Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stomach Cancer Concept Map
Stomach Cancer Concept Map
Uploaded by
NikkaDablioCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Utrecht Gender Dysphoria Scale PDFDocument16 pagesUtrecht Gender Dysphoria Scale PDFTherese EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Obesity Research PaperDocument10 pagesObesity Research PaperPaige-Hill88% (16)
- Syndromic Gastric PolypsDocument15 pagesSyndromic Gastric PolypsTheDrakairNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On Renal FailureDocument1 pageConcept Map On Renal FailureJessilda Damian VeranoNo ratings yet
- The Social Dilemma ReviewDocument5 pagesThe Social Dilemma ReviewNikkaDablio100% (1)
- Health and Fitness in Senior Years: Group MembersDocument35 pagesHealth and Fitness in Senior Years: Group MembersSiti Halimatus Saadiah100% (1)
- 0304 ConsultantoncallDocument4 pages0304 Consultantoncallnessimmounir1173No ratings yet
- Lacpacan Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLacpacan Breast Cancer Concept MapRIZI LACPACANNo ratings yet
- Group D Members:: Kidney Liver PancreasDocument1 pageGroup D Members:: Kidney Liver PancreasCourtney KateNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Document13 pagesPediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Isabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Genome Poster 2009Document1 pageGenome Poster 2009ISAAC LEWNo ratings yet
- Gems Opt Select Brochure 2021 v6 3Document2 pagesGems Opt Select Brochure 2021 v6 3Bongani West VuthaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Amoeba - SarcodinaDocument14 pagesWeek 3 - Amoeba - SarcodinaShine CalarananNo ratings yet
- 5sample - Gastrointestinal System Notes - 3rd Ed OptimizedDocument28 pages5sample - Gastrointestinal System Notes - 3rd Ed OptimizedAlexis Tobar100% (2)
- GDM PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesGDM PathophysiologyShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- HZ SummaryDocument1 pageHZ SummaryPratzNo ratings yet
- All Charts Final Exam 1 PDFDocument294 pagesAll Charts Final Exam 1 PDFYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Azathioprine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAzathioprine Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado100% (1)
- Gynaecology Revision PDFDocument13 pagesGynaecology Revision PDFAadhi AadhiNo ratings yet
- DRUGDocument4 pagesDRUGPINKI DEBNo ratings yet
- Tables ProtozoaDocument14 pagesTables ProtozoaJanette Monica BarriosNo ratings yet
- Poster Caitlin BrennanDocument1 pagePoster Caitlin Brennansagun maharjanNo ratings yet
- Medical Prefixes and SuffixesDocument12 pagesMedical Prefixes and SuffixesKrishnanunni KLNo ratings yet
- Severe: Severe Persis4ng Symptoms of One or More Of: Gastrointes Nal SkinDocument2 pagesSevere: Severe Persis4ng Symptoms of One or More Of: Gastrointes Nal SkinSanjuy GarzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5ozmanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesWeek 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Colorect: Patient's Name: F.V Age: 64 Years OldDocument3 pagesColorect: Patient's Name: F.V Age: 64 Years OldGenynne Ragasa100% (1)
- Biowords v2Document3 pagesBiowords v2Hiezeyl Ymana GuntangNo ratings yet
- Drug To Xi CitiesDocument1 pageDrug To Xi CitiesGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Trematodes ScheduleDocument1 pageTrematodes ScheduleDr-positive EnergyNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea-Vomiting Pathway-Primary Care MAY 2015Document2 pagesDiarrhoea-Vomiting Pathway-Primary Care MAY 2015nimraNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13Document6 pages2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13A HNo ratings yet
- Viii. PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesViii. Pathophysiologymacedon145377No ratings yet
- Chapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney DisordersDocument40 pagesChapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abdominal PainDocument4 pagesApproach To Abdominal PainShamen KohNo ratings yet
- HISTORY & EXAMINATION Edited 228Document11 pagesHISTORY & EXAMINATION Edited 228Saurabh LamkhadeNo ratings yet
- 01 Sick Bird SyndromeDocument1 page01 Sick Bird SyndromeAli BakNo ratings yet
- MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3Document1 pageMUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3MICHELLIN VAN MUGOTNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal DisordersJerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- T2 DM Seizure 1Document1 pageT2 DM Seizure 1Mika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism Care MapDocument1 pageHypoparathyroidism Care MapDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Ashap Medical Terminology Chapter 1Document1 pageAshap Medical Terminology Chapter 1Lorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- Legend: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageLegend: PathophysiologyMikhail LamayoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm 2: Diarrhea: Signalment/History/Exam Polyuria DiarrheaDocument1 pageAlgorithm 2: Diarrhea: Signalment/History/Exam Polyuria DiarrheaAli BakNo ratings yet
