Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Black and Brown Business Brochure
Black and Brown Business Brochure
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hippo Education Hippo EM - Dermatology Written SummaryDocument7 pagesHippo Education Hippo EM - Dermatology Written Summarykaylawilliam01100% (1)
- International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS)Document7 pagesInternational Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS)Dy RPNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Nursing Care On Women Who Have Undergone Abdominal Hysterectomy at Post-Operative Work in Government Head Quarters Hospital, Kancheepuram, District, TamilnaduDocument2 pagesEffectiveness of Nursing Care On Women Who Have Undergone Abdominal Hysterectomy at Post-Operative Work in Government Head Quarters Hospital, Kancheepuram, District, TamilnaduInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Man Ther 2013 Barra LópezDocument7 pagesMan Ther 2013 Barra LópezRuggiero CannitoNo ratings yet
- Acu Back PelvicPain in Pregnancy RCT 1Document6 pagesAcu Back PelvicPain in Pregnancy RCT 1QuackeryNo ratings yet
- To Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Pectoral Nerve Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Breast SurgeriesDocument4 pagesTo Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Pectoral Nerve Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Breast SurgeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Successful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyDocument3 pagesSuccessful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyEres TriasaNo ratings yet
- IJNER - 597 - 27 07 2018 Paper - R - 21Document7 pagesIJNER - 597 - 27 07 2018 Paper - R - 21Yuning tyas Nursyah FitriNo ratings yet
- Medip, ISJ-5301 ODocument4 pagesMedip, ISJ-5301 OJesus EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Measurement of Posterior Shoulder ExibilityDocument4 pagesClinical Measurement of Posterior Shoulder ExibilityPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Hysterectomy CASE STUDYDocument18 pagesVaginal Hysterectomy CASE STUDYJeannie RobisNo ratings yet
- The Normal and Pathologic Postpartum UterusDocument10 pagesThe Normal and Pathologic Postpartum UterusAlberto BrahmNo ratings yet
- Chapter No# 1: Definition of Cesarean SectionDocument27 pagesChapter No# 1: Definition of Cesarean SectionRabiaNo ratings yet
- Recurrence of Ovarian Endometrioma After Laparoscopic ExcisionDocument4 pagesRecurrence of Ovarian Endometrioma After Laparoscopic ExcisionPutri Tamara DasantosNo ratings yet
- Hysterectomy .: Presented By: Dr. Rommy Yorinda PutraDocument32 pagesHysterectomy .: Presented By: Dr. Rommy Yorinda Putrarommy yorindaNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy For Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesPhysiotherapy For Radical MastectomySURAJNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreDocument27 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreJyotiNo ratings yet
- Onset of Complications Following Cervical Manipulation Due To Malpractice in Osteopathic Treatment: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesOnset of Complications Following Cervical Manipulation Due To Malpractice in Osteopathic Treatment: A Case ReportRui Pedro PereiraNo ratings yet
- MRM JournalDocument11 pagesMRM JournalKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- EFFECTS OF MOBILIZATION WITH MOVEMENT ON Shoulder PainDocument8 pagesEFFECTS OF MOBILIZATION WITH MOVEMENT ON Shoulder PainDimasPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study To Determine The Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy Treatment With and Without Kaltenborn Mobilization On Pain and Shoulder Mobility in Frozen Shoulder PatientsDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study To Determine The Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy Treatment With and Without Kaltenborn Mobilization On Pain and Shoulder Mobility in Frozen Shoulder Patientsfi.afifah NurNo ratings yet
- GynaeDocument8 pagesGynaeGokul DevNo ratings yet
- Randomised, Controlled Outcome Study of Active Mobilisation Compared With Collar Therapy For Whiplash InjuryDocument5 pagesRandomised, Controlled Outcome Study of Active Mobilisation Compared With Collar Therapy For Whiplash Injuryririn rahmayeniNo ratings yet
- Case 1 49y.o. With Medical Algorithm - Surgery 2 Juanillo - 12.01.15Document6 pagesCase 1 49y.o. With Medical Algorithm - Surgery 2 Juanillo - 12.01.15นีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonics Sonochemistry: Jae-Seong Lee, Gi-Youn Hong, Byung-Joon Park, Tea-Eung KimDocument6 pagesUltrasonics Sonochemistry: Jae-Seong Lee, Gi-Youn Hong, Byung-Joon Park, Tea-Eung KimTantonio Tri PutraNo ratings yet
