Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 viewsCONTRACT
CONTRACT
Uploaded by
Sherlock Yookie1. A contract is a meeting of the minds between two or more parties that creates obligations or duties. It involves an agreement whereby the parties bind themselves to certain terms.
2. The key elements of a valid contract include offer, acceptance, and consideration. Contracts must also comply with legal requirements and public policy.
3. Contracts are governed by principles of autonomy, where parties have freedom to establish terms, and obligatoriness, where valid contracts are legally binding and enforceable. Mutuality and reciprocity mean obligations are mutual between parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Contracts Because They Have To ComplyDocument6 pagesContracts Because They Have To ComplyAnna Biella Dacaymat PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts Book IV: Civil Code of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesObligations and Contracts Book IV: Civil Code of The PhilippinesJeramae LuterioNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument3 pagesCONTRACTSsweetestcitrus13No ratings yet
- Contracts ObliDocument32 pagesContracts ObliAnsherina FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Contracts: Definition, Classification, and DistinctionsDocument20 pagesContracts: Definition, Classification, and DistinctionsKyle BandolaNo ratings yet
- Article 1305: Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 - Contracts, General ProvisionsDocument15 pagesArticle 1305: Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 - Contracts, General ProvisionsBryne SarillanaNo ratings yet
- Contracts: 1. DEFINITION. The NCC Defines A Contract As "A Meeting of Minds Between Two Persons Whereby (Art. 1305, NCC)Document9 pagesContracts: 1. DEFINITION. The NCC Defines A Contract As "A Meeting of Minds Between Two Persons Whereby (Art. 1305, NCC)VIRILITER AGITENo ratings yet
- Contracts Basic ConceptsDocument14 pagesContracts Basic ConceptsCory RitaNo ratings yet
- Title II - ContractsDocument3 pagesTitle II - ContractsSha Napoles100% (1)
- Handouts For The Law On ContractsDocument5 pagesHandouts For The Law On ContractsHannah Jane UmbayNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument3 pagesContractsJillian PizarroNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS Chapter 1Document17 pagesCONTRACTS Chapter 1LabLab ChattoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Moody PrincessNo ratings yet
- Sales Notes For Prelim2Document11 pagesSales Notes For Prelim2gongsilogNo ratings yet
- ComlawDocument3 pagesComlawANNE GRACE MOSQUEDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6Sheila FernándezNo ratings yet
- Oblicon PrefinalsDocument15 pagesOblicon PrefinalsFrancis Therese RosalesNo ratings yet
- Contracts: General ProvisionsDocument8 pagesContracts: General ProvisionsVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- General Provisions of ContractsDocument42 pagesGeneral Provisions of ContractsShan Marie RusianaNo ratings yet
- Contracts Art. 1305Document4 pagesContracts Art. 1305chxrlttxNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument4 pagesLaw On ContractsRizza OlanoNo ratings yet
- 1 Part 2: ContractsDocument6 pages1 Part 2: ContractsPrei BaltazarNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument23 pagesCONTRACTSAllyza Mae Araojo LumboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. General ProvisionsDocument9 pagesChapter 1. General ProvisionsRose Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3602 ContractsDocument13 pagesRFBT.3602 ContractsGrezel Mae ProvidoNo ratings yet
- C. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsDocument12 pagesC. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsElla Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Tittle II ContractsDocument3 pagesOBLICON Tittle II Contracts2023303601No ratings yet
- Obligations FinalDocument114 pagesObligations FinalWency CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesOblicon Midterm ReviewerKing PerezNo ratings yet
- I. Contracts in GeneralDocument57 pagesI. Contracts in GeneralVal Escobar MagumunNo ratings yet
- Contracts ART. 1305 1368Document16 pagesContracts ART. 1305 1368Nathalie BermudezNo ratings yet
- Prof. Roentgen F. Bronce: Credit TransactionsDocument13 pagesProf. Roentgen F. Bronce: Credit TransactionsAnnaNo ratings yet
- Credit Midterms ReviewerDocument83 pagesCredit Midterms Reviewermelaniem_1No ratings yet
- Classification of ContractsDocument97 pagesClassification of ContractsAngelo Otañes GasatanNo ratings yet
- A. CHAP 1 - 1305 - 1317Document8 pagesA. CHAP 1 - 1305 - 1317Jes MariamNo ratings yet
- Notes On Oblicon - Part 3Document15 pagesNotes On Oblicon - Part 3Xelly J.No ratings yet
- Pre Finals Reviewer FinalDocument14 pagesPre Finals Reviewer FinalAises Minoza100% (1)
- Sanchez Roman-A Juridical Convention Manifested inDocument10 pagesSanchez Roman-A Juridical Convention Manifested insakuraNo ratings yet
- Contracts (Oblicon Reviewer)Document15 pagesContracts (Oblicon Reviewer)Bryan AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Title Ii ContractsDocument7 pagesTitle Ii Contractsyanice coleen diazNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS - General ProvisionsDocument6 pagesCONTRACTS - General ProvisionsJoanne Gonzales JuntillaNo ratings yet
- 02 Contracts Contracts Notes Oct 2021 PDFDocument11 pages02 Contracts Contracts Notes Oct 2021 PDFhswjushdjwkwNo ratings yet
- Buenaventura vs. Metropolitan Bank and Trust Company 799 SCRA 239 August 03 2016Document24 pagesBuenaventura vs. Metropolitan Bank and Trust Company 799 SCRA 239 August 03 2016Kristin C. Peña-San FernandoNo ratings yet
- Obligations and ContractsDocument4 pagesObligations and ContractsGabbie ScottNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For ContractsDocument9 pagesReviewer For ContractsEllaine CascarroNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument31 pagesContractscoleen dela torreNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Notes & CasesDocument54 pagesOBLICON Notes & CasesCouleen BicomongNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer ContractsDocument15 pagesOblicon Reviewer ContractsjinxNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Contract ReviewerDocument29 pagesOblicon Contract ReviewerPrincess MontalesNo ratings yet
