Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Test
Chapter 2 Test
Uploaded by
Jose SegalesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Test
Chapter 2 Test
Uploaded by
Jose SegalesCopyright:
Available Formats
End of chapter test
2 Representing relationships:
introducing functions
Section A. A calculator is not allowed
1 Which of the following sets of ordered pairs are functions?
a {(1, 1), (2, 4), (3, 3), (3, 6), (4, 8)}
b {(−1, 3), (−2, 5), (−3, 7), (−4, 9), (−5, 11)}
c {(−2, −2), (−1, −1), (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2)}
2 Which of the following relations are functions?
a b c
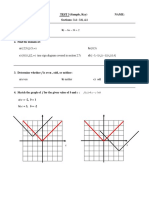
3 a Does this mapping diagram represent a function?
b State the domain and range.
4 f (x) =
3x + 5 and g ( x ) =
2 − 2x
Find:
a f ( 4) b f −1 (2 ) c f g (x) d g f ( −4 )
Solve:
e f ( x ) = −1
© Oxford University Press 2019 End of chapter test 1
End of chapter test
5 Write down the domain and range of this function:
6 Which of these are one-to-one functions?
a b
x −1
7 If f ( x ) = , find f−1(x).
x −2
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
End of chapter test
Section B. A calculator is allowed
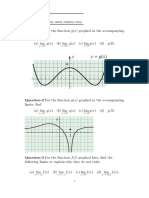
8 Use your GDC to sketch these graphs. Write down the domain and range of each:
a f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x − 3 x)
b g (= x +2
9 If l ( x )
= x 2 and m ( x ) = 2 x – 3 :
m (x)
a Find (l ◦ )
m (x)
b Sketch the function (l ◦ )
c State its domain and range.
10 If h ( = ) x + 1 and p ( x )
x 3 = x3 :
a Find x when h ( x ) = 13
b Find x when p ( x ) = −27
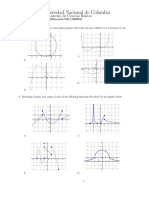
c Use a sketch to solve h ( x ) = p ( x ) .
11 Given f ( x ) =
3x − 5 and g ( x ) =
x − 2,
a Find f −1 ( x )
b Show that g −1 f( ) ( x=) 3x − 3
f (x)
Let h ( x )
= = and i ( x ) x
g (x)
c Solve h ( x ) = i ( x ) by sketching the functions.
12 Given f ( x ) = x 3 – 3 :
a Find the inverse function f −1
b If the point ( a, b ) lies on f ( x ) , what is the coordinate of its image on f −1 ( x ) ?
c Sketch them both on the same axes.
d Solve f ( x )
= f −1 ( x ) .
© Oxford University Press 2019 3
End of chapter test
Answers
1 b and c
2 a and c
3 a Yes
b The domain is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. The range is 19, 23, 29, 31.
4 a f ( 4=
) 3 ( 4) + =
5 17 c f g ( x ) = 3 (2 − 2 x ) + 5 = 11 − 6 x
b =
x 3y + 5 d g f ( −4 )
x −5 =
3y f ( −4 ) =3 ( −4 ) + 5 =−7
x −5 g ( −7 ) = 2 − 2 ( −7 ) = 16
y =
3
e 3x + 5 =−1
x −5
f −1
(x) = 3 3x = −6
x = −2
2−5
f −1 (2 ) = = −1
3
5 The domain is −6 ≤ x ≤ 4 and the range is −3 ≤ y ≤ 4
6 b
y −1
7 x =
y −2
x ( y − 2) = y − 1
xy − 2 x =y − 1
xy − y = 2 x − 1
y ( x − 1) = 2 x − 1
2x − 1
f −1 ( x ) =
x −1
8 a f ( x ) = x 2 + 2 x − 3 Domain x ∈ Range y ≥ −4
b g (=
x) x +2
Domain x ≥ −2 Range y ≥ 0
© Oxford University Press 2019 4
End of chapter test
( x ) = ( x + 3) = 4x 2 + 12x + 9
2
9 a (l ◦ m) 2
c Domain x ∈ Range y ≥ 0
10 a 3x + 1
= 1
3
3x = 12
4
x =
b x 3 = 27
−
x = −3
x =
−1.53, − 0.347, 1
.88
11 Given f ( x ) =
3x − 5 and g ( x ) =
x − 2,
a =
x 3y − 5
x +5 =
3y
x +5
f −1 ( x ) =
3
b (g −1
f ) ( x ) = (3x − 5) + 2 = 3x − 3
© Oxford University Press 2019 5
End of chapter test
x = 1.38, 3.61
12 Given f ( x ) = x 3 – 3 ,
a =
x y3 − 3
x +3 =y3
f −1 ( =
x) 3
x +3
b ( b, a)
c
d x = 1.67
© Oxford University Press 2019 6
You might also like