- Ahn Et Al-2013-BJOG An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument4 pagesAhn Et Al-2013-BJOG An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyseptianarifwandiniNo ratings yet
- Perineum Massase InterDocument13 pagesPerineum Massase InterNurul HamidahNo ratings yet
- Effect of Electrical Stimulation FolloweDocument5 pagesEffect of Electrical Stimulation FolloweNajla IrbahNo ratings yet
- Apendisitis AkutDocument17 pagesApendisitis AkutYola BondonkNo ratings yet
- Torticolis ArticuloDocument6 pagesTorticolis ArticuloCarolina Bejarano GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Heating Pads and Early Mobilization For Reducing Postoperative Shoulder Pain and Enhancing Recovery of Women Undergoing Gynecological Laparoscopic SurgeryDocument7 pagesHeating Pads and Early Mobilization For Reducing Postoperative Shoulder Pain and Enhancing Recovery of Women Undergoing Gynecological Laparoscopic SurgeryVitta ChusmeywatiNo ratings yet
- Comparing Breast-Conserving Surgery With Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesComparing Breast-Conserving Surgery With Radical MastectomyRonald Cariaco FlamesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document9 pagesJurnal 1nur aisahNo ratings yet
- Wino Cour 2014Document8 pagesWino Cour 2014Ricardo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Dodge Kegel - Breast Cancer An Illustrated Case StudyDocument2 pagesDodge Kegel - Breast Cancer An Illustrated Case StudyV ThrivikramNo ratings yet
- Medicine: Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Acupuncture and GlucocorticoidDocument3 pagesMedicine: Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Acupuncture and Glucocorticoidindra coolNo ratings yet
- Comparative of The Milch Method and The Spaso Method in The Reduction of Anterior Dislocation of ShoulderDocument4 pagesComparative of The Milch Method and The Spaso Method in The Reduction of Anterior Dislocation of ShoulderAnonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To MaitlandDocument25 pagesIntoduction To MaitlandAsad Chaudhary100% (1)
- A Prospective Study On Appendicular MassDocument4 pagesA Prospective Study On Appendicular MassA BNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Complementary ManualDocument10 pagesThe Effectiveness of Complementary ManualAli DptNo ratings yet
- Ditaranto 2004Document4 pagesDitaranto 2004karthikeyan eswaranNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Brachy 2020 01 006Document9 pages10 1016@j Brachy 2020 01 006MD Hug RobNo ratings yet
- Medsurge Reviewer-2Document12 pagesMedsurge Reviewer-2npdmbypq6jNo ratings yet
- Treatment: Al., 2014) - Surgical Excision Is Recommended For Masses WithDocument5 pagesTreatment: Al., 2014) - Surgical Excision Is Recommended For Masses WithFernanda A RahmatikaNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Among Pre and Post Surgical Breast Cancer Patients - A SurveyDocument8 pagesAwareness of Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Among Pre and Post Surgical Breast Cancer Patients - A SurveyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diafragma Ant Posterior ChainDocument7 pagesDiafragma Ant Posterior ChainJulijus MotiejunasNo ratings yet
- File PDFDocument6 pagesFile PDFJulenda CintarinovaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Manual Traction, Manual Opening Technique and Combination in Patients With Cervical Radiculopathy: Randomized Control TrialDocument6 pagesComparison Between Manual Traction, Manual Opening Technique and Combination in Patients With Cervical Radiculopathy: Randomized Control TrialEka BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- Whelan Et Al 2000 CancerDocument7 pagesWhelan Et Al 2000 Cancerkrishna shafiraNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic Uterine Artery Embolization in Second-Trimester Pregnancy Termination With Complete Placenta PreviaDocument8 pagesProphylactic Uterine Artery Embolization in Second-Trimester Pregnancy Termination With Complete Placenta PreviaAs AsNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy: Original ArticleDocument6 pagesManual Therapy: Original ArticleRyan SetyantoNo ratings yet
- Tmo en Columna CervicalDocument5 pagesTmo en Columna CervicalIvanMejiaJaramilloNo ratings yet
- Transvaginal MorcellationDocument8 pagesTransvaginal Morcellationsanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- To Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Lumbar Plexus Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Lower Limb SurgeriesDocument4 pagesTo Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Lumbar Plexus Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Lower Limb SurgeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Clinical Examination For Ong Patients 2Document19 pagesHistory Taking and Clinical Examination For Ong Patients 2Shangai GuptaNo ratings yet
