Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsNstp1 Midterm Lesson1
Nstp1 Midterm Lesson1
Uploaded by
Jonnalyn R. LiberatoEnvironmental management involves controlling human impact on the environment to preserve natural resources. It deals with the complex interaction between socio-cultural and bio-physical systems at the environment-human interface. Environmental management aims to support sustainable development through a multidisciplinary approach that integrates different perspectives and considers both short and long term impacts. Key areas that require environmental management include population increase, pollution treatment, renewable energy development, biodiversity conservation, and environmental awareness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Environmental Protection and ManagementDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Protection and ManagementZaymonne Kent LaugoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Protection and ManagementDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Protection and Managementqwerty asdfgNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Scienceprincess.pinedaNo ratings yet
- EDUC. 242 Part III - Environmental ManagementDocument5 pagesEDUC. 242 Part III - Environmental ManagementJoseph Ryan MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Nstp-Cwts Module 5Document10 pagesNstp-Cwts Module 5JUAN VICTOR MACADANGDANGNo ratings yet
- 1environmental ManagementDocument53 pages1environmental ManagementLileth Lastra QuiridoNo ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewerDocument5 pagesNSTP Revieweraceyodo000No ratings yet
- PTEN551 Lecture 97 ShowDocument49 pagesPTEN551 Lecture 97 ShowGeorge BlakeNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Environmental Ethics (English Ver)Document15 pagesTopic 5 Environmental Ethics (English Ver)nuzul hanisNo ratings yet
- Evs Notes 2Document90 pagesEvs Notes 2Ashok Kumar100% (1)
- Envi Sci Reviewer 1Document7 pagesEnvi Sci Reviewer 1Abegail Neo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Prelim Environmental EnggDocument16 pagesPrelim Environmental EnggAs ReNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Introduction To Environmental Studies and EcosystemDocument79 pagesUnit - I: Introduction To Environmental Studies and EcosystemDina GaranNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Environmental Resource Protection and Management: Week 9Document38 pagesModule 6: Environmental Resource Protection and Management: Week 9Alyssa Joanna LlorinNo ratings yet
- EED 4118 Lesson 2Document11 pagesEED 4118 Lesson 2KevinNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Environmental MGT StudentsDocument8 pagesModule 4 Environmental MGT StudentsIan Cadauan Baquiran100% (1)
- Environment Management PortfolioDocument5 pagesEnvironment Management PortfolioMichelle DupioNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Through Environmental Ethics: S RajalakshmiDocument4 pagesSustainable Development Through Environmental Ethics: S RajalakshmiMAHANTESH GNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument8 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Environmental ScienceGlycel SaldiviaNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument3 pagesMapa ConceptualFelipe Gutierrez MachadoNo ratings yet
- All Topics Evs Covered Bba FTDocument26 pagesAll Topics Evs Covered Bba FTAxiiNo ratings yet
- Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technology Mati CityDocument13 pagesDavao Oriental State College of Science and Technology Mati CityHeartyAquinoBasocNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument17 pages1 IntroductionAuto NomousNo ratings yet
- Environmental Ethics and Gandhian Approach: Module - 7Document11 pagesEnvironmental Ethics and Gandhian Approach: Module - 7chandra_53754271No ratings yet
- People and Earths EcosystemDocument4 pagesPeople and Earths EcosystemJolina T. OrongNo ratings yet
- Ema 111Document5 pagesEma 111bulukuian50% (1)
- National Environmental Policy and StrategiesDocument18 pagesNational Environmental Policy and StrategiesAyushi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 .... Importance of Environmental ProtectionDocument15 pagesModule 1 .... Importance of Environmental ProtectionEUNICE CIELO MARIE LIMNo ratings yet
- NSTP SemisDocument52 pagesNSTP SemishiimleoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Scope & ImportanceDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Scope & ImportanceNANCY DEBORAHNo ratings yet
- Lesson NotesDocument9 pagesLesson NotesMartin NgechuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education PDFDocument44 pagesEnvironmental Education PDFMadhuNo ratings yet
