Professional Documents
Culture Documents
INDEX in ENG Economics
INDEX in ENG Economics
Uploaded by
Mark SmithOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
INDEX in ENG Economics
INDEX in ENG Economics
Uploaded by
Mark SmithCopyright:
Available Formats
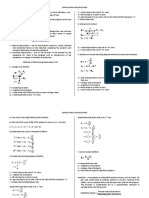
ENGINEERING ECONOMICS (INDEX)
FORMULA SYMBOLS/NOTATION
Total Costs TC=C f + C v C f = Total fixed costs
C v = Total Variable Costs
Total Revenue TR=p •D p = price
D= Demand
Profit Profit=TR - TC TR = Total Revenue
TC = Total Costs
Law of Demand
Relationship of Price p=a-bD a= intercept on the price y(axis)
& Demand b= slope, the amount by which D
increases for each unit decrease in p
D= Demand
P= Price
Total Revenue a
w/ D’=
2b
TR= p×D= (a-bD)×D= aD-b D 2
Profit Profit = TR-TC
= (aD-b D 2)-(C f + C v D )
= -C f + ¿ ¿
Demand that will a−+ C v
maximize profit D*=
2b
Indexes In k = reference year (e.g., 2000) for
C n=C k ( ) which cost or price of item its known.
Ik
n= year for which cost or price is to be
estimated (n>k)
C n= estimated cost or price of item in
year n.
C k = cost or price of item in reference
year k.
Power-Sizing CA S A x C A= cost for plant A
Technique =( ) C B= cost for plant B
CB SB
SA
x S A = size of plant A
C A = CB ( ) S B= size of plant B
SB
X= cost-capacity factor to reflect
economics of scale
n
Learning Curve Zu =K (u ) u= the output unit number
Zu = the number of input resource
units needed to produce output unit
u;
K= the number of input resource units
needed to produce the first output
unit;
s= the learning curve slope parameter
expressed as a decimal (s=0.9 for a
90% learning curve)
log s
n= = the learning curve
log 2
exponent.
Interest Interest = ending amount – beginning amount
IR or ROR(%) Interest accrued per unit time IR = Interest Rate
IR = ×100%
Original Amount ROR = Rate Of Return
Nominal Interest r=im
Rate
Effective interest i= r/m i= effective interest rate per
rate per compounding period
compounding period r= nominal interest rate per year
m= number of compounding periods
per year
Effective annual r m
i a= [1+ ¿ ¿ −1
interest rate m
i a=[1+i ¿¿ m-1
Simple Interest I = PNI P= Principal amount borrowed
N= number of interest periods
i= interest rate per interest period
Single-Payment 𝐹 = future sum of money; the
Compound-Amount equivalent worth of one or more cash
Factor (𝑭/𝑷) flows at a reference point in time
called the future
𝐴 = end-of-period cash flows in a
series of equal payment (uniform
series) continuing for a specified
number of periods, starting at the end
of the first period and continuing
through the last period, also often
called annuity
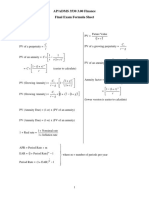
Finding the Interest
Rate Given P, F, and
N
Uniform Series
Present Worth
Factor (𝑷/𝑨)
Capital Recovery
Factor (𝑨/𝑷)
Sinking Fund Factor
(𝑨/𝑭)
Uniform Series
Compound Amount
Factor (𝑭/𝑨)
Arithmetic Gradient
Factors (𝑷/𝑮 𝒂𝒏𝒅
𝑨/𝑮)
Geometric Gradient
Series Factors
Present Worth (PW) 𝑃𝑊 (𝑖%) = 𝐹0 (1 + 𝑖) 0 + 𝐹1 (1 + 𝑖) −1 + 𝐹2 (1 + 𝑖) i = minimum attractive rate or return
Method −2 + ⋯ + 𝐹𝑛 (1 + 𝑖) –𝑛 (MARR)
Or k = index for each compounding
𝑃𝑊 (𝑖%) = ∑𝐹𝑘 (1 + 𝑖) ^ −k period (0 <k
PW= (P/A,i,n)+(P/F,i,n)
Future Worth (FW) 𝐹𝑊 (𝑖%) = 𝐹0 (1 + 𝑖) 𝑛 + 𝐹1 (1 + 𝑖) 𝑛−1 + 𝐹2 (1 +
Method 𝑖) 𝑛−2 + ⋯ + 𝐹𝑛 (1 + 𝑖) 0
Or
𝐹𝑊(𝑖%) = ∑𝐹𝑘 (1 + 𝑖) 𝑛−k
Annual Worth (AW) 𝐴𝑊 (𝑖%) = 𝑅 − 𝐸 – 𝐶R
Method 𝐶𝑅 (%) = 𝐼 × (𝐴/𝑃, 𝑖%, 𝑛) − 𝑆𝑉 × (𝐴/𝐹, 1%, 𝑛)
