Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 viewsBio MXQ
Bio MXQ
Uploaded by
Maheen ishfaqCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Chemical Pathology Questions For DiplomaDocument11 pagesChemical Pathology Questions For DiplomaSAMMY50% (2)
- Family and Consumer Life Skill/SciencesDocument16 pagesFamily and Consumer Life Skill/SciencesCherry Lyn Galagar100% (4)
- Phlebotomy TestDocument11 pagesPhlebotomy TestRaquel Girón75% (4)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management in Banking Sector-A Case Study of PNBDocument27 pagesCustomer Relationship Management in Banking Sector-A Case Study of PNBmanicoolgal4u100% (1)
- Mass and Heat Transfer Analysis of Mass Cont Actors and Heat Ex Changers (Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering)Document405 pagesMass and Heat Transfer Analysis of Mass Cont Actors and Heat Ex Changers (Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering)Kaliyaram Viswambaram100% (1)
- ch19 PDFDocument60 pagesch19 PDFMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 CirculatoryDocument6 pagesPractice Questions 1 CirculatoryAdelaide Fleona Marie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Eritrosit, Plasma Dan HBDocument20 pagesLatihan Soal Eritrosit, Plasma Dan HBHayckal Hasanal MNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing On Circulatory and Respiratory QuestionsDocument28 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing On Circulatory and Respiratory QuestionsyormahdNo ratings yet
- A and P II: Test I Review Questions On Cardiovascular SystemDocument50 pagesA and P II: Test I Review Questions On Cardiovascular SystemMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Q For MLTDocument11 pagesSAMPLE Q For MLTdursaabdurezak5240No ratings yet
- First Year Complete Physiology MCQ Bank by Team DR Of2027-28Document284 pagesFirst Year Complete Physiology MCQ Bank by Team DR Of2027-28ammejan10100% (2)
- Exercise Circulatory 4.1Document7 pagesExercise Circulatory 4.1adriana D oleoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document12 pagesPaper 2Yeim Khay MoNo ratings yet
- Blood MCQ New 5Document21 pagesBlood MCQ New 5Omar HNo ratings yet
- Ch. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsAsad YaminNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test BankDocument27 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test Bankdulciethanhonjja4100% (37)
- Review and Assessment (The Component of The Blood)Document5 pagesReview and Assessment (The Component of The Blood)DruunNo ratings yet
- General Medicine MCQDocument73 pagesGeneral Medicine MCQkhalida shaik begumNo ratings yet
- 8th Mid McqsDocument25 pages8th Mid McqsMuhammad Uzair GujjarNo ratings yet
- Blood Test2Document4 pagesBlood Test2Sheba Dan de WiseNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document33 pagesCH 19Blythe Williams100% (2)
- 150 Most Important General Science MCQ: Gauhati B.Ed EntranceDocument31 pages150 Most Important General Science MCQ: Gauhati B.Ed EntranceAjoy SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDF Test Bank For Human Biology 16Th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument45 pagesPDF Test Bank For Human Biology 16Th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht Online Ebook Full Chaptertimothy.owens520100% (4)
- IGCSE I Past PapersDocument13 pagesIGCSE I Past PapersDana Al-WakilNo ratings yet
- MCQ On BloodDocument11 pagesMCQ On Bloodgpay98No ratings yet
- Questions - Answered. (Lectures 1 4) 1Document13 pagesQuestions - Answered. (Lectures 1 4) 1ahmedabdalnaser87No ratings yet
- Vocabulary ReviewDocument18 pagesVocabulary Reviewduonghi3lpsNo ratings yet
- PRELIM Exam in Science 9Document5 pagesPRELIM Exam in Science 9Mohammad Javier D. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- FilDocument6 pagesFilLadyxyrell Mandahinog ParbaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument5 pagesBloodNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- MCQ On ErythropoiesisDocument6 pagesMCQ On ErythropoiesisIrekton GGNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerG06 Guela, Aliyah NicoleNo ratings yet
- Test 9 BDSDocument11 pagesTest 9 BDSrababNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document8 pagesGrade 8Mohammad Zaid Sayaheen50% (2)