- US For Epidural. Anesth Analg 2017Document6 pagesUS For Epidural. Anesth Analg 2017tarekabdelkarem927No ratings yet
- 48 Akansel Casestudy 10 2Document7 pages48 Akansel Casestudy 10 2Maria Fudji HastutiNo ratings yet
- Tendinitis Calcificante en Hombro. Comparación Ondas Choque Vs AgujaDocument7 pagesTendinitis Calcificante en Hombro. Comparación Ondas Choque Vs AgujaAJ CésarNo ratings yet
- Role of Physiotherapy in Supporting Recovery From Breast Cancer TreatmentDocument11 pagesRole of Physiotherapy in Supporting Recovery From Breast Cancer TreatmentJesusNavarrete97No ratings yet
- O Gfshds Jjjp4Document12 pagesO Gfshds Jjjp4BentaigaNo ratings yet
- How to Perform Ultrasonography in EndometriosisFrom EverandHow to Perform Ultrasonography in EndometriosisStefano GuerrieroNo ratings yet
- NCP Part 1 Overview of NCPDocument23 pagesNCP Part 1 Overview of NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument3 pages(August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet TherapyMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Document6 pages10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- MedsheetDocument2 pagesMedsheetMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PDocument2 pages7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Passive Ent Pe2qDocument1 pagePassive Ent Pe2qMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- AKI vs. CKD FinalDocument1 pageAKI vs. CKD FinalMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Annotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Document5 pagesAnnotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FINAL MedsheetDocument1 pageFINAL MedsheetMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCP (Ravera)Document11 pagesFHP and NCP (Ravera)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Reminder: Help Guide You inDocument33 pagesReminder: Help Guide You inMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- D.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Document15 pagesD.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- PDF 1Document101 pagesPDF 1Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapDocument1 page(REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsDocument30 pagesOrthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCPDocument12 pagesFHP and NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer - Group 12Document1 pageProstate Cancer - Group 12Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataDocument5 pagesSurvey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Bajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Document8 pagesBajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- World Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForDocument9 pagesWorld Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Fin - Post Operative Thyroidectomy CareDocument2 pagesFin - Post Operative Thyroidectomy CareMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument39 pagesProstate CancerMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Fractures - LeafletDocument2 pagesFractures - LeafletMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous and Intradermal ChecklistDocument5 pagesSubcutaneous and Intradermal ChecklistMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Care of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Document2 pagesCare of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Care 2 Year Waiting Diseases-1Document20 pagesCare 2 Year Waiting Diseases-1Rudra yadavNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rujukan Tahun 2022Document22 pagesLaporan Rujukan Tahun 2022PUSKESMAS PITUNo ratings yet
- Additional Heart Sounds-Part 1 (Third and Fourth Heart Sounds)Document10 pagesAdditional Heart Sounds-Part 1 (Third and Fourth Heart Sounds)Emmanuel Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Complication of Exodontia - 230507 - 034739Document9 pagesComplication of Exodontia - 230507 - 034739Mohammed K. AljaberyNo ratings yet
- JPMHH 5 2 110 118Document9 pagesJPMHH 5 2 110 118TANUJIT MONDALNo ratings yet
- Bacte MnemonicsDocument10 pagesBacte MnemonicsIan Leo SantosNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorder Thesis Statementqpftgehig100% (2)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument28 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseZhe Kang LimNo ratings yet
- Capital PunishmentDocument2 pagesCapital Punishmentsarahzainal80No ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls in Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic MovimentDocument7 pagesClinical Pearls in Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic Movimentrafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- Linezolid Induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy.8Document3 pagesLinezolid Induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy.8arga LiannNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudySamson, SatomiNo ratings yet