- 1st Periodical Examination in Gen. MathDocument2 pages1st Periodical Examination in Gen. MathAndrea Patricia93% (14)
- Year 1 Summer English Activity Booklet Lower AbilityDocument20 pagesYear 1 Summer English Activity Booklet Lower AbilitySam EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: 1 A B C D EDocument6 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: 1 A B C D EJohnNo ratings yet
- MATH 2413 Calculus I Prerequisite ReviewDocument6 pagesMATH 2413 Calculus I Prerequisite ReviewAnaNo ratings yet
- GCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsDocument5 pagesGCSEAndIGCSEFM FunctionsQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Template Week 01Document35 pagesTemplate Week 01Yazish KavinaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1SureshNo ratings yet
- Functions WorksheetDocument3 pagesFunctions WorksheetDevika TannaNo ratings yet
- MA5158 Practice Problems-Unit2Document3 pagesMA5158 Practice Problems-Unit2Mithun arjunNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument5 pagesQUIZReteshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- GenMath First QuaterlyDocument5 pagesGenMath First QuaterlyEmelyn Malillin100% (1)
- Prelims Math 212Document4 pagesPrelims Math 212ana valenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math W1 LAS3Document2 pagesGen Math W1 LAS3TJ gatmaitanNo ratings yet
- Math Review Pre-CalculusDocument6 pagesMath Review Pre-CalculusAmyNo ratings yet
- 1 Section 1.1: MATH 029-01 Review Packet For Chapter 1 September 11, 2019Document2 pages1 Section 1.1: MATH 029-01 Review Packet For Chapter 1 September 11, 2019FunmathNo ratings yet
- Quiz Like Questions From Unit 6-10Document8 pagesQuiz Like Questions From Unit 6-10Lucie StudgeNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math CH 1Document2 pagesDiscrete Math CH 1RS Fashion HouseNo ratings yet
- Solution Final ExamDocument9 pagesSolution Final ExamArbi HassenNo ratings yet
- Le 01Document2 pagesLe 01Kevin SilvaNo ratings yet
- A2h 1ST Sem Final Exam Review Part 1Document8 pagesA2h 1ST Sem Final Exam Review Part 1Dylan PagoagaNo ratings yet
- A2h 1st Sem Final Exam Review Part 1Document8 pagesA2h 1st Sem Final Exam Review Part 1Dylan PagoagaNo ratings yet
- HK2 2022Document5 pagesHK2 2022lasma.dundureNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 1sDocument3 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 1sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- MATH 131 Tutorial 2 2024Document2 pagesMATH 131 Tutorial 2 2024jamakonke8No ratings yet
- Practice Problems Final ExamDocument6 pagesPractice Problems Final ExamGyasi AnningNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument8 pagesFunctiongabriellestewart334No ratings yet
- Final Instrument (2019.05.15)Document8 pagesFinal Instrument (2019.05.15)Rochedel AsuncionNo ratings yet
- MA2002 AY2023 2024 Sem 1 Midterm Test r1 SolDocument7 pagesMA2002 AY2023 2024 Sem 1 Midterm Test r1 SolMadeleine YanNo ratings yet
- MATH 102 Tutorial 4 - Limits and ContinuityDocument2 pagesMATH 102 Tutorial 4 - Limits and ContinuityMpho TsheoleNo ratings yet
- Calculus1PracticeMidterm1 SolDocument12 pagesCalculus1PracticeMidterm1 SolNgan PhanNo ratings yet
- MATH 153 TEST 3 (Sample, Key) Name: Sections: 3.4 - 3.8, 4.1Document4 pagesMATH 153 TEST 3 (Sample, Key) Name: Sections: 3.4 - 3.8, 4.1Link ZeldaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - QuestionsDocument21 pagesMathematics - QuestionsMichelli YonathaNo ratings yet