- Lab Technician-10Document3 pagesLab Technician-10AHAMED SHIFAANNo ratings yet
- 101 Modul Hebat Bio 2021 - PDF - Eng-47-55Document9 pages101 Modul Hebat Bio 2021 - PDF - Eng-47-55BF CLNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids Extra MaterialDocument42 pagesBody Fluids Extra MaterialpreitaphilenaNo ratings yet
- Blood Questions Human Physiology PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Questions Human Physiology PDFARUSHI ARVIND100% (2)
- E04f18mm AnswersDocument6 pagesE04f18mm AnswersMike MullerNo ratings yet
- Soalan Objektif Mac2014Document2 pagesSoalan Objektif Mac2014Siti NajwaNo ratings yet
- 1stQ G9 Test QuestionsDocument5 pages1stQ G9 Test QuestionsMichNo ratings yet
- Biology SPM Forecast PapersDocument21 pagesBiology SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document4 pagesScience 9Maria Elaine Feranil33% (3)
- Lab Technologist-4Document32 pagesLab Technologist-4AHAMED SHIFAANNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument8 pagesHematologyHawaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Exam CardioAPFinalExamStudyGuideDocument19 pagesExam CardioAPFinalExamStudyGuideGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- First QuarterDocument6 pagesFirst QuarterDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument50 pagesFull Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Online PDF All Chapterkeelymacewcndu488100% (5)
- Blood Module Theory 18 05 21 FinalDocument87 pagesBlood Module Theory 18 05 21 FinalAmsha MangiNo ratings yet
- Module 12 The Composition and Function of BloodDocument11 pagesModule 12 The Composition and Function of BloodMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- NDA Biology Questions With AnswersDocument4 pagesNDA Biology Questions With Answerskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- G9 ExamDocument3 pagesG9 ExamLuke LunaNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument2 pagesQUIZChristine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Bio Sidra Test Chap 9,10 MdcatDocument13 pagesBio Sidra Test Chap 9,10 MdcatGhulam zahraNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation QuestionsDocument3 pagesBlood Circulation QuestionsMo GamerNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Summary TestDocument4 pages1st Quarter Summary TestAris Herrera AbesNo ratings yet
- S9 Q4 M1 Transport and Excretion and Respiration and Energy Exchange QuizDocument3 pagesS9 Q4 M1 Transport and Excretion and Respiration and Energy Exchange QuizJermae DizonNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Full ChapterDocument50 pages(Download PDF) Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Full Chapterkucharinoj62100% (7)
- A& P II Assignment 2Document5 pagesA& P II Assignment 2hepnandeNo ratings yet
- Sebial Vs SebialDocument4 pagesSebial Vs SebialNC BergoniaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pages3rd Quarter ReviewerKoch RyleNo ratings yet
- MM Certification QuestionsDocument13 pagesMM Certification Questionssmiler21No ratings yet
- 254 Scra 307 - Spouses Trinidad Vs Ang FULLDocument46 pages254 Scra 307 - Spouses Trinidad Vs Ang FULLRonald Alasa-as AtigNo ratings yet
- IA Article Defence Witness Statements 19 November 2020Document3 pagesIA Article Defence Witness Statements 19 November 2020Sara ChessaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Teacher Development Through Exploring Classroom Processes PDFDocument5 pagesIntroduction Teacher Development Through Exploring Classroom Processes PDFLuzke CalleNo ratings yet
- Evening Street Review Number 31Document181 pagesEvening Street Review Number 31Barbara BergmannNo ratings yet
- My Five Senses - Webquest RubricDocument1 pageMy Five Senses - Webquest Rubricapi-279898036No ratings yet
- 2020 A New Frontier in Pelvic Fracture Pain Control in The ED Successful Use of The Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) BlockDocument5 pages2020 A New Frontier in Pelvic Fracture Pain Control in The ED Successful Use of The Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) Block林煒No ratings yet
- Linear Programming: Basic Concepts: Irwin/Mcgraw-HillDocument30 pagesLinear Programming: Basic Concepts: Irwin/Mcgraw-Hillgttrans111No ratings yet