- NUR 3032 Pancreatic, Biliary, and Hepatic Disorders Study PlanDocument6 pagesNUR 3032 Pancreatic, Biliary, and Hepatic Disorders Study PlanThalia FortuneNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Document32 pagesBacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument4 pagesDrug Study FormRhea LaplanaNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0923753419544970Document6 pagesPi Is 0923753419544970AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis Aguda Guías ClínicasDocument1 pagePancreatitis Aguda Guías Clínicaslbritez7No ratings yet
- DRUG - NDocument1 pageDRUG - NaizatiangcoNo ratings yet
- A3 Plant KingdomDocument1 pageA3 Plant KingdomMeenakshi VermaNo ratings yet
- Skema AnalisaDocument2 pagesSkema AnalisaAhmad MukhlisNo ratings yet
- Histopathological Features in Anemia DisordersDocument1 pageHistopathological Features in Anemia Disorderskoki74No ratings yet
- Drug Study Camillus MabiniDocument5 pagesDrug Study Camillus MabiniJonh Carlo LopezNo ratings yet
- Parasites High YoieldDocument4 pagesParasites High Yoieldnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Animals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)Document5 pagesAnimals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)krisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- NoteDocument9 pagesNote65O6O78 ฐิติพันธ์ เพชรกระจายแสงNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMuhammad Jefri LukmanNo ratings yet
- PGI Reyes StomachDocument124 pagesPGI Reyes StomachMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- AmebasDocument3 pagesAmebasNaomi NicoleNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology 1: - Non MotileDocument27 pagesBacteriology 1: - Non MotileYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- En DoDocument2 pagesEn Dofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesDocument11 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- OB WorkbookDocument13 pagesOB WorkbookNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Theories of AgingDocument4 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Theories of AgingNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- TFN - BennerDocument1 pageTFN - BennerNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Physiologic ChangesDocument25 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Physiologic ChangesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patients With Pneumonia and Pulmonary EmbolismDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patients With Pneumonia and Pulmonary EmbolismNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- 19th Century RizalDocument2 pages19th Century RizalNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument27 pagesPsoriasisNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Sihay - Ang Silid NG BuhayDocument5 pagesSihay - Ang Silid NG BuhayNikkaDablio100% (1)
- Nikka Dablio - ACTIVITY 1 The Paradox of Our TimeDocument1 pageNikka Dablio - ACTIVITY 1 The Paradox of Our TimeNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University: Department of BiologyDocument4 pagesCentral Mindanao University: Department of BiologyNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Datasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersDocument14 pagesDatasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Map of Region IIIDocument8 pagesMap of Region IIINikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabia Written ReportDocument3 pagesSaudi Arabia Written ReportNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Patterns of StrugglesDocument2 pagesPatterns of StrugglesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Vijaya DiagnosticsDocument3 pagesVijaya DiagnosticssampathNo ratings yet
- Women The Skilled Architect of The SocietyDocument4 pagesWomen The Skilled Architect of The SocietyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Space Closure Using Simple Mechanics in Compromised First Molar Extraction Spaces: Case SeriesDocument9 pagesOrthodontic Space Closure Using Simple Mechanics in Compromised First Molar Extraction Spaces: Case SeriesHabeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- 2048 Wal LA Clarification Deficiency CA FSHC PKTDocument7 pages2048 Wal LA Clarification Deficiency CA FSHC PKTJuliana GallardoNo ratings yet
- Resume of DR Pramod Nanda - Manager in Health Care Professional 2021Document10 pagesResume of DR Pramod Nanda - Manager in Health Care Professional 2021Dr Pramod NandaNo ratings yet
- The Paediatric Voice Clinic: Ian Smillie, Kirsy Mcmanus, Wendy Cohen, Elizabeth Lawson, David Macgregor WynneDocument5 pagesThe Paediatric Voice Clinic: Ian Smillie, Kirsy Mcmanus, Wendy Cohen, Elizabeth Lawson, David Macgregor WynneCarolina UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Pilar College of Zamboanga City, IncDocument14 pagesPilar College of Zamboanga City, IncIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Alternative FeedingDocument36 pagesAlternative FeedingEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- History of MedicineDocument24 pagesHistory of MedicineРоман КравецьNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip Palate TherapyDocument5 pagesCleft Lip Palate TherapyNathalieCaracaNo ratings yet
- English Project 2Document34 pagesEnglish Project 2HARSHNo ratings yet
- OralcholecystographyDocument13 pagesOralcholecystographySuman PokhrelNo ratings yet