Internal Rate of ∑𝑅𝑘 (𝑃/𝐹, 𝑖 ∗%, 𝑘) 𝑛 𝑘=0 = ∑𝐸𝑘 (𝑃/𝐹, 𝑖 ∗%, 𝑘) 𝑛 R = net revenues or savings for the kth
Return (IRR) Method 𝑘=0 year
Or E = net expenditures including
𝑃𝑊 = 0 = ∑𝑅𝑘(𝑃/𝐹, 𝑖 ∗%, 𝑘) 𝑛 𝑘=0 − ∑𝐸𝑘(𝑃/𝐹, 𝑖 ∗ investments for the kth year
%, 𝑘) n = project life (or study period)
Benefit/Cost Ratio 𝐵/𝐶 = 𝐴𝑊 AW = annual worth B = annual
Method (𝑏𝑒𝑛𝑒𝑓𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡)/ 𝐴𝑊 equivalent worth of benefits of the
(𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑒𝑑 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑗𝑒𝑐𝑡) proposed project
CR = capital recovery cost
O & M = equivalent annual operating
and maintenance expenses of the
proposed project
Conventional B/C 𝐵/𝐶 = 𝐵/ 𝐶𝑅 + (𝑂&𝑀)
ratio:
Modified B/C ratio: 𝐵/𝐶 = 𝐵 − (𝑂&𝑀) / 𝐶𝑅
Capitalized 𝐶𝐸𝐴 = 𝑃 = 𝐴(𝑃/𝐴, 𝑖%, ∞)
Equivalent Amount 𝐶𝐸𝐴 = 𝑃 = 𝐴 ( 1 /𝑖 )
(CEA) or Capitalized
Worth (CW) Method
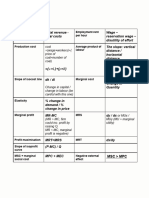
DEPRECIATION
Depreciation 𝑑𝑘 = annual depreciation deduction in
Methods year k (1 < N)
𝑑𝑘 ∗ = cumulative depreciation
Straight-line through year k 𝐵
Method 𝑉𝑘 = book value at end of year k
B = cost basis, including allowable
adjustments
𝑆𝑉𝑁 = estimated salvage value at end
of year N
N = depreciable life of the asset in
years
Sum-of-the-years-
Digits (SYD) Method
Declining Balance
Method
Sinking Fund A’ = C (A/F, i%, n) A' = sinking fund deposit
Method C = purchase price of replacement
asset – net salvage value of current
The depreciation in year k, which includes asset
interest earned at that time, is given as: n = useful life of current asset
i = annual interest rate
You might also like
- Engineering Economy 3Document37 pagesEngineering Economy 3Steven SengNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management-Summer TrainingDocument43 pagesInventory Management-Summer Trainingrudranilbag100% (3)
- Formule Blad CME: C (N K) +W + +W +W + +W I 1 M MDocument3 pagesFormule Blad CME: C (N K) +W + +W +W + +W I 1 M MLente ChristanNo ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument5 pagesDepreciationKenny CantilaNo ratings yet
- (Formula Sheet) EMEM 533Document3 pages(Formula Sheet) EMEM 533Almaz ZhNo ratings yet
- Marginal Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesMarginal Analysis PDFjose_dino10005190No ratings yet
- 01-Types of CostsDocument39 pages01-Types of Costsasif malikNo ratings yet
- 2-Cost Concept and Breakeven AnalysisDocument28 pages2-Cost Concept and Breakeven Analysistrishajoyocampo01818No ratings yet
- DepreciationDocument4 pagesDepreciationMART MATICNo ratings yet
- Break Even New2Document39 pagesBreak Even New2thomasNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet FMDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet FMAbdullah ShahNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet FinanceDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Financemostafa daherNo ratings yet
- N-AM025 Topic 3 (APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION & INTEGRATION IN ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS)Document63 pagesN-AM025 Topic 3 (APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION & INTEGRATION IN ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS)nurauniatiqah49No ratings yet
- Adms3530f18 Final Exam Formula Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesAdms3530f18 Final Exam Formula Sheet PDFSandy SandNo ratings yet
