Professional Documents
Culture Documents
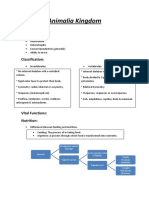
Functions of The Organelles of An Animal Cell
Functions of The Organelles of An Animal Cell
Uploaded by
mburu. hOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Functions of The Organelles of An Animal Cell
Functions of The Organelles of An Animal Cell
Uploaded by
mburu. hCopyright:
Available Formats
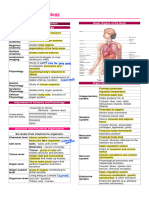
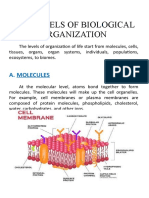
Functions of the organelles of an animal cell.
The cell membrane is a double-layered membrane made up of phospholipids that surrounds the
entire cell. The membrane is selectively permeable and allows only certain molecules to pass through.
Cytosol is the fluid present within a cell that is made up of water and ions such as potassium, proteins
and small molecules.
Cytoskeleton is the network of tubules and filaments found throughout the cytoplasm. It provides
proper shape to the cell and plays a role in cell signalling.
The nucleus contains the genetic material DNA located in the nucleolus region of the nucleus. The
nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell by a nuclear membrane. It also regulated the growth and
division of cells.
Ribosomes are found freely in the cytoplasm of the cell or attached to the membranes of endoplasmic
reticulum. They help in the synthesis of proteins.
The endoplasmic membrane consists of a network of membranous sacs called cisternae that
branches off from the nuclear membrane. It is of two types, rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth
endoplasmic reticulum. It helps in transporting proteins synthesised by the ribosomes.
The vesicles help in transporting molecules from one organelle to another.
Golgi apparatus receives proteins from endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into vesicles.
Mitochondria is also known as the “powerhouse of the cell”. The process of cellular respiration occurs
here during which energy is released in the form of ATP.
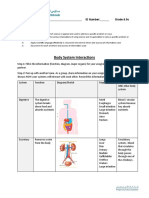
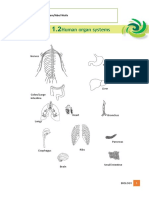
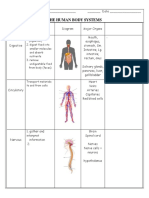
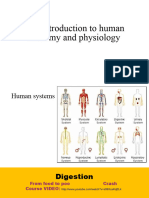
The Organ system of the body
Organs
Functions
Organ system
Skin
Barrier to invading organisms and chemicals
Integumentary Hair
Temperature control
Subcutaneous tissue
Supports and moves body Bones
Protects internal organs Cartilage
Skeletal Mineral storage Ligaments
Blood formation Bone marrow
Locomotion Muscles
Muscular Heat production Tendons
Brain
Spinal cord
Coordinates activities of other organ systems
Nerves
Nervous Responds to sensations
Eyes
Ears
Endocrine Regulates body functions by chemicals (hormones) Pituitary gland
Parathyroid gland
Thyroid gland
Adrenal gland
Thymus
Pancreas
Gonads
Heart
Transports oxygen and nutrients to tissues
Blood
Cardiovascular Removes waste products
Blood vessels
Spleen
Returns tissue fluid to blood Lymph nodes
Lymphatic Defends against foreign organisms Thymus
Lymphatic vessels
Lungs
Trachea
Oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange Larynx
Respiratory
Nasal cavities
Pharynx
Stomach
Intestinal tract
Processes foods Liver
Digestive Absorption of nutrients into body Pancreas
Esophagus
Salivary glands
Kidneys
Elimination of wastes
Urinary bladder
Urinary Regulates pH and volume of blood
Urethra
Ovaries
Uterus
Produces germ cells (eggs and sperm) Mammary glands
Reproductive Environment for growth of fetus (female) Testes
Prostate gland
External genitalia
You might also like
- Test Bank For Human Anatomy 6th Edition Michael Mckinley Valerie Oloughlin Elizabeth Pennefather ObrienDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Human Anatomy 6th Edition Michael Mckinley Valerie Oloughlin Elizabeth Pennefather ObrienMatthew Anderson100% (38)
- Test Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition by StanfieldDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition by Stanfieldjohnlipceqgkjnbt100% (48)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Cza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy (An Orientation) : Dr. Tanveer Ahmed KhanDocument67 pagesHuman Anatomy (An Orientation) : Dr. Tanveer Ahmed KhanShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Body Systems, Functions, and OrgansDocument2 pagesBody Systems, Functions, and Organssandhiya padmanabanNo ratings yet
- Body SystemDocument2 pagesBody SystemKD F2021No ratings yet
- Chap-1-2 2Document20 pagesChap-1-2 2Salmone, Jhon DevonVILLARNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: An OrientationDocument21 pagesThe Human Body: An OrientationKeanna ZurriagaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsDocument13 pagesDifferentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsShivani HiteshNo ratings yet
- Functions Control Reproduction Movement Body Maintenance TransportationDocument1 pageFunctions Control Reproduction Movement Body Maintenance TransportationMariam RahimNo ratings yet