- YgvugcuDocument8 pagesYgvugcuAlii ZyNo ratings yet
- Oblicon FinalsDocument113 pagesOblicon Finalseloixxa samNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesOblicon Midterm ReviewerPaulo SantosNo ratings yet
- Written Report Lawon ObliconDocument60 pagesWritten Report Lawon ObliconMaria Zaira Aure TorioNo ratings yet
- Nov 19,20,21 Transcriptions ObliDocument2 pagesNov 19,20,21 Transcriptions ObliAmanda ButtkissNo ratings yet
- 2007 Midterm Reviewer: Obligations and Contracts JanuaryDocument18 pages2007 Midterm Reviewer: Obligations and Contracts JanuaryseanNo ratings yet
- Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 General ProvisionsDocument19 pagesTitle Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 General ProvisionsAlpheus Shem ROJASNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Midterm ReviewerDocument18 pagesOblicon Midterm Reviewerkatreena ysabelle100% (15)
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesFrom EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesNo ratings yet
- Capitulation Surrender: Victory's Cost, The Anatomy of Yielding in ConflictFrom EverandCapitulation Surrender: Victory's Cost, The Anatomy of Yielding in ConflictNo ratings yet
- Dasini VS PhilDocument42 pagesDasini VS PhilSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Cases EthicsDocument36 pagesCases EthicsSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Statutory Construction CasesDocument83 pagesStatutory Construction CasesSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Notes For FinalsDocument2 pagesCriminal Law Notes For FinalsSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Framework For Preparation and Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument34 pagesChapter 2 - Framework For Preparation and Presentation of Financial StatementsSumit PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment 6 Mortgage Lab Part 1Document3 pagesWritten Assignment 6 Mortgage Lab Part 1api-344188992No ratings yet
- Prelim ExaminationDocument9 pagesPrelim ExaminationShannel Angelica Claire RiveraNo ratings yet
- Monthly Payment Plan AgreementDocument3 pagesMonthly Payment Plan AgreementRia KudoNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument118 pagesAccountingReshmi R Nair100% (1)
- Creditors Self-HelpDocument6 pagesCreditors Self-HelpBen DibeelaNo ratings yet
- Application For Loan: Philippine Public School Teachers AssociationDocument5 pagesApplication For Loan: Philippine Public School Teachers AssociationAlijar KasimNo ratings yet
- Chemalite B - BDocument1 pageChemalite B - BadityaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of Deposits by CompaniesDocument51 pagesAcceptance of Deposits by Companiesjhanani karthikaNo ratings yet
- Afl Peaksun Enterprises and Export Corporation Pgaksun: 2F Peaksun Building 1505 Princeton St. Mandaluyong CityDocument4 pagesAfl Peaksun Enterprises and Export Corporation Pgaksun: 2F Peaksun Building 1505 Princeton St. Mandaluyong CityCarlo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Madhurima Case Study Project ReportDocument12 pagesMadhurima Case Study Project ReportA PLUS M FOODSNo ratings yet
- Prudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingDocument53 pagesPrudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingMUNTHA ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Remedies in Bankruptcy SummaryDocument5 pagesRemedies in Bankruptcy SummaryKhairun Nisaazwani100% (4)
- OBLICON by Atty. Anselmo S. Rodiel IVDocument43 pagesOBLICON by Atty. Anselmo S. Rodiel IVAnselmo Rodiel IVNo ratings yet
- Self Made Reviewer - Law On Obligations-Nature and EffectsDocument2 pagesSelf Made Reviewer - Law On Obligations-Nature and EffectsVincent Louie TumilbaNo ratings yet
- Gov AcctngDocument15 pagesGov AcctngAtiene VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Local Development Investment ProgramDocument48 pagesLocal Development Investment ProgramJetley Joy Pitogo100% (1)
- Complete Mcqs For ObliconDocument41 pagesComplete Mcqs For ObliconMarian Roa100% (1)
- Suggested Answer CAP II (Dec 2018) All Subjects PDFDocument123 pagesSuggested Answer CAP II (Dec 2018) All Subjects PDFDipendra kumar MehtaNo ratings yet
- LIBOR Transition Update: Author: Kevin LiddyDocument13 pagesLIBOR Transition Update: Author: Kevin LiddyShyam P SharmaNo ratings yet
- Term Loan - 19225247 - 2024 - 03 - 22 - 21 - 39Document4 pagesTerm Loan - 19225247 - 2024 - 03 - 22 - 21 - 39maltemayur37No ratings yet
- Go Airlines (India) LimitedDocument115 pagesGo Airlines (India) Limitedshubham ranaNo ratings yet
- Master Budget Sample ProblemsDocument14 pagesMaster Budget Sample ProblemscykablyatNo ratings yet
- B7AF102 Financial Accounting May 2020Document9 pagesB7AF102 Financial Accounting May 2020dayahNo ratings yet
- Accounts RTP Foundation Nov 2020Document25 pagesAccounts RTP Foundation Nov 2020Jayasurya MuruganathanNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Analysis in ICICI Bank SWATI KUMARIDocument80 pagesCredit Risk Analysis in ICICI Bank SWATI KUMARIAmit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Northern Motors, Inc. Vs Coquia, 68 SCRA 374 G.R. No. L-40018 December 15, 1975Document4 pagesNorthern Motors, Inc. Vs Coquia, 68 SCRA 374 G.R. No. L-40018 December 15, 1975Al Jay MejosNo ratings yet
- Institute and Faculty of Actuaries: Subject CT1 - Financial Mathematics Core TechnicalDocument5 pagesInstitute and Faculty of Actuaries: Subject CT1 - Financial Mathematics Core TechnicalfeererereNo ratings yet
- POA Section 10Document15 pagesPOA Section 10kxng ultimateNo ratings yet
- ACC-March-QP & Memo-2019-Gr10Document15 pagesACC-March-QP & Memo-2019-Gr10VSQUARE COMNo ratings yet
CONTRACT
CONTRACT
Uploaded by
Sherlock Yookie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views11 pages1. A contract is a meeting of the minds between two or more parties that creates obligations or duties. It involves an agreement whereby the parties bind themselves to certain terms.