- Visual Images of How To Accomplish The Measurement: Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (Muac) / Waist-Hip RatioDocument5 pagesVisual Images of How To Accomplish The Measurement: Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (Muac) / Waist-Hip RatioggggangNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Risk Management FrameworkDocument51 pagesImplementing A Risk Management FrameworkSayyid ShalahuddinNo ratings yet
- British Council Historical ReportDocument12 pagesBritish Council Historical ReportBrock TernovNo ratings yet
- SSITM Newsletter - "Lakshya" - July-Sept11Document8 pagesSSITM Newsletter - "Lakshya" - July-Sept11Saket JeswaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityDocument43 pagesChapter II - The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityLes SircNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-31408 April 22, 1991Document1 pageG.R. No. L-31408 April 22, 1991Kikoy IlaganNo ratings yet
- PeramalanDocument6 pagesPeramalanN LailyNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 - Perilaku BiayaDocument40 pagesBab 2 - Perilaku BiayaAndy ReynaldyyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Market Orientation, Entrepreneurial Orientation, and Firm Performance in Thai Smes: The Mediating Role of Marketing CapabilitiesDocument25 pagesRelationship Between Market Orientation, Entrepreneurial Orientation, and Firm Performance in Thai Smes: The Mediating Role of Marketing CapabilitiesMahipal18No ratings yet
- Plant Disease in SugarncaneDocument20 pagesPlant Disease in SugarncaneMalik HashmatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AlgebraDocument477 pagesIntroduction To AlgebraFranknire IgNo ratings yet
- Information AgeDocument33 pagesInformation AgeRheajen Mae RebamonteNo ratings yet
- Ms - Shruti Vs Baldev Singh and Others On 23 May, 2017Document8 pagesMs - Shruti Vs Baldev Singh and Others On 23 May, 2017spgkumar7733No ratings yet
- TABLE OF CONTENTS RpmsDocument3 pagesTABLE OF CONTENTS RpmsJaps De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Greetings - Wordsearch: Worksheet #2Document2 pagesGreetings - Wordsearch: Worksheet #2Yacely HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Cassie Ann Ross Goddard College Mfaia PortfolioDocument77 pagesCassie Ann Ross Goddard College Mfaia Portfolioapi-279277913No ratings yet
- Oral Presentation RubricDocument1 pageOral Presentation RubricMikha NauliNo ratings yet
Bio MXQ
Bio MXQ
Uploaded by
Maheen ishfaq0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views6 pagesOriginal Title
bio mxq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views6 pagesBio MXQ
Bio MXQ
Uploaded by
Maheen ishfaqCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
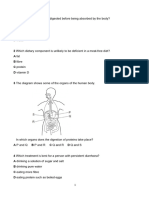
1. Which cells destroy harmful microorganisms in the blood?
A goblet cells B Platelets C red blood cells D white blood cells
2. What is the fluid in the blood called?
A lymph B Mucus C Plasma D tissue fluid
3. Where are red blood cells produced?
A heart B lungs C bone marrow D blood
4. Most of the volume of normal human blood is composed of:
Red cell B white cell C platelets D plasma
5. Erythrocyte is another name for a
A red cell B white cell C platelets D phagocyte
6. Red blood cells make up .................percent of blood
A 54 % B 45 % C 56 % D 1 %
7. What is needed to make the haemoglobin in red blood cells?
A calcium B iron C roughage D vitamin D
8. Which substance is transported by haemoglobin?
A nitrogen B oxygen C urea D water
9. Which blood cells pick up and carry oxygen?
A red blood cells B White blood cells C platelets D lymphocytes
10. What gives blood its color?
A haemoglobin B Oxyhaemoglobin C oxygen D iron
11. Where does haemoglobin become oxyhaemoglobin?
A heart B kidneys C liver D lungs
12. Which cells destroy harmful microorganisms in the blood?
A goblet cells B platelets C red blood cells D white blood cells
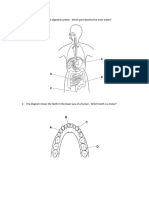
13. What causes the transfer of materials between capillaries and tissue
fluid?
A active transport B blood pressure C capillarity D osmosis
14. Which of the following blood components provide the major defense for
our bodies against invading
bacteria and viruses?
A red cell B white cell C platelets D erythrocytes
15. In a person with a low platelet level, which process is slower than
normal?