- Final Review Worksheet 11thDocument28 pagesFinal Review Worksheet 11thElec AzNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- Anatomy Notes - Lecture 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Notes - Lecture 1ellieNo ratings yet
- Body System Interactions: Criterion DDocument4 pagesBody System Interactions: Criterion DReem AlmeheiriNo ratings yet
- Science7 - q2 - slk3 - Level of Biological Organization - v1Document18 pagesScience7 - q2 - slk3 - Level of Biological Organization - v1alain presillasNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument38 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyDeva ChiruNo ratings yet
- Orientatioin of The Human BodyDocument57 pagesOrientatioin of The Human BodyJackson JastariNo ratings yet
- System in Human BodyDocument1 pageSystem in Human BodyIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- 21.12.22 Lec-1 Science With NumberDocument6 pages21.12.22 Lec-1 Science With NumberMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Animalia Kingdom: CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesAnimalia Kingdom: CharacteristicsIldefonso MuñozNo ratings yet
- Cells To Tissues To Organs Graphic Organizer ExampleDocument2 pagesCells To Tissues To Organs Graphic Organizer Exampleapi-431603797No ratings yet
- Biological Effects of RadiationsDocument9 pagesBiological Effects of RadiationsAmmaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnatomyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 AnatomyinitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalDocument8 pagesMod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.2 Human Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesAns 1.2 Human Organ SystemsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Introduction of PHYSIOLOGY - 2Document19 pages2 - The Introduction of PHYSIOLOGY - 2Ramadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- 11 Organ SystemsDocument12 pages11 Organ Systemsprincessfarah hussinNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems of The Human Body and Their IntegrationDocument1 pageOrgan Systems of The Human Body and Their IntegrationUsman GulNo ratings yet
- U1 The Human Body 5Document12 pagesU1 The Human Body 5Francisco RosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesHimiko JacksonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Ch1 To Ch6Document30 pagesReviewer - Ch1 To Ch6cpagente01No ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument4 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDave Chadha100% (1)
- Marieb - CH - 01 - Lecture - Doc (Edited)Document3 pagesMarieb - CH - 01 - Lecture - Doc (Edited)Dustin RamosNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic 1Document3 pagesAssignment Topic 1Charlyn CasabalNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOLOGYElla May TimoteoNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: An Orientation: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncDocument51 pagesThe Human Body: An Orientation: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncMohammad DweibNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganDocument8 pagesAnatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument4 pagesHuman Body Systemsoiu7hjjs100% (15)
- Human Body, Cells, TissuesDocument6 pagesHuman Body, Cells, Tissuesjaspreetsinghmehrok100% (1)
- Learning Guide Introduction To BodyDocument3 pagesLearning Guide Introduction To BodyAutumn ReadNo ratings yet
- CH 18 Endo F 2017Document152 pagesCH 18 Endo F 2017Julia100% (1)
- Physiology and Pathophysiology IntroductionDocument39 pagesPhysiology and Pathophysiology Introductionbasmala.a.zahranNo ratings yet
- Internal Anatomy of FishDocument18 pagesInternal Anatomy of FishPokemongo Shu TingNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemsDocument29 pagesHuman Body SystemsMatt Nupen100% (1)
- Physiology Basic HomeostaticDocument19 pagesPhysiology Basic Homeostaticjoycelynhandoyo22No ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Introduction and OrientationDocument24 pagesThe Human Body Introduction and OrientationAshishNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- 1 A The Human Body IntroDocument24 pages1 A The Human Body IntroMurugesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physiology and HomeostasisDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Physiology and HomeostasismnaeditzNo ratings yet
- Human Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsDocument9 pagesHuman Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Reviewerain't your saintessNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Systems: - NotesDocument2 pagesThe Human Body Systems: - NotesGil Perez VelizNo ratings yet
- Elsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurviveDocument4 pagesElsci LT 2.2: Chapter 8: Animals' Need To SurvivelemonNo ratings yet