- F - Wardina Wirasari - 2020461434 - Case StudyDocument5 pagesF - Wardina Wirasari - 2020461434 - Case StudyMOHD MU'IZZ MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- Health FormDocument2 pagesHealth FormChristine BacordoNo ratings yet
- WAEC May-June Form TemplateDocument1 pageWAEC May-June Form TemplateAlani BankoleNo ratings yet
- Prisons and Health, 9 Infectious Diseases in PrisonDocument8 pagesPrisons and Health, 9 Infectious Diseases in PrisonBam ManNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form 1Document1 pageHealth Declaration Form 1April Mae O. MacalesNo ratings yet
- FOUR Types of AssessmentDocument2 pagesFOUR Types of AssessmentKristine CustodioNo ratings yet
- HEALTH Lesson 1Document6 pagesHEALTH Lesson 1GM EstradaNo ratings yet
- AsyeywtyqwytqtyqDocument6 pagesAsyeywtyqwytqtyqRobee Camille Desabelle-SumatraNo ratings yet
- Bfhajhgcterial Pnfeufmjgonia PosterDocument1 pageBfhajhgcterial Pnfeufmjgonia PosterRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument44 pagesCase PresPhilia FeliceNo ratings yet
- ABACAVIRDocument2 pagesABACAVIRDela Cruz, Katherine MaeNo ratings yet
- Case Sheet DM&HTNDocument4 pagesCase Sheet DM&HTNChristina M.No ratings yet
- Headache Oet ReadingDocument22 pagesHeadache Oet ReadinglianausinNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument15 pagesHemophiliakirara hatakeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batch 3 - Kristele Marie Joy CuaDocument26 pagesDrug Study Batch 3 - Kristele Marie Joy CuaKristele Marie Joy CuaNo ratings yet
- STAR D ReanalysisDocument27 pagesSTAR D ReanalysisSamadhi SilesNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Translational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Translational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features PDFjohn.taylor275100% (26)
Black and Brown Business Brochure
Black and Brown Business Brochure
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Black and Brown Business Brochure
Black and Brown Business Brochure
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoCopyright:
Available Formats
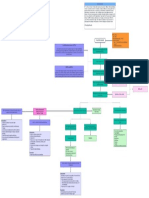
MANAGEMENT
Equivalent Exercises
1. Forehead touch Care of Patients with
2. Rope turning
Medical
Mastectomy
3. Oulley motion or rope sliding
4. Toweling
5. Elbow pull-in
1. Radiation Therapy 6. Arm bending
2. Chemotherapy 7. Back scratcher
3. Hormonal Therapy
4. Targeted Therapy
5. Drug Therapy Recent Advancements
Nursing Murotal Therapy for Postoperative Pain
Setiawan and colleagues (2021) said that
murotal therapy, which involves
Care of Draining Tubes listening to the Quran being recited
1. Follow manufacturers instruction depending on slowly, had a significant impact on pain
the drainage or evacuator device used such as levels following mastectomy surgery.
Hemovac or Jackson-Pratt Murotal intervention for 6 days showed
2. Measure the amount and color of the drainage a reduction in the patient's pain scale
in using the calibration found at the from 4 to 1.
drainage/evacuator device.
3. Clamp drainage tubing if needed then empty the
Multi-supportive Nursing on the
drainage.
Postoperative Rehabilitation of Breast
4. Press drainage or evacuator device while
draining fluid. Cancer Patients
5. Continuously press the drainage/evacuator Tang (2021) found that multi-supportive
device before closing the port. nursing plays a positive role in
6. Add drainage to the intake and output record. promoting the postoperative
rehabilitation of breast cancer (BC)
Post-op Mastectomy Exercises patients who underwent radical
1. Early Post-op Exercises (24-36 hours) mastectomies.
Coughing and deep breathing exercises
Flex legs every 2 hours
Turn to sides every 2 hours
REFERENCES
Hinkle, J. L., & Cheever, K. H. (2018). Brunner and Suddarth’s textbook of
Assist to ambulate medical-surgical nursing. Wolters Kluwer India Pvt Ltd.
LeMone, P., Burke, K., & Bauldoff, G. (2011). Medical-Surgical Nursing: Critical
thinking in patient care (5th ed.). Pearson Education Limited..
1. 3rd to 6th Post-op Day Lewis, S. L., Bucher, L., Heitkemper, M. M., Harding, M. M., Kwong, J., & Roberts,
D. (2016). Medical-Surgical Nursing-E-Book: Assessment and Management of
Hand squeezing Clinical Problems (9th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. Submitted by:
Hair brushing Newton, E., & Grethlein, S. (2018). Breast examination. Retrieved on October 29,
2022 from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1909276-overview. Bugas, Rigel Mae
Setiawan, H., Ariyanto, H., & Oktavia, W. (2021). A case study: Murotal Tacastacas, Hannah Dianella
3. 7th Post-op Day distraction to reduce pain level among post-mastectomy patients.
International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS), 4(3), 325-331.