2. The key elements of a valid contract include offer, acceptance, and consideration. Contracts must also comply with legal requirements and public policy.
3. Contracts are governed by principles of autonomy, where parties have freedom to establish terms, and obligatoriness, where valid contracts are legally binding and enforceable. Mutuality and reciprocity mean obligations are mutual between parties.
Original Description:
obligations and contracts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. A contract is a meeting of the minds between two or more parties that creates obligations or duties. It involves an agreement whereby the parties bind themselves to certain terms.
2. The key elements of a valid contract include offer, acceptance, and consideration. Contracts must also comply with legal requirements and public policy.
3. Contracts are governed by principles of autonomy, where parties have freedom to establish terms, and obligatoriness, where valid contracts are legally binding and enforceable. Mutuality and reciprocity mean obligations are mutual between parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views11 pagesCONTRACT
CONTRACT
Uploaded by
Sherlock Yookie1. A contract is a meeting of the minds between two or more parties that creates obligations or duties. It involves an agreement whereby the parties bind themselves to certain terms.
2. The key elements of a valid contract include offer, acceptance, and consideration. Contracts must also comply with legal requirements and public policy.
3. Contracts are governed by principles of autonomy, where parties have freedom to establish terms, and obligatoriness, where valid contracts are legally binding and enforceable. Mutuality and reciprocity mean obligations are mutual between parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
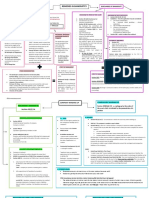
CONTRACT- is a meeting of the According to cause
minds of two persons whereby one
1. onerous- there is an interchange
binds himself with respect to other, to
of equivalent valuable
giver something or to render some
consideration
service.
2. gratuitous/ lucrative- this is
- Agreement of 2 or more FREE, thus one party receives
persons for the purpose of no equivalent prestation except
creating, modifying, or a feeling that one has been
extinguishing a juridical generous or liberal
relation between them. 3. remunerative — (one where
- juridical convention manifested one prestation is given for a
in legal form, by virtue of benefit or service that had been
which, one or more persons (or rendered PREVI¬ OUSLY)
parties) bind themselves in According to importance or
favor of another or others, or dependence of one upon another:
reciprocally, to the fulfillment
of a prestation to give, to do or 1. principal- the contract can stand
not to do. alone by itself and does not
depend its validity u[pon
social agreemet- not a contract another ocntractt
because it cannot be enforced by 2. accessory- depends upon
action in the court of justice. another contract
ELEMENTS OF A CONTRACT 3. preparatory- as means to an end
1. essential elements- a contract According to parties onligated:
cannot exist without them 1. unilateral- creates an obligation
2. natural eloements- on the part of only one of the
3. accidental parties
classification sof contract 2. bilateral/ synalagmatic- both
parties are required to render
as to perfection or formation:
reciprocal prestations
1. consensual- mere consent
according to name or designation:
2. real- by delivery
3. formal or solemn- Those where 1. nominate - contract is given a
special formalities are essential special or particular name
before the contract may be
perfected
2. innominate) contratos 3. Consummation- terms are
innominados)- no special performed and contract is
bname fully executed
according to the risk of fulfillment:
1. commutative- when the CHARACTERISTICS/ PRINCIPLE
undertaking of one party is OF CONTRACTS
considered equivalent of that of
1. AUTONOMY OF
the other
CONTRACTS
2. aleatory- fulfillment is
dependent upon chance, thus ARTICLE 1306: THE
the values vary because of the CONTRACTING PARTIES MAY
risk of chance ESTABLISH SUCH
STIPULATIONS, CLAUSES,
according to time:
TERMS AND CONDITIONS AS
1. executed — (one completed at THEY MAY DEEM CONVENIENT
the time the contract is entered PROVIDED, THEY ARE NOT
into, that is, the obligations are CONTRATRY TO LAW, MORALS,
complied with at this time GOOD CUSTOMS, PUBLIC
2. executory — (one where the ORDER OR PUBLIC POLICY.
prestations are to be com¬ plied
VALID CONTRACTS- THOSE
with at some future time
THAT MEET ALL THE LEGAL
according to subject matter: REQUIREMENTS AND
LIMITATIONS FOR THE TYPE OF
1. things
AGREEMENT INVOLVED AND
2. rights/credits
ARE LEGALLY BINDING AND
3. services
ENFORCEABLE.
