Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer Hci
Reviewer Hci
Uploaded by
Hanna Galinato0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThis document discusses different methods of data collection including probability and non-probability sampling techniques. It defines key terms like population, sample size, and margins of error. Quantitative and qualitative data are described as well as different survey methods like questionnaires. Probability sampling uses random selection to choose a representative sample while non-probability sampling cannot predict who will be selected. The document provides examples of sampling techniques and considerations for determining appropriate sample sizes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different methods of data collection including probability and non-probability sampling techniques. It defines key terms like population, sample size, and margins of error. Quantitative and qualitative data are described as well as different survey methods like questionnaires. Probability sampling uses random selection to choose a representative sample while non-probability sampling cannot predict who will be selected. The document provides examples of sampling techniques and considerations for determining appropriate sample sizes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesReviewer Hci
Reviewer Hci
Uploaded by
Hanna GalinatoThis document discusses different methods of data collection including probability and non-probability sampling techniques. It defines key terms like population, sample size, and margins of error. Quantitative and qualitative data are described as well as different survey methods like questionnaires. Probability sampling uses random selection to choose a representative sample while non-probability sampling cannot predict who will be selected. The document provides examples of sampling techniques and considerations for determining appropriate sample sizes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Data collection is defined as the Probability Sampling - representative sample.
process of gathering and measuring Techniques:
information on variables of interest, in 1. Simple random sampling
an established systematic fashion that 2. Systematic sampling
enables one to answer queries, stated 3. Stratified sampling
research questions, test hypotheses, 4. Clustered sampling
and evaluate outcomes.
Non-Probability Sampling - Subjects chosen by
THE IMPORTANCE OF DATA COLLECTION researcher. Hence, who will be selected cannot
1. Data empowers you to make informed be predicted
decisions. Techniques:
2. Data helps you identify problems. 1. Convenience sampling
3. Data allows you to develop accurate 2. Quota sampling
theories. 3. Judgement (or Purposive) Sampling
4. Data will back up your arguments 4. Snowball sampling
5. Data makes your approach strategic.
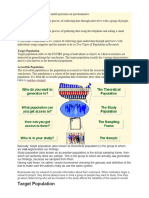
6. Data helps you get your hand-on POPULATION - This is a complete set of
funding elements (persons or objects).
7. Data tells you what you’re doing.
8. Data saves you time Target Population - The target population, also
9. Data increases your return on assets known as the theoretical population, refers to
10. Data improves quality of life the ENTIRE group of individuals.
Quantitative data is usually expressed in Accessible Population - study population. In
numerical form and can represent size, length, which the researchers can apply their
duration, amount, price, and so on. conclusions.
- Subset of the target population
-likely to provide answers to questions such as
who? when? where? what? Sample size is the number of completed
responses your survey receives.
Qualitative data is usually not easily
measurable as quantitative and can be gained Calculation of Sample Size
through observation or open-ended survey or
interview questions. Population size: The total number of people in
the group you are trying to study.
-is most likely to provide answers to questions
such as “why?”and “how?” How? Margin of error: A percentage that tells you
how much you can expect your survey results to
SAMPLING - selecting a suitable sample, or a reflect the views of the overall population.
representative part of a population.
Sampling confidence level: A percentage that
reveals how confident you can be that the
population would select an answer within a
certain range.
Survey - A well-defined and well-
written set of questions to which an
individual is asked to respond.
• typically self-administered by an
individual,
• ability to get a large number of
responses quickly from a population
• “questionnaire,” which is the list
of questions, and the “survey,” which is
The z-score is the number of standard the complete methodological approach,
deviations a given proportion is away from the
mean. To find the right z-score to use, refer to Benefits
the table below: - relatively low cost. Surveys can be
used for many different research goals.
-very useful for getting an overview, or
a “snapshot,” of a user population
- do not require advanced tools for
development
- most likely to get approval from
an institutional review board.
Drawbacks
•If you want a smaller margin of error, you must
have a larger sample size given the same
population.
• The higher the sampling confidence level you
want to have, the larger your sample size will
need to be.
Questionnaires - a research instrument
consisting of a series of questions
Types of Questionnaires
1. Web-based Questionnaire - A new and
inevitably growing methodology is the
use of internet-based research.