- ODB - Bio (Human Anatomy)Document3 pagesODB - Bio (Human Anatomy)aloevera1994No ratings yet
- 9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument75 pages9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiologydmnnfn8hkgNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsDocument84 pages2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular Organismswickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Intro.Document9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Intro.ANDREA GRAZILLE NAVAIRANo ratings yet
- Anaphy PrelimsDocument4 pagesAnaphy PrelimsKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- How Do I Carry Out A Resonance Test?Document1 pageHow Do I Carry Out A Resonance Test?Inayattullah KhamkerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysam.ieeballesterNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument48 pagesGeneticsmburu. hNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument27 pagesDiabetes Mellitusmburu. hNo ratings yet
- Biological Organization...Document34 pagesBiological Organization...mburu. hNo ratings yet
- Bank Rate and Transmission Mechanisms of Monetary Policy in Kenya - by Francis MwegaDocument21 pagesBank Rate and Transmission Mechanisms of Monetary Policy in Kenya - by Francis Mwegamburu. hNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Response To Policy News in Kenya - by Ann Kamau and Rose NgugiDocument32 pagesExchange Rate Response To Policy News in Kenya - by Ann Kamau and Rose Ngugimburu. hNo ratings yet
- A Note On Term Structure and Inflationary Expectations in Kenya - by Francis MwegaDocument14 pagesA Note On Term Structure and Inflationary Expectations in Kenya - by Francis Mwegamburu. hNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Chapter 2 With Complete SolutionsDocument6 pagesMedical Terminology Chapter 2 With Complete SolutionsGregg ProducerNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Structural Organisation in Animals NEET 2023 - Free PDF DownloadDocument26 pagesRevision Notes On Structural Organisation in Animals NEET 2023 - Free PDF Downloadmadam photonNo ratings yet
- S7 - Q2 - Summative Test 2Document6 pagesS7 - Q2 - Summative Test 2Raniel LacuarinNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument28 pagesBloodIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document11 pagesChapter 1-4Vy ThachNo ratings yet
- Embryology ObgDocument36 pagesEmbryology ObgsamrusangaliNo ratings yet
- Activity 3B - Animal Tissues (Muscular & Nervous Tissue) - Activity SheetDocument8 pagesActivity 3B - Animal Tissues (Muscular & Nervous Tissue) - Activity SheetKristine VibarNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument20 pagesOral CavityadileidalaaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1-NewDocument20 pagesLab 1-NewHajira NusretNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Mapeh, Epp2.1Document13 pagesSummative Test Mapeh, Epp2.1jellyB RafaelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants-1Document80 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants-1aditya kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument14 pagesSkeletal SystemBea MiguelaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by WhitakerDocument6 pagesComprehensive Perinatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care 4th Edition by WhitakerlunaNo ratings yet
- KINE 2031 Test 4 NotesDocument16 pagesKINE 2031 Test 4 NotesnokiaNo ratings yet
- Dicot-Monocot Stem AnatomyDocument6 pagesDicot-Monocot Stem AnatomyAdlet100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Integumentary SystemDocument41 pagesLesson 3 Integumentary SystemShida HuaEiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Histology USDocument7 pagesLecture Histology USالهاشميNo ratings yet
- Bone Development Andbone Growth-0Document28 pagesBone Development Andbone Growth-0Aruli AruliNo ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument3 pagesPhysical EducationLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 PracticalsDocument7 pagesGrade 9 PracticalsAlan JeethNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemSri Ganesh ComputersNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Anatomy Physiology 2nd Edition Kenneth Saladin Robin McfarlandDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Anatomy Physiology 2nd Edition Kenneth Saladin Robin McfarlandAntonio Demetro100% (34)
- 2021 Expt 12 Pre Lab - Mammal Organ SystemDocument5 pages2021 Expt 12 Pre Lab - Mammal Organ SystemNUR NAJWA BINTI MOHD RAFIE MoeNo ratings yet
- Assig# 3 Pathology - Docx (Ali Aasam Khan CU-1774-2020)Document21 pagesAssig# 3 Pathology - Docx (Ali Aasam Khan CU-1774-2020)Ali Aasam KhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology FINAL REVIEWDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology FINAL REVIEWSinda GnanasunderamNo ratings yet
- Dactyloscopy 1st Prelim Exam.Document3 pagesDactyloscopy 1st Prelim Exam.Ocyub Avlas OdnamraNo ratings yet