Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECE 131 Unit 6 - Part 2 - k4
ECE 131 Unit 6 - Part 2 - k4
Uploaded by
abhi shek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views17 pagesCyber physical systems integrate computation, networking, and physical processes to monitor and control the physical world. A cyber physical system is composed of highly integrated computation, communication, control, and physical elements. The internet of things refers to a system of interconnected objects that can collect and exchange data using embedded sensors to monitor and control physical systems and processes. Cloud computing delivers computing resources and services over the internet to provide flexible, scalable access to data, applications, and computing power. Important applications of IoT include wearables, healthcare, agriculture, smart grids/energy savings, automobiles, and manufacturing.
Original Description:
Original Title
ECE 131 unit 6_ part 2_k4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCyber physical systems integrate computation, networking, and physical processes to monitor and control the physical world. A cyber physical system is composed of highly integrated computation, communication, control, and physical elements. The internet of things refers to a system of interconnected objects that can collect and exchange data using embedded sensors to monitor and control physical systems and processes. Cloud computing delivers computing resources and services over the internet to provide flexible, scalable access to data, applications, and computing power. Important applications of IoT include wearables, healthcare, agriculture, smart grids/energy savings, automobiles, and manufacturing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views17 pagesECE 131 Unit 6 - Part 2 - k4
ECE 131 Unit 6 - Part 2 - k4
Uploaded by
abhi shekCyber physical systems integrate computation, networking, and physical processes to monitor and control the physical world. A cyber physical system is composed of highly integrated computation, communication, control, and physical elements. The internet of things refers to a system of interconnected objects that can collect and exchange data using embedded sensors to monitor and control physical systems and processes. Cloud computing delivers computing resources and services over the internet to provide flexible, scalable access to data, applications, and computing power. Important applications of IoT include wearables, healthcare, agriculture, smart grids/energy savings, automobiles, and manufacturing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 17
Cyber Physical Systems
Cyber Physical Systems
• A cyberphysical system is a computer system in which a mechanism is controlled
or monitored by computer-based algorithms
• Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are integrations of computation, networking,
and physical processes. Embedded computers and networks monitor and control
the physical processes, with feedback loops where physical processes affect
computations and vice versa.
• Cyber-Physical System (CPS), a new generation of digital system, mainly focuses on
complex interdependencies and integration between cyberspace and physical world. A
CPS is composed of highly-integrated computation, communication, control,
and physical elements.
Cyber Physical Systems
Internet of things
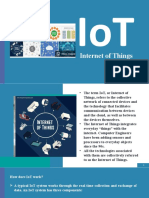
• The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a system of interrelated, internet-connected
objects that are able to collect and transfer data over a wireless network without
human intervention. The personal or business possibilities are endless.
• In short, the Internet of Things refers to the rapidly growing network of
connected objects that are able to collect and exchange data using embedded
sensors. Thermostats, cars, lights, refrigerators, and more appliances can all be
connected to the IoT.
• An IoT system consists of sensors/devices which “talk” to the cloud through some
kind of connectivity. Once the data gets to the cloud, software processes it and
then might decide to perform an action, such as sending an alert or automatically
adjusting the sensors/devices without the need for the user.
• The IoT provides a platform that creates opportunities for people to connect
these devices and control them with big data technology, which in return will
promote efficiency in performance, economic benefits and minimize the need for
human involvement. It's the most important development of the 21st century.
IOT
• The Internet of Things (IOT) is a worldwide network of intercommunicating
devices. It integrates the ubiquitous communications, pervasive computing, and
ambient intelligence. IOT is a vision where “things”, especially everyday objects,
such as all home appliances, furniture, clothes, vehicles, roads and smart
materials, etc. are readable, recognizable, locatable, addressable and/or
controllable via the Internet.
Cloud Computing
• Simply put, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including
servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—
over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and
economies of scale.
• Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources,
especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct
active management by the user. The term is generally used to describe data
centers available to many users over the Internet.
• A simple definition of cloud computing involves delivering different types of
services over the Internet. ... You can access it from just about any computer that
has internet access. For businesses, cloud computing means improved
collaboration and productivity, as well as significant cost reductions.
Important applications of IOT
• Wearables.
• Virtual glasses, fitness bands to monitor for example calorie expenditure and
heart beats, or GPS tracking belts, are just some examples
of wearable devices that we have been using for some time now. Companies
such as Google, Apple, Samsung and others have developed and introduced the
Internet of Things and the application thereof into our daily lives.
• These are small and energy efficient devices, which are equipped with sensors,
with the necessary hardware for measurements and readings, and with software to
collect and organize data and information about users.
Health.