2. Paper-pencil Questionnaire - It can be
used to a large number of people that
enables the researcher to save time and
money.
You might also like
- Evaluating and Adapting MaterialsDocument31 pagesEvaluating and Adapting MaterialsWinterMae BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Ppe Research 2 - Week 1Document11 pagesPpe Research 2 - Week 1MARIE GRACE APARRENo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Engg Data AnalysisDocument4 pagesLecture Notes in Engg Data AnalysisRenmark MartinezNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Method: Survey Data Collection: Noraidah Sahari at Ashaari 0389216751/0192719286Document99 pagesQuantitative Method: Survey Data Collection: Noraidah Sahari at Ashaari 0389216751/0192719286hazwanNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology of NokiaDocument3 pagesResearch Methodology of NokiaRAJ0% (1)
- (Reafor) Term Paper 2Document5 pages(Reafor) Term Paper 2Bernadette Briones OberosNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document50 pagesDay 4arifaNo ratings yet
- MetlitDocument4 pagesMetlitZulfa jasmine Camilia fadilahNo ratings yet
- Self - Learning Module For Senior High School LearnersDocument33 pagesSelf - Learning Module For Senior High School LearnersEdeth SubongNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 2 - Short Question and Answer: Part A - Short QuestionsDocument8 pagesAssessment Task 2 - Short Question and Answer: Part A - Short QuestionsMemay Methawee100% (1)
- Descriptive Research Validity: Sampling MethodDocument2 pagesDescriptive Research Validity: Sampling MethodQueency Tabora-MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Tipsheet2 Survey Research enDocument2 pagesTipsheet2 Survey Research enSayma AkterNo ratings yet
- Chap10 Questionnaire Survey and ErrorsDocument33 pagesChap10 Questionnaire Survey and Errorsshakilshaon13No ratings yet
- Group ReportDocument32 pagesGroup ReportLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument22 pagesResearch MethodologyNaresh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Binder EdaDocument5 pagesBinder Edapalacioaya28No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document9 pagesUnit 3Taveri RajkhowaNo ratings yet
- Survey and Correlational Week 2Document52 pagesSurvey and Correlational Week 2Kasthuri SuppiahNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument4 pagesResearchKriza EstocadoNo ratings yet
- BSN 3-1 Group 1 - Research InstrumentsDocument19 pagesBSN 3-1 Group 1 - Research InstrumentsAnabelle RicoNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument3 pagesResearch ReviewerCris Antonette AbataNo ratings yet
- Lecture Two-Data CollectionDocument30 pagesLecture Two-Data CollectionAnon YmousNo ratings yet
- Types of KnowledgeDocument28 pagesTypes of KnowledgePraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- EDADocument4 pagesEDARoma Angela AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument10 pagesResearch MethodologyMuthu ManikandanNo ratings yet
- PRACRES Reviewer Mods 5 8Document8 pagesPRACRES Reviewer Mods 5 8Purple YannaNo ratings yet
- Baseline Data Collection TrainingDocument61 pagesBaseline Data Collection TrainingHaika AndrewNo ratings yet
- Data Collection (Quantitative Research) : ChecklistsDocument4 pagesData Collection (Quantitative Research) : ChecklistsRonald DiazNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data Analysis: Marcelino YuDocument46 pagesEngineering Data Analysis: Marcelino YuManny AcostaNo ratings yet
- Research MethodDocument7 pagesResearch MethodBinth caderNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Handouts 5Document5 pagesPR1 - Handouts 5Donald EspirituNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Research Overview PDFDocument14 pages1.1 Research Overview PDFJamal BaatharNo ratings yet
- Finals - ReviewerDocument17 pagesFinals - ReviewerCharmy Rose FranciscoNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerThe HowlNo ratings yet
- Eda ReviewerDocument15 pagesEda Reviewer22-04639No ratings yet
- Research Design and Sampling TechniquesDocument63 pagesResearch Design and Sampling TechniquesFerland CalisoNo ratings yet
