Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HVAC System
HVAC System
Uploaded by
Hiba Kasmi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesThe document calculates the airflow and heating requirements for an industrial garage workshop. It determines that the workshop needs a minimum airflow of 28539.648 cubic meters per hour. It then calculates that this requires a duct with a diameter of 9 inches made of stainless steel. The weight of a 9 inch stainless steel duct is estimated to be 3.27 kg per meter. It then calculates the shear force on a 1 foot section of the duct to be 11.43 Newtons.
Original Description:
Original Title
HVAC system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document calculates the airflow and heating requirements for an industrial garage workshop. It determines that the workshop needs a minimum airflow of 28539.648 cubic meters per hour. It then calculates that this requires a duct with a diameter of 9 inches made of stainless steel. The weight of a 9 inch stainless steel duct is estimated to be 3.27 kg per meter. It then calculates the shear force on a 1 foot section of the duct to be 11.43 Newtons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesHVAC System
HVAC System
Uploaded by
Hiba KasmiThe document calculates the airflow and heating requirements for an industrial garage workshop. It determines that the workshop needs a minimum airflow of 28539.648 cubic meters per hour. It then calculates that this requires a duct with a diameter of 9 inches made of stainless steel. The weight of a 9 inch stainless steel duct is estimated to be 3.27 kg per meter. It then calculates the shear force on a 1 foot section of the duct to be 11.43 Newtons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
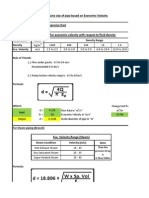
Calcul du débit :
Selon R13 Annexe III:
Baie de lavage: Garage d’entretien
⇒ Taux minimal de changements d’air par heure = 4
𝑚3 /ℎ 𝑑′ 𝑎𝑖𝑟
Or = 𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 ℎ𝑒𝑢𝑟𝑒 ∗ [3,6 + ℎ𝑎𝑢𝑡𝑒𝑢𝑟 𝑑𝑢 𝑛𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑎𝑢 𝑑𝑒 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑎𝑖𝑙 𝑒𝑛 𝑚è𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠]
𝑚2
Or la hauteur du niveau de travail = 14 pi = 1,2 m
Débit = CAH * (3,6+1,2) * S
Or S = 160 pi * 100 pi = 48,768m * 30,48 m = 1486,45 m2
Débit = 4 * 4,8 * 1486,45 = 28539,648 m3/h = 1675,78 cfm
Calcul de la quantité de chaleur:
Q = m * Cp * ΔT
𝐷é𝑏𝑖𝑡 28539,648
Or m = * ρair = * 1,292 = 10,24 kg/s
3600 3600
Cp air = 1000 J/Kg
ΔT = Tdésirée - Textérieure = Tdésirée – 40°C
Selon r13 annexe IV :
Travail pénible en position debout, notamment forage et travail manuel avec outils lourds
Tdésirée=12°C
ΔT=12-40=-28°C
Q = m * Cp * ΔT = 10,24 * 1000 * (-28) = 286720 J/s
Les calculs suivants concernent la branche principale :
Main branch v=3000 ft/min
v=15.2 m/s
-2500< v < 4000 fpm High pressure system: pression = [1500 Pa,2500 Pa]
D: Duct diameter = 9 in
Pressure loss 1 inH2O/100ft
Duct type: Circular stainless steel ducts.
There are two available commercial ducts: rectangular and circular ducts, the best suited
geometry for our problem is the circular duct given that we deal with high pressure HVAC
system.
There are 4 ducts type that are commonly used in HVAC systems:
Flexible ducts
Rigid ducts: Sheet metal ducts, Fiberglass ducts and fiberboard ducts
The best duct type for our HVAC system is the sheet metal ducts because it is commonly used
in industries. It is characterized by its light weight, durability, easy installation and
maintenance.
As for the material we have galvanized mild steel with rust resistant Zinc coating that allows
better airflow and protection against mold and fungus growth. The stainless steel ducts offer a
superior corrosion resistance from moisture and is widely used in industries.
Détermination du poids de la conduite:
Galvanized steel ducts: Density = 7.800 kg/m3
Stainless steel ducts: Density = 7.500 kg/m3
The two densities are close to each other so we can use the Galvanized steel ducts tab to
extract the weight.