According to
FREEDOM TO CONTRACT-
ARTICLE III, SECT. 10 OF
STATGES OF CONTRACT CONSTITUTION- right to enter into
contract that is legally valid. – NOT
1. PREPARATION- ABSOLUTE
negotiations
2. Perfection- parties came to LIMITATIONS ON
an agreement CONTRACTUAL STIPULATIOPNS
1. LAW- contract must be in c. Rules on the most analogous
accordance with (comparable)
MANDATORY AND d. Customs of the place
prohibitive law.
4 KINDS OF INNOMINATE
- Law is superior to a contract
CONTRACTS
pactum commissorium- mortrage 1. Do ut des- I give that you may
contract- a clause prviding that give
motrtrage will automatically own the 2. Do ut facias- I give that you
property mortraged if debt is not paid may do
at maturity 3. Facto ut des- I do that you may
2. By morals- deals with right and give
wrong and with human 4. Facto ut facias- I do that you
conscience- may do
3. By good customs- habits and Pactum de non alienando
practices followed and enforced
by the society . Pactum commissorium:
4. By public order - public safety. Pactum commissorium is "a stipulation
5. By public policy- contract is empowering the creditor to
contrary to public policy if it appropriate the thing given as
has atendency to injure the guaranty for the fulfillment of the
obligation in the event the obligor fails
public.\ to live up to his undertakings, without
ARTICLE 1307. INNOMINATE further formality, such as foreclosure
proceedings, and a public sale."
CONTRACTS SHALL B
REGULATED BY THE elements of pactum commissorium:
STIPULATIOMS PF THE PARTIES,
(1) There should be a property
BY THE PROVISIONS OF TITLES I mortgaged by way of security for the
AND II OF THIS BOOK, BY THE payment of the principal obligation;
RULES GOVERNING THE MOST and
ANALOGOUS NOMINATE (2) There should be a stipulation for
CONTRACTS AND BY THE automatic appropriation by the creditor
of the thing mortgaged in case of non-
CUSTOMS OF THE PLACE. payment of the principal obligation
within the stipulated period
GOVERNING RULES FOR
INNOMINATE CONTRACTS
a. Stipulations
b. Titles I and ii of oblicon
Dragnet Clause: A blanket What are the basic principles of
mortgage clause, which makes contracts? Understand and analyze the
available future loans without need of contract
executing another set of security
documents, has long been recognized attributes of autonomy, obligatoriness,
in our jurisprudence. It is meant to mutuality, relativity or privity?
save time, loan closing charges,
additional legal services, recording What makes the obligatory force of
fees, and other costs. A blanket contracts
mortgage clause is designed to lower
the cost of loans to borrowers, at the What is Mutuality of Contracts? Is
same time making the business of it the same as Reciprocity?
lending more profitable to banks.
Settled is the rule that mortgages RECIPROCITY- the quality or state of
securing future loans are valid and being reciprocal : mutual dependence,
legal contracts. action, or influence.
In Lease What is Relativity/Privity of
Contractual Relations?
In Employment Contracts
What is a Stipulations Pour Autrui
Prohibition to Marry Clause:
(A. 1311, par. 2)
Non-involvement clause:
In Dealership/Distributorship
M4- CONTRACTS AND
Contracts
NATURAL OBLIGATIONS
Exclusivity Clause: Avon (MLGREYES)
Cosmetics v. Luna, 511 S 376 as
compared with
Page 6 of 10
In Partnership Agreements
Pactum leonine
What are contracts Creating Real
But what
Rights (A. 1312)
is a contract? Is it the same as an
What are contracts in Fraud of
agreement? What are synonymous
Creditors (A. 1313 in rel. to A. 1381
legal terms?
[3])
What is Tortious or Intentional
Interference in contractual
relations? What are the
remedies of the aggrieved party? of conflict between letter and
(A. 1314) intent?
What are the steps in contract What are defective contracts? In
formation? How do we differentiate terms of defectiveness, which one is
between Essential, least and
Accidental and Natural Elements of most defective? What accounts for
a their defectiveness? Study the
remedies
Contract?
available for defective contracts.
What are the elements of and
factors affecting consent? What are the rescissible contracts?
Is the enumeration in the law
Every contract must have object (s).
exclusive?
Is the object of a contract the same
as the What are the voidable/annullable
contracts? Remedies?
object of an obligation? Is a
contract object always a thing?
What is cause? Is it the same as What makes a contract
consideration? Motive? unenforceable? What is the
importance of the E-Commerce law
When is a contract simulated?
for enforceability of contracts?
What are the forms of simulation of
contracts?
What are the kinds of contract Is a void contract identical to an
cause? inexistent contract? What is the
source of their nullity? Is the
Are all contracts required by law to
operative fact doctrine applicable to
be formal or solemn? Is form or
void/inexistent contracts?
solemnity always
What are natural obligations?
in writing?
Enumerate the specific natural
When a contract is in writing, what obligations set forth in the Civil
are the grounds for its reformation? Code. Do natural obligations have
What are the basic rules in the same essential elements as civil
interpretation of contracts? What obligations?
should prevail in case
FIRST DISCUSSION FOR FINALS: Sabinian Doctrine- the contract
should not be contrary to law,
ART. 1305 CONTRACTS-
public policy etc.
connection, juridical tie between
debtor and creditor.