- 464 - Emt 405 NoteDocument43 pages464 - Emt 405 NoteManfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Human ValuesDocument4 pagesSustainability and Human ValuesSoraya Mhae Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ec (Part 1)Document25 pagesUnit 1 Ec (Part 1)Utkarsh bajajNo ratings yet
- 2021 Esm 410 Topic Environmental ManagementDocument11 pages2021 Esm 410 Topic Environmental ManagementEdwardsNo ratings yet
- Evs Unit-I 2Document21 pagesEvs Unit-I 29tytmrx5zjNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies (First Pages)Document9 pagesEnvironmental Studies (First Pages)shaista rafiqueNo ratings yet
- Significance of Environmental ScienceDocument12 pagesSignificance of Environmental ScienceMaliCk TaimoorNo ratings yet
- EVS, NotesDocument81 pagesEVS, NotesANANT AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - Environmental Awareness and ProtectionDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Environmental Awareness and Protectionkella shrimpNo ratings yet
- Environment and Management ReadyDocument175 pagesEnvironment and Management ReadySaid AgouzalNo ratings yet
- Focal and Sub ThemesDocument3 pagesFocal and Sub ThemesbirendrasinghrathiaNo ratings yet
- Environnmental Science Topic 1 5Document7 pagesEnvironnmental Science Topic 1 5Natalie NomorosaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies & Disaster Management: Course InstructorDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Studies & Disaster Management: Course InstructorImtiyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Handout #5 Eco LiteracyDocument3 pagesHandout #5 Eco Literacydionald sichonNo ratings yet
- Evs Ist and 2nd Unit HalfDocument63 pagesEvs Ist and 2nd Unit Half000luci2No ratings yet
- Notes EvsDocument143 pagesNotes EvsAshutosh ThelkarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Lecture 1Document57 pagesUnit - 1 Lecture 1Suneel KumarNo ratings yet
- Let's Take Care of The Ambitious Environmont: Yesica Padilla Yuris Ortega Shirly Peña Yurleys RestrepoDocument17 pagesLet's Take Care of The Ambitious Environmont: Yesica Padilla Yuris Ortega Shirly Peña Yurleys RestrepoyessikNo ratings yet
- Evm RevisionDocument7 pagesEvm Revisionfosejo7119No ratings yet
- Group 5Document24 pagesGroup 5tomaag2000No ratings yet
- NSTP Final ExamDocument43 pagesNSTP Final ExamWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Environmental Protection and Mngt. Isu AngadananDocument9 pagesModule 4 Environmental Protection and Mngt. Isu AngadananWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies - Unit 1 Entire UnitDocument53 pagesEnvironmental Studies - Unit 1 Entire UnitRudyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies Lecture NotesDocument155 pagesEnvironmental Studies Lecture NotesAMOL DIGHENo ratings yet
- Module 1 EnvironmentDocument9 pagesModule 1 EnvironmentVidhyashree YadavNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument6 pagesMultidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesWiz Calvin ManutdNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: A Manual for Assessment PractitionersFrom EverandEcosystems and Human Well-Being: A Manual for Assessment PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Tata Consultancy Services LimitedDocument21 pagesTata Consultancy Services Limitedsanjeev kumar100% (1)
- Circular Economy - Recycling Waste To WealthDocument64 pagesCircular Economy - Recycling Waste To Wealthvipul.gnu2602No ratings yet
- From Malthus To Sustainable Energy-Theoretical Orientations To Reforming The Energy SectorDocument19 pagesFrom Malthus To Sustainable Energy-Theoretical Orientations To Reforming The Energy Sectorraum123No ratings yet
- History of ForestryDocument18 pagesHistory of ForestryShaheryar AliNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Mineral Industry in The Economic Industry in The Economic Development of AfricaDocument29 pagesThe Role of The Mineral Industry in The Economic Industry in The Economic Development of AfricamaxiluuvNo ratings yet
- Natural Resource Management in The Mountain Environment: - Experiences From The Doon Valley, IndiaDocument77 pagesNatural Resource Management in The Mountain Environment: - Experiences From The Doon Valley, Indiasameer AhadNo ratings yet
- (Studyplan) Combined Defense Services CDS - Booklist, Strategy, Free Study Material, Previous Papers, Cutoffs, Physical Medical - Mrunal PDFDocument24 pages(Studyplan) Combined Defense Services CDS - Booklist, Strategy, Free Study Material, Previous Papers, Cutoffs, Physical Medical - Mrunal PDFAnurag VermaNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Project TangaDocument18 pagesMangrove Project TangaKapinga GaudenceNo ratings yet
- Alatish National Park General Management Plan DraftDocument197 pagesAlatish National Park General Management Plan DraftAbeje Zewdie100% (4)
