Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ict - CSS 9 - Q3 - W1-3
Ict - CSS 9 - Q3 - W1-3
Uploaded by
Joy Dolorzo MahilumOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ict - CSS 9 - Q3 - W1-3
Ict - CSS 9 - Q3 - W1-3
Uploaded by
Joy Dolorzo MahilumCopyright:
Available Formats
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Name : ______________________________________________
Grade Level : ______________________________________________
Section : ______________________________________________
Date : ______________________________________________
Quarter/Week : Quarter 3/Week 1-3
______________________________________________
CSS-ICT 9
Preparing and Interpreting Technical Drawing
Specific Objective/s
This Learning Activity Module (LAS) was designed and written with you in mind. It
is here to help you master Preparing and Interpreting Technical Drawing. The scope of
this module permits it to be used in many different learning situations. The language
used recognizes the diverse vocabulary level of students. The lessons are arranged to
follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be
changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using.
The LAS is divided into four (4) learning outcomes, namely:
LO1 -
LO2 - interpret technical drawing;
LO3 - prepare/make changes to electrical/electronic schematics and drawing;
LO4 - store technical drawings and equipment.
After going through this Learning Activity Sheets, you are expected to:
1. Select correct technical drawing in accordance with the job requirement;
2. Segregate technical drawings in accordance with the types and kinds of
drawings;
3. Recognize components, assemblies, or objects as required;
4. Identify and interpret symbols used in the drawing;
5. Check and validate drawing against job requirements or equipment in
accordance with standard operating procedures;
6. Identify correct drawing; select and use equipment in accordance with job
requirements;
7. Identify tasks to be undertaken for care and maintenance to company
procedures;
MELC:
Preparing and Interpreting Technical Drawing.
(TLE_IACSS9-12PITD-IIg-h-14)
(TLE_IACSS9-12PITD-IIg-i-15)
(TLE_IACSS9-12PITD-IIg-j-16)
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 1
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Directions/Instructions
In this Learning Activity Sheet, you will study about technical drawing and how to
interpret symbols, components, assemblies or object and look at how to create and use
flow charts, and explore how they can help you to solve problems in your processes.
Notes to the Students
1. Study the lessons and answer religiously the activities. These will guide you on what
you will learn at the end of this Learning Activity Sheet.
2. Discover what you already know by answering the learning activities.
3. Apply what you have learned in real-life situation.
Activity
Activity 1:
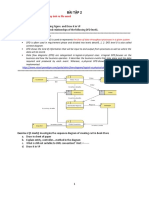
Directions: Look at the incomplete flowchart below, place them in order by
connecting the steps in developing a flowchart using an arrow. Flowchart must begin
with ―Start‖ and finish with ―End‖.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 2
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Procedure
Flowchart
A flowchart is a diagram that portrays the existence and flow of steps in a process
using graphic symbols. This method is also known as a "flow diagram."
What Are the Elements of a Flowchart?
Systems analysts also use flowcharts to visualize the sequence of processes in a
business system. A useful tool for developing a viable business system as well as
troubleshooting and improving an existing one. The terminator, method, subprocess,
decision, arrow lines, and connectors are all components of a flowchart.
Elements Function
Terminator - is represented by a small rectangle with curved corners. A terminator
appears at the start and at the end of a flowchart. The end terminator
appears only once on a single flowchart.
Process - is represented by a rectangle. It refers to an action in a business process. It
must be described clearly and concisely. A process can be described using a
single verb noun phrase; for example, "Order Office Supplies." The same level
of detail must be kept in processes on a single flowchart.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 3
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Sub- - is represented by a rectangle with double lines on each side. A sub- process is
process a major process that could be broken up into simpler processes developed
into another flowchart.
Decision - is represented by a diamond. A process that can answer a decision of "yes" or
"no" requires a decision box.
Connector - is represented by a small circle or a connector box and is labelled using
letters. A flowchart written on a single page is clearer than a flowchart on
several pages. A connector ensures that the processes are connected
logically and correctly on several pages.
Arrow - drawn in one direction, preferably from top to bottom, keep a flowchart
Lines clear. Avoid arrow lines that loop because this could indicate redundancy in
the business process.
When should teams use flowcharts?