The weight of a 9 in (250 mm) stainless steel duct is 2.93 lbs/ft
26 gage is used for the duct size below 300 mm and thickness is 0.5mm
In our case Duct size =9 in = 229 mm
Weight=2.2 lbs/ft=3,27 Kg/m
Poids de la conduite : P= Weight x g = 3,27 x 9,81 = 32,0787 N/m (Force de traction)
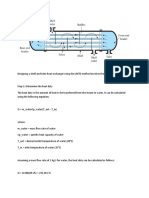
Calcul de la force de cisaillement :
1 ft =305 mm, 9 in = 229 mm
Volume=Pi x D2 x L / 4 = Pi x 0.229 x 0.305 / 4 = 0.0125 m3
Application du PFD sur 1ft de la conduite :
ΣFext=m.a (Les forces sont en forme Vectorielle)
Feq+P=m.a (Les forces sont en forme Vectorielle)
Projection sur l’axe x(vecteur) :
Féq=m.a
ρ = m/V m = ρ .V = 1.204 * 0.0125 = 0.015 Kg
On suppose qu’à l’instant t=0s, v= 0 m/s et qu’à t= 0.02 s v= 15.2 m/s
Pourquoi t= 0.02 s ? v=L/t t=L/v=0.305/15,2=0.02s (L=1ft=305mm)
a=15.2/0.02=762.5 m/s2
Féq = 0.015 * 762.5 =11.43 N.
Supports des conduites :
Horizontal Ductwork:
You might also like
- 3-D WheelDocument24 pages3-D WheelKim Ciudadano29% (7)
- Pumping and Piping Systems: Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Engineering Cagayan de Oro CityDocument34 pagesPumping and Piping Systems: Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan College of Engineering Cagayan de Oro CityGab LibetarioNo ratings yet
- Trash Rack CalculationDocument8 pagesTrash Rack Calculationsumit67% (3)
- Chemical Engineering Design of The Spray DryerDocument6 pagesChemical Engineering Design of The Spray Dryervictor100% (2)
- Picc ConstructionDocument17 pagesPicc ConstructionMachalyn Chua50% (2)
- Bag Filter Calculations, Mr. Bokaian'sDocument24 pagesBag Filter Calculations, Mr. Bokaian'sMohsen Ardestani100% (6)
- Burner CalculationDocument6 pagesBurner CalculationAnonymous 3ESYcrKP100% (4)
- PPE AssignmentDocument16 pagesPPE AssignmentlibbissujessyNo ratings yet
- Demister Sizing Using Normal Flow Conversion:: Customer: Enquiry No: Item No: DateDocument3 pagesDemister Sizing Using Normal Flow Conversion:: Customer: Enquiry No: Item No: Daterakesh3487100% (2)
- Calculation and Design of Packed Column For AcidDocument14 pagesCalculation and Design of Packed Column For AcidDavid Lambert100% (1)
- Buoyancy Calculation Report For 10INCH PipelineDocument7 pagesBuoyancy Calculation Report For 10INCH PipelineEmmanuel LawrenceNo ratings yet
- A House Built On A Riverside...Document8 pagesA House Built On A Riverside...ErsanİmamoğullarıNo ratings yet
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceFrom EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cyclic Plate Load TestDocument16 pagesCyclic Plate Load TestNithin Sudersanan83% (6)
- 5 - Hydro Power PlantsDocument73 pages5 - Hydro Power Plants2003_335100% (1)
- Venturi Scrubber Design CalculationDocument2 pagesVenturi Scrubber Design CalculationAnil DhamankarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design of MixerDocument10 pagesMechanical Design of MixerGabriel AyauNo ratings yet
- PED Ch1Document17 pagesPED Ch1dpatel 2310No ratings yet
- Penstock CaalculationDocument3 pagesPenstock CaalculationGertjan DuniceriNo ratings yet
- SCOPE:: Design Input DataDocument7 pagesSCOPE:: Design Input DataEmmanuel LawrenceNo ratings yet
- CPD Assognment CH-19048Document9 pagesCPD Assognment CH-19048Mehreen NaveedNo ratings yet
- Line Size of Pipe Based On Economic VelocityDocument19 pagesLine Size of Pipe Based On Economic Velocitymabrouk2013No ratings yet
- Pipe Size CalcDocument19 pagesPipe Size Calcnitin_bir100% (2)
- DesignTable For PipeSys - Pressure DropDocument54 pagesDesignTable For PipeSys - Pressure DropKlich77No ratings yet