- Chapter 10 - Environmental ScienceDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - Environmental SciencehanashchinalynNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Applied EconomicsDocument23 pages1 Introduction To Applied Economicsivear luarezNo ratings yet
- Natres Pe Benito MidtermsDocument27 pagesNatres Pe Benito MidtermsJay TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Environment Law ProjectDocument31 pagesEnvironment Law ProjectAmulya KaushikNo ratings yet
- Community Resource MappingDocument4 pagesCommunity Resource MappingdineshmarginalNo ratings yet
- 1 Business Studies - XI (Subhash Dey)Document44 pages1 Business Studies - XI (Subhash Dey)priya tiwari100% (1)
- 09 Social Science Key Notes Eco Ch1 People As ResourcesDocument3 pages09 Social Science Key Notes Eco Ch1 People As ResourcesSACHIN TAAK50% (2)
- Ge6351 PDFDocument202 pagesGe6351 PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Project (Unfinished)Document18 pagesSustainability Project (Unfinished)Lavanya SothiNo ratings yet
- Lewis' Industrialization by Invitation Strategy and Resource Based Manufacturing. Steel Production in T&T - B. Tewarie and R. HoseinDocument30 pagesLewis' Industrialization by Invitation Strategy and Resource Based Manufacturing. Steel Production in T&T - B. Tewarie and R. HoseinRachel Rose100% (3)
- 211 SynopsisDocument7 pages211 SynopsisRAJESH MEENANo ratings yet
- Hbsc3203 Chemistry II Full Version Reading BrickDocument324 pagesHbsc3203 Chemistry II Full Version Reading BrickAisyah NazifahNo ratings yet
- EVS Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesEVS Important QuestionsSelvaraj AyyasamyNo ratings yet
- PH.D Research ProposalDocument12 pagesPH.D Research ProposalDr AnwarNo ratings yet
- Seminar SuratDocument10 pagesSeminar Suratharit_ecNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter 1 NotesDocument7 pagesGeography Chapter 1 NotesMkjNo ratings yet
- Draft Tech Report QuarryDocument24 pagesDraft Tech Report QuarryvnilNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Natural ResourcesDocument11 pagesConservation of Natural ResourcesNick ParweenNo ratings yet
- SBGR SampleDocument54 pagesSBGR SampleGeen Abrasado0% (1)
- Plastic Resource Recycling Strategy1Document1 pagePlastic Resource Recycling Strategy1yamakunNo ratings yet
- Market Failure Tutor2uDocument28 pagesMarket Failure Tutor2usharmat1963No ratings yet
Nstp1 Midterm Lesson1
Nstp1 Midterm Lesson1
Uploaded by
Jonnalyn R. Liberato0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesEnvironmental management involves controlling human impact on the environment to preserve natural resources. It deals with the complex interaction between socio-cultural and bio-physical systems at the environment-human interface. Environmental management aims to support sustainable development through a multidisciplinary approach that integrates different perspectives and considers both short and long term impacts. Key areas that require environmental management include population increase, pollution treatment, renewable energy development, biodiversity conservation, and environmental awareness.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEnvironmental management involves controlling human impact on the environment to preserve natural resources. It deals with the complex interaction between socio-cultural and bio-physical systems at the environment-human interface. Environmental management aims to support sustainable development through a multidisciplinary approach that integrates different perspectives and considers both short and long term impacts. Key areas that require environmental management include population increase, pollution treatment, renewable energy development, biodiversity conservation, and environmental awareness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesNstp1 Midterm Lesson1
Nstp1 Midterm Lesson1
Uploaded by
Jonnalyn R. LiberatoEnvironmental management involves controlling human impact on the environment to preserve natural resources. It deals with the complex interaction between socio-cultural and bio-physical systems at the environment-human interface. Environmental management aims to support sustainable development through a multidisciplinary approach that integrates different perspectives and considers both short and long term impacts. Key areas that require environmental management include population increase, pollution treatment, renewable energy development, biodiversity conservation, and environmental awareness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
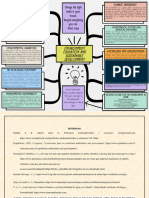
NSTP1 LESSON #01 WHAT IS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION -Environmental management is concerned with the man environmental
“ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AND MANAGEMENT” interface, the complex boundary where bio-physical and socio cultural
systems interact (Hare, 1970).