An as-is flowchart will help the team and those who are involved in the process
understand how it actually functions at the outset of the process improvement efforts.
The team might find it useful to compare this as-is flowchart with a diagram of how the
process should operate. Later, the team will develop a flowchart of the way a process is
supposed to work and document how it really functions. Your team may want to create
an ideal flowchart to show how you would ultimately like the process to be performed at
some point.
Benefits of Using Flowcharts
1. Promote understanding of a process.
Different people may have different views on how a method works. A flowchart will
assist you in reaching an agreement on the sequence of events. Flowcharts help
comprehension in a way that written procedures do not. A good flowchart can take the
place of pages of text.
2. Provide a tool for training employees.
Flowcharts can be very helpful in training employees to perform the process
according to standardized procedures because of the way they visually lay out the
sequence of process steps.
3. Identify problem areas and opportunities for process improvement.
Problem areas become more visible once you break down the process steps and
diagram them. Analyzing decision points, redundant steps, and rework loops will help
you spot opportunities for simplifying and optimizing your process.
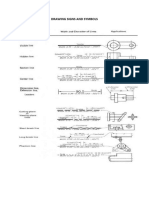
Basic Flowchart Symbols
Flowcharts uses symbols that have specific meaning and are connected by arrow that
shows the flow from one step to another:
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 4
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Symbol Name Description
Oval Ovals indicate both the starting point and the ending point of the
process steps.
Box A box represents an individual step or activity in the process.
Diamond A diamond shows a decision point, such as yes/no or go/no-go.
Each path emerging from the diamond must be labeled with one of
the possible answers.
Circle A circle indicates that a particular step is connected to another
page or part of the Flowchart. A letter placed in the circle clarifies
the continuation.
Triangle A triangle shows where an in process measurement occurs.
Figure 1. Flowchart Structure
Figure 1. shows the flowchart structure, its process on how to create the flowchart.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 5
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Figure 2. Example flowchart how to log in to your Facebook Account
Figure 2. shows the flowchart structure on how to log in to your Facebook Account.
How do you interpret flowcharts?
A Flowchart If you use a Flowchart to analyze what is happening, it will help you
understand your process and uncover ways to improve it. Interpreting your Flowchart
will help you to:
• Identify who are involved in the process.
• Formulate theories about root causes.
• Identify ways to simplify the process.
• Determine how to carry out and implement changes to the process.
• Locate cost-added-only steps.
• Provide training on how the process works or should work.
Below is a sequence of steps that will help you through an orderly analysis of your
flowchart.
Step 1 - Examine each process step for the conditions mentioned below, which suggest
that the process needs to be improved:
Bottlenecks. These are parts in the process where it slows down. These may be caused
by redundant or unnecessary steps, rework, lack of capacity, or other factors.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 6
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Weak links. These are steps where problems arise due to insufficient training of process
workers, equipment that needs to be repaired or replaced, or inadequate technical
documentation. "Inform the drill leader and improvise" is one of the weak links.
Poorly defined steps. Steps which are not clearly defined may be interpreted and
performed differently by each person involved which leads to variations of process.
"Improvise" is a poorly defined step in the weak link cited above.
Step 2 - Examine each symbol for a decision. You may want to keep track of how often a
"yes" or "no" response is given at decision points denoted by a diamond-shaped symbol. If
the majority of decisions are taken in one direction, you will be able to eliminate this
decision point.
Step 3 - Take a look at each rework loop. Processes with multiple checks result in
rework and waste. Examine the tasks that come before the rework loop to see which ones
can be changed. Look for ways to cut the loop or get rid of it altogether.
Step 4 - Examine each symbol for action. Does the step help produce a key quality trait
into the end product? If not, consider getting rid of it.
Types of Flowchart
There are three main types of flowcharts, namely linear, deployment, and opportunity
besides the three levels of detail used to categorize Flowcharts. The level of detail can be
represented as macro, mini, or micro for each of these types.
1. Linear Flowchart. A linear flowchart is a diagram that depicts the order in which
work steps in a process are completed. This tool can assist in the identification of rework
as well as redundant or unnecessary steps in a process.