- Class No: 60630, 60631, 60632 (SPRING 2022)Document3 pagesClass No: 60630, 60631, 60632 (SPRING 2022)Devilish LuciferNo ratings yet
- MATH 1241 Final Exam FALL 2012 Part I, No Calculators AllowedDocument12 pagesMATH 1241 Final Exam FALL 2012 Part I, No Calculators AllowedAestes KeiNo ratings yet
- Genmath LP - Operation FunctionsDocument3 pagesGenmath LP - Operation FunctionsClyde EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Math 31 Chapter 10 and 11 LessonsDocument26 pagesMath 31 Chapter 10 and 11 LessonsSam PanickerNo ratings yet
- Section A: Multiple Choices (12 Marks)Document8 pagesSection A: Multiple Choices (12 Marks)Ghith WhiuNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1Document36 pagesExercise Chapter 1Samuel Sim Shien ShuangNo ratings yet
- Q4 Basic Calculus Week 1 TasksDocument1 pageQ4 Basic Calculus Week 1 TasksLila KystNo ratings yet
- MAT1110 Tutorial 3Document3 pagesMAT1110 Tutorial 3daisymbewe8No ratings yet
- 12th Class Maths Guess Paper 2024Document19 pages12th Class Maths Guess Paper 2024Tahir SaleemNo ratings yet
- W#2 M#1 Operation On FunctionsDocument6 pagesW#2 M#1 Operation On FunctionsIsabel PerezNo ratings yet
- Math1012 Worhsheet IIDocument3 pagesMath1012 Worhsheet IIAlex HaymeNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their GraphsDocument6 pagesFunctions and Their GraphsRicardo PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- 2023 MAV MathsMethods Trial Exam 1 SolutionsDocument10 pages2023 MAV MathsMethods Trial Exam 1 Solutionsmiddoka101No ratings yet
- 201 Nya 05 2019 1Document3 pages201 Nya 05 2019 1rhl5761No ratings yet
- e 5792Document7 pagese 5792sevag002816No ratings yet
- 100 Ways To Motivate OthersDocument38 pages100 Ways To Motivate OthersonyejekweNo ratings yet
- MAT 1320 DGD WorkbookDocument120 pagesMAT 1320 DGD WorkbookAurora BedggoodNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Math 170Document5 pagesExam 3 Math 170hthaier4062No ratings yet
- MTH 112 Function and GeomentryDocument68 pagesMTH 112 Function and GeomentryMoluno Sarah100% (1)
- MATH 1103 Common Final Exam Multiple Choice Section Fall 2009Document10 pagesMATH 1103 Common Final Exam Multiple Choice Section Fall 2009MaucaNo ratings yet
- PracTestC PDFDocument4 pagesPracTestC PDFMihirNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Mathematics Extension 1: Use The Google Form Multiple-Choice Answer Sheet For Questions 1-10Document3 pagesYear 11 Mathematics Extension 1: Use The Google Form Multiple-Choice Answer Sheet For Questions 1-10Andric NelsonNo ratings yet
- Math 113/114, Midterm Exam, Version I Solutions: X 4 4 X 5 X +9 - 3 X - X X 6Document3 pagesMath 113/114, Midterm Exam, Version I Solutions: X 4 4 X 5 X +9 - 3 X - X X 6examkillerNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Performance Task - Q1 - W1-W4Document5 pagesGeneral Mathematics Performance Task - Q1 - W1-W4Rhoda May Bermejo TrompetaNo ratings yet
- Maths Lecturer 2021paperDocument48 pagesMaths Lecturer 2021papergeetadevirawat29No ratings yet
- OldexamsDocument12 pagesOldexamsAmaru JiNo ratings yet