Arm Swings Stanford Medicine 25. (2020). Breast exam. Retrieved on October 29, 2022 from
www.stanfordmedicine25.stanford.edu/the25/BreastExam.html
Arm Circling Tang, X. (2021). The effect of multi-supportive nursing on the postoperative Submitted to:
Pendulum Swing rehabilitation of breast cancer patients. American Journal of Translational
Asst. Prof. Zorinna M. Luague, RN, MN
Research, 13(6), 7327.
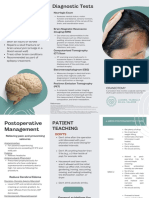
Assessment and Diagnostic 2. Mammography
Mastectomy Findings
1. Abnormal Assessment Findings during
Using low-dose x-ray equipment to view the anatomy
of the breasts, mammography is a breast imaging
procedure that helps in the early detection and
- nipple-areola complex and breast tissue Inspection of the Breasts diagnosis of malignant or benign disease.
removal
Retraction Signs
3. Contrast Mammography
When a patient expresses bloody nipple discharge,
Indications experiences spontaneous nipple discharge, or has a
single dilated duct shown on mammography, it is
done to assess any abnormality inside the duct.
1. Malignant condition of the breast/s
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) 4. Ultrasonography
Invasive Cancer Increased Venous Prominence To help identify fluid-filled cysts from other lesions,
ultrasonography (ultrasound) is utilized as a
2. Benign condition of the breast/s diagnostic auxiliary to mammography. The region to
be photographed is covered with a thin layer of
Cysts lubricating jelly.
Fibroadenomas
5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Benign Profilerative Breast Disease
Mammography has been usefully supplemented by
Peau d’Orange (Edema) the highly sensitive diagnostic technique known as
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the breast.
Types of
Mastectomy COMPLICATIONS
1. Lymphedema
1. Total Mastectomy - removes the It is an issue characterized by a persistent
breast and nipple-areola complex Nipple Inversion enlargement of an extremity as a result of
but omits axillary lymph node impaired lymphatic drainage.
dissection (ALND). 2. Hematoma or Seroma Formation
2. Modified Radical Mastectomy - May develop within the first 12 hours of
removes breast tissue, nipple-areola surgery, whether it is a mastectomy or breast
complex, and a portion of the axillary conservation.
3. Infection
lymph nodes.
This threat may be increased among patients
3. Radical Mastectomy - removes Acute Mastitis (Inflammation of the Breasts)
with diseases including diabetes,
entire breast, axillary lymph nodes, Paget Disease (Malignancy of Mammary Ducts) immunological problems, senior age, and
and pectoral muscles. people who practice poor personal hygiene.
4. Partial mastectomy - removes the 4. Postmastectomy Pain Syndrome
entire tumor along with a margin of Symptoms include pain in the chest and upper
healthy surrounding tissue. arms, tingling down the arm, numbness,
shooting or pricking pain, and excruciating
itching.
You might also like
- Hippo Education Hippo EM - Dermatology Written SummaryDocument7 pagesHippo Education Hippo EM - Dermatology Written Summarykaylawilliam01100% (1)
- International Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS)Document7 pagesInternational Journal of Nursing and Health Services (IJNHS)Dy RPNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Nursing Care On Women Who Have Undergone Abdominal Hysterectomy at Post-Operative Work in Government Head Quarters Hospital, Kancheepuram, District, TamilnaduDocument2 pagesEffectiveness of Nursing Care On Women Who Have Undergone Abdominal Hysterectomy at Post-Operative Work in Government Head Quarters Hospital, Kancheepuram, District, TamilnaduInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Man Ther 2013 Barra LópezDocument7 pagesMan Ther 2013 Barra LópezRuggiero CannitoNo ratings yet
- Acu Back PelvicPain in Pregnancy RCT 1Document6 pagesAcu Back PelvicPain in Pregnancy RCT 1QuackeryNo ratings yet
- To Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Pectoral Nerve Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Breast SurgeriesDocument4 pagesTo Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Pectoral Nerve Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Breast SurgeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Successful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyDocument3 pagesSuccessful Conservative Treatment of Microinvasive Cervical Cancer During PregnancyEres TriasaNo ratings yet
- IJNER - 597 - 27 07 2018 Paper - R - 21Document7 pagesIJNER - 597 - 27 07 2018 Paper - R - 21Yuning tyas Nursyah FitriNo ratings yet
- Medip, ISJ-5301 ODocument4 pagesMedip, ISJ-5301 OJesus EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Measurement of Posterior Shoulder ExibilityDocument4 pagesClinical Measurement of Posterior Shoulder ExibilityPrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Hysterectomy CASE STUDYDocument18 pagesVaginal Hysterectomy CASE STUDYJeannie RobisNo ratings yet