2. Deployment Flowchart. A deployment flowchart portrays the actual process flow
while also defining the individuals or groups involved at each point. Customer-supplier
relationships are characterized by horizontal lines. This type of diagram illustrates where
individuals or groups fit into the mechanism and how they communicate with one
another throughout.
How do we construct a linear flowchart?
The following are the seven steps for developing a linear flowchart
1. Define the process to be flowcharted and why it is flowcharted.
2. Put together the right people to develop the flowchart—those operators, technicians, or
office workers who are actually part in the process.
3. Define the process boundaries—the starting and ending points.
• Determine the major activities or sub processes that are part in the process.
• Define what is not included in the scope of the process to get rid of any doubt or
confusion about the boundaries. This may also help create the scope of related
processes.
4. Enumerate the activities, decisions, and steps to be followed. If your team is not sure
about a step, mark it to be deliberated later.
5. Put the steps in the correct order. It's sometimes easier to start with the last step and
work your way backwards.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 7
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
6. Assign flowchart symbols (i.e. boxes, diamonds, and triangles) .
7. Review and assign a title to the Flowchart.
Activity
Activity 2:
Directions: Read and analyze each statement. Write check (/) if the statement is correct
and (x) if otherwise.
_________1. A flowchart is a diagram that uses graphic symbols to depict the nature and
flow of the steps in a process. Another name for this tool is "flow diagram."
_________2. A flowchart is commonly used by systems analysts to visualize the series of
processes in a business system.
_________3. A terminator is represented by a small rectangle with curved corners.
_________4. A process is represented by a rectangle. It must be described clearly and
concisely.
_________5. A sub-process is represented by a rectangle with double lines on each side.
_________6. A decision is represented by a diamond. A process that can answer a decision
of "yes" or "no" requires a decision box.
_________7. A connector is represented by a big circle or a connector box and is labelled
using letters.
_________8. Arrow lines drawn in one direction, preferably from top to bottom, keep a
flowchart clear.
_________9. One of the Benefits of Using Flowcharts is to promote understanding of a
process.
_________10. Box indicate both the starting point and the ending point of the process
steps.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 8
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Activity
Activity 3
Directions: Analyze the importance of using flowchart in Five (5) to Ten (10) sentences.
How does it affect the procedures or steps you are going to take?
___________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Activity
Activity 4.
Directions: Using the basic symbols used for flowchart, make your own simple flow
chart to illustrate the process of how to cook rice.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 9
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Closure
What I have learned in this activity?
1. I have learned that_________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. I need to know more about_________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 10
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Answer Key
X
/
/
X
/
/
scoring /
for /
rubrics / may vary.
See / Answers
Activity 4 Activity 2 Activity 1 and 3
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 11
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
References
Ramilo, R. V., & Pasco, D. M. (n.d.). Computer Hardware Servicing. K to 12 - Technology
and Livelihood Education.
Blanco, E. (2017, September 12). CSS NC II learning Module. Retrieved June 03, 2020,
from https://www.slideshare.net/edmundblanco/css-nc-ii-learningmodule
K to 12 Basic Education Curriculum Technology Livelihood Education Learning module -
Computer hardware servicing
https://kupdf.net/download/common-tools-and-equipment-for-computersystem-
servicing_5a2f023ce2b6f5f679a8c411_pdf
Department of Education, SOCCSKSARGEN Region. TLE CSS Quarter 1 Module 5:
Preparing and Interpreting Technical Drawing.
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 12
NOT FOR SALE
Schools Division of Koronadal City
City of Koronadal
Editor’s Note
This Learning Activity Sheet (LAS) was developed by DepEd Koronadal
City Division with the primary objective of preparing for and addressing the
new normal. Contents of this LAS were based on DepEd’s Most Essential
Competencies (MELC). This is a supplementary material to be used by all
learners of Koronadal City Division in all public schools beginning SY 2020-
2021. The process of LR development was observed in the production of this
LAS. We highly encourage feedbacks, comments, and recommendations.