A antibody formation B blood clotting C oxygen carriage D phagocytosis
16. Which of the following is the function of white blood cells?
A Transport oxygen. B Maintain homeostasis.
C Defend against infection. D Produce haemoglobin
17. Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma?
A carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose B carbon dioxide, oxygen and
haemoglobin
C glucose, hormones and urea D oxygen, urea and starch
18. Which group contains substances that are all carried in the blood?
A amino acids, carbon dioxide and cellulose B glucose, glycogen and lactic
acid
C oestrogen, oxygen and starch D salts, testosterone and urea
19. Which of the following statements about erythrocytes is correct?
A They fight infection B They clot blood C They lack a nucleus
20. What would happen to red blood cells if the haem group were removed
from haemoglobin?
A Red blood cells would not be able to bind oxygen.
B Red blood cells would not be able to reproduce.
C White blood cells would not be able to reproduce.
D Blood clot formation would be inhibited.
21. What is a function of the human blood system?
A. carrying eggs from the ovary to the uterus
B. carrying glucose from the gut to the liver
C. carrying partly digested food from the mouth to the stomach
D. carrying urine from the kidney to the bladder
22. A hospital patient who is feeling unwell is given a blood test. The results
of the blood test show a very
low level of platelets. What effect will this have?
A The blood will be unable to transport nutrients, hormones and carbon
dioxide.
B The blood will not be able to carry as much oxygen to the tissues as
normal.
C There will be a greater risk of bleeding because the blood will take longer
to clot.
D There will be a greater risk of infection because the blood cannot make
antibodies.
How much oxygen would red blood cells be likely to carry
when leaving the same muscle after contraction? A 40%
B 60% C 90% D 100%
e
A to carry glucose B to carry oxygen C to defend
against disease D to make the blood cells
You might also like
- Chemical Pathology Questions For DiplomaDocument11 pagesChemical Pathology Questions For DiplomaSAMMY50% (2)
- Family and Consumer Life Skill/SciencesDocument16 pagesFamily and Consumer Life Skill/SciencesCherry Lyn Galagar100% (4)
- Phlebotomy TestDocument11 pagesPhlebotomy TestRaquel Girón75% (4)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management in Banking Sector-A Case Study of PNBDocument27 pagesCustomer Relationship Management in Banking Sector-A Case Study of PNBmanicoolgal4u100% (1)
- Mass and Heat Transfer Analysis of Mass Cont Actors and Heat Ex Changers (Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering)Document405 pagesMass and Heat Transfer Analysis of Mass Cont Actors and Heat Ex Changers (Cambridge Series in Chemical Engineering)Kaliyaram Viswambaram100% (1)
- ch19 PDFDocument60 pagesch19 PDFMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 CirculatoryDocument6 pagesPractice Questions 1 CirculatoryAdelaide Fleona Marie TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Eritrosit, Plasma Dan HBDocument20 pagesLatihan Soal Eritrosit, Plasma Dan HBHayckal Hasanal MNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing On Circulatory and Respiratory QuestionsDocument28 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing On Circulatory and Respiratory QuestionsyormahdNo ratings yet
- A and P II: Test I Review Questions On Cardiovascular SystemDocument50 pagesA and P II: Test I Review Questions On Cardiovascular SystemMartina MicicNo ratings yet
- SAMPLE Q For MLTDocument11 pagesSAMPLE Q For MLTdursaabdurezak5240No ratings yet
- First Year Complete Physiology MCQ Bank by Team DR Of2027-28Document284 pagesFirst Year Complete Physiology MCQ Bank by Team DR Of2027-28ammejan10100% (2)
- Exercise Circulatory 4.1Document7 pagesExercise Circulatory 4.1adriana D oleoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document12 pagesPaper 2Yeim Khay MoNo ratings yet
- Blood MCQ New 5Document21 pagesBlood MCQ New 5Omar HNo ratings yet
- Ch. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsAsad YaminNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test BankDocument27 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test Bankdulciethanhonjja4100% (37)