- The Normal and Pathologic Postpartum UterusDocument10 pagesThe Normal and Pathologic Postpartum UterusAlberto BrahmNo ratings yet
- Chapter No# 1: Definition of Cesarean SectionDocument27 pagesChapter No# 1: Definition of Cesarean SectionRabiaNo ratings yet
- Recurrence of Ovarian Endometrioma After Laparoscopic ExcisionDocument4 pagesRecurrence of Ovarian Endometrioma After Laparoscopic ExcisionPutri Tamara DasantosNo ratings yet
- Hysterectomy .: Presented By: Dr. Rommy Yorinda PutraDocument32 pagesHysterectomy .: Presented By: Dr. Rommy Yorinda Putrarommy yorindaNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy For Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesPhysiotherapy For Radical MastectomySURAJNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreDocument27 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka, BangaloreJyotiNo ratings yet
- Onset of Complications Following Cervical Manipulation Due To Malpractice in Osteopathic Treatment: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesOnset of Complications Following Cervical Manipulation Due To Malpractice in Osteopathic Treatment: A Case ReportRui Pedro PereiraNo ratings yet
- MRM JournalDocument11 pagesMRM JournalKeanu PeraltaNo ratings yet
- EFFECTS OF MOBILIZATION WITH MOVEMENT ON Shoulder PainDocument8 pagesEFFECTS OF MOBILIZATION WITH MOVEMENT ON Shoulder PainDimasPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study To Determine The Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy Treatment With and Without Kaltenborn Mobilization On Pain and Shoulder Mobility in Frozen Shoulder PatientsDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study To Determine The Efficacy of Routine Physical Therapy Treatment With and Without Kaltenborn Mobilization On Pain and Shoulder Mobility in Frozen Shoulder Patientsfi.afifah NurNo ratings yet
- GynaeDocument8 pagesGynaeGokul DevNo ratings yet
- Randomised, Controlled Outcome Study of Active Mobilisation Compared With Collar Therapy For Whiplash InjuryDocument5 pagesRandomised, Controlled Outcome Study of Active Mobilisation Compared With Collar Therapy For Whiplash Injuryririn rahmayeniNo ratings yet
- Case 1 49y.o. With Medical Algorithm - Surgery 2 Juanillo - 12.01.15Document6 pagesCase 1 49y.o. With Medical Algorithm - Surgery 2 Juanillo - 12.01.15นีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonics Sonochemistry: Jae-Seong Lee, Gi-Youn Hong, Byung-Joon Park, Tea-Eung KimDocument6 pagesUltrasonics Sonochemistry: Jae-Seong Lee, Gi-Youn Hong, Byung-Joon Park, Tea-Eung KimTantonio Tri PutraNo ratings yet
- Ahn Et Al-2013-BJOG An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDocument4 pagesAhn Et Al-2013-BJOG An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyseptianarifwandiniNo ratings yet
- Perineum Massase InterDocument13 pagesPerineum Massase InterNurul HamidahNo ratings yet
- Effect of Electrical Stimulation FolloweDocument5 pagesEffect of Electrical Stimulation FolloweNajla IrbahNo ratings yet
- Apendisitis AkutDocument17 pagesApendisitis AkutYola BondonkNo ratings yet
- Torticolis ArticuloDocument6 pagesTorticolis ArticuloCarolina Bejarano GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Heating Pads and Early Mobilization For Reducing Postoperative Shoulder Pain and Enhancing Recovery of Women Undergoing Gynecological Laparoscopic SurgeryDocument7 pagesHeating Pads and Early Mobilization For Reducing Postoperative Shoulder Pain and Enhancing Recovery of Women Undergoing Gynecological Laparoscopic SurgeryVitta ChusmeywatiNo ratings yet
- Comparing Breast-Conserving Surgery With Radical MastectomyDocument6 pagesComparing Breast-Conserving Surgery With Radical MastectomyRonald Cariaco FlamesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document9 pagesJurnal 1nur aisahNo ratings yet
- Wino Cour 2014Document8 pagesWino Cour 2014Ricardo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Dodge Kegel - Breast Cancer An Illustrated Case StudyDocument2 pagesDodge Kegel - Breast Cancer An Illustrated Case StudyV ThrivikramNo ratings yet
- Medicine: Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Acupuncture and GlucocorticoidDocument3 pagesMedicine: Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Acupuncture and Glucocorticoidindra coolNo ratings yet
- Comparative of The Milch Method and The Spaso Method in The Reduction of Anterior Dislocation of ShoulderDocument4 pagesComparative of The Milch Method and The Spaso Method in The Reduction of Anterior Dislocation of ShoulderAnonymous UTUWFODCEYNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To MaitlandDocument25 pagesIntoduction To MaitlandAsad Chaudhary100% (1)