- D464 Formula SheetDocument13 pagesD464 Formula Sheetyomaira.bastidas.ysNo ratings yet
- Depreciation, Capital Recovery and Break Even AnalysisDocument6 pagesDepreciation, Capital Recovery and Break Even AnalysisMa. Angeline GlifoneaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet MAF 302 Corporate FinanceDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet MAF 302 Corporate FinanceWill LeeNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow PV R CF PV RG: FCF NPV Initial T RDocument2 pagesCash Flow PV R CF PV RG: FCF NPV Initial T RMindaugas PinčiukovasNo ratings yet
- FIN10670 - Formula Sheet - Final TestDocument2 pagesFIN10670 - Formula Sheet - Final TestSean ZhangNo ratings yet
- Exam Cheat Sheet VSJDocument3 pagesExam Cheat Sheet VSJMinh ANhNo ratings yet
- ECU Formulas (Modules 1+2) Trinity CollegeDocument4 pagesECU Formulas (Modules 1+2) Trinity CollegemihsovyaNo ratings yet
- Cost of CapitalDocument18 pagesCost of CapitalRajesh NangaliaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument20 pagesFormulasWilliam ZeNo ratings yet
- Formulae sheet: σ r a) 1 (r a r Document1 pageFormulae sheet: σ r a) 1 (r a r Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 8 PDFVasudev SinghNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimate, Elements of Cost & Break-Even Analysis (Lecture 2)Document33 pagesCost Estimate, Elements of Cost & Break-Even Analysis (Lecture 2)dhesNo ratings yet
- The FRM Part I: Formula Guide: Value and Risk ModelsDocument10 pagesThe FRM Part I: Formula Guide: Value and Risk ModelsJavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Interest Rates That Vary With Time: I A I CWDocument3 pagesInterest Rates That Vary With Time: I A I CWTepe HolmNo ratings yet
- Eng EcoDocument1 pageEng EcoMonique OrugaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy - Lecture6Document40 pagesEngineering Economy - Lecture6Aly Bueser75% (4)
- Midterm MathDocument4 pagesMidterm MathTuong TranNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Short-Term Solvency RatiosDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet Short-Term Solvency RatiosNguyễn Ngọc Phương LinhNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument7 pagesFormula SheetvermillionmiserNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2-Point - Elasticity-of-DemandDocument4 pagesWorksheet 2-Point - Elasticity-of-DemandFran YNo ratings yet
- POM Final FormulaDocument5 pagesPOM Final FormulaShawron weevNo ratings yet
- 05 Depresiasi Pajak Hutang Deni JaenudinDocument39 pages05 Depresiasi Pajak Hutang Deni JaenudinDENI JAENUDINNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument7 pagesFormula SheetanasfinkileNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy Lecture6Document40 pagesEngineering Economy Lecture6Jaed CaraigNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Equations Korea UniversityDocument2 pagesFinancial Management Equations Korea UniversityTom DNo ratings yet
- ACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Document6 pagesACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Waheed ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Formula-Sheet-for-the-SAT MathsDocument4 pagesFormula-Sheet-for-the-SAT MathsYumon KoNo ratings yet
- Maths Gen FormulaeDocument2 pagesMaths Gen FormulaeartisharmafjNo ratings yet
