Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsAna Integ
Ana Integ
Uploaded by
Brent ValdespinaThe integumentary system consists of the skin and its derivatives. The skin acts as a protective barrier and has several layers, including the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and glands. Other components of the integumentary system include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair, and nails. The skin regulates body temperature and protects against damage, with its layers, cells, glands, and pigment providing these critical functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerLly Isidoro100% (2)
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesClassification Test For HydrocarbonsIz Alcausin100% (1)
- Anaphy Topic 3 IntegralDocument3 pagesAnaphy Topic 3 Integral박제라No ratings yet
- MOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Document41 pagesMOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Suez AyomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Integumentary SystemClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System 1Akemi LeeNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument10 pagesSkinKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Skinbody MemranesDocument3 pagesModule 3 Skinbody MemranesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDocument5 pagesCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- 04 INTEGUMENTARY PowerpointDocument22 pages04 INTEGUMENTARY Powerpointct328100% (3)
- Integumantary SystemDocument36 pagesIntegumantary SystemAXHYIANE MARGAUXNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary System PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary System PDFStefanie Henry100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemDocument27 pagesPowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Integument System ActivityDocument5 pagesIntegument System ActivityeywatsarawatNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 & 6Document18 pagesTopic 5 & 6PhoebeNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pages5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Mia Rev4Document4 pagesAnaphy Mia Rev4antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument7 pagesSkin and Body MembranesJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-Walker100% (2)
- The Integumentary System: Prepared By: Dr. Ma. Brenda C. Pancho Far Eastern University Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument99 pagesThe Integumentary System: Prepared By: Dr. Ma. Brenda C. Pancho Far Eastern University Anatomy and PhysiologyShamira Monique Almayda AlumisinNo ratings yet
- 6 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages6 Integumentary SystemPrincess kyle anicoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Skin and Appendages (PFOS-1 2014-15 Students Version)Document24 pagesSkin and Appendages (PFOS-1 2014-15 Students Version)Chris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- Burns SemDocument29 pagesBurns SemEsther Marie SazonNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument55 pagesSkinRachita BhayekarNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument8 pagesSkin and Body MembranesVincent AlgarmeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1Document15 pagesBIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1KellyPatrick SpencerNo ratings yet
- B 11 IntegumentDocument15 pagesB 11 Integumentpancit cantonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Fapc 111Document12 pagesIntegumentary System Fapc 111Marquisha Fiona De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Document40 pagesSKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Sadia SohailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- CH 5: Integumentary SystemDocument36 pagesCH 5: Integumentary SystemHurtlock HurtlockNo ratings yet
- Integuementary System ReviewerDocument10 pagesInteguementary System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Document4 pagesZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Integumentary SystemDocument31 pages2.5 Integumentary Systemhaiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Document4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNo ratings yet
- I) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueDocument44 pagesI) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueSaralitaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The SkinDocument32 pagesHistology of The SkinAbdishakur AdanNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesFunctions of The Integumentary SystemRoan MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Physiology of INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM FK PDFDocument84 pagesPhysiology of INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM FK PDFdaris agharidNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemAliyah ZalzosNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal CollegeDocument64 pagesThe Integumentary System: Prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal CollegeRaul ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Integumentary SystemDocument26 pagesHistology of The Integumentary Systemchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Integumentary Systemllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Skin ModifiedDocument33 pagesAnatomy of Skin ModifiedHarishchandra Yanamandala VenkataNo ratings yet
