault DiagnosticsDocument2 pagesAut0motive Fault DiagnosticsChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlpavanNo ratings yet
- Oodp Syllabus in DetailDocument3 pagesOodp Syllabus in Detailvasudevn1No ratings yet
- IOT Proj - Report 1Document31 pagesIOT Proj - Report 1Diksha NasaNo ratings yet
- IOT Proj - ReportDocument17 pagesIOT Proj - ReportDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- ASTW RA03 PracticalManualDocument18 pagesASTW RA03 PracticalManualDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Final Record Analog Consists of All The Materials That U Can Get Full MarksDocument171 pagesFinal Record Analog Consists of All The Materials That U Can Get Full MarksDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- IJSRP Paper Submission Format Single ColumnDocument3 pagesIJSRP Paper Submission Format Single ColumnDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- MC250 International Preselection Kit 2023 (Updated Oct 22)Document31 pagesMC250 International Preselection Kit 2023 (Updated Oct 22)Diksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Online Food Delivery App FoodieDocument12 pagesOnline Food Delivery App FoodieDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- SRM University BrochureDocument58 pagesSRM University Brochuresridhar ramanaNo ratings yet
- CGI Shortlist For Further ProcessDocument4 pagesCGI Shortlist For Further Processhari sriNo ratings yet
- Research Opportunities in "Semiconductor Materials and Devices" ROSMD-2020Document2 pagesResearch Opportunities in "Semiconductor Materials and Devices" ROSMD-2020Jayden Andrik V MNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument5 pagesLetterpushpakNo ratings yet
- Yoga For Modern Age - 1Document181 pagesYoga For Modern Age - 1GayathriNo ratings yet
- Technologies in Disaster ManagementDocument1 pageTechnologies in Disaster ManagementPablo GBNo ratings yet
- The Campus Newspaper of SRM University: Volume 2 Number 5Document24 pagesThe Campus Newspaper of SRM University: Volume 2 Number 5sonirocksNo ratings yet
- Bba SRMDocument10 pagesBba SRMLorance ChinnuNo ratings yet
- Handbook 2017 18Document266 pagesHandbook 2017 18sakthivel vedachalamNo ratings yet
- M.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering) : With Additional Specialization in Data Science and Machine LearningDocument15 pagesM.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering) : With Additional Specialization in Data Science and Machine Learningguru_maheshNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument4 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - Controlsateesh shivhareNo ratings yet
- SRMIST Scholarship InfoDocument14 pagesSRMIST Scholarship InfoGokulNo ratings yet
- Lab Front Sheet - MergedDocument112 pagesLab Front Sheet - MergedBennetNo ratings yet
- SRM University SRM FeekartDocument1 pageSRM University SRM FeekartJosé FranciscoNo ratings yet
- SRM Ist-Brochure - Iceabm2023Document6 pagesSRM Ist-Brochure - Iceabm2023Mahendra Singh DhoniNo ratings yet
- List of State Nursing Council Recognised Institutions Offering Post Basic Diploma Programme Inspected Under Section 13 and 14 of INC Act For The Academic Year 2020-2021Document16 pagesList of State Nursing Council Recognised Institutions Offering Post Basic Diploma Programme Inspected Under Section 13 and 14 of INC Act For The Academic Year 2020-2021Anmol GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mci Status of Medical Colleges For Admission For The Academic Year 2009-2010Document31 pagesMci Status of Medical Colleges For Admission For The Academic Year 2009-2010Aimhigh_PPMNo ratings yet
- Alankrrit Bali: Career ObjectiveDocument4 pagesAlankrrit Bali: Career ObjectivearupNo ratings yet
- Compare SRM IST Chennai Vs MSRIT Bangalore Vs University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering Vs VIT VDocument4 pagesCompare SRM IST Chennai Vs MSRIT Bangalore Vs University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering Vs VIT VRakshith NNo ratings yet
- Front Page, BONOFIDE & IndexDocument3 pagesFront Page, BONOFIDE & IndexVijay SudarsanNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Guide To Entrance ExamDocument40 pagesDokumen - Tips Guide To Entrance ExamGlynicka joyce GarciaNo ratings yet
- SRM Brochure 2016 PDFDocument20 pagesSRM Brochure 2016 PDFsriniefsNo ratings yet
- Civil SRMIST Workshop Jan 2023Document1 pageCivil SRMIST Workshop Jan 2023Dinesh RamoNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Application FORM 2020Document2 pagesB.Tech Application FORM 2020uthaya uthranNo ratings yet
- Sensors SyllabusDocument2 pagesSensors Syllabusdirector.sportssrmistNo ratings yet
- SRM MbaDocument13 pagesSRM MbaSasidharan GovindarajanNo ratings yet
- Final Brochure FDocument8 pagesFinal Brochure FpritiNo ratings yet
- 5-14 NewDocument9 pages5-14 NewVASUDEVAN N (RC2113003011006)No ratings yet
- DR - Dillibabu - 5.4.23Document2 pagesDR - Dillibabu - 5.4.23TechnetNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology: (Deemed To Be University U/s 3 of UGC Act, 1956)Document2 pagesSRM Institute of Science and Technology: (Deemed To Be University U/s 3 of UGC Act, 1956)Girijashankar KhuntiaNo ratings yet