ENVIRONMENT -An approach which goes beyond natural resource management,
-All the living and nonliving factors affecting an organism and to encompass the political and social as well as the natural
environment (Clarke, 1999).
ultimately determining its form and survival.
-It is an attempt to control human impact on and the interaction with
-All external factors influencing the life and activity of people, plants
the environment in order to preserve natural resources.
and animals.
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION - At the global scale and in the broadest sense, environmental
According to UNESCO: management
“Environmental education is a learning process that increases people’s involves the
knowledge and awareness about the environment and associated * Oceans
challenges, develops the necessary skills and expertise to address the * Fresh water systems
challenges, and fosters attitudes, motivations and commitments to * Land and
make informed decisions and take responsible actions.” * Atmosphere
But following the sustainability principle of scale it can be equally
GOALS OF ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION applied to any ecosystem from a tropical forest to a home garden.
-To improve the quality of environment.
-To create awareness among the people on environmental problems CHARACTERISTIC OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
and conservation. 1. It deals with world affected by humans;
-To create an atmosphere so that people participate in decision- 2. It supports sustainable development
making and develop the capabilities to evaluate the developmental 3. It demands a multidisciplinary approach;
programs. 4. It has to integrate different development view points;
5. The time-scale involved extends the short term and concern ranges
THE COMPONENTS OF ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION ARE: from
1.Awareness – Awareness about environment and its problem. local to global;
2.Knowledge – Basic knowledge about environment. 6. It seeks to integrate natural & social science, policy making and
3.Attitude – a sense of responsibility towards the environment. planning
4.Skills – Skills to solve environmental problems. This Environmental management implies an element of conscious
5.Participation – Participate in programs related to environmental. choice from a variety of alternative proposals and furthermore that
such a choice
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION involves purposeful commitment for recognized and desired
- Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural objectives.
environment by individuals, organizations and governments, for the
benefits of both the natural environment and humans. AREAS THAT NEED ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
-Population increase and health services
-Treatment of pollutants (air, water, and solid) generated from various
sources CONCEPT OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
-Pollution level in air and soil -Is a pattern of resource use, that aims to meet human needs while
-Development of non-polluting renewable energy sources like wind, preserving the environment so that these needs can be met not only in
solar, biomass etc. the present, but also for generations to come.
-Solid waste utilization through recycling -The development initiatives be initiated in such a way that the future
-Biodiversity conservation generations
-Environmental awareness in society can enjoy the benefits of Nature without any compromise.
