Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Three Stages of Fetal Development
Three Stages of Fetal Development
Uploaded by
mellowlilydee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pages1) The fetal development process occurs over three main stages: preembryonic, embryonic, and fetal.
2) During the embryonic stage from weeks 3 to 8, fetal structures like the placenta, amniotic membranes, and organs begin to form.
3) The placenta functions to support the growing fetus by producing hormones, filtering waste, and facilitating nutrient/gas exchange between mother and fetus via the umbilical cord and blood vessels.
Original Description:
Three Stages of Fetal Development
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The fetal development process occurs over three main stages: preembryonic, embryonic, and fetal.
2) During the embryonic stage from weeks 3 to 8, fetal structures like the placenta, amniotic membranes, and organs begin to form.
3) The placenta functions to support the growing fetus by producing hormones, filtering waste, and facilitating nutrient/gas exchange between mother and fetus via the umbilical cord and blood vessels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesThree Stages of Fetal Development
Three Stages of Fetal Development
Uploaded by
mellowlilydee1) The fetal development process occurs over three main stages: preembryonic, embryonic, and fetal.
2) During the embryonic stage from weeks 3 to 8, fetal structures like the placenta, amniotic membranes, and organs begin to form.
3) The placenta functions to support the growing fetus by producing hormones, filtering waste, and facilitating nutrient/gas exchange between mother and fetus via the umbilical cord and blood vessels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
uterine cavity in 720
Three Stages of Fetal Development
• Cleavages create a ball of 16 - 50
cells called a morula, which divides
Preembryoni Embryonic Fetal stage: into cells that form fetal structures
c stage: stage: ( eight week
( fertilization ( weeks 3 until birth ) • Blastocysts - inner cells form the
through the through the embryo and the amnion
second week ) eighth week ) • Trophoblasts - outer cells form the
embryonic membranes, Chorion and placenta
• Embryoblast/inner cell mast –
portion that will form the embryo
Fertilization - union of the ovum and
sperm in the outer 3rd of the fallopian
• Implantation in the
tube creating a zygote
endometrium occurs
• The union restores the diploid number of
between the 8th to 10th day.
46 chromosomes
Apposition – blastocyst brushes
3 separate factors of fertilization
against the rich uterine endometrium.
1. Equal maturation of both sperm and
Adhesion – it attaches to the surface
ovum
of the endometrium
2. Ability of the sperm to reach the ovum
Invasion – settle down into its soft folds
3. Ability of the sperm to penetrate the zona
pellucida and cell membrane and achieve
•Fetal membranes start forming
fertilization
around the time of implantation
• When ovum is extruded from a
• Decidua “falling off” endometrial lining
graafian follicle – it is surrounded
by a mucopolysaccharide fluid
• Chorionic villi – form the placenta
(zona pellucida)and a circle of
– Central core - produce various placental
corona radiata or circle of cells
hormones, such as hCG,
somatomammotropin (human placental
• An ejaculation of semen averages 2.5 ml
lactogen [hPL]), estrogen, and progesterone.
of fluid containing 50 to 200ml million
- middle layer, the cytotrophoblast or
spermatozoa/ml (400ml
sperm/ejacultation)
Langhans’ layer – provide protection
• Sperm reach the cervix within 90 seconds
and the fallopian 5minutes after deposition
PLACENTA - “pancake,”
Capacitation – is the process consist of changes
Placenta
in the plasma membrane of the sperm head,
• Functioning by end of the 3rd wk.
which
• Produces hormones that control the
reveal the sperm-binding receptor sites.
basic physiology of the mother and near
term mature fetal organs for life outside
All of the spermatozoa that achieve capacitation
of the uterus
reach the ovum and cluster around theprotective
• Protects the fetus from immune attack
layer of corona cells.
