Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leadership
Leadership
Uploaded by
Usama IdreesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leadership
Leadership
Uploaded by
Usama IdreesCopyright:
Available Formats
Q. Who is a Leader?
Ans. Leadership is the art of motivating and influencing others to exert the best of their
labors towards achieving a common, shared goal.
Q. What do the best Leaders do?
Challenge the process. They challenge conventional beliefs and practices and create
constructive change.
Inspire a shared vision. They appeal to peoples values and motivate them to care
about an important mission.
Enable others to act. They give people access to information and give them the
power to perform to their full potential.
Model the way. They do not just tell people what to do but are living examples of the
ideals they believe in.
Encourage the heart. They show appreciation, provide rewards, and use various
approaches to motivate people in positive ways.
Vision, with reference, to Leadership is a clear choice of positive values that communicate
and inspire pride among individuals among the organization for achieving a desirable future
state. A vision should be both ideal (communicating standards of excellence) and unique
(different than other organizations).
A leader must have a vision
Effective articulation required for achieving shared values and goals
Making clear where the organization is heading
A sound vision is not based on personal needs, but those of stakeholders,
Leaders should stay abreast of environmental changes
Q. Differentiate between a leader and a manager.
Managers
o Focus on work (technical and conceptual skills / informational and decisional
roles)
o Have workers (theory X)
o Plan, organize and control
o Focus on day-to-day complexities, survival and profits
o Authoritative, risk-averse, dominant
o Structuring the organization, staffing, monitoring performance
Leaders
o Focus on people (interpersonal skills and roles)
o Have followers (theory Y)
o If they lead along with planning, organizing, and controlling then both
o Long term prosperity and success
o Democratic, open communicator, feedback provider
o Inspiring people to accomplish a great vision
Supervisory Leadership involves basic management functions of providing support.
Guidance and corrective feedback for day-to-day activities.
Strategic Leadership incorporates ‘true leadership’ activities which give purpose to an
organization i.e., a mental image for the positive future (vision).
Effective followers
Volunteer to handle tasks or help accomplish goals
Accept assignments in a willing manner
Exhibit loyalty to the group
Voice differences of opinion, but support the group’s decisions
Maintain a positive attitude
Work effectively as members
Think independently but also committed to group targets and organizational goals
Hold performance standards higher than required or set
Power is the capability and authority over others to influence them.
Legitimate power
o Right to control the actions of others, employees formally obligated to comply
o Leads to compliance
Reward Power
o Compliance for rewards – when leader controls rewards
o Leads to compliance
Coercive Power
o Compliance to avoid punishments – when leader can take punishing corrective
action – rises as you climb the hierarchical ladder
o Leads to resistance
Referent power
o Leading by example / personality or characteristics that people want to follow
– compliance for desires of approval, admiration, learning to be a leader
o Leads to commitment
Expert Power
o Exceptional skills in some specific field – specialist
o Leads to commitment
There are three approaches to understanding and studying leadership.
The trait approach studies the common characteristics that effective leaders share
o Drive
Need for achievement, improvement, ambition
o Leadership Motivation
Want and commitment to lead
High need for power to influence others to derive satisfaction from
leading
Power exercised in moral and socially constructive ways is an
important aspect of effective leadership
o Integrity
Honesty improves trust and credibility – induces follower commitment
o Self – Confidence
Overcoming stress
Bouncing back in uncertainty
Self - management
o Knowledge Pool
Expert power
Interpretation abilities
Thinking capacity beyond average minds
Great comprehension
o Emotional Intelligence
Understanding other’s emotions and objectives (empathy)
Social skills, social awareness
The behavior approach attempts to identify how leaders conduct themselves or act,
especially towards others. Three general categories of behavior approaches are:
o Task Performance is about the leader’s efforts to meet deadlines, budgets,
targets etc. It focuses on quantity, quality, time, cost and accuracy.
Concern for production
Directive leadership
Initiating structure
Closeness of supervision
o Group maintenance focuses on how leaders execute their interpersonal roles
and utilize their ‘people’ skills.
Concern for people
Supportive leadership
Harmonious work environment
Social stability of workplace
Satisfaction of group members
Leader – member exchange theory (LMX) importance of sound
behavior towards individuals on personal basis
Overall comfort, appreciation and stress reduction
Mutual obligation, respect, open communication are cornerstones of a
satisfied group
o Participation in Decision Making
agile shifting between democratic (mutual decision making – group
maintenance) and autocratic (virtual decision making – task
performance)
mixture of the elements of both in relevant situations
laissez – faire (characterized by an absence of managerial decision
making)
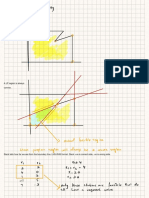
o Blake and Mouton’s Leadership Grid (link)
Features (Five Leadership Styles)
Impoverished Management (1,1) more of a laissez faire
approach, minimal effort on management
Country Club Management (1,9) friendly atmosphere /
workers expect leniency and results in lower performance
Middle-of-the-Road Management (5,5) satisficing task and
maintenance behavior to get work done with resolved conflicts
and satisfactory production levels and morale
Authority Compliance – Task Management (9,1) targets
achieved but difficult to sustain same behavior in the longer
term as employee morale is low – human elements interfere to
a minimum degree – more autocratic- theory X
Team Management (9,9) McGregor theory Y, productivity,
then enhanced productivity due to increase morale and
motivation. Mutual respect, commitment to people and work.