- Research Instrument and Data Collection in Languange Learning Validity and Reliability of Research DataDocument13 pagesResearch Instrument and Data Collection in Languange Learning Validity and Reliability of Research Datamuhammad fattah100% (1)
- Q2 Module 2 - Sample and Sampling TechniquesDocument8 pagesQ2 Module 2 - Sample and Sampling TechniquesJester Guballa de LeonNo ratings yet
- ENT SG Unit7 Lesson3 FinalDocument15 pagesENT SG Unit7 Lesson3 FinalSopheia MargaretNo ratings yet
- IV - Understanding Ways To Collect DataDocument6 pagesIV - Understanding Ways To Collect DataJesseca Jean Aguilar Sepillo100% (6)
- 2 QUANTITATIVE METHODS Lesson 1Document23 pages2 QUANTITATIVE METHODS Lesson 1Anne LopesNo ratings yet
- Question 9 - Business ResearchDocument3 pagesQuestion 9 - Business Researchmy nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument30 pagesChapter ThreeMohamed DaudNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Science 12 PR2 S1 M2 W1Document12 pagesHybrid Science 12 PR2 S1 M2 W1Katrina De VeraNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialsDocument5 pagesStudy MaterialsBles SonNo ratings yet
- Nature of Quantitative Research: Time Frame: Week 1 & 2Document19 pagesNature of Quantitative Research: Time Frame: Week 1 & 2Marhmello PadriqueNo ratings yet
- SFT L 2 RVWRDocument5 pagesSFT L 2 RVWRRegi Garcia DoriaNo ratings yet
- How To Create Your Chapter III Part 1Document36 pagesHow To Create Your Chapter III Part 1Jonel OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Research SubDocument5 pagesResearch SubKyra Aliyah SambranoNo ratings yet
- Research - Data CollectionDocument20 pagesResearch - Data CollectionEiren CollinsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Practical Research 2Document6 pagesReviewer in Practical Research 2Astro LunaNo ratings yet
- Level/dimension (S) OutcomesDocument20 pagesLevel/dimension (S) Outcomesbiancacamillequiazon100% (3)
- Data Collection: By: Dr. Ritchie G. Macalanda Assistant Principal IIDocument56 pagesData Collection: By: Dr. Ritchie G. Macalanda Assistant Principal IInica pidlaoanNo ratings yet
- Research MethodoloyDocument13 pagesResearch MethodoloyNivedita SolankeNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods Lesson 1Document20 pagesQuantitative Methods Lesson 1Camille EspinoNo ratings yet
- PR2 Handout3Document3 pagesPR2 Handout3Shahanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods Lesson 1Document20 pagesQuantitative Methods Lesson 1Camille EspinoNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Population in ResearchDocument6 pagesTwo Types of Population in Researchcatherineyandoc37No ratings yet
- Consumer Research-2Document31 pagesConsumer Research-2king hoboNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument10 pagesUnit 1: Nature of Inquiry and ResearchJep DatulNo ratings yet
- Research Methods and Methods in Context Revision Notes for AS Level and A Level Sociology, AQA FocusFrom EverandResearch Methods and Methods in Context Revision Notes for AS Level and A Level Sociology, AQA FocusNo ratings yet
- 98 364 Database FundamentalsDocument5 pages98 364 Database FundamentalsHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- IT0079 - Laboratory Exercise 6.2Document16 pagesIT0079 - Laboratory Exercise 6.2Hanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Elective Web System ReviewerDocument266 pagesElective Web System ReviewerHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Network Protocols and ServicesDocument89 pagesModule 3 - Network Protocols and ServicesHanna Galinato100% (1)
- Info Assurance ReviewerDocument71 pagesInfo Assurance ReviewerHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- TEch Eng Type of Business LetterDocument10 pagesTEch Eng Type of Business LetterHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- LA4 Ohm's LawDocument20 pagesLA4 Ohm's LawHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- 12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Document The NetworkDocument5 pages12.6.1 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Document The NetworkHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- LA5 - Ohm's Law Circuits Data SheetDocument3 pagesLA5 - Ohm's Law Circuits Data SheetHanna GalinatoNo ratings yet
