Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 viewsProkaryotic Cell VS Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cell VS Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
ATAY, JUSTINE MAVE S.The document compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus, while eukaryotic cells do. Some key differences are that prokaryotic cells are smaller, have DNA not associated with histones, divide via binary fission, have a simpler cell wall, and do not have membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have DNA associated with histones, divide via mitosis or meiosis, have a more complex cell wall, and have membrane-bound organelles with transcription occurring in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell: Comparison ChartDocument5 pagesEukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell: Comparison ChartMission Aid100% (1)
- Biological Chemistry (Midterms)Document3 pagesBiological Chemistry (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Checking For UnderstandingDocument5 pagesDistinguishing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Checking For UnderstandingPamela Isabelle TabiraraNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryoticG- 6 ODL Trisha Mae Clemente100% (1)
- The Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesDocument1 pageThe Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesEnrique the ThirdNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMDocument27 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMcfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Document3 pagesProkaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Anime KpopNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lec2b - Hidden World of CellsDocument15 pagesGenbio Lec2b - Hidden World of CellsRaymart abresinosNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1Document15 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1porchypepita37No ratings yet
- Venn Diagram Comparison (Cells) - B-1 Herrera, Sean Blair E.Document2 pagesVenn Diagram Comparison (Cells) - B-1 Herrera, Sean Blair E.santa gabrielNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Enrique III C Pacudan General Biology - Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Cells 12 Blessed Sante of Cori July 17, 2019Document1 pageEnrique III C Pacudan General Biology - Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Cells 12 Blessed Sante of Cori July 17, 2019Enrique the ThirdNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellshaji1234554No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and EukaryoteDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and Eukaryotejocelynmillano115No ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn DiagramDocument1 pageProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn DiagramAndrea JastillanaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsClaire JosephNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2Document2 pagesAndaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2Rj AndayaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 4 - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument11 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 4 - Mitosis - MeiosisAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument65 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Terms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesTerms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsSlay SacedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellDocument1 pageDifferences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellSunidhi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cabucana, Paul Lester Finals BacteDocument91 pagesCabucana, Paul Lester Finals BactePaul LesterNo ratings yet
- 2.classification of Living ThingsDocument2 pages2.classification of Living ThingsBirukNo ratings yet
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Zool Lab 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesZool Lab 2 Reviewerqbcngqrrq5No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- ProtozoansDocument13 pagesProtozoansGabrielle ForgetNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenDocument11 pagesEukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenAdnan Malik100% (2)
- Unit 2 Cells Digital PacketDocument22 pagesUnit 2 Cells Digital PacketTevin KimNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure - AP BiologyDocument9 pagesCellular Structure - AP Biologyejung26No ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- GB1 Module 1.2Document4 pagesGB1 Module 1.2beatriz OndilloNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDocument26 pagesNMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDax Arcega100% (1)
- NmatstudyguideupdatedpdfDocument26 pagesNmatstudyguideupdatedpdfRafael GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Prokalytic Vs EurokalyticDocument1 pageProkalytic Vs EurokalyticJessielyn DangananNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Sept. 12 13Document46 pagesGen Bio Sept. 12 13Jessica RaymundoNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeSK BuntunNo ratings yet
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
Prokaryotic Cell VS Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cell VS Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
ATAY, JUSTINE MAVE S.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThe document compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus, while eukaryotic cells do. Some key differences are that prokaryotic cells are smaller, have DNA not associated with histones, divide via binary fission, have a simpler cell wall, and do not have membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have DNA associated with histones, divide via mitosis or meiosis, have a more complex cell wall, and have membrane-bound organelles with transcription occurring in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm.
Original Description:
Original Title
PROKARYOTIC CELL VS EUKARYOTIC CELL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus, while eukaryotic cells do. Some key differences are that prokaryotic cells are smaller, have DNA not associated with histones, divide via binary fission, have a simpler cell wall, and do not have membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have DNA associated with histones, divide via mitosis or meiosis, have a more complex cell wall, and have membrane-bound organelles with transcription occurring in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesProkaryotic Cell VS Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cell VS Eukaryotic Cell
Uploaded by
ATAY, JUSTINE MAVE S.The document compares and contrasts prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus, while eukaryotic cells do. Some key differences are that prokaryotic cells are smaller, have DNA not associated with histones, divide via binary fission, have a simpler cell wall, and do not have membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, have DNA associated with histones, divide via mitosis or meiosis, have a more complex cell wall, and have membrane-bound organelles with transcription occurring in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
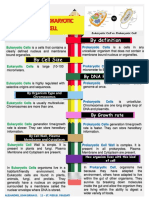
PROKARYOTIC CELL VS.