- Skin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPDocument59 pagesSkin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPJosephine SNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument44 pagesSkin and Body Membranesquiaballares19No ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument54 pagesSkin and Body MembranesEzekiel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aanatomy of Skin & Lesions 2Document77 pagesAanatomy of Skin & Lesions 2AdiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System LectureDocument157 pagesIntegumentary System LecturesnpjavierNo ratings yet
- Histology Skin & AppendagesDocument44 pagesHistology Skin & AppendagesMathew JosephNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - ANAPHYDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System - ANAPHYmariaNo ratings yet
- Body MembranesDocument10 pagesBody MembranesCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemLindley PareñoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System (Skin)Document35 pagesIntegumentary System (Skin)Holly TadesseNo ratings yet
- Lab Oral MucosaDocument46 pagesLab Oral Mucosapachara.p65No ratings yet
- Ana MuscDocument4 pagesAna MuscBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument49 pagesCirculatory SystemBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Ana NervDocument5 pagesAna NervBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System II Blood VesselsDocument7 pagesCirculatory System II Blood VesselsBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Test Bank DownloadDocument14 pagesJava Programming 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Test Bank DownloadAmos Hubert100% (15)
- Maa 2.10 Exponential EquationsDocument28 pagesMaa 2.10 Exponential EquationsMuborakNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Disaster-Proof Socialized Housing and Community CenterDocument18 pagesA Proposed Disaster-Proof Socialized Housing and Community CenterEunice VargasNo ratings yet
- Technology Education 042011 CebuDocument25 pagesTechnology Education 042011 CebuCoolbuster.NetNo ratings yet
- New Mecellose FMC-23021 Technical Report - 151214Document7 pagesNew Mecellose FMC-23021 Technical Report - 151214Paul Chende100% (1)
- 385C Waw1-Up PDFDocument4 pages385C Waw1-Up PDFJUNA RUSANDI SNo ratings yet
- FTW Carnivore Diet 2 Week ChallengeDocument3 pagesFTW Carnivore Diet 2 Week ChallengeJeniffer DáliaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineers DrawingDocument67 pagesCivil Engineers Drawingstruban8337No ratings yet
- AssignmentFile 867 01122023143532Document2 pagesAssignmentFile 867 01122023143532Prince DograNo ratings yet
- China Has More 'Nuclear Warheads' On Ballistic Missiles Than USn - ReportDocument21 pagesChina Has More 'Nuclear Warheads' On Ballistic Missiles Than USn - ReportRoddy PfeifferNo ratings yet
- A Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsDocument4 pagesA Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsMohammad Arif KamalNo ratings yet
- Conference 125Document10 pagesConference 125N P SrinivasaraoNo ratings yet
- Bioethanol Production From Banana Peels Using Different PretreatmentsDocument6 pagesBioethanol Production From Banana Peels Using Different PretreatmentsabdulhamidNo ratings yet
- Halpin TsaiDocument4 pagesHalpin Tsaimusic freakNo ratings yet
- Changes To Food Webs - Ecosystems and Habitats - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizeDocument8 pagesChanges To Food Webs - Ecosystems and Habitats - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesizeb2.dakurahNo ratings yet
- Bose Headset ManualDocument36 pagesBose Headset ManualKevinKadlec100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Living World 7th Edition Johnson Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living World 7th Edition Johnson Test Bank PDFgilbertsantiago6b9w1100% (14)
- SWT5 TimDocument90 pagesSWT5 TimDiệu Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Filipino CultureDocument9 pagesFilipino CultureJonna ChingcoNo ratings yet
- BOW - CSS 10 - Quarter 4Document3 pagesBOW - CSS 10 - Quarter 4CHRISTINE RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Car 66Document54 pagesCar 66Sha-Shib Aviation Academy67% (3)
- PECE0416 FTDocument2 pagesPECE0416 FTKenneth VallespinNo ratings yet
- Green Finance PCLDocument38 pagesGreen Finance PCLAbha AbhaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Rekayasa GempaDocument7 pagesJurnal Internasional Rekayasa GempaArdyas Fambayu Putra DyasNo ratings yet
- Expansion of Cements. Cause and ControlDocument2 pagesExpansion of Cements. Cause and ControlCristián JiménezNo ratings yet
- Que Stio N No Type (MC Q/SAT) CO Mapp Ing Answer KeyDocument24 pagesQue Stio N No Type (MC Q/SAT) CO Mapp Ing Answer Key9103SHIVAM JANANo ratings yet
- C AnnulationDocument15 pagesC AnnulationSaffronMaeNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing QUESTION BANKDocument5 pagesDigital Signal Processing QUESTION BANKSaran SekaranNo ratings yet