- A Prospective Study On Appendicular MassDocument4 pagesA Prospective Study On Appendicular MassA BNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Complementary ManualDocument10 pagesThe Effectiveness of Complementary ManualAli DptNo ratings yet
- Ditaranto 2004Document4 pagesDitaranto 2004karthikeyan eswaranNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Brachy 2020 01 006Document9 pages10 1016@j Brachy 2020 01 006MD Hug RobNo ratings yet
- Medsurge Reviewer-2Document12 pagesMedsurge Reviewer-2npdmbypq6jNo ratings yet
- Treatment: Al., 2014) - Surgical Excision Is Recommended For Masses WithDocument5 pagesTreatment: Al., 2014) - Surgical Excision Is Recommended For Masses WithFernanda A RahmatikaNo ratings yet
- Awareness of Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Among Pre and Post Surgical Breast Cancer Patients - A SurveyDocument8 pagesAwareness of Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Among Pre and Post Surgical Breast Cancer Patients - A SurveyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diafragma Ant Posterior ChainDocument7 pagesDiafragma Ant Posterior ChainJulijus MotiejunasNo ratings yet
- File PDFDocument6 pagesFile PDFJulenda CintarinovaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Manual Traction, Manual Opening Technique and Combination in Patients With Cervical Radiculopathy: Randomized Control TrialDocument6 pagesComparison Between Manual Traction, Manual Opening Technique and Combination in Patients With Cervical Radiculopathy: Randomized Control TrialEka BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- Whelan Et Al 2000 CancerDocument7 pagesWhelan Et Al 2000 Cancerkrishna shafiraNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic Uterine Artery Embolization in Second-Trimester Pregnancy Termination With Complete Placenta PreviaDocument8 pagesProphylactic Uterine Artery Embolization in Second-Trimester Pregnancy Termination With Complete Placenta PreviaAs AsNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy: Original ArticleDocument6 pagesManual Therapy: Original ArticleRyan SetyantoNo ratings yet
- Tmo en Columna CervicalDocument5 pagesTmo en Columna CervicalIvanMejiaJaramilloNo ratings yet
- Transvaginal MorcellationDocument8 pagesTransvaginal Morcellationsanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- To Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Lumbar Plexus Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Lower Limb SurgeriesDocument4 pagesTo Evaluate The Efficacy of Ultrasonography Guided Lumbar Plexus Block For Postoperative Analgesia in Lower Limb SurgeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Clinical Examination For Ong Patients 2Document19 pagesHistory Taking and Clinical Examination For Ong Patients 2Shangai GuptaNo ratings yet
- US For Epidural. Anesth Analg 2017Document6 pagesUS For Epidural. Anesth Analg 2017tarekabdelkarem927No ratings yet
- 48 Akansel Casestudy 10 2Document7 pages48 Akansel Casestudy 10 2Maria Fudji HastutiNo ratings yet
- Tendinitis Calcificante en Hombro. Comparación Ondas Choque Vs AgujaDocument7 pagesTendinitis Calcificante en Hombro. Comparación Ondas Choque Vs AgujaAJ CésarNo ratings yet
- Role of Physiotherapy in Supporting Recovery From Breast Cancer TreatmentDocument11 pagesRole of Physiotherapy in Supporting Recovery From Breast Cancer TreatmentJesusNavarrete97No ratings yet
- O Gfshds Jjjp4Document12 pagesO Gfshds Jjjp4BentaigaNo ratings yet
- How to Perform Ultrasonography in EndometriosisFrom EverandHow to Perform Ultrasonography in EndometriosisStefano GuerrieroNo ratings yet
- NCP Part 1 Overview of NCPDocument23 pagesNCP Part 1 Overview of NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument3 pages(August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet TherapyMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Document6 pages10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- MedsheetDocument2 pagesMedsheetMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PDocument2 pages7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Passive Ent Pe2qDocument1 pagePassive Ent Pe2qMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- AKI vs. CKD FinalDocument1 pageAKI vs. CKD FinalMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Annotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Document5 pagesAnnotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FINAL MedsheetDocument1 pageFINAL MedsheetMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCP (Ravera)Document11 pagesFHP and NCP (Ravera)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Reminder: Help Guide You inDocument33 pagesReminder: Help Guide You inMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- D.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Document15 pagesD.