Professional Documents
Culture Documents
91d2dOM PPT-8 (Aggregate Planning) Part II
91d2dOM PPT-8 (Aggregate Planning) Part II
Uploaded by
AdityaVikramBhadauriaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
91d2dOM PPT-8 (Aggregate Planning) Part II
91d2dOM PPT-8 (Aggregate Planning) Part II
Uploaded by
AdityaVikramBhadauriaCopyright:
Available Formats
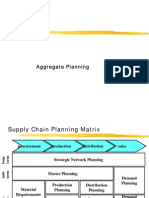
RESOURCE PLANNING
Course Instructor: Dr. Swati Singh Course: MBA- II
Amity Business School
Dr. Swati Singh
This is a sub-set of APP which makes use of actual customers orders for the purpose of capacity planning & resource allocation It is a function of independent demand i.e. of customers & specifies exactly what is to be produced It determines production schedule for individual product i.e. it specifies how many end items are to be produced within specified period (week, months, quarter) of short-range planning horizon It includes all demands from product sales, warehouse replenishment, spares & inter-plant requirements It determines actual material requirement for production Material
Master Production Schedule Determines Requirement plan Determines
Dr. Swati Singh
Capacity Planning
Master Production Schedule
Finished Goods Stock
Plant Production Capacity Finished Goods Demanded
Aggregate Production Planning
Purchase Orders to arrive
Plant Work Force
Master Production Schedule
Material Requirements Planning
Raw Material Stock
Raw Material Purchase Orders
Dr. Swati Singh 3
It is done for dependent demand inventory & also schedule production activities Its key inputs are:
End product requirements product structure data Lead-time Inventory Status
It is most useful for complex products, job shops & assemble-to-order system It is done through Bills of Materials It helps in ensuring availability of materials at the right time & at the right place
Dr. Swati Singh 4
It contains list of materials along with quantity required to produce one unit of product
Its structure consists of all end products i.e. subassemblies, parts, raw materials etc.
Dr. Swati Singh
B (1) Ladder back subassembly
C (1) Seat Subassembly
D (2) Front Legs
E (4) Leg supports
F (2) Back Legs
G (4) Back Slats
H (1) Seat Frame
I (1) Seat Cushion
J (4) Seat frame boards
Dr. Swati Singh
B (3)
C (1)
D (2)
E (1)
F (3)
H (2)
I (2)
J (1)
F (4)
G (2)
F (1)
G (3)
G = (2*1*3*10) + (3*2*1*10) = 60+60 = 120 F = (3*3*10) + (1*2*1*10) + (4*2*10) = 190 J = 20 Dr. Swati Singh H = 20
A LT=1
B (3) LT=2
C (2) LT=1
D (2) LT=2
Dr. Swati Singh
Work No.
Weeks
1
Item: A Quantity = 1 LT = 1 Gross Requirement Quantity on hand Net Requirement Planned order Receipts Planned order Releases Gross Requirement Quantity on hand Net Requirement Planned order Receipts Planned order Releases Gross Requirement Quantity on hand Net Requirement Planned order Receipts Planned order Releases Gross Requirement Quantity on hand Net Requirement Planned order Receipts Planned order Releases
6
100 0 100 100
100 300 100 200 200 200 200 0 200 200 200 400 0 400 400 400
Dr. Swati Singh 9
Item: B Quantity = 3 LT = 2
Item: C Quantity = 2 LT = 1
Item: D Quantity = 2 LT = 2
It is an enlarged version of MRP It ties the basic MRP system to companys financial system and to other core & supporting processes MRP II ultimately evolves into Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) It consists of: Business Planning Forecasting/Demand Management Purchasing Inventory control Master Production Schedule (MPS) Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
Dr. Swati Singh 10
You might also like
- Assessment Method 2 - Project-Part D: Instructions To StudentsDocument8 pagesAssessment Method 2 - Project-Part D: Instructions To StudentsJyoti VermaNo ratings yet
- Project Charter - Royal India Gym ClubDocument5 pagesProject Charter - Royal India Gym Clubkunal100% (1)
- MRP Nigel SlackDocument18 pagesMRP Nigel Slackwanara_seta3384No ratings yet
- Ciq Financials MethodologyDocument25 pagesCiq Financials Methodologysanti_hago50% (2)
- Thai Consumers Behavior Towards Fast FashionDocument6 pagesThai Consumers Behavior Towards Fast FashionMurni Ni WayanNo ratings yet
- Tax Provision Relating To FTZ, Infrastructure Sector and Backward AreaDocument22 pagesTax Provision Relating To FTZ, Infrastructure Sector and Backward Areapadum chetry86% (7)
- Production Planning Control AssignmentDocument13 pagesProduction Planning Control AssignmentKulmohan116No ratings yet
- Material Requirement PlanningDocument5 pagesMaterial Requirement Planningshwa_jn889No ratings yet
- Aggregate Planning & SchedulingDocument33 pagesAggregate Planning & SchedulingjanettegandaNo ratings yet