SCTC-
- Meeting of minds: euphemism.
IN EMPLOYMENT
Refers to consent: one cannot
create a contract by himself. PROHIBITION TO MARRIAGE
- There must be at least 2 parties Can a contract ban you from getting
to perfect a contract married?
AUTOCONTRACT- there are 2 - If the contractual ban of
parties involving only 1 person: that marriage is absolute (means
person is exercising 2 capacities. that employee is banned to
Example: sale and purchase of marry anyone anytime
property belonging to the principal anywhere), null and void.
when the buyer is the agent. - Valid ban- there must be
legitimate business interest.
I own property and want to sell it, but
- Why ban? To avoid conflict of
no time to look for buyer, I will
interest. To avoid leaking the
appoint agent to sell a property.
confidential information.
What if the agent want to buy the
IN LOAN CONTRACT
property/- if the prinicipal expresses
consent for the agent to buy the - AUTOMATIC ESCALATION
property, the autocontract will apply. CLAUSE: stipulation in loan
Cause and consideration- to give or contract or prom note
to render service. authorizing the creditor to
unilaterally increase the interest
Once contract is perfected it give rise rate of the loan. VOID. It
to civil obli. destroys mutuality of contracts
PERFECTED CONTRACT because any modification of the
CHARATERISTICS original terms during must be
mutually agreed.
1. Autonomy- independence of - VOID. It permits only increase
contract. Freedom of contracts. but there is no opportunity in
decrease of interest rate.
AUTOMATIC ADJUSTMENT not need to execute new
CLAUSE: mortgage.
- Interest rate is adjusted. IN MORTGAGE CONTRACT
- Floating rate of interest. PACTUM NON ALIENA
- VALID: it is not purely
- Prohibiting the lessor from
potestative on the part of the
selling the property: VOID.
lender, interest rate increases or
- VALID: IF THERE IS A
decreases based on the
CONSENT.
government or agency sets.
EXCLUSIVENESS CLAUSE- for
Index interest=- fixed rate of interest.
protection of business… example:
IN LOAN WITH MORTGAGES
NON-INVOLVEMENT CLAUSE-
PACTUM COMMISURIUM: when an employer forbids the
employee from accepting employment
- a stipulation empowering the
creditor to appropriate the thing
for A LIMITIED PERIOD of 2 uears
given as guaranty for the WITH ANOTHER COMPANY-
fulfillment of the obligation in VALID.
the event the obligor fails to live
up to his undertakings, without 2. OBLIGATORY-
further formality, such as 3. MUTUALITY- the law
foreclosure proceedings, and a presumes that the parties
public sale." occupy equal position with one
- Kukunin gamit ni debtor para
another from the moment of
pag di nakabayad, kanya na
gamit.
negotiation. Must be
- ILLEGAL. NULL AND VOID:
maintained until contract is
fulfilled. EQUAL
- DRAGNET CLASE: NOT
PROHIBITED.- multiple loans
BARGAINING POWER.
are obtain by same debtor from - The enforcement of contract
same creditor. Pag di muist be by the parties and
nakabayad si debtor, iclose ang subject to what the contract
mortgage. – nabayaran loan 1
provides. The validity of the
and nagloan loan 2, those
succeeding now will now be performance of the contract
cpvered by the original mortage cannot be left to a 3rd
instruments. person.exxept when the
- Valid because it affords the contract contains ARBITRAL
parties convenience for they do OR ADR CLAUSE: provisions
in case of dispute they agree to - Stipulation in favor of 3rd
submit their dispute to person
arbitrator. Neither party can file
REQUISITES
an action incpurt before
submitting controversy in - The the contract must grant
ADR. favor to a 3rd person
- (beneficiary)
- That the 3rd person has accepted
IN CONTRACT OF ADHESION
that economic favor or benefit
- Contract where all the - That the sti[pulation must be
stipulations are provided for by merely a part of main contract
only one party. - That the stipulation pour autrui
- NOT VOID because one party is not subject to conditions and
has choice to accept or nopt all legal compensation, must be an
the provisions ion the absolute grant
stipulaytion. - That neither parties of the main
- Not valid if: - it contains contract is an agent of 3rd
contrary to law etc. person
ABSOLUTE EXEMPTION
Case: baluyot.
FROM LIABILITY: VOID. –
if one oproviiosn or some are 2. Art. 1314. Contracts which
grossly disadvatagous to the have been violated at the
rights of then other party. inducement of a 3rd person
4. RELATIVITY(PRIVATY OF - 3rd person without consent in
CONTRACT)- contract takes the contract may be held liable.
effect only by the parties
Paepal si 3rd person. REQUISITES
however it can be transmissible
by heirs or successors. - The the contract must grant
- Contracts cannot create a right favor to a 3rd person
to a 3rd persons. (beneficiary)
- Strangers to contract cannot - That the 3rd person has accepted
benefit and has no rights and that economic favor or benefit
obligations. - That the sti[pulation must be
EXCEPTION: merely a part of main contract
- That the stipulation pour autrui
1. If the contract contains is not subject to conditions and
stipulation pour autrui
legal compensation, must be an OFFER requires parties offerer and
absolute grant offeree.
- That neither parties of the main
Offer- first step in negotiation of a
contract is an agent of 3rd contract.
person
- IOUS INTERFERENCE article OFFER VS COUNTER OFFER
26 (alienation of .: breach of COUNTER OFFER= new offer to
contract results. meet the needs being asked by the
REMEDIES FOR AGGRIVED person being offered to.