- Review and Assessment (The Component of The Blood)Document5 pagesReview and Assessment (The Component of The Blood)DruunNo ratings yet
- General Medicine MCQDocument73 pagesGeneral Medicine MCQkhalida shaik begumNo ratings yet
- 8th Mid McqsDocument25 pages8th Mid McqsMuhammad Uzair GujjarNo ratings yet
- Blood Test2Document4 pagesBlood Test2Sheba Dan de WiseNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document33 pagesCH 19Blythe Williams100% (2)
- 150 Most Important General Science MCQ: Gauhati B.Ed EntranceDocument31 pages150 Most Important General Science MCQ: Gauhati B.Ed EntranceAjoy SharmaNo ratings yet
- PDF Test Bank For Human Biology 16Th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht Online Ebook Full ChapterDocument45 pagesPDF Test Bank For Human Biology 16Th Edition Sylvia Mader Michael Windelspecht Online Ebook Full Chaptertimothy.owens520100% (4)
- IGCSE I Past PapersDocument13 pagesIGCSE I Past PapersDana Al-WakilNo ratings yet
- MCQ On BloodDocument11 pagesMCQ On Bloodgpay98No ratings yet
- Questions - Answered. (Lectures 1 4) 1Document13 pagesQuestions - Answered. (Lectures 1 4) 1ahmedabdalnaser87No ratings yet
- Vocabulary ReviewDocument18 pagesVocabulary Reviewduonghi3lpsNo ratings yet
- PRELIM Exam in Science 9Document5 pagesPRELIM Exam in Science 9Mohammad Javier D. DimaporoNo ratings yet
- FilDocument6 pagesFilLadyxyrell Mandahinog ParbaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument5 pagesBloodNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- MCQ On ErythropoiesisDocument6 pagesMCQ On ErythropoiesisIrekton GGNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerG06 Guela, Aliyah NicoleNo ratings yet
- Test 9 BDSDocument11 pagesTest 9 BDSrababNo ratings yet
- Grade 8Document8 pagesGrade 8Mohammad Zaid Sayaheen50% (2)
- Lab Technician-10Document3 pagesLab Technician-10AHAMED SHIFAANNo ratings yet
- 101 Modul Hebat Bio 2021 - PDF - Eng-47-55Document9 pages101 Modul Hebat Bio 2021 - PDF - Eng-47-55BF CLNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids Extra MaterialDocument42 pagesBody Fluids Extra MaterialpreitaphilenaNo ratings yet
- Blood Questions Human Physiology PDFDocument5 pagesBlood Questions Human Physiology PDFARUSHI ARVIND100% (2)
- E04f18mm AnswersDocument6 pagesE04f18mm AnswersMike MullerNo ratings yet
- Soalan Objektif Mac2014Document2 pagesSoalan Objektif Mac2014Siti NajwaNo ratings yet
- 1stQ G9 Test QuestionsDocument5 pages1stQ G9 Test QuestionsMichNo ratings yet
- Biology SPM Forecast PapersDocument21 pagesBiology SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document4 pagesScience 9Maria Elaine Feranil33% (3)
- Lab Technologist-4Document32 pagesLab Technologist-4AHAMED SHIFAANNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument8 pagesHematologyHawaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Exam CardioAPFinalExamStudyGuideDocument19 pagesExam CardioAPFinalExamStudyGuideGustavo OlguinNo ratings yet
- First QuarterDocument6 pagesFirst QuarterDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Full Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument50 pagesFull Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Online PDF All Chapterkeelymacewcndu488100% (5)
- Blood Module Theory 18 05 21 FinalDocument87 pagesBlood Module Theory 18 05 21 FinalAmsha MangiNo ratings yet
- Module 12 The Composition and Function of BloodDocument11 pagesModule 12 The Composition and Function of BloodMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- NDA Biology Questions With AnswersDocument4 pagesNDA Biology Questions With Answerskumar HarshNo ratings yet
- G9 ExamDocument3 pagesG9 ExamLuke LunaNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument2 pagesQUIZChristine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Bio Sidra Test Chap 9,10 MdcatDocument13 pagesBio Sidra Test Chap 9,10 MdcatGhulam zahraNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation QuestionsDocument3 pagesBlood Circulation QuestionsMo GamerNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Summary TestDocument4 pages1st Quarter Summary TestAris Herrera AbesNo ratings yet