Learning Activity Sheet Development Team
Writer : James Aldrin S. Estabillo and Arnold John B. De Vera
Editor : Latreia E. Estabillo
Lay-out Artist : Arvin M. Tejada
Reviewer/s : Evelyn C. Frusa PhD and Grace J. Miravalles
Management : Crispin A. Soliven Jr., CESE - SDS
Levi B. Butihen – ASDS
Prima A. Roullo – CID Chief
Grace J. Miravalles - EPS, EPP/TLE
Evelyn C. Frusa PhD – EPS-LRMDS
For inquiries or feedback, please write or call:
Department of Education – Koronadal City Division
Learning Resource Management System (LRMS)
Corner Rizal Street- Jaycee Avenue, Brgy. Zone IV, City of Koronadal
Telephone No.: (083) 877-5362
Learning Activity Sheet in ICT-CSS 9 13
You might also like
- Wickes UnderlayDocument2 pagesWickes UnderlayfloodanddrainageNo ratings yet
- Scale SkillsDocument35 pagesScale Skillspengwang728100% (1)
- Tradersworld GannDocument91 pagesTradersworld Gannnicolas arias100% (3)
- TLE-ICT-CSS-9-Q2 - Module-5-6 PITDDocument22 pagesTLE-ICT-CSS-9-Q2 - Module-5-6 PITDemerson elardoNo ratings yet
- G7 8 CSS Explo Module 4Document27 pagesG7 8 CSS Explo Module 4Heart NicoleNo ratings yet
- Tle Computer Systems Servicing - 9: Let Us DiscoverDocument4 pagesTle Computer Systems Servicing - 9: Let Us DiscoverWilma Montis-AbendanNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Technical DrawingDocument24 pagesDifferent Kinds of Technical DrawingRhea Mae Vequizo Balbido100% (1)
- G7 8 CSS Explo Module 4Document23 pagesG7 8 CSS Explo Module 4harurutNo ratings yet
- 10 LAS WEEk1-Basic SymbolsDocument10 pages10 LAS WEEk1-Basic SymbolsJenelyn RusianaNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Interpret Technical DrawingDocument5 pagesPrepare and Interpret Technical DrawingDwin Rosco75% (4)
- FlowchartDocument25 pagesFlowchartMichelle Anne Dalupang DayagNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument3 pagesFlowchartMarivic CastillanoNo ratings yet
- CSS 7 - 8 SSLMs 5Document4 pagesCSS 7 - 8 SSLMs 5Florenda IguinNo ratings yet
- Shepherdville College: What Are The Elements of A Flowchart?Document10 pagesShepherdville College: What Are The Elements of A Flowchart?Den SeguenzaNo ratings yet
- Tools For Quality ImprovementDocument64 pagesTools For Quality ImprovementMOHAMED YOUSEFNo ratings yet
- Tools For Quality ImprovementDocument65 pagesTools For Quality ImprovementAuraNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument24 pagesFlowchartDanilo AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Identifying Technical DrawingsDocument25 pagesIdentifying Technical DrawingsRobert kite Clemente100% (1)
- Tools For Quality ImprovementDocument65 pagesTools For Quality ImprovementThiago LealNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 ICT - Week 6 (Student's Copy)Document6 pagesTLE 8 ICT - Week 6 (Student's Copy)KAREN ONGCOL JUMALONNo ratings yet
- Las Grade 10 Ict 2Document3 pagesLas Grade 10 Ict 2Jenelyn RusianaNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 - Q2 - W6 (Reymondsumaylo)Document3 pagesTle 9 - Q2 - W6 (Reymondsumaylo)REYMOND SUMAYLONo ratings yet
- CHS 8 - 3rd Q - Module 3Document12 pagesCHS 8 - 3rd Q - Module 3kreamerNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Madas RevDocument3 pagesFlowchart Madas Revs4tr10.d1m4sNo ratings yet
- Modular December-VacationDocument14 pagesModular December-VacationAprilcarlcaspe SabasNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart DefinitionDocument9 pagesFlow Chart DefinitionFarooqNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart Definition: What Is FlowchartDocument9 pagesFlow Chart Definition: What Is FlowchartRamakrishna KaturiNo ratings yet
- Q2M3Document13 pagesQ2M3Russel GuratNo ratings yet