EUKARYOTIC CELL
I. DEFINITION OF TERMS
Prokaryotes – organisms which do not have true nucleus. These organisms have prokaryotic cell. Pro
means “before”, karyum means “kernel or nut” which refers to the nucleus.
Prokaryotic – having a characteristic of being a prokaryote
Examples of Prokaryotes:
1. Bacteria (coccus, bacillus, streptococcus (sing.), staphylococcus (plu.))
Eukaryotes – organisms that have true nucleus. Eu means “true”.
Examples of Eukaryotes:
1. Plants
2. Animals
3. Humans
4. Fungi
5. Protozoans
6. Algae
2 TYPES OF EUKARYOTIC CELL :
1. Plant Cell
2. Animal Cell
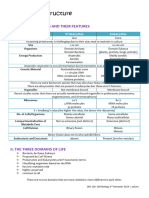
II. COMPARISON
INDICATORS PROKARYOTIC CELL EUKARYOTIC CELL
SIZE Smaller Large; some vary in size
DNA Not associated with histories Associated with histories
DIVISION Usually by binary fission Mitosis/Meiosis
CELL WALL Simple Complex
ORGANELLES Not membrane bond Membrane bond
TRANSCRIPT AND Occurs together Transcription happens in the
TRANSLATION nucleus while translation
happens in cytoplasm
You might also like
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell: Comparison ChartDocument5 pagesEukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell: Comparison ChartMission Aid100% (1)
- Biological Chemistry (Midterms)Document3 pagesBiological Chemistry (Midterms)ale.cristianNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Checking For UnderstandingDocument5 pagesDistinguishing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Checking For UnderstandingPamela Isabelle TabiraraNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Bacteriology LectureDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryoticDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryoticG- 6 ODL Trisha Mae Clemente100% (1)
- The Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesDocument1 pageThe Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Their SimilaritiesEnrique the ThirdNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMDocument27 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMcfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Arsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesArsenii Vasylchenko The Cell CycleАрсений ВасильченкоNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Document3 pagesProkaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Anime KpopNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Genbio Lec2b - Hidden World of CellsDocument15 pagesGenbio Lec2b - Hidden World of CellsRaymart abresinosNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1Document15 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic Cells bsn1porchypepita37No ratings yet
- Venn Diagram Comparison (Cells) - B-1 Herrera, Sean Blair E.Document2 pagesVenn Diagram Comparison (Cells) - B-1 Herrera, Sean Blair E.santa gabrielNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Enrique III C Pacudan General Biology - Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Cells 12 Blessed Sante of Cori July 17, 2019Document1 pageEnrique III C Pacudan General Biology - Eukaryotic Vs Prokaryotic Cells 12 Blessed Sante of Cori July 17, 2019Enrique the ThirdNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- EUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Document2 pagesEUKARYOTIC VS PROKARYOTIC Week 2Alea AicoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellshaji1234554No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and EukaryoteDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Prokaryote and Eukaryotejocelynmillano115No ratings yet
- Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pagesCell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn DiagramDocument1 pageProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn DiagramAndrea JastillanaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsClaire JosephNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2Document2 pagesAndaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2Rj AndayaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 4 - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument11 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 4 - Mitosis - MeiosisAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument65 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Terms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesTerms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsSlay SacedaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellDocument1 pageDifferences Between Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellSunidhi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cabucana, Paul Lester Finals BacteDocument91 pagesCabucana, Paul Lester Finals BactePaul LesterNo ratings yet
- 2.classification of Living ThingsDocument2 pages2.classification of Living ThingsBirukNo ratings yet
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Zool Lab 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesZool Lab 2 Reviewerqbcngqrrq5No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- ProtozoansDocument13 pagesProtozoansGabrielle ForgetNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenDocument11 pagesEukaryotic Cell Vs Prokaryotic Cell - Difference and Comparison - DiffenAdnan Malik100% (2)
- Unit 2 Cells Digital PacketDocument22 pagesUnit 2 Cells Digital PacketTevin KimNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure - AP BiologyDocument9 pagesCellular Structure - AP Biologyejung26No ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- GB1 Module 1.2Document4 pagesGB1 Module 1.2beatriz OndilloNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDocument26 pagesNMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDax Arcega100% (1)
- NmatstudyguideupdatedpdfDocument26 pagesNmatstudyguideupdatedpdfRafael GoldbergNo ratings yet
- Prokalytic Vs EurokalyticDocument1 pageProkalytic Vs EurokalyticJessielyn DangananNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Sept. 12 13Document46 pagesGen Bio Sept. 12 13Jessica RaymundoNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeDocument6 pagesThere Are Three Distinct Domains of LifeSK BuntunNo ratings yet
- Module 3-P. E. CellsDocument4 pagesModule 3-P. E. CellsRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)