Ana Integ
Ana Integ
Uploaded by
Brent Valdespina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesThe integumentary system consists of the skin and its derivatives. The skin acts as a protective barrier and has several layers, including the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and glands. Other components of the integumentary system include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair, and nails. The skin regulates body temperature and protects against damage, with its layers, cells, glands, and pigment providing these critical functions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ana-Integ
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe integumentary system consists of the skin and its derivatives. The skin acts as a protective barrier and has several layers, including the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and glands. Other components of the integumentary system include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair, and nails. The skin regulates body temperature and protects against damage, with its layers, cells, glands, and pigment providing these critical functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesAna Integ
Ana Integ
Uploaded by
Brent ValdespinaThe integumentary system consists of the skin and its derivatives. The skin acts as a protective barrier and has several layers, including the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and glands. Other components of the integumentary system include sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair, and nails. The skin regulates body temperature and protects against damage, with its layers, cells, glands, and pigment providing these critical functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
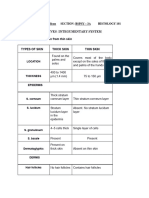
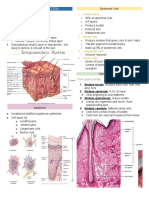
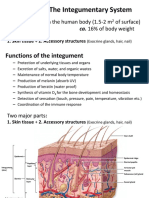
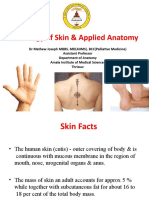
The Integumentary System Protects against mechanical damage, chemical damage,
Skin and Body Membranes bacterial damage, thermal damage, ultraviolet
Function of body membranes radiation, desiccation
Line or cover body surfaces Aids in heat regulation
Protect body surfaces Aids in excretion of urea and uric acid
Lubricate body surfaces Synthesizes vitamin D
Classification of Body Membranes Skin Structure
Epithelial membranes Epidermis – outer layer
Cutaneous membrane Stratified squamous epithelium
Mucous membrane – mucosa; wet membrane Often keratinized (hardened by keratin)
Serous membrane – serosa Dermis
Connective tissue membranes Dense connective tissue
Collagen and elastin
Cutaneous Membrane Deep to dermis is the hypodermis
Cutaneous membrane = skin Subcutaneous
A dry membrane Not part of the skin
Outermost protective boundary Anchors skin to underlying organs
Superficial epidermis Composed mostly of adipose tissue
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Underlying dermis Epidermis Layers
Mostly dense (fibrous) connective tissue Stratum basale/germinativum (basal)
Single layer of basophilic tall columnar cells with
Mucous Membranes mitotic figures
Surface epithelium Most cells undergo mitosis or germination
Underlying loose connective tissue (lamina propria) Youngest skin cells or melanocytes
Lines body cavities that open to the exterior surface Stratum spinosum (spiny)
Digestive Urinary Polyhedral cells with intercellular ridges
Respiratory Reproductive connecting cells
Often adapted for absorption or secretion Spiny and has desmosomes
Wet membranes bathed in secretions Stratum granulosum (granular)
With keratohyaline granules/glycolipids
Serous Membranes Stratum lucidum (clear)
Surface simple squamous epithelium Non-nucleated cells that occurs only in thick skin
Underlying areolar connective tissue likes soles and palms
Lines open body cavities that are closed to the exterior Stratum corneum (corny)
of the body Superficial layer of dead cornified cells
Occur in pairs – parietal (outer) and visceral (inner) Scrubs off whenever you bathe
Serous layers separated by serous fluid Thickest epidermis layer
Specific serous membranes
Peritoneum – abdominal cavity Various Cells of the Epidermis
Pleura – around the lungs Keratinocytes – produce keratin
Pericardium – around the heart Melanocytes – produce melanin
Langerhans cells – with immunological function
Connective Tissue Membrane Merkel cells – as mechanoreceptors
Synovial membrane
Areolar connective tissue only Melanin
Lines fibrous capsules surrounding joints Pigment (melanin) produced by melanocytes
Color is yellow to brown to black
Skin as Cutaneous Membrane Melanocytes are mostly in the stratum basale
A dry membrane Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetics
Outermost protective boundary and exposure to sunlight
Superficial epidermis
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Dermis
Underlying dermis Papillary layer – upper dermal layer
Mostly dense connective tissue Projections called dermal papillae
Pain receptors and touch receptors
Skin (cutaneous membrane) derivatives Capillary loops for nutrients