- Math 101C Assignment 1Document2 pagesMath 101C Assignment 1Jonassen KenrickNo ratings yet
- MATH 1010 Final Exam Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMATH 1010 Final Exam Formula SheetAayush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 EquationsDocument1 pageExam 2 EquationsFatma SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Sub Fibonacci Heaps HandoutDocument10 pagesSub Fibonacci Heaps HandoutVinay MishraNo ratings yet
- CV6216 2123 S2 TPwwf1B-After-tax AnalysisDocument12 pagesCV6216 2123 S2 TPwwf1B-After-tax AnalysisZJ XNo ratings yet
- Benefit Cost AnalysisDocument20 pagesBenefit Cost AnalysisrazNo ratings yet
- Marjorie ArevaloDocument22 pagesMarjorie ArevaloFrancis CayananNo ratings yet
- 4.2. Reasoning of NoptDocument5 pages4.2. Reasoning of NoptДаринаNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives NotesDocument12 pagesApplication of Derivatives NotesSamuel NDATIMANANo ratings yet
- Depreciation: Definition of TermsDocument6 pagesDepreciation: Definition of TermsGlyzel DizonNo ratings yet
- Type of CostDocument38 pagesType of CostNabeel BashirNo ratings yet
- Gmat Quant Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGmat Quant Cheat SheetWalterNo ratings yet
- Hedging Interest Rate RiskDocument14 pagesHedging Interest Rate RiskVictor ManuelNo ratings yet
- AIST Math Practice TestDocument21 pagesAIST Math Practice TestnourNo ratings yet
- Product and Service DesignDocument60 pagesProduct and Service DesignGlobal internetNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet FinanceDocument1 pageCheat Sheet FinanceGhitaNo ratings yet
- 16, 17 EoqDocument15 pages16, 17 EoqGayathri SantoshNo ratings yet
- 4 Year Lectures EPM 401A Electrical Power Systems 2A (Economic Dispatch)Document45 pages4 Year Lectures EPM 401A Electrical Power Systems 2A (Economic Dispatch)Fady MichealNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- WeirsDocument2 pagesWeirsMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Post HarvestDocument2 pagesPost HarvestMark SmithNo ratings yet
- (New Updated) Fittness ContractDocument1 page(New Updated) Fittness ContractMark SmithNo ratings yet
- 3is Research Mod 8Document7 pages3is Research Mod 8Mark Smith100% (1)
- Assignment No. 5 - Linear DE - 1st OrderDocument1 pageAssignment No. 5 - Linear DE - 1st OrderMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Appendix DDocument3 pagesAppendix DMark SmithNo ratings yet
- International Anti Corruption Day InfographicsDocument15 pagesInternational Anti Corruption Day InfographicsMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Review of DifferentiationDocument3 pagesReview of DifferentiationMark SmithNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET NO. 5 - Simple Harmonic MotionDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET NO. 5 - Simple Harmonic MotionMark SmithNo ratings yet
- Rajasthan VAT Technical GuideDocument170 pagesRajasthan VAT Technical GuideSuraj Shenoy NagarNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary Ledger: Department of Public Works and HighwaysDocument629 pagesSubsidiary Ledger: Department of Public Works and HighwaysKenneth Cyrus OlivarNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Documentary Requirements InfrastructureDocument4 pagesChecklist of Documentary Requirements InfrastructureQaimah MikunugNo ratings yet