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP)Document49 pagesMaterial Requirement Planning (MRP)shahadat112No ratings yet
- Module 9 - Resource PlanningDocument31 pagesModule 9 - Resource PlanningAnton WilliamsNo ratings yet
- M & L ManufacturingDocument10 pagesM & L ManufacturingYash Gode0% (1)
- LDP 604 - Lecture 7 Designing Projects Using Common Tools (Full Permission) PDFDocument5 pagesLDP 604 - Lecture 7 Designing Projects Using Common Tools (Full Permission) PDFKennedy KorirNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Production Planning - Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesAggregate Production Planning - Lecture NotesJim Mathilakathu100% (1)
- ProposalCall FBR NCPDocument8 pagesProposalCall FBR NCPMickey Dalbehera100% (1)
- Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Institute of Management & TechnologyDocument2 pagesDr. B. R. Ambedkar Institute of Management & Technologyarchana_sree13No ratings yet
- The Design of Batik Stamp Tool Scraping Working Table Using Ergonomics PrinciplesDocument9 pagesThe Design of Batik Stamp Tool Scraping Working Table Using Ergonomics Principlestika_nandaNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Production PlanningDocument129 pagesPengenalan Production PlanningAkhmad SultonNo ratings yet
- Master Production ScheduleDocument9 pagesMaster Production ScheduleglamboyzNo ratings yet
- Revisionary Test Paper - Intermediate - Syllabus 2012 - Dec 2015 Paper-9: Operations Management & Information SystemsDocument43 pagesRevisionary Test Paper - Intermediate - Syllabus 2012 - Dec 2015 Paper-9: Operations Management & Information SystemsmanasaavvaruNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Project Cost ManagementDocument88 pages1.7. Project Cost Managementdeanz_75100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityVinayak PandlaNo ratings yet
- 499-Article Text-1931-1-10-20181201 PDFDocument6 pages499-Article Text-1931-1-10-20181201 PDFKrisna YudhaNo ratings yet
- Report Aggregate PDFDocument29 pagesReport Aggregate PDFRianita SaviraNo ratings yet
- Planning Production ActivitiesDocument21 pagesPlanning Production ActivitiesBeytullah Gültekin ÇetinerNo ratings yet
- Material Requirements PlanningDocument15 pagesMaterial Requirements PlanningRayeed AliNo ratings yet
- 07 Constraint Management - KrajewskiDocument38 pages07 Constraint Management - KrajewskiAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Planning in Manufacturing Systems: Forecasting (Chapter 2)Document6 pagesLevels of Planning in Manufacturing Systems: Forecasting (Chapter 2)Modather SalahNo ratings yet
- 05 E2 - Exercise - SF, MFGDocument4 pages05 E2 - Exercise - SF, MFGAjinkya YadavNo ratings yet
- Mpcproblems Institute of TechnologyDocument39 pagesMpcproblems Institute of TechnologyvundavilliravindraNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 Identify Application Areas of Industrial Management.: (CLO1, PLO2:DK 1 & DK 4)Document4 pages1.3.1 Identify Application Areas of Industrial Management.: (CLO1, PLO2:DK 1 & DK 4)Siti FatimahNo ratings yet
- Material Requirement Planning (MRP)Document55 pagesMaterial Requirement Planning (MRP)Lisa CarlsonNo ratings yet
- Sy - Bcom CP Sem 4Document14 pagesSy - Bcom CP Sem 4Akki GalaNo ratings yet
- C C C C: CCCCCCDocument6 pagesC C C C: CCCCCCJZShah12No ratings yet
- Aggregate PlanningDocument57 pagesAggregate Planningamitr_scribdNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 MRP ProfesorDocument42 pagesChapter4 MRP ProfesorMiguel Angel Vera ArévaloNo ratings yet
- Bio Gen Prin 221107Document6 pagesBio Gen Prin 221107rakeshkjain3440No ratings yet
- PM AssignmentDocument9 pagesPM AssignmentShakiraNo ratings yet
- Om2 Session 11 MRP SJDocument16 pagesOm2 Session 11 MRP SJUdit ChhedaNo ratings yet
- MRPDocument32 pagesMRPvictorNo ratings yet
- BoG 4.4.13 From PrincipalDocument45 pagesBoG 4.4.13 From PrincipalkrishnanandNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Units Decompose It Disaggregate ItDocument20 pagesAggregate Units Decompose It Disaggregate ItRetno DwiNo ratings yet
- TLP Modul 3Document32 pagesTLP Modul 3Fauzan MiracleNo ratings yet
- Info 620 Exam 2 Study Guide PDFDocument4 pagesInfo 620 Exam 2 Study Guide PDFюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document21 pagesChapter 01Bogdan GligorNo ratings yet
- Capacity Utilization For Product Mix Using Operation Based Time Standard EvaluationDocument6 pagesCapacity Utilization For Product Mix Using Operation Based Time Standard EvaluationInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- OPM101Exam3vAKEY 000Document5 pagesOPM101Exam3vAKEY 000Cliff StewardNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document76 pagesUnit 1Aditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 2 - MRPDocument9 pagesStudy Guide 2 - MRPAustin Parker100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - Review QuestionsSaif SokkarNo ratings yet