-Sustainable development is a development that meet the needs of the
SIGNIFICANCE OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT present
-Environmental Management is an approach which integrates without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their
Ecology, Policy making, Planning and Social development. own needs
Its main objectives are as follows:
a. To prevent and solve environmental problems. LESSON #02
b. To establish limits PRINCIPLES OF ENVIRONMENT AND ENVIRONMENTAL
c. To develop research institutions and monitoring systems. LAWS
d. To warn threats and identify opportunities.
e. To suggest measures for resource conservation. PRINCIPLES OF ENVIRONMENT
f. To develop a strategy for the improvement of quality. 1. NATURE KNOWS BEST
g. To suggest long-term and short-term policies for sustainable -This principle is the most basic and, in fact, encompasses all the
development. others. In essence people must not go against the natural process if
h. To identify new technology for future development they would like to ensure a continuous and steady supply of resources.
In nature, nutrients pass from the environment to the organism and
CONCEPT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT back to the environment. Any disruption in the cycle can bring about
-It’s an attempt to control human impact on and interaction with the imbalance.
environment in order to preserve natural resources 2. ALL FORMS OF LIFE ARE IMPORTANT
-Environmental management focuses on the improvement of human -Each organism plays a fundamental role in nature. All living things
welfare for present and future generations. must be considered valuable in the maintenance of stability in an
-Administrative functions that develop, implement, and monitor the ecosystem. It is easy to appreciate the beautiful butterflies especially
environmental knowing their important role in pollination.
policy of an organization. 3. EVERYTHING IS CONNECTED TO EVERYTHING ELSE
-Environmental management implies not only a mere management of -In an ecosystem, all components interact with each other to ensure
environment the system is continued. Any outside interference may result in an
but it is essentially the management of various activities with imbalance. Deforestation in the mountains may affect the lowlands,
intolerable constraints imposed by the environment itself and with full resulting in floods, drought, or erosion. What happens in one country
consideration of ecological factors. may even affect other countries.
-Thus it involves environmental planning, conservation of resources, 4. EVERYTHING CHANGES
environmental -The only permanent thing is change. Change may be linear, cyclical,
status evaluation and environmental legislation and administration.
or random. An example of linear change is the evolution of a species. yet human activities often change the environment and destroy or
Cyclical changes is the eruption of a volcano, like Mt. Pinatubo damage natural resources. Sustainable development strives for human
bringing great upheaval in many parts of Luzon progress without threatening the environment.
5. EVERYTHING MUST GO SOMEWHERE
-When a piece of paper is thrown away, it disappears from sight ENVIRONMENTAL LAWS
but it does not cease to exist. It simply goes somewhere else. Wastes
can either be pollutants or resources. We need to change or "throw- REPUBLIC ACT 9003
away" society attitude in order to develop better methods of waste ECOLOGICAL SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT ACT of 2000
management and recycling. -Provides the legal framework for the country’s systematic,
6. OURS IS A FINITE EARTH comprehensive and ecological solid waste management program that
-The earth's resources can be classified as either renewable or shall ensure protection of public health and the environment. It
nonrenewable. Renewable resources, like water, air, plants, underscores, among other things, the need to create the necessary
and animals, can easily be replenished by natural cycles. institutional mechanisms and incentives, as well as imposes penalties
Nonrenewable resources, like minerals, oil, and coal cannot for acts in violation of any of its provisions.
be replenished through natural cycles. Awareness of the
earth's limited resources should lead to a conscious effort to REPUBLIC ACT NO. 9729
change one’s attitude as a consumer. CLIMATE CHANGE ACT OF 2009
7. NATURE IS BEAUTIFUL AND WE ARE STEWARDS OF
GOD’S CREATION An act mainstreaming climate change into
-This principle is inherent in most religious and tribal beliefs. government policy formulations, establishing the
Teachings of Christianity, Buddhism, and Islam enjoin everyone to framework strategy and program on climate
respect all life and order of nature. This law also tells us that there are change, creating for this purpose the climate
limits to the population that an area can support to prevent exhaustion change commission and for other purposes.