Criticisms
9,9 not ideal every time
Over simplistic – impression that no other style exists
Leadership styles are dynamic forces cannot be put on some
grid
Advantages
Guiding principal for studying management and implementing
it.
Flexile organizations adapt according to needs and sustain
competitive advantages
Situational Approach implies that universal traits and behaviors do not exist, and that
leadership is not an absolute concept restricted to some specific criteria. Depending
on the situation leadership behavior varies accordingly.
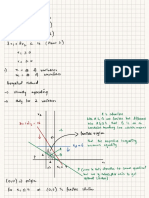
o Fiedler’s Contingency Model (link)
There is no one best style of leadership / leader’s effectiveness depends
on the situation
Result of two factors
Leadership Style
o Leadership style is fixed and can be measured using a
scale called Least Preferred Co-worker (LPC) scale.
o The scale can be used to generate a cumulative score
based on the leader’s perception of a co-worker’s
attitude, traits and character.
Situational favorableness
o Leader – Member relationship – trust, loyalty,
confidence the team puts in the leader – favorable
o Task structure
Clear and defined, structured
Vague and ambiguous, unstructured if
teammates do not possess the relevant
knowledge – favorableness
o Leader’s position power (strong or weak) to direct,
reward or punish
Greater power more favorableness
Application of the model
Identify your leadership
o Low LPC – task oriented (primary emphasis is on
completion of task, meeting deadlines, accomplishing
goals, matching targets) – effective when factors are
very unfavorable or very favorable
o High LPC – relationship oriented (maintenance
behaviors) - effective when factors are middle of the
road
Identify the extent of situational favorableness
o Leader - member relations good or poor – level of trust,
loyalty
o Task structured or unstructured - Expertise of solving
problems and giving structure to unstructured tasks
o Strong or weak power over team
Determine the effective leadership style
Advantages
Extremely well-researched and relevant
A flexible theory (contingency theory)
Disadvantages
LPC scale is subjective
LPC score is valid to only closely supervised groups
Not valid in every situation – complex / having many
components of measurement
Leaders cannot change their styles but be assigned to situations
of their favorableness.
Leader placement rather than policy placement and formulation
o Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Theory
theory postulating that measuring employee’s psychological and job
maturity determine maintenance or task-oriented behaviors’ relevance.
Life cycle theory of leadership
Job maturity
Level of skill and expertise employees possess for doing their
tasks
psychological maturity
Self-confidence and self-EQ
Application
Highly - mature followers require neither - do not need to be
reminded of deadlines and targets – less task performance
behavior needed – put their trust in the leader – less
maintenance behavior required
Medium maturity followers require personal attention and
maintenance
Low maturity – performance related
Advantages
Fairly simple
Treat different people differently reminder
Then treating same individual differently as he gets more
mature
Disadvantages
Fairly straightforward
Ignores other aspects – relations, power, task structure
Charismatic Leader: One who is positively dominant, self-aware, and has a strong
conviction in the moral righteousness of his beliefs. They incorporate an inspiring, clear
vision into their agenda and arouse a sense of excitement and adventure in followers.
Transformational leaders strive to transform people’s personal interests into organizational
values, revitalizing organizations.
Transactional Leaders believe management is similar to accounting with a series of
transactions which involve their legitimate, reward and coercive powers. However,
management is more inclined towards human science, comprehension and its effective
administration.
Level 5 Leadership considered to be the ultimate leadership style which uses a combination
of strong professional determination and humility that builds enduring greatness. It is a blend
of flexible approaches incorporating elements of both transactional and transformational
leaderships. Leader expands his satisfaction source from fulfilment of personal needs to
fulfillment of organizational goals and objectives.
Authentic Leadership follows the common good for common people approach and leaders
transcend their personal objectives to organizational goals and objectives. They care about
‘public’ interests on a macro level (community, organizational, or group). They are ethically
mature.
Pseudo-transformational leaders will throw great stories of communal achievements but in
reality, will only focus on personal needs and let personal interest take precedence over
followers’ needs.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Class 13 PDFDocument4 pagesClass 13 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 PDFDocument39 pagesNotes 1 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 5 PDFDocument80 pagesNotes 5 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 3 PDFDocument3 pagesNotes 3 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 4 PDFDocument2 pagesNotes 4 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 PDFDocument17 pagesNotes 2 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 11 PDFDocument4 pagesClass 11 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 9 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 9 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PDFDocument1 pageClass 12 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 10 PDFDocument2 pagesClass 10 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 8 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 8 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 7 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 7 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Opti PDFDocument2 pagesClass 7 Opti PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document1 pageClass 1Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 5 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 5 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document2 pagesClass 3Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 4Document3 pagesClass 4Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 2Document2 pagesClass 2Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- A1Document1 pageA1Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- UsamaIdreesDocument4 pagesUsamaIdreesUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument10 pagesHuman Resource ManagementUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument8 pagesLeadershipUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Managing The Diverse WorkforceDocument4 pagesManaging The Diverse WorkforceUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- GP (G9) FinalDocument21 pagesGP (G9) FinalUsama IdreesNo ratings yet