- S9 Q4 M1 Transport and Excretion and Respiration and Energy Exchange QuizDocument3 pagesS9 Q4 M1 Transport and Excretion and Respiration and Energy Exchange QuizJermae DizonNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Full ChapterDocument50 pages(Download PDF) Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Canadian 4th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Full Chapterkucharinoj62100% (7)
- A& P II Assignment 2Document5 pagesA& P II Assignment 2hepnandeNo ratings yet
- Sebial Vs SebialDocument4 pagesSebial Vs SebialNC BergoniaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pages3rd Quarter ReviewerKoch RyleNo ratings yet
- MM Certification QuestionsDocument13 pagesMM Certification Questionssmiler21No ratings yet
- 254 Scra 307 - Spouses Trinidad Vs Ang FULLDocument46 pages254 Scra 307 - Spouses Trinidad Vs Ang FULLRonald Alasa-as AtigNo ratings yet
- IA Article Defence Witness Statements 19 November 2020Document3 pagesIA Article Defence Witness Statements 19 November 2020Sara ChessaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Teacher Development Through Exploring Classroom Processes PDFDocument5 pagesIntroduction Teacher Development Through Exploring Classroom Processes PDFLuzke CalleNo ratings yet
- Evening Street Review Number 31Document181 pagesEvening Street Review Number 31Barbara BergmannNo ratings yet
- My Five Senses - Webquest RubricDocument1 pageMy Five Senses - Webquest Rubricapi-279898036No ratings yet
- 2020 A New Frontier in Pelvic Fracture Pain Control in The ED Successful Use of The Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) BlockDocument5 pages2020 A New Frontier in Pelvic Fracture Pain Control in The ED Successful Use of The Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) Block林煒No ratings yet
- Linear Programming: Basic Concepts: Irwin/Mcgraw-HillDocument30 pagesLinear Programming: Basic Concepts: Irwin/Mcgraw-Hillgttrans111No ratings yet
- Visual Images of How To Accomplish The Measurement: Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (Muac) / Waist-Hip RatioDocument5 pagesVisual Images of How To Accomplish The Measurement: Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (Muac) / Waist-Hip RatioggggangNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Risk Management FrameworkDocument51 pagesImplementing A Risk Management FrameworkSayyid ShalahuddinNo ratings yet
- British Council Historical ReportDocument12 pagesBritish Council Historical ReportBrock TernovNo ratings yet
- SSITM Newsletter - "Lakshya" - July-Sept11Document8 pagesSSITM Newsletter - "Lakshya" - July-Sept11Saket JeswaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityDocument43 pagesChapter II - The Teacher in The Classroom and CommunityLes SircNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-31408 April 22, 1991Document1 pageG.R. No. L-31408 April 22, 1991Kikoy IlaganNo ratings yet
- PeramalanDocument6 pagesPeramalanN LailyNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 - Perilaku BiayaDocument40 pagesBab 2 - Perilaku BiayaAndy ReynaldyyNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Market Orientation, Entrepreneurial Orientation, and Firm Performance in Thai Smes: The Mediating Role of Marketing CapabilitiesDocument25 pagesRelationship Between Market Orientation, Entrepreneurial Orientation, and Firm Performance in Thai Smes: The Mediating Role of Marketing CapabilitiesMahipal18No ratings yet
- Plant Disease in SugarncaneDocument20 pagesPlant Disease in SugarncaneMalik HashmatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AlgebraDocument477 pagesIntroduction To AlgebraFranknire IgNo ratings yet
- Information AgeDocument33 pagesInformation AgeRheajen Mae RebamonteNo ratings yet
- Ms - Shruti Vs Baldev Singh and Others On 23 May, 2017Document8 pagesMs - Shruti Vs Baldev Singh and Others On 23 May, 2017spgkumar7733No ratings yet
- TABLE OF CONTENTS RpmsDocument3 pagesTABLE OF CONTENTS RpmsJaps De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Greetings - Wordsearch: Worksheet #2Document2 pagesGreetings - Wordsearch: Worksheet #2Yacely HuamaniNo ratings yet
- Cassie Ann Ross Goddard College Mfaia PortfolioDocument77 pagesCassie Ann Ross Goddard College Mfaia Portfolioapi-279277913No ratings yet
- Oral Presentation RubricDocument1 pageOral Presentation RubricMikha NauliNo ratings yet