- Dear Capital Gas Egypt: Yours Sincerely ..Document11 pagesDear Capital Gas Egypt: Yours Sincerely ..Omar WardehNo ratings yet
- C Cross Sectional Area (A)Document14 pagesC Cross Sectional Area (A)Jitheesh SahadevanNo ratings yet
- OPTIMIZATION (Economic Balance) What, Why, Aims/objectives Essential Features Simple Model, Methods of Solving Application: Insulation EvaporationDocument93 pagesOPTIMIZATION (Economic Balance) What, Why, Aims/objectives Essential Features Simple Model, Methods of Solving Application: Insulation EvaporationRyle Arbon100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Project FinalDocument16 pagesHeat Exchanger Project FinalChristopher CameronNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop CalculationDocument6 pagesPressure Drop CalculationNaveen Pete100% (2)
- Pipie Size CalcDocument7 pagesPipie Size Calczaksonu91221No ratings yet
- Master Calc HVAC SubmittalsDocument29 pagesMaster Calc HVAC Submittalshasanadel88No ratings yet
- Piping Related FormulasDocument16 pagesPiping Related Formulasnike_y2kNo ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing and CalculationsDocument17 pagesPipe Sizing and CalculationsJaykumar100% (7)
- Pipe Calculation Report - Revised - 2Document6 pagesPipe Calculation Report - Revised - 2Poom PPWNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document6 pagesLec 2hhjjrr22331No ratings yet
- Pipe Calculation Report - RevisedDocument6 pagesPipe Calculation Report - RevisedPoom PPWNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument8 pagesHeat TransferLorna AhlaamiNo ratings yet
- @S V All FansDocument19 pages@S V All Fanshasanadel88No ratings yet
- Thickness CalculationsDocument6 pagesThickness Calculationsvijayunity100% (1)
- Design of Heat ExchangerDocument26 pagesDesign of Heat ExchangerSatish YadavNo ratings yet
- Analytical Calculation of Automatic Sprinkler Fire Extinguishing System (Sfes)Document20 pagesAnalytical Calculation of Automatic Sprinkler Fire Extinguishing System (Sfes)IRJMETS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Pipe CalculationDocument26 pagesPipe CalculationRavindra S. JivaniNo ratings yet
- Process Calculations & Fan Audit Module in Cement IndustryDocument99 pagesProcess Calculations & Fan Audit Module in Cement IndustryNITITN ASNANINo ratings yet
- Ventilation Fans All RevisedDocument6 pagesVentilation Fans All RevisedBilal Hussein SousNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignCharito Sollera AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- From Table We KnowDocument5 pagesFrom Table We KnowTaha ZakiNo ratings yet
- Ductulator May 2010Document10 pagesDuctulator May 2010Arshavin Watashi Wa100% (1)
- Mechanical Design For Sieve Plate ColumnDocument14 pagesMechanical Design For Sieve Plate ColumnIan Zuhair II100% (1)
- Problem PipingDocument79 pagesProblem PipingSiddhi MhatreNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 8, Slice 3 "Destructors" to "Diameter"From EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 8, Slice 3 "Destructors" to "Diameter"No ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Scientific American, Vol. XXXVII.—No. 2. [New Series.], July 14, 1877 A Weekly Journal Of Practical Information, Art, Science, Mechanics, Chemistry, And ManufacturesFrom EverandScientific American, Vol. XXXVII.—No. 2. [New Series.], July 14, 1877 A Weekly Journal Of Practical Information, Art, Science, Mechanics, Chemistry, And ManufacturesNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168No ratings yet