PARTY MIRROR IMAGE- accepting the
- Can file a suit. Action for counter offer. – acceptance is absolute
injunction to stop the 2 STEPS IN CONSENT-
termination of the contract ACCEPTANCE AND OFFER.
- 3rd is liable because of
fraudelkent inducement\ COGNITION THEORY- knowledge
3. CONTRACTS CREATING came to the offerer when letter of
REAL RIGHTS- art 1312 acceptance is delivered to the offerer.
- Realn right: right or interest ARTICKE 1323:
over a specifc thing.
When an offer has been accepted and
4. In contracs entered into to
the oferee dies,
defraud creditors art 1313.
- Parties to the fraud can be held CONVEYED- offerer received the
liable under an action pauliana. letter of acceptance.
DISCUSSION Both parties must be alive and
capacitated.
OFFER- proposal indicating
willingness o enter into a contract. ARTICLE 1347
It must have: CONTRACT IN RAFFLE LOTTO,
ETC= contract of sale.
- Terms and conditions
- Price/consideration ARTICLE 1348.
- Object NEXT TOPIC UNTIL DEFECTIVE
BUSINESS ADSS FOR SALE is not CONTRACTS
an offer. – mere intention to make an IF CONTRACT IS VOID- IT HAS
offer. NO EFFECT
VICES OF CONSENT - INTIMIDATION- creates fear
in mind of the party
1. VICES OF CAPACITY
- UNDUE INFLUENCE: family
- Minority: below 18 do not have
relations between the parties,
consenting capacity to enter to
relationship causes
a contract.
disadvanatges. Implicit
- . Consent is Vested upon the
pressure. Improper pressure.
parents or guradians
- MISTAKE and fraud must be
- Incase of misrepresentation, the
suffered from one party and
minor would be bound by the
related to the object of the
contract. – fraud.
contract.
- - if sale of necessity, minor can
- FRAUD- dolo causante: fraud
enter.
committed in order to obtain
- INSANITY: legally
consent ro a contract
incapacitated and cannot enter
1. Active fraud- using
into contract. Consent is Vested
machinations
upon the guradians
2. Passive fraud- concealment
( guardianchip: person
of a material fact regarding
appointed by the court)
the terms, object and cause.
- MUTE: no facility of
expression- cannot enter to Opinion intended to deceive and lead
contract unless able to read and the party into error.
write. MUTUAL MISTAKE between the
2. VICES OF WILL- the parties parties, as a rule, the contract will be
were legally incapacitated when rendered void.
consent is exhanges but one of
them was a victim of subgotion/ MUTUAL FRAUD- both parties
committed fraud but not to each other
– destruction in the agency of a but to third person. If mutual fraud
person amounts to absolute simulation,
- Interferenece in the VOID it completely fictitious.
- Violnce or force, intimidation Relative simukation= Both partied
or duress, undue influence, enter into true contravt with an
mistake, fraud. apparent contract. Intent to deceive.
- VIOLENCE MUST BE Happens to tax evasion.
IRRESISTABLE- physical
OBJECT OF CONTRACT- subject CONTRACTS COVERED BY
matter; thing or service. Tangible or STATUTE OF FRAUDS WRITNG
intangible things. REQUIRED
The ff cannot be a valid object of 1. ANY AGREEMENT THAT
contract: SHALL NOT BE
PERFORMWED WITHIN
1. Inalienable property- CASE OF
ONE YEAR
PENTACAPITAL or LIM
2. SPECIAL PROMISE TO
- Property belongs to the state
ANSWER FOR THE
2. POLITICAL RIGHTS
DEBTM], DEFUALT OR
3. FUTURE INHERITANCE
MISCARRIAGE OF
CUASE/CONSIDERATION ANOTHER
3. In consideration of marriage
- Purpose that each party had in
4. –
mind when consent is given
- All contracts have valid cause
- Cause exist when contract is NOVEMBER 16 DISCUSSION
perfercted
TIU VS PLATINUM
KINDS OF CAUSES DEL CASTILLO
1. Onerous- expectation of
delivery of a thing with NON-INVOLVEMENT CLAUSE-
value. Exchange of value prohibits employee to accept any
employment in competing company.
TEST TO VALIDITY OF NON-
Falsity of cause- void contract. INVOLVEMENT CLAUSE
DONATION OF IMMOVABLE- 1. AS TO TIME
IT MUST BE IN WRITING- IN 2. PLACE
ORDER TO HAVE A VALID 3. Business
DONATION FOR 5K HIGHER
ANOUT
Last case: LIMSON VS CA
FORM FOR ENFORCEABLITY
Earnest money and option money
1403.