Sweat glands Hairs Result in fingerprints
Sebaceous glands Nails Reticular layer – deepest skin layer
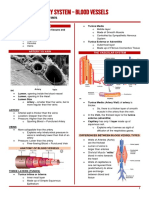
Skin Functions Blood vessels
Glands
Nerve receptors
Normal Skin Color Determinants 4. Nails
Melanin – yellow, brown or black pigments Scale-like modifications of the epidermis
Carotene – orange-yellow pigment from vegetables Heavily keratinized
Hemoglobin – red coloring from blood cells in dermal Stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed
capillaries – oxygen The thickened proximal area called the nail matrix is
Redness or erythema – blushing responsible for nail growth
Jaundice or yellow cast – liver disorder where excess Lack of pigment makes them colorless
bile pigments are absorbed in the blood Appear pink due to blood vessels underneath
Cyanosis – bluish discoloration of skin White crescent – lunula – thickened nail matrix
Appendages of the Skin Nail Structures
1. Sebaceous glands or oil glands Each nail has three parts
Produce oil Free edge
Lubricant for skin Body
Kills bacteria Root of nail
Result in blackheads and acne when clogged Eponychium – proximal nail fold that projects onto the
Most with ducts that empty into hair follicles nail body – often called cuticle
Glands are activated at puberty Nail matrix – contains nerves, lymph, blood vessels
Nail bed – skin below the nail plate
2. Sweat glands or sudoriferous/perspiration glands Nail sinus – where the nail root is inserted
Widely distributed in skin Free edge – anterior margin of the nail plate
Two types Hyponychium – between free edge and fingertip skin
Eccrine Nail wall – cutaneous fold overlapping the sides and
Open via duct to pore on skin surface proximal end
Apocrine or odoriferous glands Paronychium – border tissue around the nail
Ducts empty into hair follicles
In axilla (armpits), mammary areola Skin Homeostatic Imbalances
(breasts), labia majora (genital) and Infections
circumanal region (anus) Athletes foot – tinea pedis
Responsible for body odor Caused by fungal infection on feet
Boils and carbuncles
Sweat and Its Function Caused by bacterial infection – Staphylococcus
Composition aureus – in hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Mostly water and some metabolic waste Cold sores – fever blisters
Fatty acids and proteins (apocrine only) Caused by herpes simplex viral infection usually
Function on lips and in oral mucosa of the mouth
Helps dissipate excess heat
Excretes waste products Infections and allergies
Acidic nature inhibits bacteria growth Contact dermatitis
Odor is from associated bacteria Exposures to certain chemicals cause allergic
Lysozyme – enzyme found in sweat and tears reaction
Impetigo
3. Hair Pink, water-filled, raised lesions around the mouth
Produced by hair bulb caused by staphylococcus bacterial infection
Consists of hard keratinized epithelial cells Psoriasis
Melanocytes provide pigment for hair color Cause is unknown but chronic
Triggered by trauma, infection, stress
Hair Anatomy
Central core called the medulla Burns
Cortex surrounds medulla Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat,
Cuticle on outside of cortex formed from a single layer electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals
of cells that overlap like shingles on a roof to keep Nearly every body system is affected when skin is
hairs separated severely damages
Most heavily keratinized to provide strength Associated dangers
Worn more at tips to cause split ends Dehydration Circulatory shock
Associated Hair Structures Electrolyte imbalance Infection
Hair follicle – dermal (provides blood vessels) and
epidermal sheath surround hair root Rules of Nines
Arrector pilli – smooth muscle cause the hair to stand Way to determine the extent of burns
up – goose bumps Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation
Sebaceous (oil) gland Each area represents about 9%
Sweat gland Classified according to their severity (depth)
Severity of Burns
First-degree burns
Only epidermis is damaged
Skin is red and swollen
Partial-thickness burn that heals quickly
Second degree burns
Epidermis and upper dermis are damaged
Skin is red with blisters
Partial-thickness burn that heals w/o scar
Third-degree burns
Destroys entire skin layer
Burn is gray-white or black
Nerve endings destroyed so not painful
Full-thickness burn that does not heal and grafting
is necessary
Fourth-degree burns
Extend through the skin to injure muscle,
ligaments, tendons, nerves, blood vessels, and
bones
These burns always require medical treatment
Critical Burns
Burns are considered critical if:
Over 25% of body has second degree burns
Over 10% of the body has third degree burns
Third degree burns on the face, hands, feet
Skin Cancer
Cancer – abnormal cell mass
Benign
o Does not spread (encapsulated)
Malignant
o Metastasized (moves) to other parts of body
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer
Skin Cancer Types
Basal cell carcinoma
Least malignant
Most common type
Arises from stratum basale that no longer makes
keratin and stays in place
Squamous cell carcinoma
Arises from stratum spinosum
Metastasizes to lymph nodes
Early removal allows a good chance of cure