• The use of wearables or sensors connected to patients, allows doctors
to monitor a patient's condition outside the hospital and in real-
time. Through continuously monitoring certain metrics and automatic
alerts on their vital signs, the Internet of Things helps to improve the
care for patients and the prevention of lethal events in high-risk
patients.
• Another use is the integration of IoT technology into hospital beds,
giving way to smart beds, equipped with special sensors to observe
vital signs, blood pressure, oximeter and body temperature, among
others.
Agriculture
• Smart farms are a fact. The quality of soil is crucial to produce good
crops, and the Internet of Things offers farmers the possibility to
access detailed knowledge and valuable information of their soil
condition.
• Through the implementation of IoT sensors, a significant amount of
data can be obtained on the state and stages of the soil. Information
such as soil moisture, level of acidity, the presence of certain
nutrients, temperature and many other chemical characteristics,
helps farmers control irrigation, make water use more efficient,
specify the best times to start sowing, and even discover the
presence of diseases in plants and soil.
Smart grid and energy saving
• The progressive use of intelligent energy meters, or meters equipped with sensors,
and the installation of sensors in different strategic points that go from the
production plants to the different distribution points, allows better monitoring and
control of the electrical network.
• IoT can be used in customer side in smart meters to measure different types of
parameters, intelligent power consumption, interoperability between different
networks, charging and discharging of electric vehicles, manage energy efficiency
and power demand.
• By establishing a bidirectional communication between the service provider
company and the end user, information of enormous value can be obtained for the
detection of faults, decision making and repair thereof.
• It also allows offering valuable information to the end user about their
consumption patterns and about the best ways to reduce or adjust their energy
expenditure.
Smart Grid
IOT in automobiles
• IoT infused semi-autonomous cars take on-spot decisions while partly
controlling the vehicle operations to avoid accidents and reduce the
load from the driver. Along with different proximity sensors and
cameras, cars are integrated with IoT systems to reduce human error
and make driving more comfortable and safe.
IOT in automobiles
Manufacturing
• Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a way to digital transformation in
manufacturing. Industrial IoT employs a network of sensors to collect critical
production data and uses cloud software to turn this data into valuable insights
about the efficiency of the manufacturing operations.
You might also like
- Home Automation Using IOT With Integration of Solar Based Energy SystemDocument23 pagesHome Automation Using IOT With Integration of Solar Based Energy Systemswati100% (1)
- Internet of ThingsDocument17 pagesInternet of ThingsmastermasterNo ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesNewtons 2nd Law Practice ProblemsJehmmaRosalesCarpisoNo ratings yet
- Iot Components:: Internet of ThingsDocument4 pagesIot Components:: Internet of ThingsHizkiaNo ratings yet
- ITELEC3207 Module1 Introduction-to-IoTDocument8 pagesITELEC3207 Module1 Introduction-to-IoTPatricia AnnNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - IoTDocument113 pagesUNIT 1 - IoTCharveer “CHARVEERTV” tvNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument68 pagesInternet of Thingsgilvantalosig0618No ratings yet
- Module 1 IOTDocument103 pagesModule 1 IOTu2001170No ratings yet
- Green Internet of Things For Smart World: Y. Mani Kiran KumarDocument21 pagesGreen Internet of Things For Smart World: Y. Mani Kiran KumarAmalNo ratings yet
- 1.3 IoTDocument27 pages1.3 IoTkishoreNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things: SEPTEMBER 20, 2017Document5 pagesInternet of Things: SEPTEMBER 20, 2017mundal minatiNo ratings yet
- Dast Unit1Document8 pagesDast Unit1Karunya MannavaNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument6 pagesInternet of ThingsKartik AayushNo ratings yet
- Emergence of IoTDocument10 pagesEmergence of IoTnalasupreet27No ratings yet
- Untitleddesign Original 2Document11 pagesUntitleddesign Original 2Misba KhanNo ratings yet
- IoT QB AnsDocument25 pagesIoT QB Ansvijay amrutkarNo ratings yet
- Cloud Customer Architecture For Iot: Executive OverviewDocument22 pagesCloud Customer Architecture For Iot: Executive OverviewRuqaiya KhanamNo ratings yet