Option contract
You might also like
- Contracts Because They Have To ComplyDocument6 pagesContracts Because They Have To ComplyAnna Biella Dacaymat PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts Book IV: Civil Code of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesObligations and Contracts Book IV: Civil Code of The PhilippinesJeramae LuterioNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument3 pagesCONTRACTSsweetestcitrus13No ratings yet
- Contracts ObliDocument32 pagesContracts ObliAnsherina FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Contracts: Definition, Classification, and DistinctionsDocument20 pagesContracts: Definition, Classification, and DistinctionsKyle BandolaNo ratings yet
- Article 1305: Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 - Contracts, General ProvisionsDocument15 pagesArticle 1305: Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 - Contracts, General ProvisionsBryne SarillanaNo ratings yet
- Contracts: 1. DEFINITION. The NCC Defines A Contract As "A Meeting of Minds Between Two Persons Whereby (Art. 1305, NCC)Document9 pagesContracts: 1. DEFINITION. The NCC Defines A Contract As "A Meeting of Minds Between Two Persons Whereby (Art. 1305, NCC)VIRILITER AGITENo ratings yet
- Contracts Basic ConceptsDocument14 pagesContracts Basic ConceptsCory RitaNo ratings yet
- Title II - ContractsDocument3 pagesTitle II - ContractsSha Napoles100% (1)
- Handouts For The Law On ContractsDocument5 pagesHandouts For The Law On ContractsHannah Jane UmbayNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument3 pagesContractsJillian PizarroNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS Chapter 1Document17 pagesCONTRACTS Chapter 1LabLab ChattoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Moody PrincessNo ratings yet
- Sales Notes For Prelim2Document11 pagesSales Notes For Prelim2gongsilogNo ratings yet
- ComlawDocument3 pagesComlawANNE GRACE MOSQUEDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6Sheila FernándezNo ratings yet
- Oblicon PrefinalsDocument15 pagesOblicon PrefinalsFrancis Therese RosalesNo ratings yet
- Contracts: General ProvisionsDocument8 pagesContracts: General ProvisionsVenz LacreNo ratings yet
- General Provisions of ContractsDocument42 pagesGeneral Provisions of ContractsShan Marie RusianaNo ratings yet
- Contracts Art. 1305Document4 pagesContracts Art. 1305chxrlttxNo ratings yet
- Law On ContractsDocument4 pagesLaw On ContractsRizza OlanoNo ratings yet
- 1 Part 2: ContractsDocument6 pages1 Part 2: ContractsPrei BaltazarNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTSDocument23 pagesCONTRACTSAllyza Mae Araojo LumboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. General ProvisionsDocument9 pagesChapter 1. General ProvisionsRose Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3602 ContractsDocument13 pagesRFBT.3602 ContractsGrezel Mae ProvidoNo ratings yet
- C. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsDocument12 pagesC. All Contracts Are Agreements But Not All Agreements Are ContractsElla Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Tittle II ContractsDocument3 pagesOBLICON Tittle II Contracts2023303601No ratings yet
- Obligations FinalDocument114 pagesObligations FinalWency CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesOblicon Midterm ReviewerKing PerezNo ratings yet
- I. Contracts in GeneralDocument57 pagesI. Contracts in GeneralVal Escobar MagumunNo ratings yet
- Contracts ART. 1305 1368Document16 pagesContracts ART. 1305 1368Nathalie BermudezNo ratings yet
- Prof. Roentgen F. Bronce: Credit TransactionsDocument13 pagesProf. Roentgen F. Bronce: Credit TransactionsAnnaNo ratings yet
- Credit Midterms ReviewerDocument83 pagesCredit Midterms Reviewermelaniem_1No ratings yet
- Classification of ContractsDocument97 pagesClassification of ContractsAngelo Otañes GasatanNo ratings yet
- A. CHAP 1 - 1305 - 1317Document8 pagesA. CHAP 1 - 1305 - 1317Jes MariamNo ratings yet
- Notes On Oblicon - Part 3Document15 pagesNotes On Oblicon - Part 3Xelly J.No ratings yet
- Pre Finals Reviewer FinalDocument14 pagesPre Finals Reviewer FinalAises Minoza100% (1)
- Sanchez Roman-A Juridical Convention Manifested inDocument10 pagesSanchez Roman-A Juridical Convention Manifested insakuraNo ratings yet
- Contracts (Oblicon Reviewer)Document15 pagesContracts (Oblicon Reviewer)Bryan AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Title Ii ContractsDocument7 pagesTitle Ii Contractsyanice coleen diazNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS - General ProvisionsDocument6 pagesCONTRACTS - General ProvisionsJoanne Gonzales JuntillaNo ratings yet
- 02 Contracts Contracts Notes Oct 2021 PDFDocument11 pages02 Contracts Contracts Notes Oct 2021 PDFhswjushdjwkwNo ratings yet
- Buenaventura vs. Metropolitan Bank and Trust Company 799 SCRA 239 August 03 2016Document24 pagesBuenaventura vs. Metropolitan Bank and Trust Company 799 SCRA 239 August 03 2016Kristin C. Peña-San FernandoNo ratings yet
- Obligations and ContractsDocument4 pagesObligations and ContractsGabbie ScottNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For ContractsDocument9 pagesReviewer For ContractsEllaine CascarroNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument31 pagesContractscoleen dela torreNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Notes & CasesDocument54 pagesOBLICON Notes & CasesCouleen BicomongNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer ContractsDocument15 pagesOblicon Reviewer ContractsjinxNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Contract ReviewerDocument29 pagesOblicon Contract ReviewerPrincess MontalesNo ratings yet
- YgvugcuDocument8 pagesYgvugcuAlii ZyNo ratings yet