Malignant melanoma
Most deadly of skin cancers
Cancer of melanocytes
Metastasizes rapidly to lymph and blood vessels
Detection uses ABCD rule
ABCD Rule
A = Asymmetry
Two sides of pigmented mole do not match
B = Border irregularity
Borders of mole are not smooth
C = Color
Different colors in pigmented area
D = Diameter
Spot is larger then 6 mm in diameter
You might also like
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerLly Isidoro100% (2)
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument5 pagesClassification Test For HydrocarbonsIz Alcausin100% (1)
- Anaphy Topic 3 IntegralDocument3 pagesAnaphy Topic 3 Integral박제라No ratings yet
- MOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Document41 pagesMOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Suez AyomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Integumentary SystemClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System 1Akemi LeeNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument10 pagesSkinKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Skinbody MemranesDocument3 pagesModule 3 Skinbody MemranesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDocument5 pagesCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- 04 INTEGUMENTARY PowerpointDocument22 pages04 INTEGUMENTARY Powerpointct328100% (3)
- Integumantary SystemDocument36 pagesIntegumantary SystemAXHYIANE MARGAUXNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary System PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary System PDFStefanie Henry100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemCarmela Cordon FelixNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemDocument27 pagesPowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Integument System ActivityDocument5 pagesIntegument System ActivityeywatsarawatNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 & 6Document18 pagesTopic 5 & 6PhoebeNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pages5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Mia Rev4Document4 pagesAnaphy Mia Rev4antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument7 pagesSkin and Body MembranesJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-Walker100% (2)
- The Integumentary System: Prepared By: Dr. Ma. Brenda C. Pancho Far Eastern University Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument99 pagesThe Integumentary System: Prepared By: Dr. Ma. Brenda C. Pancho Far Eastern University Anatomy and PhysiologyShamira Monique Almayda AlumisinNo ratings yet
- 6 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages6 Integumentary SystemPrincess kyle anicoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Skin and Appendages (PFOS-1 2014-15 Students Version)Document24 pagesSkin and Appendages (PFOS-1 2014-15 Students Version)Chris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- Burns SemDocument29 pagesBurns SemEsther Marie SazonNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument55 pagesSkinRachita BhayekarNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument8 pagesSkin and Body MembranesVincent AlgarmeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1Document15 pagesBIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1KellyPatrick SpencerNo ratings yet
- B 11 IntegumentDocument15 pagesB 11 Integumentpancit cantonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Fapc 111Document12 pagesIntegumentary System Fapc 111Marquisha Fiona De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Document40 pagesSKIN STRUCTURE &FUNCTION Lec 1Sadia SohailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Anatomy and PhysiologyAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- CH 5: Integumentary SystemDocument36 pagesCH 5: Integumentary SystemHurtlock HurtlockNo ratings yet
- Integuementary System ReviewerDocument10 pagesInteguementary System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Document4 pagesZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Integumentary SystemDocument31 pages2.5 Integumentary Systemhaiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Document4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNo ratings yet
- I) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueDocument44 pagesI) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueSaralitaNo ratings yet
- Histology of The SkinDocument32 pagesHistology of The SkinAbdishakur AdanNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesFunctions of The Integumentary SystemRoan MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Physiology of INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM FK PDFDocument84 pagesPhysiology of INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM FK PDFdaris agharidNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemAliyah ZalzosNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal CollegeDocument64 pagesThe Integumentary System: Prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal CollegeRaul ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Integumentary SystemDocument26 pagesHistology of The Integumentary Systemchocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Integumentary Systemllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Skin ModifiedDocument33 pagesAnatomy of Skin ModifiedHarishchandra Yanamandala VenkataNo ratings yet