of resources, limits to the amount of yield that an area can produce at a REPUBLIC ACT 9275
particular time to maintain its ability to sustain life. PHILIPPINE CLEAN WATER ACT OF 2004
8. THE AMOUNT OF LIFE NATURE CAN SUPPORT IS LIMITED
-Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals of a given The law aims to protect the country's water bodies from
species which can be supported by a particular habitat or ecosystem pollution from land-based sources (industries and commercial
without damaging it. For example, a typical Filipino bahay kubo can establishments, agriculture and community/household
only support a limited number of family members; the presence of too activities). It provides for comprehensive and integrated
many residents results in overcrowding. Therefore, nature has its own
processes or mechanisms to regulate the population of a species within strategy to prevent and minimize pollution through a multi-
or environment. sectoral and participatory approach involving all the
9. HUMAN PROGRESS MUST CONSIDER ITS EFFECT ON
NATURE stakeholders.
-Sustainable development meets the needs of the present without REPUBLIC ACT 8749
comprising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. PHILIPPINE CLEAN AIR ACT OF 1999
Development is viewed as essential in improving the quality of human
life, Polluter’s must pay. This is the principle
behind this act.
The law aims to achieve and maintain
clean air that meets the National Air Quality
guideline values for criteria pollutants,
throughout the Philippines, while minimizing
the possible associated impacts to the
economy.
You might also like
- Environmental Protection and ManagementDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Protection and ManagementZaymonne Kent LaugoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Protection and ManagementDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Protection and Managementqwerty asdfgNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Scienceprincess.pinedaNo ratings yet
- EDUC. 242 Part III - Environmental ManagementDocument5 pagesEDUC. 242 Part III - Environmental ManagementJoseph Ryan MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Nstp-Cwts Module 5Document10 pagesNstp-Cwts Module 5JUAN VICTOR MACADANGDANGNo ratings yet
- 1environmental ManagementDocument53 pages1environmental ManagementLileth Lastra QuiridoNo ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewerDocument5 pagesNSTP Revieweraceyodo000No ratings yet
- PTEN551 Lecture 97 ShowDocument49 pagesPTEN551 Lecture 97 ShowGeorge BlakeNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Environmental Ethics (English Ver)Document15 pagesTopic 5 Environmental Ethics (English Ver)nuzul hanisNo ratings yet
- Evs Notes 2Document90 pagesEvs Notes 2Ashok Kumar100% (1)
- Envi Sci Reviewer 1Document7 pagesEnvi Sci Reviewer 1Abegail Neo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Prelim Environmental EnggDocument16 pagesPrelim Environmental EnggAs ReNo ratings yet
- Unit - I: Introduction To Environmental Studies and EcosystemDocument79 pagesUnit - I: Introduction To Environmental Studies and EcosystemDina GaranNo ratings yet
- Module 6: Environmental Resource Protection and Management: Week 9Document38 pagesModule 6: Environmental Resource Protection and Management: Week 9Alyssa Joanna LlorinNo ratings yet
- EED 4118 Lesson 2Document11 pagesEED 4118 Lesson 2KevinNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Environmental MGT StudentsDocument8 pagesModule 4 Environmental MGT StudentsIan Cadauan Baquiran100% (1)
- Environment Management PortfolioDocument5 pagesEnvironment Management PortfolioMichelle DupioNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Through Environmental Ethics: S RajalakshmiDocument4 pagesSustainable Development Through Environmental Ethics: S RajalakshmiMAHANTESH GNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument8 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Environmental ScienceGlycel SaldiviaNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument3 pagesMapa ConceptualFelipe Gutierrez MachadoNo ratings yet
- All Topics Evs Covered Bba FTDocument26 pagesAll Topics Evs Covered Bba FTAxiiNo ratings yet
- Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technology Mati CityDocument13 pagesDavao Oriental State College of Science and Technology Mati CityHeartyAquinoBasocNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument17 pages1 IntroductionAuto NomousNo ratings yet
- Environmental Ethics and Gandhian Approach: Module - 7Document11 pagesEnvironmental Ethics and Gandhian Approach: Module - 7chandra_53754271No ratings yet
- People and Earths EcosystemDocument4 pagesPeople and Earths EcosystemJolina T. OrongNo ratings yet
- Ema 111Document5 pagesEma 111bulukuian50% (1)
- National Environmental Policy and StrategiesDocument18 pagesNational Environmental Policy and StrategiesAyushi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 .... Importance of Environmental ProtectionDocument15 pagesModule 1 .... Importance of Environmental ProtectionEUNICE CIELO MARIE LIMNo ratings yet
- NSTP SemisDocument52 pagesNSTP SemishiimleoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Scope & ImportanceDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Scope & ImportanceNANCY DEBORAHNo ratings yet
- Lesson NotesDocument9 pagesLesson NotesMartin NgechuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Education PDFDocument44 pagesEnvironmental Education PDFMadhuNo ratings yet
- 464 - Emt 405 NoteDocument43 pages464 - Emt 405 NoteManfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Human ValuesDocument4 pagesSustainability and Human ValuesSoraya Mhae Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ec (Part 1)Document25 pagesUnit 1 Ec (Part 1)Utkarsh bajajNo ratings yet
- 2021 Esm 410 Topic Environmental ManagementDocument11 pages2021 Esm 410 Topic Environmental ManagementEdwardsNo ratings yet
- Evs Unit-I 2Document21 pagesEvs Unit-I 29tytmrx5zjNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies (First Pages)Document9 pagesEnvironmental Studies (First Pages)shaista rafiqueNo ratings yet
- Significance of Environmental ScienceDocument12 pagesSignificance of Environmental ScienceMaliCk TaimoorNo ratings yet
- EVS, NotesDocument81 pagesEVS, NotesANANT AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - Environmental Awareness and ProtectionDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 5 - Environmental Awareness and Protectionkella shrimpNo ratings yet
- Environment and Management ReadyDocument175 pagesEnvironment and Management ReadySaid AgouzalNo ratings yet
- Focal and Sub ThemesDocument3 pagesFocal and Sub ThemesbirendrasinghrathiaNo ratings yet
- Environnmental Science Topic 1 5Document7 pagesEnvironnmental Science Topic 1 5Natalie NomorosaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies & Disaster Management: Course InstructorDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Studies & Disaster Management: Course InstructorImtiyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Handout #5 Eco LiteracyDocument3 pagesHandout #5 Eco Literacydionald sichonNo ratings yet
- Evs Ist and 2nd Unit HalfDocument63 pagesEvs Ist and 2nd Unit Half000luci2No ratings yet
- Notes EvsDocument143 pagesNotes EvsAshutosh ThelkarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Lecture 1Document57 pagesUnit - 1 Lecture 1Suneel KumarNo ratings yet
- Let's Take Care of The Ambitious Environmont: Yesica Padilla Yuris Ortega Shirly Peña Yurleys RestrepoDocument17 pagesLet's Take Care of The Ambitious Environmont: Yesica Padilla Yuris Ortega Shirly Peña Yurleys RestrepoyessikNo ratings yet
- Evm RevisionDocument7 pagesEvm Revisionfosejo7119No ratings yet
- Group 5Document24 pagesGroup 5tomaag2000No ratings yet
- NSTP Final ExamDocument43 pagesNSTP Final ExamWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Environmental Protection and Mngt. Isu AngadananDocument9 pagesModule 4 Environmental Protection and Mngt. Isu AngadananWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies - Unit 1 Entire UnitDocument53 pagesEnvironmental Studies - Unit 1 Entire UnitRudyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies Lecture NotesDocument155 pagesEnvironmental Studies Lecture NotesAMOL DIGHENo ratings yet