- Session 4 - FlowChartDocument8 pagesSession 4 - FlowChartGandavadi VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Programming and FlowchartingDocument33 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Programming and FlowchartingRamachandran Nambissan TmNo ratings yet
- Css q2 Week6 g11Document4 pagesCss q2 Week6 g11Jandeil GurreaNo ratings yet
- No. 7 LP CSS Technical DrawingDocument11 pagesNo. 7 LP CSS Technical DrawingJamie GoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document11 pagesLesson 4안아ANANo ratings yet
- Tools For Quality ImprovementDocument64 pagesTools For Quality Improvementmuzammil21_adNo ratings yet
- CP12 Module WK 1Document11 pagesCP12 Module WK 1Lyka Aunice L. LacsonNo ratings yet
- Flowcharting PDFDocument11 pagesFlowcharting PDFJordan Tagao ColcolNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument6 pagesFlowchartyleno_meNo ratings yet
- Prepare Interpret Technical DrawingDocument31 pagesPrepare Interpret Technical DrawingMariel Balmes HernandezNo ratings yet
- Identify Different Kinds of Technical DrawingsDocument25 pagesIdentify Different Kinds of Technical Drawingsallan tomasNo ratings yet
- Identify Different Kinds of Technical DrawingDocument22 pagesIdentify Different Kinds of Technical DrawingBendict Vinsmoke100% (3)
- FlowchartDocument16 pagesFlowchartNhatz Gallosa MarticioNo ratings yet
- Flow ChartDocument7 pagesFlow ChartMuhammad Atif Qaim KhaniNo ratings yet
- W6-1. BPE and FlowchartsDocument25 pagesW6-1. BPE and FlowchartsMANI 96 FFNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Programming Ass 3Document21 pagesFlowchart Programming Ass 3BETHANY LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Programming Ass 3Document21 pagesFlowchart Programming Ass 3BETHANY LABRADORNo ratings yet
- PT&TK 2022 BaiTap2Document8 pagesPT&TK 2022 BaiTap2Mai LyNo ratings yet
- A Flowchart Is Simply A Graphical Representation of StepsDocument20 pagesA Flowchart Is Simply A Graphical Representation of StepsMelwalizwe Whyted ZimbaNo ratings yet
- NOS: Certificate in Computer Applications - : Online Course MaterialDocument9 pagesNOS: Certificate in Computer Applications - : Online Course Materialsrikanth_earavelliNo ratings yet
- Balagat - Renz-MOLINO-CpE 3216L - E2Document6 pagesBalagat - Renz-MOLINO-CpE 3216L - E2RenzNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Quezon CityDocument2 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Quezon CityStephanie BesanaNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument5 pagesFlowchartmahendra shuklaNo ratings yet
- Technical DrawingDocument59 pagesTechnical DrawingcyrelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Comp1l Flowchart PDFDocument6 pagesLecture 5 Comp1l Flowchart PDFCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Computer-Programming - Las Q2 M1 Flowcharting Shelaine PacienteDocument13 pagesComputer-Programming - Las Q2 M1 Flowcharting Shelaine PacienteSamuel DanosNo ratings yet
- 2 FlowchartDocument28 pages2 Flowchartbishnoisumit1229No ratings yet
- Preparing and Interpreting Technical DrawingDocument17 pagesPreparing and Interpreting Technical Drawingracquel jimenezNo ratings yet
- 1 FlowchartDocument28 pages1 FlowchartKaMaL MeHtANo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Drawing A Flow ChartDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Drawing A Flow ChartMaedenne JamneNo ratings yet
- Ict8 Q1 M7 PPTDocument47 pagesIct8 Q1 M7 PPTTsukareta TsukiNo ratings yet
- Bethany Labrador Bsit-A1: 1. What Are The Advantages of Using Flowchart?Document9 pagesBethany Labrador Bsit-A1: 1. What Are The Advantages of Using Flowchart?BETHANY LABRADORNo ratings yet
- The One-Page Project Manager for Execution: Drive Strategy and Solve Problems with a Single Sheet of PaperFrom EverandThe One-Page Project Manager for Execution: Drive Strategy and Solve Problems with a Single Sheet of PaperNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1 Tle CarpentryDocument2 pagesPerformance Task 1 Tle CarpentryJoy Dolorzo MahilumNo ratings yet