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- PDF 1Document101 pagesPDF 1Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapDocument1 page(REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsDocument30 pagesOrthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCPDocument12 pagesFHP and NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer - Group 12Document1 pageProstate Cancer - Group 12Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataDocument5 pagesSurvey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Bajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Document8 pagesBajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- World Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForDocument9 pagesWorld Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Fin - Post Operative Thyroidectomy CareDocument2 pagesFin - Post Operative Thyroidectomy CareMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument39 pagesProstate CancerMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Fractures - LeafletDocument2 pagesFractures - LeafletMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous and Intradermal ChecklistDocument5 pagesSubcutaneous and Intradermal ChecklistMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Care of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Document2 pagesCare of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Care 2 Year Waiting Diseases-1Document20 pagesCare 2 Year Waiting Diseases-1Rudra yadavNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rujukan Tahun 2022Document22 pagesLaporan Rujukan Tahun 2022PUSKESMAS PITUNo ratings yet
- Additional Heart Sounds-Part 1 (Third and Fourth Heart Sounds)Document10 pagesAdditional Heart Sounds-Part 1 (Third and Fourth Heart Sounds)Emmanuel Andrew Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Complication of Exodontia - 230507 - 034739Document9 pagesComplication of Exodontia - 230507 - 034739Mohammed K. AljaberyNo ratings yet
- JPMHH 5 2 110 118Document9 pagesJPMHH 5 2 110 118TANUJIT MONDALNo ratings yet
- Bacte MnemonicsDocument10 pagesBacte MnemonicsIan Leo SantosNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorder Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorder Thesis Statementqpftgehig100% (2)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument28 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseZhe Kang LimNo ratings yet
- Capital PunishmentDocument2 pagesCapital Punishmentsarahzainal80No ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls in Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic MovimentDocument7 pagesClinical Pearls in Tremor and Other Hyperkinetic Movimentrafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- Linezolid Induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy.8Document3 pagesLinezolid Induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy.8arga LiannNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudySamson, SatomiNo ratings yet
- F - Wardina Wirasari - 2020461434 - Case StudyDocument5 pagesF - Wardina Wirasari - 2020461434 - Case StudyMOHD MU'IZZ MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- Health FormDocument2 pagesHealth FormChristine BacordoNo ratings yet
- WAEC May-June Form TemplateDocument1 pageWAEC May-June Form TemplateAlani BankoleNo ratings yet
- Prisons and Health, 9 Infectious Diseases in PrisonDocument8 pagesPrisons and Health, 9 Infectious Diseases in PrisonBam ManNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form 1Document1 pageHealth Declaration Form 1April Mae O. MacalesNo ratings yet
- FOUR Types of AssessmentDocument2 pagesFOUR Types of AssessmentKristine CustodioNo ratings yet
- HEALTH Lesson 1Document6 pagesHEALTH Lesson 1GM EstradaNo ratings yet
- AsyeywtyqwytqtyqDocument6 pagesAsyeywtyqwytqtyqRobee Camille Desabelle-SumatraNo ratings yet
- Bfhajhgcterial Pnfeufmjgonia PosterDocument1 pageBfhajhgcterial Pnfeufmjgonia PosterRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument44 pagesCase PresPhilia FeliceNo ratings yet
- ABACAVIRDocument2 pagesABACAVIRDela Cruz, Katherine MaeNo ratings yet
- Case Sheet DM&HTNDocument4 pagesCase Sheet DM&HTNChristina M.No ratings yet
- Headache Oet ReadingDocument22 pagesHeadache Oet ReadinglianausinNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument15 pagesHemophiliakirara hatakeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batch 3 - Kristele Marie Joy CuaDocument26 pagesDrug Study Batch 3 - Kristele Marie Joy CuaKristele Marie Joy CuaNo ratings yet
- STAR D ReanalysisDocument27 pagesSTAR D ReanalysisSamadhi SilesNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Translational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Translational Autoimmunity Volume 3 Autoimmune Disease Associated With Different Clinical Features PDFjohn.taylor275100% (26)