Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ME 7 - Activity 8
ME 7 - Activity 8
Uploaded by
Rygen Faye Del RosarioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 7 - Activity 8
ME 7 - Activity 8
Uploaded by
Rygen Faye Del RosarioCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 7 – Activity 8
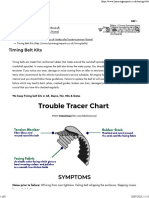
I.Name five (5) common belt problems in a Table, indicating each problem's causes and
recommended remedies. (See example and format below)
Sample:
Problem Cause Remedy
An object falling into Replace with a new, matched
Broken belts
or hitting the drive set of belts
Problem Cause/s Remedy/ies
Check drive, align non-
1. uneven wear of the aligned pulleys or replace
belt section Pulleys do not align them if necessary,
Strong belt vibration change the belt
Check tension,
retention belt if
necessary
Leakage of the engine
2. contamination of the or engine Remove leak, change
belt compartment (such as the belt
leakage of oil,
antifreeze, etc.)
3. breakage and fraying
Belt tension
of base compound/belt
too low/high Change belt
section
Lifetime exceeded Set correct tension
Foreign bodies
4. belt running noise
Tension too low Re-tension
Lifetime exceeded Change belt
Change belt, set the correct
tension
5. wear the tooth Remove foreign objects,
Tension too high/low
flank/root cracks ensure the cover is
Action of foreign bodies
and tooth shearing positioned properly, change
Fixed timing belt
the belt
pulley and/or tension
Detect causes ( e.g., faulty
idler
bearing) and find remedies,
change the belt
II. Answer the following:
1. Discuss the concept of a two-pulley system.
System consisting of two pulleys with a rope running around them to lift a load.
Using two or more pulleys reduces the amount of effort needed. For example,
When a person uses two or more pulleys in a system, then the system also
multiplies the force applied besides changing its direction. This works with one
fixed and one movable pulley in a system, it essentially doubles the weight of
the load you could lift without help from another person based on the weight
you can lift.
2. Define and Discuss the Basics of Belt Drive.
It is defined as a transmission system that uses a flexible strip to transfer power.
The turning disk is connected by a belt drive to the electric motor. A rubber belt
drive is used to transfer power from one pulley to another. A belt drive is a
transmission system that uses a flexible strip to transfer power. Belt drive, in
machinery, is a pair of pulleys attached to usually parallel shafts and connected
by an encircling flexible belt that can serve to transmit.
3. Name Four Types of Belt.
Round belts
V belts
Flat belts
Timing/toothed belts
4. Misalignment is one of the most common causes of premature belt failure. Explain
how it affects the belt performance.
Misalignment may be caused during assembly or develop over time, due to
thermal expansion, components shifting, or improper reassembly after
maintenance. The resulting vibration may be radial or axial (in line with the axis
of the machine) or both. Misalignment is one of the most common causes of
premature belt failure. Depending on its severity, misalignment can gradually
reduce belt performance by increasing wear and fatigue. Or, it can destroy a
belt in a matter of hours or days. While the forms of misalignment may be
fairly well understood, accurate measurements and acceptable limits must be
determined if maintenance personnel are to take corrective action.
Misalignment can either be quantified mathematically or be compared to some
general rules of thumb for quicker and easier results. Misalignment can be an
obstacle to satisfactory synchronous and V-belt drive performance. In many
cases, it is not easily detectable in complex drive applications. Maintenance
technicians should also check related components, such as brackets and
platforms, for proper design and placement. These parts must be strong
enough to withstand the peak forces exerted by the belt drive without bending
or flexing.
III. List at least three (3) primary considerations when selecting the proper pulley for a
design project. Discuss your answers by highlighting the significance of these
considerations.
Before we select the correct pulley from the available options, there are several
specific pieces of information you will need. In general, however, there are three main
considerations when selecting the right pulley for your project:
1. Size
2. Drive vs. driven requirements
3. Special consideration (noise, chemical resistance, etc.)
These are the primary considerations when selecting the proper pulley for a design
project. The size is very necessary that needs to be considered first because if we know
the size of the pulley we will use, it minimizes the cost of replacement due to unfitted or
improper size. Next, the drive and driven requirements should also be considered which
will lead you on how it will use and the requirements must be taken into account. Lastly,
the noise, chemical resistance, and other matters on the pulley.