- Parametric Ism in Urban DesignDocument13 pagesParametric Ism in Urban DesignReem Bakri100% (1)
- Mirzaei FractureMechanicsLecture PDFDocument61 pagesMirzaei FractureMechanicsLecture PDFkoohestani_afshinNo ratings yet
- Caisson RC DesignDocument1 pageCaisson RC DesignnurNo ratings yet
- EJN-00625 Installation of Manual Pull Valves in Deluge Systems For SOLPEDocument4 pagesEJN-00625 Installation of Manual Pull Valves in Deluge Systems For SOLPESARAVANAN ARUMUGAMNo ratings yet
- Repairs of D-Wall Exposed ReinforcementDocument7 pagesRepairs of D-Wall Exposed Reinforcement陈勇No ratings yet
- Parker 4MA SeriesDocument154 pagesParker 4MA SeriesSuhartoyo HcNo ratings yet
- Best Practice: Heat Exchanger and Horizontal Vessel Foundation Design GuideDocument55 pagesBest Practice: Heat Exchanger and Horizontal Vessel Foundation Design Guideomar mahmoudNo ratings yet
- IA Masonry SHS Q3 LAS1 FINALDocument9 pagesIA Masonry SHS Q3 LAS1 FINALIVY FAULVENo ratings yet
- Iso Checklist Rev02Document4 pagesIso Checklist Rev02Hemant Shinde100% (1)
- Sugar CaneMill V5.1Document7 pagesSugar CaneMill V5.1uksraj100% (1)
- BearingsDocument3 pagesBearingsMeet DhabaliaNo ratings yet
- Design of Flexible Pavement Using Industrial WasteDocument5 pagesDesign of Flexible Pavement Using Industrial WasteInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Soil PresentationDocument33 pagesSoil PresentationjrsvalenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Construction.: (Change of Address January 2011)Document6 pagesConstruction.: (Change of Address January 2011)Noerman Adi PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Fire Doors 101 Testing Certification BeyondDocument55 pagesFire Doors 101 Testing Certification BeyondAsoka Kumarasiri JayawardanaNo ratings yet
- Sp208-04ex 5Document17 pagesSp208-04ex 5Žarko LazićNo ratings yet
- EA Revolving DoorDocument4 pagesEA Revolving DoorzitreeNo ratings yet
- Marketonline - in Online Market Yellow Pages in South Delhi, Excel Media Services 2Document2 pagesMarketonline - in Online Market Yellow Pages in South Delhi, Excel Media Services 2kaminiNo ratings yet
- ASIF - Civil EngDocument4 pagesASIF - Civil EngDhanu NikkuNo ratings yet
- Delay Analysis Methods in Construction ProjectsDocument10 pagesDelay Analysis Methods in Construction ProjectsRajanRanjan100% (1)
- Bill 4F Bengkel Penyejukbekuan & Penyaman UdaraDocument62 pagesBill 4F Bengkel Penyejukbekuan & Penyaman Udaranoraaesya 82No ratings yet
- Pier ColumnDocument156 pagesPier ColumnMRMAKBARNo ratings yet
- Basic Soil Properties From CPT in Bangkok Clay For Highway DesignDocument8 pagesBasic Soil Properties From CPT in Bangkok Clay For Highway DesigntangkokhongNo ratings yet
- RTD NM RRP Construction Safety Security Plan PDFDocument366 pagesRTD NM RRP Construction Safety Security Plan PDFTarun KathpaliaNo ratings yet
- Solana Spas and Hot Tubs Owners Manuals 2003 PDFDocument67 pagesSolana Spas and Hot Tubs Owners Manuals 2003 PDFKitty FallaNo ratings yet
- The Unique Challenges of Planning A New Town: The Gandhinagar ExperienceDocument17 pagesThe Unique Challenges of Planning A New Town: The Gandhinagar ExperienceAnushka AnandNo ratings yet
- CE6302Document14 pagesCE6302Daniel MabengoNo ratings yet























































![Scientific American, Vol. XXXVII.—No. 2. [New Series.], July 14, 1877
A Weekly Journal Of Practical Information, Art, Science,
Mechanics, Chemistry, And Manufactures](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/187114288/149x198/c199ff44cf/1579708199?v=1)