by the mother
• Removes waste produced by the fetus
Spermatozoa releases hyaluronidase (a
the rate of uteroplacental blood flow in
proteolytic
pregnancy increases from about 50 ml/min
enzyme) to dissolve the layer protecting the ovum
at 10 weeks to 500 to 600 ml/min at term
• Zygote undergoes cleavages
Braxton Hicks contractions- barely
(mitosis) as it is transported to the
noticeable uterine contractions
Embryonic and Fetal Structures • AMNION – inner most part
• Placental barrier prevents the mix of - produce amniotic fluid
maternal blood with fetal blood - produce phospholipids
Placental Hormones Amniotic Fluid
• Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) • Surrounds embryo,
• Human placental lactogen (hPL) • Helps maintain a constant body
• Estrogen, progesterone temperature for the fetus
• Relaxin • Permits symmetric growth and
development
UTERINE PERFUSION AND PLACENTAL • Cushions the fetus from trauma
CIRCULATION - are most efficient when the
mother lies on her left side Amniotic Fluid Function
• Allows the umbilical cord to be relatively
VENA CAVA SYNDROME - At term a placenta free of compression
weighs 400 to 600 g (1 • Promotes fetal movement to enhance
lb), one-sixth the weight of the newborn musculoskeletal development
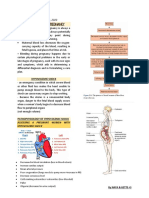
ENDOCRINE FUNCTION UMBILICAL CORD
Human Chorionic Umbilical cord
• Life line between mother and embryo
• act as a fail-safe measure to ensure the • 1 large vein & 2 small arteries (AVA)
corpus luteum of the ovary continues to • Wharton’s jelly surrounds the blood
produce progesterone and estrogen so the vessels preventing compression
endometrium of the uterus is maintained • Term length 21 in. / 3/4 in. wide
• Central insertion site on the placenta
• play a role in suppressing the maternal
immunologic response so placental tissue • Rate of blood flow at term – 350ml/min
is not detected and rejected as a foreign
substance. • Hypocoiling – assoc. maternal
hypertension
PROGESTERONE - “hormone that maintains
pregnancy.” • Hypercoiling – assoc. respiratory distress
- reduce the contractility of the uterus in the newborn
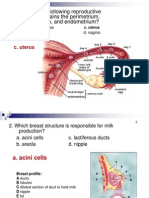
ESTROGEN - “hormone of women” Origin and Development of Organ Systems
- contributes to the woman’s mammary
gland development • STEM CELLS – totipotent, pluripotent,
- stimulates uterine growth multipotent
Human Placental Lactogen (Human • ZYGOTE GROWTH – CEPHALOCAUDAL
Chorionic Somatomammotropin) DIRECTION
- promotes mammary gland (breast) CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
growth
• forms as early as the 16th day of life and
- regulates maternal glucose, protein, and beats as early as the 24th
fat levels • sixth or seventh week - septum that
divides the heart into chambers develops
AMNIOTIC MEMBRANES • Seventh week - heart valves develop
• 10th to 12th week - heartbeat may be
• CHORION – outer mostpart heard with a Doppler instrument
Fetal Circulation • approximately 35 weeks, there is a surge
in the production of lecithin, which then
• Needed to sustain the fetus becomes the chief component by a ratio of 2:1.
• Must develop quickly and accurately
since the fetal nutrient needs Increase NERVOUS SYSTEM
as the embryo advances to a fetus
• Oxygen received from the placenta • 3RD WEEK – neural plate apparent
• Placenta functions for the fetal lungs • 8th WEEK – brain waves can be detected
and liver on EEG
• 24 WEEKS – ear is capable of responding
Three unique shunts to sound; eyes exhibit pupillary reaction
• Ductus Venosus
• Foramen Ovale ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
• Ductus Arteriosus
• The fetal pancreas produces insulin
FETAL HEMOGLOBIN needed by the fetus (insulin is one of the
few substances that does not cross the
• hemoglobin is more concentrated placenta from the mother to the fetus).
• a newborn’s hemoglobin level is about • The thyroid and parathyroid glands play
17.1 g/100 ml compared with a normal vital roles in fetal metabolic function and
adult level of 11 g/100 ml; calcium balance.
• a newborn’s hematocrit is about 53% • The fetal adrenal glands supply a
compared with a normal adult level of 45 precursor necessary for estrogen
synthesis by the placenta.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.
• 3RD WEEK - the respiratory and digestive
tracts exist as a single tube • 6TH WEEK – rapid intestinal growth
• 4TH WEEK - a septum begins to divide the • Meconium is sticky in consistency and
esophagus from the trachea; lung buds appears black or dark
appear on TRACHEA • vitamin K
Other important respiratory developmental DIGESTIVE TRACT
milestones
include: • 36 WEEKS - secrete enzymes
• Spontaneous respiratory practice movements
begin as • LIVER – active throughout intrauterine life
early as 3 months gestation and continue
throughout MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
pregnancy.