IV. Discuss the working principles of stepped pulleys.
The step pulley is always operated in pairs, and when the belt is changed on one
pulley, it is also changed on the corresponding pulley on the other side of the belt. Pulleys
often have a groove around their circumference that guides a chain, cable, belt, or rope.
Most step pulley assemblies are cast from liquid materials; some of the very high-end
pulleys, however, are forged from solid billet material such as aluminum or steel. The
billet step pulley is much truer when spinning than a cast version; there is a great cost
difference between the two, however, with the billet costing much more. Some designs
utilize separate and independent pulleys to make up the arrangement, although this is
not a true step pulley.
You might also like
- Audi A4 (B6, B7) Repair Manual: 2002-2008 - ExcerptDocument6 pagesAudi A4 (B6, B7) Repair Manual: 2002-2008 - ExcerptBentley Publishers45% (58)
- Report Roller ChainDocument11 pagesReport Roller ChainPejuangHati100% (1)
- Belt and Chain DrivesDocument10 pagesBelt and Chain DrivesJagdip ShethNo ratings yet
- Gates Agri Catalogue English 2008Document374 pagesGates Agri Catalogue English 2008Andrey GyrychNo ratings yet
- V-Belt Drives 0905Document3 pagesV-Belt Drives 0905FV AllanNo ratings yet
- Pulley Alignment ProceduDocument9 pagesPulley Alignment ProceduJosh Watts100% (2)
- Tabla Tension Correas Gates PDFDocument4 pagesTabla Tension Correas Gates PDFHarold BurgosNo ratings yet
- CB How To Use CB ProperlyDocument25 pagesCB How To Use CB ProperlyBraydi VeraNo ratings yet
- V BeltsDocument14 pagesV BeltsLaka 98No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document39 pagesChapter 3amiranurul50% (2)
- Tabla Tension Correas GatesDocument4 pagesTabla Tension Correas Gatesvibrador0% (1)
- DTS Two Marks QADocument12 pagesDTS Two Marks QASoundararajanNo ratings yet
- Glosarios de Correas Transportadoras Letras M - Z y Archivo AdicionalDocument63 pagesGlosarios de Correas Transportadoras Letras M - Z y Archivo AdicionalJosé BocicNo ratings yet
- Hydrocam Bolt Tensioners PDFDocument74 pagesHydrocam Bolt Tensioners PDFVíctor Hugo Carvajal GaticaNo ratings yet
- Dmm-Ii QBDocument34 pagesDmm-Ii QBmahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- Belt Drives CalculationDocument15 pagesBelt Drives CalculationmalharNo ratings yet
- Belt Tensioners Crucial RoleDocument3 pagesBelt Tensioners Crucial RoleAnonymous YLfOYKGzNo ratings yet
- Problems Related To ExcessiveDocument2 pagesProblems Related To ExcessiveVicky ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Drive Belt Troubleshooting GuideDocument12 pagesDrive Belt Troubleshooting GuideQuang Nguyen HuynhNo ratings yet
- MD2 Unit4Document3 pagesMD2 Unit4Shivam TripathiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine - AssignmentDocument12 pagesTheory of Machine - AssignmentNeo NianshouNo ratings yet
- ConveyorDocument14 pagesConveyorchenkok_90No ratings yet
- Maintenance & Troubleshooting Guide: Sprocket & Gear, IncDocument12 pagesMaintenance & Troubleshooting Guide: Sprocket & Gear, IncGarry Yan DiazNo ratings yet
- SMP Conveyer BeltDocument8 pagesSMP Conveyer BeltMELCO JITPLNo ratings yet
- AutoTTHowTensionerWorks433 0796Document1 pageAutoTTHowTensionerWorks433 0796Srinivasan ThirunavukkarasuNo ratings yet
- FailureDocument8 pagesFailurehd.gholipourNo ratings yet
- Tension of Pulley AlignmentDocument3 pagesTension of Pulley AlignmentnguyennhatbaoNo ratings yet
- Distribution Conductor StringingDocument21 pagesDistribution Conductor Stringingmadhava_srinivasan174No ratings yet