- QB PPCDocument45 pagesQB PPCA. ANBU RAJ Mech - Asst.ProfNo ratings yet
- S. No. Description Page No.: 7 Test Plan Review ChecklistDocument25 pagesS. No. Description Page No.: 7 Test Plan Review ChecklistHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- ISYS6300 Business Process Fundamental: Week 7 The Production CycleDocument39 pagesISYS6300 Business Process Fundamental: Week 7 The Production CycleEdwar ArmandesNo ratings yet
- MEIE3284 Lecture 02 Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageMEIE3284 Lecture 02 Practice ProblemsGark LopNo ratings yet
- Mcom 2012Document306 pagesMcom 2012Amol KastureNo ratings yet
- PPC 1 - An IntroDocument22 pagesPPC 1 - An IntroLinda Devi YuniarsihNo ratings yet
- Process and Product MetricsDocument38 pagesProcess and Product Metricsneerajrithaliya221020No ratings yet
- Production PlanningDocument57 pagesProduction PlanningNP100% (1)
- Mrp-Erp-Om: 2-508-97 Production and Operations ManagementDocument41 pagesMrp-Erp-Om: 2-508-97 Production and Operations ManagementRogil Jacob DanielNo ratings yet
- OM Lecture 4 (MRP)Document83 pagesOM Lecture 4 (MRP)kalineczka.rausNo ratings yet
- Case Study U.S. StrollersDocument4 pagesCase Study U.S. StrollersAnonymous LW8Q1Xq3TH50% (2)
- IT1566 (BPIS) Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Business ProcessesDocument3 pagesIT1566 (BPIS) Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Business ProcessesjaslynNo ratings yet
- Taxationlaw BarlisDocument11 pagesTaxationlaw Barlisjade123_129No ratings yet
- Tanishq Case StudyDocument5 pagesTanishq Case StudyAnkita BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Puji Rejeki PDFDocument19 pagesCompany Profile Puji Rejeki PDFR Dimas Tri NugrohoNo ratings yet
- FinalM&a Group 7 Nov 22 V1Document39 pagesFinalM&a Group 7 Nov 22 V1Alok GoelNo ratings yet
- 20131201180129005Document12 pages20131201180129005GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Companion To Neo-Schumpeterian EconomicsDocument1,229 pagesCompanion To Neo-Schumpeterian EconomicsFAUSTINOESTEBAN100% (2)
- Company ProfileDocument7 pagesCompany ProfilefithaarunNo ratings yet
- Travel Invoice: Means of TransportDocument5 pagesTravel Invoice: Means of TransportAnonymous qj6xa7v6biNo ratings yet
- SchedulingDocument9 pagesSchedulingVivek SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Insurance - Rate MakingDocument78 pagesInsurance - Rate Makingthefactorbook100% (1)
- Recume, CVDocument3 pagesRecume, CVkunjan2165No ratings yet
- Definitions of E CommernceDocument7 pagesDefinitions of E CommernceTusiime Wa Kachope SamsonNo ratings yet
- Factorytalk View Se FaqDocument5 pagesFactorytalk View Se FaqmihacraciunNo ratings yet
- Soa 0000000007093223Document3 pagesSoa 0000000007093223daisy.gatewaygroupNo ratings yet
- Nothing Happens Until The Sale Is MadeDocument29 pagesNothing Happens Until The Sale Is Madesroa2009No ratings yet
- Renting of Toys in NewsDocument11 pagesRenting of Toys in NewssanjairailNo ratings yet
- Turnaroung - HMDocument16 pagesTurnaroung - HMraviNo ratings yet
- Cheniver Vs NLRCDocument1 pageCheniver Vs NLRCFrancisco Marvin100% (1)
- MKT 701 Lecture 6 CH 12 Addressing Competition and Driving GrowthDocument16 pagesMKT 701 Lecture 6 CH 12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growthmuhib0030100% (1)
- Saving & Investment Pattern of People in India: A Study OnDocument29 pagesSaving & Investment Pattern of People in India: A Study OnMoumita BeraNo ratings yet
- HDFC Life YoungStar Udaan IllustrationDocument2 pagesHDFC Life YoungStar Udaan IllustrationSuraj RajbharNo ratings yet
- City Lite Realty CorpDocument1 pageCity Lite Realty CorpEstrella RoseteNo ratings yet
- Alaska Milk Corporation PresentationDocument19 pagesAlaska Milk Corporation PresentationRonnie DeanNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of EvidenceDocument7 pagesAffidavit of Evidenceshivam5singh-25No ratings yet
- Role of Mutual Funds in Retail Investment-45-MfsDocument11 pagesRole of Mutual Funds in Retail Investment-45-MfsSakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Joint Rules Implementing R.A. 9520 or The Cooperative Code of The PhilippinesDocument14 pagesJoint Rules Implementing R.A. 9520 or The Cooperative Code of The PhilippinesEdd N Ros AdlawanNo ratings yet
- RTHD L3gxiktDocument2 pagesRTHD L3gxiktRobin RahmanNo ratings yet