- Skin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPDocument59 pagesSkin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPJosephine SNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument44 pagesSkin and Body Membranesquiaballares19No ratings yet
- Skin and Body MembranesDocument54 pagesSkin and Body MembranesEzekiel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Aanatomy of Skin & Lesions 2Document77 pagesAanatomy of Skin & Lesions 2AdiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System LectureDocument157 pagesIntegumentary System LecturesnpjavierNo ratings yet
- Histology Skin & AppendagesDocument44 pagesHistology Skin & AppendagesMathew JosephNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - ANAPHYDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System - ANAPHYmariaNo ratings yet
- Body MembranesDocument10 pagesBody MembranesCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary SystemLindley PareñoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System (Skin)Document35 pagesIntegumentary System (Skin)Holly TadesseNo ratings yet
- Lab Oral MucosaDocument46 pagesLab Oral Mucosapachara.p65No ratings yet
- Ana MuscDocument4 pagesAna MuscBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument49 pagesCirculatory SystemBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Ana NervDocument5 pagesAna NervBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System II Blood VesselsDocument7 pagesCirculatory System II Blood VesselsBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Test Bank DownloadDocument14 pagesJava Programming 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Test Bank DownloadAmos Hubert100% (15)
- Maa 2.10 Exponential EquationsDocument28 pagesMaa 2.10 Exponential EquationsMuborakNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Disaster-Proof Socialized Housing and Community CenterDocument18 pagesA Proposed Disaster-Proof Socialized Housing and Community CenterEunice VargasNo ratings yet
- Technology Education 042011 CebuDocument25 pagesTechnology Education 042011 CebuCoolbuster.NetNo ratings yet
- New Mecellose FMC-23021 Technical Report - 151214Document7 pagesNew Mecellose FMC-23021 Technical Report - 151214Paul Chende100% (1)
- 385C Waw1-Up PDFDocument4 pages385C Waw1-Up PDFJUNA RUSANDI SNo ratings yet
- FTW Carnivore Diet 2 Week ChallengeDocument3 pagesFTW Carnivore Diet 2 Week ChallengeJeniffer DáliaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineers DrawingDocument67 pagesCivil Engineers Drawingstruban8337No ratings yet
- AssignmentFile 867 01122023143532Document2 pagesAssignmentFile 867 01122023143532Prince DograNo ratings yet
- China Has More 'Nuclear Warheads' On Ballistic Missiles Than USn - ReportDocument21 pagesChina Has More 'Nuclear Warheads' On Ballistic Missiles Than USn - ReportRoddy PfeifferNo ratings yet
- A Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsDocument4 pagesA Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsMohammad Arif KamalNo ratings yet
- Conference 125Document10 pagesConference 125N P SrinivasaraoNo ratings yet
- Bioethanol Production From Banana Peels Using Different PretreatmentsDocument6 pagesBioethanol Production From Banana Peels Using Different PretreatmentsabdulhamidNo ratings yet
- Halpin TsaiDocument4 pagesHalpin Tsaimusic freakNo ratings yet
- Changes To Food Webs - Ecosystems and Habitats - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC BitesizeDocument8 pagesChanges To Food Webs - Ecosystems and Habitats - KS3 Biology - BBC Bitesize - BBC Bitesizeb2.dakurahNo ratings yet
- Bose Headset ManualDocument36 pagesBose Headset ManualKevinKadlec100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Living World 7th Edition Johnson Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living World 7th Edition Johnson Test Bank PDFgilbertsantiago6b9w1100% (14)
- SWT5 TimDocument90 pagesSWT5 TimDiệu Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Filipino CultureDocument9 pagesFilipino CultureJonna ChingcoNo ratings yet
- BOW - CSS 10 - Quarter 4Document3 pagesBOW - CSS 10 - Quarter 4CHRISTINE RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Car 66Document54 pagesCar 66Sha-Shib Aviation Academy67% (3)
- PECE0416 FTDocument2 pagesPECE0416 FTKenneth VallespinNo ratings yet
- Green Finance PCLDocument38 pagesGreen Finance PCLAbha AbhaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Rekayasa GempaDocument7 pagesJurnal Internasional Rekayasa GempaArdyas Fambayu Putra DyasNo ratings yet
- Expansion of Cements. Cause and ControlDocument2 pagesExpansion of Cements. Cause and ControlCristián JiménezNo ratings yet
- Que Stio N No Type (MC Q/SAT) CO Mapp Ing Answer KeyDocument24 pagesQue Stio N No Type (MC Q/SAT) CO Mapp Ing Answer Key9103SHIVAM JANANo ratings yet
- C AnnulationDocument15 pagesC AnnulationSaffronMaeNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing QUESTION BANKDocument5 pagesDigital Signal Processing QUESTION BANKSaran SekaranNo ratings yet