- M.affan SR UmerDocument15 pagesM.affan SR UmerSheikh Aasi AasiNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Presentation SlideDocument56 pagesMaintenance Presentation Slidekapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- Belt Selection ConsiderationsDocument31 pagesBelt Selection Considerationsdivyaraghavaraju100% (1)
- Belt Failure AnalysisDocument8 pagesBelt Failure AnalysisDavid ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Drive BeltsDocument7 pagesDrive BeltsOA - 09HL 729653 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet
- Chain & SprocketDocument48 pagesChain & SprocketDede KaladriNo ratings yet
- Gates Belt GuideDocument12 pagesGates Belt GuideAriel QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Report Suspension g2g5Document15 pagesReport Suspension g2g5Haikal IkwanNo ratings yet
- How To Change An Automotive BeltDocument10 pagesHow To Change An Automotive BeltInternshipNo ratings yet
- 6 - VibrationsDocument4 pages6 - VibrationsAmarjeet Singh (Assistant Professor- Mechanical Engineer)No ratings yet
- Bearings Gears Belts and Pulleys Chains and Sprockets Screw Jacks Push-Pull Rod SystemsDocument4 pagesBearings Gears Belts and Pulleys Chains and Sprockets Screw Jacks Push-Pull Rod Systemsraj mohanNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument23 pagesTerm PaperAman Goyal (B19ME004)No ratings yet
- VCT-250 - Guia de Boas Práticas (EN) (2010.12)Document2 pagesVCT-250 - Guia de Boas Práticas (EN) (2010.12)Thiago AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Clutch HandbookDocument199 pagesClutch Handbookswap d100% (1)
- Dme Double SideDocument2 pagesDme Double SideMuhammed AsifNo ratings yet
- Large Size Conveyor ChainDocument156 pagesLarge Size Conveyor ChainManatchaiSanNo ratings yet
- 106.5 - BeltsDocument10 pages106.5 - BeltsHassan GDOURANo ratings yet
- Drive Belt: ComponentsDocument3 pagesDrive Belt: Componentstin tunlinNo ratings yet
- Belt Failure AnalysisDocument4 pagesBelt Failure AnalysisTamer EmamNo ratings yet
- Block Rotation and Rope Stability PDFDocument3 pagesBlock Rotation and Rope Stability PDFAnshul AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Sprocket and ChainDocument5 pagesSprocket and ChainRhea Jane DugadugaNo ratings yet
- M.affan SR Umer - 2Document19 pagesM.affan SR Umer - 2Sheikh Aasi AasiNo ratings yet
- Kerusakan Timming BeltDocument8 pagesKerusakan Timming BeltAgus PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Bagian Bagian CraneDocument29 pagesBagian Bagian Cranerois67% (3)
- Overland Belt ConveyorsDocument13 pagesOverland Belt ConveyorsRodrigo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Belt DriveDocument76 pagesBelt DrivehaymanotNo ratings yet
- Understanding Your Boats Systems and Choices.From EverandUnderstanding Your Boats Systems and Choices.Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesFrom EverandA Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Knots: An Illustrated Practical Guide to the Essential Knot Types and their UsesFrom EverandKnots: An Illustrated Practical Guide to the Essential Knot Types and their UsesNo ratings yet
