Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture-3 - SCR
Lecture-3 - SCR
Uploaded by
different wayOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture-3 - SCR
Lecture-3 - SCR
Uploaded by
different wayCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture (3)
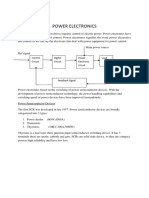
Basics of Power Electronic Components
3-Thyristors
Thyristors or Silicone Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs) are semiconductor
devices.
Why using the silicone in SCR?
It is the ideal choice because of its overall properties (thermal properties).
It is able to handle high power applications.
It is part of SCR name (although in theory the other types of semiconductor
could be used).
It’s used as rectifiers (from its name) and as electronic switching.
Thyristors are simple to use and cheap to buy, making them an ideal option for
many circuits.
That can use for applications as:
Used for phase control.
Used as AC static switches and relays.
Used for lightening systems.
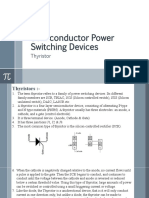
The SCR is considered as an unusual form of electronics device because it
consists of four layers rather than the three layers of the BJT. The SCR equivalent
circuit can be considered as two back to back BJTs. The first BJT with its emitter
connected to the anode of the SCR is a PNP-BJT, while a second BJT with its
emitter connected to the cathode of the SCR is an NPN-BJT. The gate (control
terminal) is connected to the base of the NPN-BJT together with the collector of
PNP-BJT as shown below.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
Like the diode, the SCR is a unidirectional device, that is it will conduct
current in one direction only, but unlike a diode, the SCR can make to operate as
either a circuit switch or as a controlled rectifying diode depending upon how the
SCR gate is triggered. In other words, SCR cannot be used for amplification. The
circuit symbol for the SCR suggests that this device acts like a controlled rectifying
diode.
The operation of a thyristors is different from other devices. Normally,
when a supply voltage is applied across a SCR (A-K), no current flows because
both BJT are not conducting. However if a supply is connected across the device,
and a small amount of current is injected into the gate (triggered), then the SCR
will "fire" and conduct. For the explanation, if the gate is triggered this will
cause current to flow in the base of TR2 and this causes to its turn on. Once TR2
is on, this cause current to flow in the base of TR1 and also its turn on, these
causes to remain pushes current through the base of TR2 even if the gate signal
is removed.
Meaning that the SCR will remain in the ON-state if the anode current ( )
is equal or greater than the Latching current, even when the gate current is
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
removed. But once anode current becomes more than latching current, the gate
losses its control and it may be removed, the SCR will continue to conduct.
For come to the OFF-state in SCR if the anode current ( ) is below the
Holding current. This means if the value of holding current is 5 mA, then the
anode current of SCR must become less than 5 mA to stop conducting. The states
of operation are shown below:
That main difference between latching and holding current of SCR is that
latching current is related to the turn-on process while holding current is related
to the turn-off process of SCR. The value of the latching current is more than that
of the holding current. The latching current is generally 2 to 3 times of the
holding current.
A typical Characteristic of SCR is as shown below. The SCR have
three modes of operation as illustrated below.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
1-Reverse blocking mode
When cathode of the thyristor is made positive with respect to anode with
switch open thyristor is reverse biased. Junctions and are reverse biased
where junction is forward biased. The device behaves as if two diodes are
connected in series with reverse voltage applied across them.
A small reverse leakage current of the order of a few mA only flows.
Now if the reverse voltage is increased, at a critical breakdown level called
reverse break over voltage , an breakdown occurs at and and the
reverse current increases rapidly. As a large current associated with
and hence more losses to the SCR.
This results in SCR damage as junction temperature may exceed its
maximum temperature rise.
2-Forward blocking mode (off-state)
When anode is positive with respect to cathode, with gate circuit open,
thyristor is said to be forward biased. Thus junctions and are forward biased
and junction is reverse biased.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
A small forward leakage current of the order of a few mA only flows.
As the forward voltage is increased, junction 2 will have a breakdown at a
voltage called forward break over voltage ; then SCR conducts.
When forward voltage is less than , SCR offers high impedance. Thus
SCR acts as an open switch in forward blocking mode, the SCR is in off-
state.
3-Forward conduction mode (on-state)
Here SCR conducts current from anode to cathode with a very small
voltage drop across it. During forward conduction mode of operation SCR is in
on-state and behave like a close switch.