- Oracle Accounts Receivables 1Document431 pagesOracle Accounts Receivables 1gangadhar1310100% (1)
- Amway Case StudyDocument8 pagesAmway Case StudyUbaid Ur Rehman KhanNo ratings yet
- Mind Tree Future OutlookDocument3 pagesMind Tree Future OutlookNilotpal MahantyNo ratings yet
- Accelerating Capital Markets Development in Emerging EconomiesDocument26 pagesAccelerating Capital Markets Development in Emerging EconomiesIchbin BinNo ratings yet
- Putnam Individual 401 (K)Document2 pagesPutnam Individual 401 (K)Putnam InvestmentsNo ratings yet
- Macro Environment of Australian Pet Wear Market For HalterDocument8 pagesMacro Environment of Australian Pet Wear Market For HalterHoang HungNo ratings yet
- (Economy) Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF), Repo, Reverse Repo, SLR, CRR, NEFT, RTGS, NDTL: Meaning ExplainedDocument14 pages(Economy) Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF), Repo, Reverse Repo, SLR, CRR, NEFT, RTGS, NDTL: Meaning Explainedsameer bakshiNo ratings yet
- TREE VALUES Havard Business SchoolDocument2 pagesTREE VALUES Havard Business SchoolparoengineerNo ratings yet
- Article 10 - Maalvinder SinghDocument8 pagesArticle 10 - Maalvinder SinghAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Development of An Advertising Program: Afjal Hossain, Associate Professor, Marketing, PSTUDocument13 pagesDevelopment of An Advertising Program: Afjal Hossain, Associate Professor, Marketing, PSTUTanvir BadhonNo ratings yet
- Liquidity and Cash ManagementDocument9 pagesLiquidity and Cash ManagementSharath MenonNo ratings yet
- Euromonitor Global Overview 2012 FinalDocument47 pagesEuromonitor Global Overview 2012 FinalNeha ShariffNo ratings yet
- Basics of Project ManagementDocument3 pagesBasics of Project ManagementWais Sadat0% (1)
- Macro - Lecture 2bDocument22 pagesMacro - Lecture 2bOtamurodNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document20 pagesCH 02nahlaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Harga Pokok Produksi Dengan Metode Activity Based Costing Untuk Mengambil Keputusan Manajemen Pada Industri Garmen CV. Surya SurabayaDocument12 pagesAnalisis Harga Pokok Produksi Dengan Metode Activity Based Costing Untuk Mengambil Keputusan Manajemen Pada Industri Garmen CV. Surya SurabayaNur Syafi'ahNo ratings yet
- Risks Involved in Transit Provision of Bus Contracts: Case Study of Transantiago, ChileDocument8 pagesRisks Involved in Transit Provision of Bus Contracts: Case Study of Transantiago, Chilealberto martinezNo ratings yet
- Purchase Consideration NumericalsDocument8 pagesPurchase Consideration NumericalsIsfh 67No ratings yet
- Marxism and "The Doll's House"Document2 pagesMarxism and "The Doll's House"FaizanAzizNo ratings yet
- Assignment EGR2302 - Ch08 PDFDocument65 pagesAssignment EGR2302 - Ch08 PDFRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document8 pagesChapter 6Bích TrầnNo ratings yet
- Solution Problem 1Document6 pagesSolution Problem 1Michelle Joy Nuyad-PantinopleNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Variable and Absorption CostingDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Variable and Absorption CostingKarthi SkNo ratings yet
- F6mys 2007 Dec PPQDocument19 pagesF6mys 2007 Dec PPQAnslem TayNo ratings yet
- Addison Mitchell - Braceros Socratic Seminar Note CatcherDocument4 pagesAddison Mitchell - Braceros Socratic Seminar Note Catcherapi-309290535No ratings yet