- Iot (1-5 Units) - 1Document103 pagesIot (1-5 Units) - 12306603No ratings yet
- Smart Cities Uusing IoTDocument25 pagesSmart Cities Uusing IoTLingam sasthaNo ratings yet
- IotDocument2 pagesIotdevan2020 MNo ratings yet
- World of Internet of Thingsapplications of IotDocument6 pagesWorld of Internet of Thingsapplications of IotKirti PatilNo ratings yet
- Iot BasicsDocument43 pagesIot BasicsFarhan SjNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things - Module5Document9 pagesThe Internet of Things - Module5Basil StalinNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 ECE3501 ETH VL2022230102387 Reference Material I 11-08-2022 IoTDocument35 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 ECE3501 ETH VL2022230102387 Reference Material I 11-08-2022 IoTAanchal VermaNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument64 pagesInternet of ThingsSriram SudheerNo ratings yet
- What Is The Internet of Things?: Internet de Las Cosas (Iot) 1 de Marzo de 2022Document3 pagesWhat Is The Internet of Things?: Internet de Las Cosas (Iot) 1 de Marzo de 2022Humberto RamosNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument9 pagesInternet of ThingsKwon NieNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document62 pagesUnit 1selvapriya biherNo ratings yet
- IoT Unit 1Document27 pagesIoT Unit 1tanishNo ratings yet
- FET CharacteristicDocument10 pagesFET CharacteristicZaid Abbas AliNo ratings yet
- 159Document10 pages159Yash VardhanNo ratings yet
- IOT - Transforming The Way We Live and WorkDocument8 pagesIOT - Transforming The Way We Live and Workgoelbhawna1801No ratings yet
- Iot (Internet of Things)Document4 pagesIot (Internet of Things)Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument19 pagesInternet of Thingssammie celeNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument11 pagesInternet of Thingsالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesLecture Notesgiordan24aNo ratings yet
- Iot AbstractDocument4 pagesIot Abstractvijay bharath reddy DinnepuNo ratings yet
- 1A.Define Iot. Describe The Characteristics of Internet of Things Iot?Document35 pages1A.Define Iot. Describe The Characteristics of Internet of Things Iot?Kummitha SravaniNo ratings yet
- Internet of ThingsDocument20 pagesInternet of Thingssnikhath20No ratings yet
- Emerging TechnologyDocument45 pagesEmerging TechnologybeuradmasuNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of IoTDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of IoTakramshaik2004No ratings yet
- Introduction To Iot Chapter 2 NotesDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Iot Chapter 2 NoteskpadmajaNo ratings yet
- Iot Internet of ThingsDocument23 pagesIot Internet of ThingsNisha HiremathNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5PART IIIIoT Applications For Value CreationsDocument26 pagesUNIT 5PART IIIIoT Applications For Value CreationsAayush KharkiaNo ratings yet
- Interinet of ThingDocument15 pagesInterinet of ThingAgmasie TsegaNo ratings yet
- SCSA1408Document137 pagesSCSA1408RamziNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.3Document52 pagesUnit 2.3sonavanepraniteeNo ratings yet
- Applications of IOT: Created by Course Code-Cap441Document9 pagesApplications of IOT: Created by Course Code-Cap441Jovan SandhuNo ratings yet
- Shahroz Khan Information System AssignmentDocument10 pagesShahroz Khan Information System AssignmentAyaanJawwadNo ratings yet
- Iot 1Document21 pagesIot 1akramshaik2004No ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Internet of Things (Iot)Document31 pagesChapter Four: Internet of Things (Iot)mahammedNo ratings yet
- Iot Unit-5Document18 pagesIot Unit-5Ashok (Ak)No ratings yet
- Internet of Things (IOT)Document17 pagesInternet of Things (IOT)hemapriyalakshsmanan27No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1jahnavisv7No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On IotDocument21 pagesA Comprehensive Study On IotAman Saxena100% (1)
- The Internet of Things and Its Future PotentialDocument6 pagesThe Internet of Things and Its Future PotentialAKNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of IotDocument15 pagesA Comprehensive Study of IotAman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things: Unit I - IntroductionDocument88 pagesInternet of Things: Unit I - IntroductionSuganthi RavindrenNo ratings yet
- IOTDocument17 pagesIOTVansh SainiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technology Overivew of Iot Unit-I Part-1Document21 pagesEmerging Technology Overivew of Iot Unit-I Part-1Manya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 - Newton Ringsfor StudentsDocument15 pagesExperiment No 3 - Newton Ringsfor Studentsabhi shekNo ratings yet