So a thyristor can easily go from forward blocking mode to forward
conduction mode by:
Applying a gate pulse between gate and cathode (Recommended), OR.
Exceeding the forward break over voltage (unintentionally), OR.
Exceeding the dv/dt Turn-On (unintentionally).
The Static dv/dt:
When the SCR is forward biased, junctions 1 and 3 are forward biased,
junction 2 reverse biased. Junction 2 behaves as a capacitor, due to the charges
existing across the junction.
If the voltage across the SCR is , the charge by Q, and capacitance by C;
then the anode current as:
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
Therefore when the rate of voltage change across the device becomes large,
the SCR may turn-ON, even if the voltage across the SCR is small (not reatch to
the forward break over voltage) but it changes in a very small time. This method
may lead to damage of SCR due to high current and so it must be avoided
To turn-OFF a thyristor after its turn-ON by:
Reverse or removed the of A-K voltage, OR.
Reduce the anode current blow holding value.
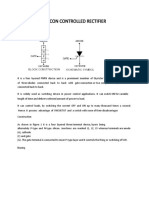
The Rectification of SCR:
A simple circuit is shown below, if the SCR is triggered at the beginning of
the half-cycle (θ = 0°), the load (lamp) will be “ON” for the full positive cycle of
the AC waveform (half-wave rectified AC–unidirectional device). If the time of
trigger pulse increases along the half-cycle (θ = 0° to 180°), the lamp is
illuminated for less time and the average voltage delivered to the lamp will also
be less, then reducing its brightness.
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
Comparison between SCR and BJT
SCR BJT
Number of Semiconductor
Layers 4 3
Number of Semiconductor 3 2
Junctions
Power Ratings Larger Smaller
Usage Switches, but not as Switches or Amplifiers.
Amplifiers.
A pulse can get the forward
Maintaining a Forward current flowing, and this A continuous input is
Current current will continue to flow required to maintain a
as long as it does not fall forward current.
below a holding value, even
when there is remove the
pulse of input current
Dr. Heba Mahmoud Soufi 12-11 -2020
You might also like
- Manual HitakeDocument46 pagesManual HitakeYudi Widodo Louser100% (1)
- Introduction To Thyristors PDFDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Thyristors PDFAnnie BordsNo ratings yet
- Power UNIT I PDFDocument39 pagesPower UNIT I PDFNoor WaleedNo ratings yet
- Ree601 PDFDocument9 pagesRee601 PDFJ JulietNo ratings yet
- Pe SCRDocument68 pagesPe SCRMuttoju VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Questions Set-2: What Are The Different Operation Regions of The SCR?Document9 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Questions Set-2: What Are The Different Operation Regions of The SCR?Uzair AfridiNo ratings yet
- Electronic NotesDocument193 pagesElectronic Notesephraimmwangi988No ratings yet
- Lecture1424354515 Removed (1) Numbered Numbered NumberedDocument43 pagesLecture1424354515 Removed (1) Numbered Numbered NumberedsiddharthasawaikarNo ratings yet
- 3Document48 pages3j4xzj8vx4No ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices (Power Switches)Document17 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices (Power Switches)yesar laftaNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument9 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifierFarishat Nusabbee An Nafs100% (1)
- POWER ELECTRONICsDocument120 pagesPOWER ELECTRONICsJeji HirboraNo ratings yet
- Solid State Fault Current LimiterDocument18 pagesSolid State Fault Current Limitersmartxdigital marketNo ratings yet
- Thyristor ValveDocument5 pagesThyristor ValveRisi SinghNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument24 pagesPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Pe FINALDocument131 pagesPe FINALAnonymous R4WpNxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Content APP&A-1Document15 pagesChapter 1 Content APP&A-1sm7526359No ratings yet
- Thyristors: What You'll Learn in Module 6.0Document41 pagesThyristors: What You'll Learn in Module 6.0LeGrand BeltranNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Module 06Document39 pagesSemiconductors Module 06IngwiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument112 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualdiegosendoyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2newDocument134 pagesChapter 2newBelayneh TadesseNo ratings yet