• Specific lung fluid with a low surface tension • 2 weeks- cartilage prototypes provide position
and low and
viscosity forms in alveoli to aid in expansion of support to the fetus.
the alveoli • 12th week - Ossification of the cartilage into
at birth; it is rapidly absorbed shortly after birth. bone
• Surfactant, a phospholipid substance, is formed begins.
and • 11th week - A fetus can be seen to move on
excreted by the alveolar cells of the lungs ultrasonography
beginning at • 16 to 20 weeks of gestation - quickening
approximately the 24th week of pregnancy.
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
SURFACTANT
• lecithin and Sphingomyelin • 8 weeks - by chromosomal analysis or
analysis of fetal cells in the mother’s
bloodstream SEX CAN BE DETERMINED
• sixth week after implantation, the gonads
(i.e., ovaries or testes) form
• 8 weeks - by chromosomal analysis or
analysis of fetal cells in the mother’s
bloodstream SEX CAN BE DETERMINED
• sixth week after implantation, the gonads
(i.e., ovaries or testes) form
URINARY SYSTEM
• 4TH WEEK -rudimentary kidney present
• 12th WEEK – urine is formed
• 16th WEEK – urine excreted into the
amniotic fluid
• At term – urine excreted at a rate of
500ml/day
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
• 36 WEEKS – subcutaneous fat begins to
be deposited underneath the skin
• LANUGO – SOFT DOWNY HAIRS
• VERNIX CASEOSA - cream cheese–like
substance
IMMUNE SYSTEM
• 20th week - Immunoglobulin (Ig) G
maternal antibodies cross the placenta
into the fetus
• 24th week of intrauterine life to give a
fetus temporary passive immunity against
Development
• Embryonic and Fetal Development
Expected Date of Birth (EDB)
• Nagele’s Rule – to calculate
the date of birth by this rule,
count backward 3 calendar
months from the 1st day of the
last menstrual period and add
7 days.
You might also like
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 6: Occurrence of EvolutionDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 6: Occurrence of EvolutionMarii100% (1)
- Culturally Competent Nursing CareDocument22 pagesCulturally Competent Nursing CareFrancia ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Presenter Eessaa ShresthaDocument72 pagesPlacenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Presenter Eessaa ShresthaEsa SthaNo ratings yet
- MCH BulletsDocument13 pagesMCH BulletsPatziedawn GonzalvoNo ratings yet
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- Physical and Physiological Changes in PregnancyDocument35 pagesPhysical and Physiological Changes in PregnancyAYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 LectureDocument4 pagesNCM 107 LectureZeheriahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Obstetrics & Midwifery CareDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Obstetrics & Midwifery CareWhirmey ChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Passenger: (Fetus and Placenta)Document24 pagesPassenger: (Fetus and Placenta)Toni DomingoNo ratings yet
- Hartmann (2005) Jama 293:2141-8 (Pubmed) : Iii. Grading of Perineal LacerationsDocument4 pagesHartmann (2005) Jama 293:2141-8 (Pubmed) : Iii. Grading of Perineal Lacerationsmary grace manalangNo ratings yet
- Abortion: Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument8 pagesAbortion: Sudden Pregnancy ComplicationsErnest canete100% (1)
- 1 NCM112 Sexually Transmitted Diseases de VeyraDocument9 pages1 NCM112 Sexually Transmitted Diseases de VeyraGrace OrdameNo ratings yet
- Obst ObjectivesDocument85 pagesObst ObjectivesManotshi MotloungNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing (PIH, GDM, HELLP Syndrome, Eclampsia and Pre-Eclampsia)Document6 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing (PIH, GDM, HELLP Syndrome, Eclampsia and Pre-Eclampsia)PAULINE BERNICE BAGUIONo ratings yet
- NCM 237-Course-OutlineDocument2 pagesNCM 237-Course-OutlineKhibul LimNo ratings yet
- Placenta Umbilical CordDocument39 pagesPlacenta Umbilical Cordbel4ronaldoeNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument333 pagesReviewerJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Icf 1Document5 pagesIcf 1nipajohnpaul7No ratings yet