- Oblicon FinalsDocument113 pagesOblicon Finalseloixxa samNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesOblicon Midterm ReviewerPaulo SantosNo ratings yet
- Written Report Lawon ObliconDocument60 pagesWritten Report Lawon ObliconMaria Zaira Aure TorioNo ratings yet
- Nov 19,20,21 Transcriptions ObliDocument2 pagesNov 19,20,21 Transcriptions ObliAmanda ButtkissNo ratings yet
- 2007 Midterm Reviewer: Obligations and Contracts JanuaryDocument18 pages2007 Midterm Reviewer: Obligations and Contracts JanuaryseanNo ratings yet
- Title Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 General ProvisionsDocument19 pagesTitle Ii. - Contracts Chapter 1 General ProvisionsAlpheus Shem ROJASNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Midterm ReviewerDocument18 pagesOblicon Midterm Reviewerkatreena ysabelle100% (15)
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesFrom EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume I of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Torts, Civil Procedure, Property, Contracts & Sales: Law School Survival GuidesNo ratings yet
- Capitulation Surrender: Victory's Cost, The Anatomy of Yielding in ConflictFrom EverandCapitulation Surrender: Victory's Cost, The Anatomy of Yielding in ConflictNo ratings yet
- Dasini VS PhilDocument42 pagesDasini VS PhilSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Cases EthicsDocument36 pagesCases EthicsSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Statutory Construction CasesDocument83 pagesStatutory Construction CasesSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Notes For FinalsDocument2 pagesCriminal Law Notes For FinalsSherlock YookieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Framework For Preparation and Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument34 pagesChapter 2 - Framework For Preparation and Presentation of Financial StatementsSumit PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment 6 Mortgage Lab Part 1Document3 pagesWritten Assignment 6 Mortgage Lab Part 1api-344188992No ratings yet
- Prelim ExaminationDocument9 pagesPrelim ExaminationShannel Angelica Claire RiveraNo ratings yet
- Monthly Payment Plan AgreementDocument3 pagesMonthly Payment Plan AgreementRia KudoNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument118 pagesAccountingReshmi R Nair100% (1)
- Creditors Self-HelpDocument6 pagesCreditors Self-HelpBen DibeelaNo ratings yet
- Application For Loan: Philippine Public School Teachers AssociationDocument5 pagesApplication For Loan: Philippine Public School Teachers AssociationAlijar KasimNo ratings yet
- Chemalite B - BDocument1 pageChemalite B - BadityaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of Deposits by CompaniesDocument51 pagesAcceptance of Deposits by Companiesjhanani karthikaNo ratings yet
- Afl Peaksun Enterprises and Export Corporation Pgaksun: 2F Peaksun Building 1505 Princeton St. Mandaluyong CityDocument4 pagesAfl Peaksun Enterprises and Export Corporation Pgaksun: 2F Peaksun Building 1505 Princeton St. Mandaluyong CityCarlo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Madhurima Case Study Project ReportDocument12 pagesMadhurima Case Study Project ReportA PLUS M FOODSNo ratings yet
- Prudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingDocument53 pagesPrudential Regulations For Corporate / Commercial BankingMUNTHA ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Remedies in Bankruptcy SummaryDocument5 pagesRemedies in Bankruptcy SummaryKhairun Nisaazwani100% (4)
- OBLICON by Atty. Anselmo S. Rodiel IVDocument43 pagesOBLICON by Atty. Anselmo S. Rodiel IVAnselmo Rodiel IVNo ratings yet
- Self Made Reviewer - Law On Obligations-Nature and EffectsDocument2 pagesSelf Made Reviewer - Law On Obligations-Nature and EffectsVincent Louie TumilbaNo ratings yet
- Gov AcctngDocument15 pagesGov AcctngAtiene VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Local Development Investment ProgramDocument48 pagesLocal Development Investment ProgramJetley Joy Pitogo100% (1)
- Complete Mcqs For ObliconDocument41 pagesComplete Mcqs For ObliconMarian Roa100% (1)
- Suggested Answer CAP II (Dec 2018) All Subjects PDFDocument123 pagesSuggested Answer CAP II (Dec 2018) All Subjects PDFDipendra kumar MehtaNo ratings yet
- LIBOR Transition Update: Author: Kevin LiddyDocument13 pagesLIBOR Transition Update: Author: Kevin LiddyShyam P SharmaNo ratings yet
- Term Loan - 19225247 - 2024 - 03 - 22 - 21 - 39Document4 pagesTerm Loan - 19225247 - 2024 - 03 - 22 - 21 - 39maltemayur37No ratings yet
- Go Airlines (India) LimitedDocument115 pagesGo Airlines (India) Limitedshubham ranaNo ratings yet
- Master Budget Sample ProblemsDocument14 pagesMaster Budget Sample ProblemscykablyatNo ratings yet
- B7AF102 Financial Accounting May 2020Document9 pagesB7AF102 Financial Accounting May 2020dayahNo ratings yet
- Accounts RTP Foundation Nov 2020Document25 pagesAccounts RTP Foundation Nov 2020Jayasurya MuruganathanNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Analysis in ICICI Bank SWATI KUMARIDocument80 pagesCredit Risk Analysis in ICICI Bank SWATI KUMARIAmit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Northern Motors, Inc. Vs Coquia, 68 SCRA 374 G.R. No. L-40018 December 15, 1975Document4 pagesNorthern Motors, Inc. Vs Coquia, 68 SCRA 374 G.R. No. L-40018 December 15, 1975Al Jay MejosNo ratings yet
- Institute and Faculty of Actuaries: Subject CT1 - Financial Mathematics Core TechnicalDocument5 pagesInstitute and Faculty of Actuaries: Subject CT1 - Financial Mathematics Core TechnicalfeererereNo ratings yet
- POA Section 10Document15 pagesPOA Section 10kxng ultimateNo ratings yet
- ACC-March-QP & Memo-2019-Gr10Document15 pagesACC-March-QP & Memo-2019-Gr10VSQUARE COMNo ratings yet