- Analisis Konflik Pengelolaan Sumberdaya Alam Di KaDocument15 pagesAnalisis Konflik Pengelolaan Sumberdaya Alam Di KaMaulanaNo ratings yet
- (Ronald E. Riggio) Introduction To Industrial Orga (Z-Lib - Org) Compressed-1-225Document225 pages(Ronald E. Riggio) Introduction To Industrial Orga (Z-Lib - Org) Compressed-1-225Widy BoyNo ratings yet
- Autonomy in Children's Learning. An Experimental and Individual Difference InvestigationDocument9 pagesAutonomy in Children's Learning. An Experimental and Individual Difference InvestigationEduardo Aguirre DavilaNo ratings yet
- History of The Filipino PeopleDocument40 pagesHistory of The Filipino Peoplekarlaloise.torrefrancaNo ratings yet
- Wicor StrategiesDocument8 pagesWicor StrategiesGabriela RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Social Exchange TheoryDocument4 pagesSocial Exchange Theorygerald paduaNo ratings yet
- Sample Lac Plan 2021 - 2022Document6 pagesSample Lac Plan 2021 - 2022Marjory Tablit100% (1)
- Lesson 1 QuizDocument2 pagesLesson 1 QuizMary Ann IsananNo ratings yet
- Sakshi Kumari (Project Work)Document11 pagesSakshi Kumari (Project Work)Abhishek Maity 3364No ratings yet
- Matrilineal Bilineal Patrilineal Consanguineous Kinship: Modules Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Grade 12)Document4 pagesMatrilineal Bilineal Patrilineal Consanguineous Kinship: Modules Understanding Culture, Society, and Politics (Grade 12)Teds TV100% (5)
- Madu Gong TssDocument22 pagesMadu Gong Tsscaseylyn taladroNo ratings yet
- Discover Sociology 3Rd Edition Chambliss Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesDiscover Sociology 3Rd Edition Chambliss Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkyle.hodges786100% (11)
- Infographics PPTDocument35 pagesInfographics PPTBurning RoseNo ratings yet
- Polyarchy: Polyarchy, Concept Coined by The American Political Scientist Robert Dahl To Denote TheDocument18 pagesPolyarchy: Polyarchy, Concept Coined by The American Political Scientist Robert Dahl To Denote ThemariamNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Theory SyllabusDocument3 pagesSoftware Engineering Theory SyllabusComputer Science & Engg, PusadNo ratings yet
- FinalChapter 3Document3 pagesFinalChapter 3Mard SumalpongNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5cohesion AND DEVELOPMENTDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 5cohesion AND DEVELOPMENTKim Zenneia UlbocNo ratings yet
- Purpose of Literature Review in ResearchDocument4 pagesPurpose of Literature Review in Researchc5pdd0qg100% (1)
- 02 - EDS-225 (2021) History of Concept of Resilience (Ian)Document25 pages02 - EDS-225 (2021) History of Concept of Resilience (Ian)Rachel KellyNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Research MethodologyDocument26 pagesSession 1 - Research MethodologykavindiNo ratings yet
- Snyder - LEARNING INTO AUTOETHNOGRAPHYDocument6 pagesSnyder - LEARNING INTO AUTOETHNOGRAPHYSINANo ratings yet
- BAA09 - Course Plan - 2T 2021 2022 - Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationDocument7 pagesBAA09 - Course Plan - 2T 2021 2022 - Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationAien EscuetaNo ratings yet
- Software Process MeaurementDocument8 pagesSoftware Process MeaurementKartheek 577No ratings yet
- Senior High School: It Poorly Structured or Too Long and DetailedDocument5 pagesSenior High School: It Poorly Structured or Too Long and DetailedDuaneNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Artist at The Beginning of The Twenty-First CentuDocument351 pagesThe Role of The Artist at The Beginning of The Twenty-First CentuLorgen OsetaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advancement IN Artificial Intelligence & Machine LearningDocument43 pagesRecent Advancement IN Artificial Intelligence & Machine LearningRAIDEN 1No ratings yet
- Technical Writing 1Document3 pagesTechnical Writing 1Ellechir JeanneNo ratings yet
- Best College For Architecture Courses in BangaloreDocument2 pagesBest College For Architecture Courses in Bangaloreardarshan01No ratings yet
- Qualitative Research DesignsDocument18 pagesQualitative Research Designsi believe in dabdab and bambamNo ratings yet