- Module 1 EnvironmentDocument9 pagesModule 1 EnvironmentVidhyashree YadavNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument6 pagesMultidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesWiz Calvin ManutdNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: A Manual for Assessment PractitionersFrom EverandEcosystems and Human Well-Being: A Manual for Assessment PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Tata Consultancy Services LimitedDocument21 pagesTata Consultancy Services Limitedsanjeev kumar100% (1)
- Circular Economy - Recycling Waste To WealthDocument64 pagesCircular Economy - Recycling Waste To Wealthvipul.gnu2602No ratings yet
- From Malthus To Sustainable Energy-Theoretical Orientations To Reforming The Energy SectorDocument19 pagesFrom Malthus To Sustainable Energy-Theoretical Orientations To Reforming The Energy Sectorraum123No ratings yet
- History of ForestryDocument18 pagesHistory of ForestryShaheryar AliNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Mineral Industry in The Economic Industry in The Economic Development of AfricaDocument29 pagesThe Role of The Mineral Industry in The Economic Industry in The Economic Development of AfricamaxiluuvNo ratings yet
- Natural Resource Management in The Mountain Environment: - Experiences From The Doon Valley, IndiaDocument77 pagesNatural Resource Management in The Mountain Environment: - Experiences From The Doon Valley, Indiasameer AhadNo ratings yet
- (Studyplan) Combined Defense Services CDS - Booklist, Strategy, Free Study Material, Previous Papers, Cutoffs, Physical Medical - Mrunal PDFDocument24 pages(Studyplan) Combined Defense Services CDS - Booklist, Strategy, Free Study Material, Previous Papers, Cutoffs, Physical Medical - Mrunal PDFAnurag VermaNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Project TangaDocument18 pagesMangrove Project TangaKapinga GaudenceNo ratings yet
- Alatish National Park General Management Plan DraftDocument197 pagesAlatish National Park General Management Plan DraftAbeje Zewdie100% (4)
- Chapter 10 - Environmental ScienceDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - Environmental SciencehanashchinalynNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Applied EconomicsDocument23 pages1 Introduction To Applied Economicsivear luarezNo ratings yet
- Natres Pe Benito MidtermsDocument27 pagesNatres Pe Benito MidtermsJay TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Environment Law ProjectDocument31 pagesEnvironment Law ProjectAmulya KaushikNo ratings yet
- Community Resource MappingDocument4 pagesCommunity Resource MappingdineshmarginalNo ratings yet
- 1 Business Studies - XI (Subhash Dey)Document44 pages1 Business Studies - XI (Subhash Dey)priya tiwari100% (1)
- 09 Social Science Key Notes Eco Ch1 People As ResourcesDocument3 pages09 Social Science Key Notes Eco Ch1 People As ResourcesSACHIN TAAK50% (2)
- Ge6351 PDFDocument202 pagesGe6351 PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Project (Unfinished)Document18 pagesSustainability Project (Unfinished)Lavanya SothiNo ratings yet
- Lewis' Industrialization by Invitation Strategy and Resource Based Manufacturing. Steel Production in T&T - B. Tewarie and R. HoseinDocument30 pagesLewis' Industrialization by Invitation Strategy and Resource Based Manufacturing. Steel Production in T&T - B. Tewarie and R. HoseinRachel Rose100% (3)
- 211 SynopsisDocument7 pages211 SynopsisRAJESH MEENANo ratings yet
- Hbsc3203 Chemistry II Full Version Reading BrickDocument324 pagesHbsc3203 Chemistry II Full Version Reading BrickAisyah NazifahNo ratings yet
- EVS Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesEVS Important QuestionsSelvaraj AyyasamyNo ratings yet
- PH.D Research ProposalDocument12 pagesPH.D Research ProposalDr AnwarNo ratings yet
- Seminar SuratDocument10 pagesSeminar Suratharit_ecNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter 1 NotesDocument7 pagesGeography Chapter 1 NotesMkjNo ratings yet
- Draft Tech Report QuarryDocument24 pagesDraft Tech Report QuarryvnilNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Natural ResourcesDocument11 pagesConservation of Natural ResourcesNick ParweenNo ratings yet
- SBGR SampleDocument54 pagesSBGR SampleGeen Abrasado0% (1)
- Plastic Resource Recycling Strategy1Document1 pagePlastic Resource Recycling Strategy1yamakunNo ratings yet
- Market Failure Tutor2uDocument28 pagesMarket Failure Tutor2usharmat1963No ratings yet