- Case Histories in Vibration Analysis and Metal Fatigue for the Practicing EngineerFrom EverandCase Histories in Vibration Analysis and Metal Fatigue for the Practicing EngineerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Eng Eco. EssayDocument1 pageEng Eco. EssayRygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Electrical SubstationDocument1 pageElectrical SubstationRygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 6Document9 pagesME 7 - Activity 6Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 2Document5 pagesME 7 - Activity 2Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 5Document5 pagesME 7 - Activity 5Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 4Document4 pagesME 7 - Activity 4Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Hilti Data Sheet-Hst PDFDocument21 pagesHilti Data Sheet-Hst PDFAnujay Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- DevOps For BeginnersDocument10 pagesDevOps For BeginnersRohit Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Architect ContactsDocument13 pagesArchitect ContactsJeevan PulekarNo ratings yet
- 10 Commandmens of KaikakuDocument3 pages10 Commandmens of Kaikakupolypro78No ratings yet
- Special Operations Forces: The French Land Defence and Security Industry AssociationDocument52 pagesSpecial Operations Forces: The French Land Defence and Security Industry AssociationTsegay Teklay50% (2)
- Fundamentals of Cad Cam CimDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Cad Cam CimRushikesh DandagwhalNo ratings yet
- ST2D PDFDocument4 pagesST2D PDFDragan MedojevicNo ratings yet
- Air Septimanie - Standard Checklist Airbus A320-232 (Locked)Document2 pagesAir Septimanie - Standard Checklist Airbus A320-232 (Locked)Dave Benedick Lariosa ApagNo ratings yet
- Machine MaintenanceDocument55 pagesMachine MaintenanceJobaerNo ratings yet
- CRDocument2 pagesCRGloria JaisonNo ratings yet
- Engine Control Module: Connector ViewsDocument11 pagesEngine Control Module: Connector Viewsluiscarlos2mdNo ratings yet
- PHP Architect - 2017 01 JanuaryDocument52 pagesPHP Architect - 2017 01 JanuaryRafi SMNo ratings yet
- Gravel and Sand SupplyDocument3 pagesGravel and Sand SupplyPhilip Dyaguit BaguhinNo ratings yet
- Presentation THREElerDocument24 pagesPresentation THREElerHector Ledesma IIINo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Probability and Statistics Engr. Darwin M. MurilloDocument4 pagesLecture Notes: Probability and Statistics Engr. Darwin M. MurilloJeremiah MalagueñoNo ratings yet
- Express VPN Activation CodeDocument5 pagesExpress VPN Activation CodeButler49JuulNo ratings yet
- Bus E-Ticket - 60578400Document2 pagesBus E-Ticket - 60578400rsahu_36No ratings yet
- Eltoboard / WWCB Production Plant: Simplified Production Flow ChartDocument1 pageEltoboard / WWCB Production Plant: Simplified Production Flow ChartNorulHishamNo ratings yet
- Steel Reconcilation TridhaatuDocument4 pagesSteel Reconcilation Tridhaatuganesh paradisecorporationNo ratings yet
- Jntuk Fee StructureDocument3 pagesJntuk Fee StructureTeja naveenNo ratings yet
- SdadDocument9 pagesSdadJconz LacaminNo ratings yet
- G Series: Lloow W Ffrreeqquueennccyy TtrraannssdduucceerrDocument2 pagesG Series: Lloow W Ffrreeqquueennccyy TtrraannssdduucceerrFrancisco EscobarNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For Architectural DesignDocument6 pagesThesis Topics For Architectural Designfc2b5myj100% (2)
- Demag DC-Com Chain HoistDocument4 pagesDemag DC-Com Chain Hoistmuhamedz100% (1)
- LID BMP Design Handbook CompleteDocument162 pagesLID BMP Design Handbook CompleteRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- Manual Zoom G1UsbDocument8 pagesManual Zoom G1UsbRogerio TabordaNo ratings yet
- Flakiness IndexDocument6 pagesFlakiness IndexChathura ChamikaraNo ratings yet
- MIT Lab Manual ExperimentsDocument23 pagesMIT Lab Manual Experimentsገብረዮውሃንስ ሃይለኪሮስNo ratings yet
- CARTÃO ANALOGICO RX3i-IC694ALG223Document6 pagesCARTÃO ANALOGICO RX3i-IC694ALG223Rodrigues NogueiraNo ratings yet
- Offshore201309 DLDocument120 pagesOffshore201309 DLmayav1No ratings yet