- Taller # 1Document5 pagesTaller # 1Juan Camilo Sierra PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- #18 Dynamic Memory AllocationDocument5 pages#18 Dynamic Memory Allocationjagriti kumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Islam in The Subcontinent-2Document5 pagesChapter 3 - Islam in The Subcontinent-2Hamayal RehanNo ratings yet
- GC 2024 04 28Document25 pagesGC 2024 04 28Angelica ToroNo ratings yet
- Permit To TeachDocument1 pagePermit To TeachLeonorBagnisonNo ratings yet
- Sonshine Education Conference PresentationDocument77 pagesSonshine Education Conference PresentationTintu MaryNo ratings yet
- SRS - Training CalendarDocument3 pagesSRS - Training CalendardeepthiNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Syllabus PSGDocument15 pagesEmbedded Systems Syllabus PSGkumaranrajNo ratings yet
- 26.the Promise of A Savior - InddDocument2 pages26.the Promise of A Savior - Inddhershey ysulatNo ratings yet
- Calc Temp Load Capable of Cable-Neher-McGrathDocument13 pagesCalc Temp Load Capable of Cable-Neher-McGrathmcavy100% (1)
- (Inspired From Sabbath School Lesson Quarterly) : Living The Advent HopeDocument1 page(Inspired From Sabbath School Lesson Quarterly) : Living The Advent HopeGreg Martin OrbegosoNo ratings yet
- NFS 320 SM MuntinlupaDocument52 pagesNFS 320 SM MuntinlupaYek Yeu Merchandising, IncNo ratings yet
- Openssl NewsDocument17 pagesOpenssl NewsunrealmailNo ratings yet
- Yulia Demydovych The Second Course, 21-z: Live Audiovisual Translation: Challenges of The JobDocument7 pagesYulia Demydovych The Second Course, 21-z: Live Audiovisual Translation: Challenges of The JobyulNo ratings yet
- January Series: Physics Specification ADocument8 pagesJanuary Series: Physics Specification AsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Method of Speaking - 2Document70 pagesMethod of Speaking - 2hasdar73No ratings yet
- What Is CAN-FDDocument41 pagesWhat Is CAN-FDSandeep MishraNo ratings yet
- Common Misconceptions of Critical ThinkingDocument16 pagesCommon Misconceptions of Critical ThinkingCarlos Eduardo Pérez CrespoNo ratings yet
- What Am I Text Version Set 3Document4 pagesWhat Am I Text Version Set 3Dung NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Gimbutas 1989Document430 pagesGimbutas 1989Elefteria OuraniosNo ratings yet
- CLI Reference 3 6Document151 pagesCLI Reference 3 6Perica MaticNo ratings yet
- Python If, If... Else, If... Elif... Else and Nested If StatementDocument9 pagesPython If, If... Else, If... Elif... Else and Nested If StatementKaleeswariNo ratings yet
- NARRATIVE REPORt On Book WeekDocument1 pageNARRATIVE REPORt On Book WeekEmmalyn PastranaNo ratings yet
- Google - Premium.professional Cloud DevOps Engineer - by .VCEplus.52q DEMODocument26 pagesGoogle - Premium.professional Cloud DevOps Engineer - by .VCEplus.52q DEMOLove Sahil Sharma100% (1)
- 8051 Notes NewDocument70 pages8051 Notes NewWajahatNo ratings yet
- Kixtart Quick Reference: If StatementDocument3 pagesKixtart Quick Reference: If StatementhboveriNo ratings yet
- 8 T3 Final Exam RevisionDocument15 pages8 T3 Final Exam RevisionThe chair jimin falls fromNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document53 pagesChapter 1Anvesh DontulaNo ratings yet
- Building Apis With Django and Django Rest Framework: Release 2.0Document53 pagesBuilding Apis With Django and Django Rest Framework: Release 2.0Santiago RahmanNo ratings yet
- Klein-Gordon EquationsDocument7 pagesKlein-Gordon EquationsCecilia DécigaNo ratings yet