- AR PresentationDocument12 pagesAR PresentationJoy Dolorzo MahilumNo ratings yet
- AGRICROP 9 Module 9Document27 pagesAGRICROP 9 Module 9Joy Dolorzo MahilumNo ratings yet
- TLE-TE 10 - Q2 - Mod2Document9 pagesTLE-TE 10 - Q2 - Mod2Joy Dolorzo MahilumNo ratings yet
- 1Ø Service Manual: Engineered For LifeDocument76 pages1Ø Service Manual: Engineered For LifejewettwaterNo ratings yet
- JSON - WikipediaDocument13 pagesJSON - WikipediadearbhupiNo ratings yet
- Haulotte HA260 PX Diesel Articulating BoomDocument2 pagesHaulotte HA260 PX Diesel Articulating BoomRizalino BargoNo ratings yet
- CODE of PRACTICE - COMPRESSED GAS CYLINDERSDocument5 pagesCODE of PRACTICE - COMPRESSED GAS CYLINDERSAkhilesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Banner Value BeamDocument20 pagesBanner Value BeamryanmackintoshNo ratings yet
- Architect Auguste Perret - Buildings, Biography & Architecture - StudyDocument6 pagesArchitect Auguste Perret - Buildings, Biography & Architecture - StudyAmaka NwegbuNo ratings yet
- Excel Skills For Business: Divyanshu SharmaDocument1 pageExcel Skills For Business: Divyanshu SharmaDivyanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- HLGuide22 23Document38 pagesHLGuide22 23Luis Gerardo Aguilar CruzNo ratings yet
- Russi Mody 2Document3 pagesRussi Mody 2rockstarchandreshNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On: Sensotronic Brake ControlDocument23 pagesA Seminar On: Sensotronic Brake ControlVed PrakashNo ratings yet
- Team Members: M.Abarna (10PX01) V. Agasthiya Priya (10PX02) K.Ajeesh (10PX03)Document50 pagesTeam Members: M.Abarna (10PX01) V. Agasthiya Priya (10PX02) K.Ajeesh (10PX03)Ashokkumar Gnanasekar NadarNo ratings yet
- Garia - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesGaria - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPradip DattaNo ratings yet
- KC & The Sunshine Band - Give It UpDocument3 pagesKC & The Sunshine Band - Give It Upluisa fernanda quitian romeroNo ratings yet
- (New) Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Rubberized Coir Fibre SheetsDocument8 pages(New) Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Beams Using Rubberized Coir Fibre SheetsPrakumarNo ratings yet
- International Business: by Charles W.L. HillDocument37 pagesInternational Business: by Charles W.L. Hilllongtran1191No ratings yet
- MECH 2001 Week 1 Le SummeryDocument14 pagesMECH 2001 Week 1 Le Summeryujjwal katyalNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic HammerDocument7 pagesPneumatic HammerShlok PatelNo ratings yet
- Girls of Gaming 6 PDFDocument123 pagesGirls of Gaming 6 PDFЗоран БлагојевићNo ratings yet
- G7 K1 Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument15 pagesG7 K1 Semi Detailed Lesson PlanJohn Carlo LucinoNo ratings yet
- PA4600 & PA6000 User Manual - Rev GDocument53 pagesPA4600 & PA6000 User Manual - Rev GjatzireNo ratings yet
- Liquid Resins Additives - EmeaDocument59 pagesLiquid Resins Additives - Emearndsb.aopNo ratings yet
- Remote Terminal Unit With 8203 - Dual RS-485 Communications ModulesDocument220 pagesRemote Terminal Unit With 8203 - Dual RS-485 Communications ModulesАлександрNo ratings yet
- Types of Franchising and AdvantagesDocument12 pagesTypes of Franchising and AdvantagesShiMeiChanNo ratings yet
- 2016-Catalog-Cover-Fire Arms-Small-FileDocument32 pages2016-Catalog-Cover-Fire Arms-Small-FileCipriano M RogerioNo ratings yet
- Tech Spec ASN 23 GHZDocument12 pagesTech Spec ASN 23 GHZFernanda B. MazoniNo ratings yet
- How To Download Course Content (Files) From Blackboard LearnDocument5 pagesHow To Download Course Content (Files) From Blackboard LearnRickyNo ratings yet
- Chemical HazardsDocument17 pagesChemical HazardsLloydy HemsworthNo ratings yet