- (OBS) 3.08b Sexually Transmitted Diseases in Pregnancy - Bongala (Nov 30)Document18 pages(OBS) 3.08b Sexually Transmitted Diseases in Pregnancy - Bongala (Nov 30)Gerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument39 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRena VilNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding & Complementary Feeding: Basic PediatricsDocument13 pagesBreastfeeding & Complementary Feeding: Basic PediatricsChristian TayagNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanRachel Ann JimenezNo ratings yet
- Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesFetal Growth and DevelopmentAngel Shaina VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and Fetal Development Abd CirculiationDocument54 pagesFertilization and Fetal Development Abd CirculiationMohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhNo ratings yet
- Community DiagnosisDocument6 pagesCommunity DiagnosisFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- CPH LecDocument46 pagesCPH LectuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 Power and PsycheDocument13 pagesNCM 102 Power and Psychelarissedeleon100% (1)
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusDocument15 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusLuna Sang-an100% (1)
- Prenatal Management (Part 5)Document36 pagesPrenatal Management (Part 5)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections StisDocument2 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Stisapi-646865632No ratings yet
- CHNIMODULEIDocument44 pagesCHNIMODULEIlagumbayjoviann1No ratings yet
- NCM 109 High Risk PregnancyDocument8 pagesNCM 109 High Risk PregnancyAngel MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Apgar Scoring: Common Tyes of BedDocument8 pagesApgar Scoring: Common Tyes of BedJANE CASSANONo ratings yet
- Cough Up 3-5ml SputumDocument28 pagesCough Up 3-5ml Sputumnipajohnpaul7No ratings yet
- Funda 4Document6 pagesFunda 4Kevin CondeNo ratings yet
- CP PHC NotesDocument27 pagesCP PHC NotesNano Ka100% (1)
- Ob 100 RatioDocument13 pagesOb 100 RatioJUANJOSEFOXNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument7 pagesVital SignsEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Practice Test Part 1Document10 pagesObstetric Nursing Practice Test Part 1yanee06No ratings yet
- Prenatal Management (Part 4)Document17 pagesPrenatal Management (Part 4)Austine James Sabenicio PantiloNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument4 pagesBleeding During PregnancyCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- Administering Tetanus Toxoid VaccineDocument2 pagesAdministering Tetanus Toxoid VaccinechateNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health Nursing - 50 Item Without RatioDocument3 pagesMaternal Health Nursing - 50 Item Without RatioDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Non Time-Bound Procedures: ProcedureDocument5 pagesNon Time-Bound Procedures: ProcedureArlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Compre MCNDocument21 pagesCompre MCNMary Ann G. CorsanesNo ratings yet
- MCP NCP Benefits SlidesDocument13 pagesMCP NCP Benefits SlidesJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument25 pagesEctopic Pregnancyfred_chandh88No ratings yet
- High - Risk PregnancyDocument110 pagesHigh - Risk PregnancyAndre DityaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference?: EINC (Ma'am Nera Galan)Document2 pagesWhat Is The Difference?: EINC (Ma'am Nera Galan)Angeline NavarroNo ratings yet
- OB QuizDocument45 pagesOB QuizJonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- 3 1-EINC - HandleDocument7 pages3 1-EINC - HandleBartolore Dayanan Kheng LeeNo ratings yet
- First Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionDocument4 pagesFirst Trimester Bleeding I. AbortionMikhaela Andree MarianoNo ratings yet
- OB Power Point Presntation 001Document50 pagesOB Power Point Presntation 001RitamariaNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 (Continuation) Postpartal Period and PediatricsDocument29 pagesNCM 101 (Continuation) Postpartal Period and PediatricsAudi Kyle SaydovenNo ratings yet
- 2011 10 10 MWF Background To Education Pack V 4Document38 pages2011 10 10 MWF Background To Education Pack V 4Jonas Marvin AnaqueNo ratings yet
- OB NotesDocument34 pagesOB NotesJillKellyNo ratings yet
- Final Checklist On Leopolds Fundic and FHTDocument3 pagesFinal Checklist On Leopolds Fundic and FHTCharlmagne LinnamNo ratings yet
- Week 8.4 MCNDocument12 pagesWeek 8.4 MCNZxiayieee JeonNo ratings yet
- NCM QuizDocument7 pagesNCM QuizKyla Marie NabongNo ratings yet
- MCN HandoutsDocument22 pagesMCN HandoutsFRANCYM PRINCESSRICH BATENGANo ratings yet
- NCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument5 pagesNCM 108 - Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusKristine BartsNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexual ReproductionJumongNo ratings yet
- UNDS111 Midterm ReviewerDocument18 pagesUNDS111 Midterm ReviewerJULIANA NICOLE TUIBUENNo ratings yet
- BSc.-3 Development - of - Chick - 1 by Suman KriDocument4 pagesBSc.-3 Development - of - Chick - 1 by Suman Krisimran kaurNo ratings yet
- Intergrated Science Paper 1Document2 pagesIntergrated Science Paper 1TubocurareNo ratings yet
- Science 5 QTR 1Document4 pagesScience 5 QTR 1ISABELITANo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Biology (GE111)Document8 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Biology (GE111)Nathaniel Victor BalerNo ratings yet
- Practical - DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF FROGDocument6 pagesPractical - DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF FROGtooba tahirNo ratings yet
- 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants PPT - Part 6Document18 pages5 Morphology of Flowering Plants PPT - Part 6Jeevan RaajNo ratings yet
- Zoology Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)Document33 pagesZoology Multiple Choice Question (GuruKpo)GuruKPO100% (2)
- I. A. Table 1: Flower Parts Illustration Example: Systematics Act. 3 Phytography: FlowerDocument19 pagesI. A. Table 1: Flower Parts Illustration Example: Systematics Act. 3 Phytography: FlowerAngeline Casis CordovaNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Randomized Study Comparing Two Commercially Available Types of Human Embryo Culture Media: G1-PLUS / G2-Plus Sequential Medium (Vitrolife) and The GL BLAST Sole Medium (Ingamed)Document4 pagesA Prospective Randomized Study Comparing Two Commercially Available Types of Human Embryo Culture Media: G1-PLUS / G2-Plus Sequential Medium (Vitrolife) and The GL BLAST Sole Medium (Ingamed)meltwithsnow163.comNo ratings yet
- A Case Discussion of Ayurvedic Management of "Vandhyatva" (Infertility)Document5 pagesA Case Discussion of Ayurvedic Management of "Vandhyatva" (Infertility)Varsha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Checkpoint AnswersDocument3 pagesEcosystem Checkpoint AnswersDearbhla HubbardNo ratings yet
- 1998-Callus Induction and Somatic Embryogenesis of Phalaenopsis PDFDocument5 pages1998-Callus Induction and Somatic Embryogenesis of Phalaenopsis PDFRobinson TroncosNo ratings yet
- G11 LifeSciences DigitalSupport Web Practice Examination Paper 2-10Document8 pagesG11 LifeSciences DigitalSupport Web Practice Examination Paper 2-10LISA LUFUSONo ratings yet
- Chapter1.2 Pollination, Pollinators & Pollination ModesDocument9 pagesChapter1.2 Pollination, Pollinators & Pollination Modesalberto saenzNo ratings yet
- Day6-She Comes FirstDocument18 pagesDay6-She Comes FirstGabrielNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Sporophytes and Gametophytes in BryophytesDocument7 pagesEvolution of Sporophytes and Gametophytes in BryophytesKhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document10 pagesChapter 10Dea GamaraNo ratings yet
- A Stem Cell Story ReflectionDocument2 pagesA Stem Cell Story ReflectionCharlize Mae ArboladuraNo ratings yet
- Class 10 How Do Organism ReproduceDocument4 pagesClass 10 How Do Organism ReproduceshonmichalNo ratings yet
- Embryo AssignmentDocument2 pagesEmbryo AssignmentA.j. MasagcaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Learning Guide: Course Audit in Maternal and Child NursingDocument18 pagesInstructional Learning Guide: Course Audit in Maternal and Child NursingMaynard PascualNo ratings yet
- PubertyDocument55 pagesPubertyMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- The Miracle of LifeDocument6 pagesThe Miracle of LifeKiseKunNo ratings yet
- TLE 101 - Unit 7 - Fruit Tree Crop ProductionDocument48 pagesTLE 101 - Unit 7 - Fruit Tree Crop ProductionAGNES TUBOLANo ratings yet
- Somatic Embryogenesis in Some Cactus and Agave SpeciesDocument10 pagesSomatic Embryogenesis in Some Cactus and Agave Specieseko susiloNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Morphology of The Reproductive System and Anatomy of Hen's EggDocument11 pagesAn Introduction To Morphology of The Reproductive System and Anatomy of Hen's EggGusti Anggih WibowoNo ratings yet
- The Modes of Natural SelectionDocument4 pagesThe Modes of Natural SelectionYam YamNo ratings yet