- Basic Triac-SCR Projects Circuits TutorialDocument7 pagesBasic Triac-SCR Projects Circuits TutorialAmmar YasserNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between BJT, FET & Thyristor: Intruder AlarmDocument26 pagesComparison Between BJT, FET & Thyristor: Intruder AlarmRojan Pradhan100% (1)
- Design of Snubber Circuit Using PspiceDocument4 pagesDesign of Snubber Circuit Using Pspiceelpatotas22No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document20 pagesLecture 2Mouath AlsebaieNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument19 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFMohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Control Circuit Digital Circuit Power Electronic Circuit LoadDocument13 pagesPower Electronics: Control Circuit Digital Circuit Power Electronic Circuit LoadNayon RoyNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Basics and Its Working IDocument9 pagesThyristor Basics and Its Working IkshitijsilawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Power SupplyDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Power SupplyBricksoe NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument30 pagesModule 1 NotesSoxamNo ratings yet
- Application of Power Electronics To PoweDocument6 pagesApplication of Power Electronics To PoweAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Turn On Turn Off Methods IIDocument14 pagesThyristor Turn On Turn Off Methods IIkshitijsilawatNo ratings yet
- I PowerDocument70 pagesI Powermisterda1307No ratings yet
- ESE63201 L6 Power ElectronicsDocument9 pagesESE63201 L6 Power Electronicsmohed_kamalNo ratings yet
- THYRISTORDocument26 pagesTHYRISTORLovely Jaze SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Power Switching DevicesDocument30 pagesSemiconductor Power Switching Devicesबृजभूषणशर्माNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger Circuit Using SCRDocument5 pagesBattery Charger Circuit Using SCRankitNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document99 pagesMod 2SREEHARI V ANo ratings yet
- PE ReviewDocument77 pagesPE ReviewJasper WangNo ratings yet
- Thyristors: Bidirectional Trigger Diode (DIAC)Document16 pagesThyristors: Bidirectional Trigger Diode (DIAC)anthonyrobertxNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2: 1. What Is SCR ? Symbol and V/I Characteristic Curve of and SCR?Document10 pagesAssignment No. 2: 1. What Is SCR ? Symbol and V/I Characteristic Curve of and SCR?Manlincon, Christian S.No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Power Semiconductor DevicesJibril JundiNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines) DhanbadDocument13 pagesIndian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines) DhanbadSirigireddy DhanalaxmiNo ratings yet
- BLDC Resonant PoleDocument8 pagesBLDC Resonant Poleav5009No ratings yet
- Power Electronics L1 DevicesDocument11 pagesPower Electronics L1 DevicesBakri BugaNo ratings yet
- SCR MechatronicsDocument50 pagesSCR MechatronicsBefu HailuNo ratings yet
- SCR, Thyristor and TriacDocument5 pagesSCR, Thyristor and TriacJon Sand100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument45 pagesPower ElectronicsMudit Prabhakar100% (3)
- Learning OutcomesDocument51 pagesLearning Outcomesdimpisingh004No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Technology For Marine EngineersDocument10 pagesElectrical and Electronic Technology For Marine EngineersMuniaFerdoushiMouNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics DevicesDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics DevicesahmedsaeedobiedNo ratings yet
- SCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsDocument5 pagesSCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsMark Kenneth Apuyan100% (1)
- Week 3 - ThyristorsDocument19 pagesWeek 3 - ThyristorsAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- ThyristorDocument7 pagesThyristortusharNo ratings yet
- Names: Thyristor Thyr IstorDocument30 pagesNames: Thyristor Thyr IstorNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument17 pagesSCR Triggering MethodssriNo ratings yet
- Special Semiconductor DevicesDocument40 pagesSpecial Semiconductor DevicesJairus OnkwaniNo ratings yet
- Transformer Control Celduc Relais Solutions: Solid State Relays (SSR)Document14 pagesTransformer Control Celduc Relais Solutions: Solid State Relays (SSR)RezaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1mrcarlo456No ratings yet