- Dielectric ConstantDocument26 pagesDielectric Constantabhi shekNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Constant - For StudentsDocument17 pagesDielectric Constant - For Studentsabhi shekNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 L3 K131Document27 pagesUnit 1 L3 K131abhi shekNo ratings yet
- L6 L7 13thseptemberDocument74 pagesL6 L7 13thseptemberabhi shekNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 L! L2 K131Document49 pagesUnit 1 L! L2 K131abhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit6 Part1 K2Document66 pagesECE131 Unit6 Part1 K2abhi shekNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 ECE131 - Part 4 - K1Document66 pagesUnit 6 ECE131 - Part 4 - K1abhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit6 Part2 k3Document38 pagesECE131 Unit6 Part2 k3abhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 UNIT5 Part4Document51 pagesECE131 UNIT5 Part4abhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 UNIT5 Part2 KDocument44 pagesECE131 UNIT5 Part2 Kabhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit2 DrKrishankumar KDocument131 pagesECE131 Unit2 DrKrishankumar Kabhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 UNIT5 Part1 KDocument32 pagesECE131 UNIT5 Part1 Kabhi shekNo ratings yet
- ECE131 UNIT5 Part3Document88 pagesECE131 UNIT5 Part3abhi shek100% (1)
- FabFilter Volcano 2Document43 pagesFabFilter Volcano 2David Esteves RuizNo ratings yet
- Nordys Daniel Jovita: Contact Number: 09505910416 Address: Aflek Tboli South CotabatoDocument2 pagesNordys Daniel Jovita: Contact Number: 09505910416 Address: Aflek Tboli South CotabatoNoreen JovitaNo ratings yet
- Tornillo Autop. P-BR ZN 10 X 3-4 (Pat-21138 + T)Document1 pageTornillo Autop. P-BR ZN 10 X 3-4 (Pat-21138 + T)L Caqui PascacioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Copulas: Mark S. Tenney Mathematical Finance Company July 18, 2003Document9 pagesIntroduction To Copulas: Mark S. Tenney Mathematical Finance Company July 18, 2003Mario CruzNo ratings yet
- DKG-329 Ats Controller: 2 Gensets + MainsDocument2 pagesDKG-329 Ats Controller: 2 Gensets + MainsmxnoxnNo ratings yet
- Senior HighschoolDocument3 pagesSenior HighschoolAngelica MathewNo ratings yet
- WPS No.: 1.203 Rev.: 4Document2 pagesWPS No.: 1.203 Rev.: 4beyNo ratings yet
- Part 1. WRICM PDFDocument22 pagesPart 1. WRICM PDFPatrick PascasioNo ratings yet
- Water Management Rules As MWELO in Los AngelesDocument2 pagesWater Management Rules As MWELO in Los AngelesPrecise Landscape Water ConservationNo ratings yet
- Color Atlas of Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument223 pagesColor Atlas of Diagnostic MicrobiologyOana Herea100% (2)
- J6-S9014 DatasheetDocument2 pagesJ6-S9014 DatasheetOreol100% (1)
- Carlyn Shear ResumeDocument1 pageCarlyn Shear ResumecarlynshearNo ratings yet
- Test3SP22 Attempt ReviewDocument22 pagesTest3SP22 Attempt ReviewTrần KhangNo ratings yet
- Afm EmergencyDocument114 pagesAfm EmergencyJimmy SteepNo ratings yet
- RT Usersguide PDFDocument36 pagesRT Usersguide PDFRoy RamosNo ratings yet
- SSM Lesson 6 For DPDocument3 pagesSSM Lesson 6 For DPapi-376078390No ratings yet
- Small Group Anger ManagementDocument4 pagesSmall Group Anger ManagementPaul SarsfieldNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument6 pagesDocxherrajohn100% (1)
- Placas DialogicDocument53 pagesPlacas DialogicJULIOLIVANo ratings yet
- Count in Ones To 20 - Identify and Represent Some Two-Digit Numbers Using Objects and PicturesDocument5 pagesCount in Ones To 20 - Identify and Represent Some Two-Digit Numbers Using Objects and Picturesmaitha ALNNo ratings yet
- Manual XolidoSign V 2 2 1 en Signed by XOLIDO SYSTEMSDocument57 pagesManual XolidoSign V 2 2 1 en Signed by XOLIDO SYSTEMSΠαναγιώτης Παυλ. ΜαρούδαςNo ratings yet
- Whitman Resume AnnotatedDocument1 pageWhitman Resume Annotatedapi-664114983No ratings yet
- Saha, 2003Document16 pagesSaha, 2003LA ArenqueNo ratings yet
- Fleetwood Town Centre PlanDocument65 pagesFleetwood Town Centre PlanPaulNo ratings yet
- Ensemble Performance: Elaine GoodmanDocument10 pagesEnsemble Performance: Elaine GoodmanizzatbukhoriNo ratings yet
- Hindu CalendarDocument18 pagesHindu CalendarSanjay Jayaratne100% (1)
- News Letter PDF April 2021Document8 pagesNews Letter PDF April 2021Vivekananda KendraNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Basics BDocument120 pagesDigital Logic Basics BFahad GhanyNo ratings yet
- Ui22 Lab1Document5 pagesUi22 Lab1dattpatel2020No ratings yet