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifier: A High Power SCRDocument8 pagesSilicon-Controlled Rectifier: A High Power SCRPaarthibba KumarNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Lecture-Linear Induction Machines-P3Document6 pagesLecture-Linear Induction Machines-P3different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Synchros P2Document7 pagesLecture Synchros P2different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Linear Induction Machines-P4Document11 pagesLecture-Linear Induction Machines-P4different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Synchros P1Document12 pagesLecture Synchros P1different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Linear Induction Machines-P2Document3 pagesLecture-Linear Induction Machines-P2different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 DIACDocument6 pagesLecture 6 DIACdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - BJTDocument10 pagesLecture 2 - BJTdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 5 TRIAC P 1 2Document9 pagesLecture 4 5 TRIAC P 1 2different wayNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1-Revision On Basic of Power Electronic ComponentsDocument11 pagesLecture-1-Revision On Basic of Power Electronic Componentsdifferent wayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy 2021Document4 pagesEngineering Economy 2021different wayNo ratings yet
- DMART-Case StudyDocument4 pagesDMART-Case Studykowsalyasr1503No ratings yet
- Motherboard: ZIF Dipp AT AT ATXDocument3 pagesMotherboard: ZIF Dipp AT AT ATXapi-19519104No ratings yet
- Procurement Profile OptionsDocument7 pagesProcurement Profile OptionseBodhisathva SolutionsNo ratings yet
- 722 8340 (Telefax)Document8 pages722 8340 (Telefax)pastilan001No ratings yet
- RocketpreepayDocument5 pagesRocketpreepayMizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Metric-Based Classifiers: Nuno Vasconcelos (Ken Kreutz-Delgado)Document32 pagesMetric-Based Classifiers: Nuno Vasconcelos (Ken Kreutz-Delgado)Manu VegaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Discrete Mathematics Part 1Document17 pagesLecture Notes in Discrete Mathematics Part 1Moch DedyNo ratings yet
- Digital Systems Project: IITB CPUDocument7 pagesDigital Systems Project: IITB CPUAnoushka DeyNo ratings yet
- Jntuk r20 Unit-I Deep Learning Techniques (WWW - Jntumaterials.co - In)Document23 pagesJntuk r20 Unit-I Deep Learning Techniques (WWW - Jntumaterials.co - In)TARUN SAI PRADEEPNo ratings yet
- G7167 G5668 G7137 Multisampler SerMa en SD 29000237Document521 pagesG7167 G5668 G7137 Multisampler SerMa en SD 29000237Hoàng Anh LêNo ratings yet
- Communication Theory Two MarksDocument40 pagesCommunication Theory Two Markssenthilkumar100% (1)
- Manual Configuración Routers 4GDocument168 pagesManual Configuración Routers 4GDaniel MartinNo ratings yet
- ELEN1000 Lab Cover Sheet - LAB 1Document10 pagesELEN1000 Lab Cover Sheet - LAB 1Francis GomesNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Understand Kerberos Authentication and Domain SecurityDocument22 pages4.2 Understand Kerberos Authentication and Domain SecurityChitra TamilchelvanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Industrial AutomationDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Industrial Automationc5dg36am100% (1)
- CPNR 9 1 Cli Ref GuideDocument245 pagesCPNR 9 1 Cli Ref GuidealexNo ratings yet
- FiCEB - Spreadsheet - V01Document49 pagesFiCEB - Spreadsheet - V01Valiente ImperatorNo ratings yet
- Beneficiary Registration File FormatDocument7 pagesBeneficiary Registration File Formatsukha singhNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 (Function Module) AnsDocument11 pagesLab 8 (Function Module) Ansmebele8069No ratings yet
- W4A1Document4 pagesW4A1Mira BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Gas Leakage Alarm Mini ProjectDocument6 pagesGas Leakage Alarm Mini Projectarunajoseph92_868114100% (1)
- EasyNote TJ66Document188 pagesEasyNote TJ66correos34No ratings yet
- TNY277PNDocument2 pagesTNY277PNAdj100% (2)
- Java HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap - W3resourceDocument6 pagesJava HashMap, LinkedHashMap and TreeMap - W3resourcePradeep Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Pointers and Modular Programming: Mirza Mohammad Lutfe ElahiDocument31 pagesPointers and Modular Programming: Mirza Mohammad Lutfe ElahiRahib ridoyNo ratings yet
- JMP-2 (CPK Analysis)Document30 pagesJMP-2 (CPK Analysis)aditya_ranjan7158No ratings yet
- SAP New Digital Access LicensingDocument9 pagesSAP New Digital Access LicensingAnishNo ratings yet
- Declaration and Access Modifiers PDFDocument69 pagesDeclaration and Access Modifiers PDFMurthy MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- VMware WorkstationDocument406 pagesVMware WorkstationsocrazNo ratings yet