- FS Nicotine Mouth SprayDocument11 pagesFS Nicotine Mouth SprayAdnan DugonjicNo ratings yet
- 06 AQU347 Course Notes Chapter 1Document13 pages06 AQU347 Course Notes Chapter 1Nurul Syafiqah Binti ShaidanNo ratings yet
- PDF Hypertension A Companion To Braunwalds Heart Disease 3Rd Edition George L Bakris Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Hypertension A Companion To Braunwalds Heart Disease 3Rd Edition George L Bakris Ebook Full Chapteriris.russell843100% (3)
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeDocument35 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeTiffany Jane Huertas100% (1)
- 2021 Examining The Black U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate and How ToDocument2 pages2021 Examining The Black U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate and How ToCece JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ab Omas A L Ulceration Andtympanyofcalves: Tessa S. MarshallDocument12 pagesAb Omas A L Ulceration Andtympanyofcalves: Tessa S. Marshallana lauraNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Complications and Prognosis LastDocument42 pagesBreast Cancer Complications and Prognosis Lastalalmaee1No ratings yet
- Spinal ShockDocument82 pagesSpinal ShockPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- Big Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseDocument7 pagesBig Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseHernán GiménezNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology CH 8Document139 pagesMedical Terminology CH 8ياسين المسطوNo ratings yet
- DEVPSY Reviewer - Chapters 1-6Document17 pagesDEVPSY Reviewer - Chapters 1-6Charmaine FloresNo ratings yet
- Development and Testing of ATime Resolved Personal Ozone MonitorDocument80 pagesDevelopment and Testing of ATime Resolved Personal Ozone MonitorJijo SagaiNo ratings yet
- A Study On Work From Home, Motivation & Productivity of Employees in Indian Population During COVID-19 PandemicDocument15 pagesA Study On Work From Home, Motivation & Productivity of Employees in Indian Population During COVID-19 Pandemicمعن الفاعوريNo ratings yet
- Laporan Bulanan Pasien CT - Scan 2016Document165 pagesLaporan Bulanan Pasien CT - Scan 2016Fera NurrizaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing Must Knows by Dr. Chris G. SorongonDocument2 pagesOncology Nursing Must Knows by Dr. Chris G. SorongonAleandro DizonNo ratings yet
Stomach Cancer Concept Map
Stomach Cancer Concept Map
Uploaded by
NikkaDablioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stomach Cancer Concept Map
Stomach Cancer Concept Map
Uploaded by
NikkaDablioCopyright:
Available Formats
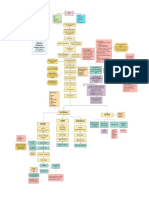
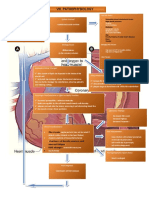
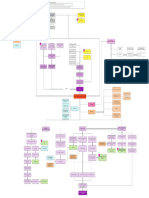
STOMACH CA
A disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach
Nomal gastric mucosa
- Age - Median age 70
- Helicobacter pylori infection
- Sex - 2:1 Male: Female Acquisition of - Chronic gastritis (Atrophic type)
- Family History Helicobacter pylori - Hypochlahydria
- Blood type A group - Intestinal metaplasia
- Pernicious Anemia - Smoking & Alcohol Abuse
- Genomic Instability - Obesity
- Genetic Defect of CDH1 gene - Dietary Factors (Pickled/ Cured/ Processed)
- Hereditary Non-polyposis Colorectal Cancer (HPCC) - Occupational Exposure
- Familial gastric carcinoma syndrome - Low socioeconomic status
Asymptomatic Symptomatic
acquisition acquisition
- Stool antigen test
- Stool PCR test
- Urea breath test
- Upper endoscopy exam
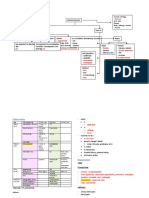
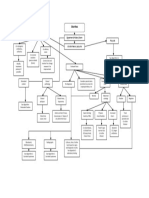
Familial Sporadic Smoking and Alcohol Chronic H. pylori Infection
Higly Salted Foods (Accounts 80% of Gastric
Consumption
Cancer)
Loss of function mutation in Induces hypergastrinemia & Increase production of Ache or burning pain in
Sporadic Diffuse Type Sporadic Intestinal Type Chronic inflamation of gastric your stomach (abdomen),
the tumour suppressor gene endogenous mutations protaglandins that maintain
CHD1 gastric mucosal integrity mucusa Nausea, Bloating
Preventions of
Gastric Cancer Loss of E-Cadherin
Loss of function Gain of function mutation in the Promotes epithelial cell Irritates the Atrophic Gastritis - Proton pump inhibitors
mutation of APC gene gene encoding B-Catenin proliferation stomach lining - Bismuth subsalicylate
Loss of function - Histamine (h-2) blockers
Codes cell adhesion mutation in tumor
protein E-Cadherin supressor gene CDH1 Favours bacterial growth and Severe stomach
Dietary Modifictions continuation of chronic (abdominal pain) & Bloody
inflamation Headache
Screening & Eradication of and black tarry stools
Rash
H. pylori infection Increases H. pylori
Increase signaling via Dizziness
Wnt pathway colonization
Nausea
- Reduce intake of salt & salted foods Hypermethylation Silencing of CDH1 promoter Loss of appropriate glands Flatulence
- Avoid food that containes high nitrate (Mucosal atrophy) Constipation
level Mutation of TP53 Diarrhea
- Reduce intake of red meat
- Increase intake of fruits and
vegetables Decreases E-Cadherin
Loss of function - Physical exam and health history Transformation of the cells in the
expression
mutation in BAX gene & - Blood chemistry studies lining of upper digestive tract
CDKN2A - Complete blood count
- Upper endoscopy
BRCA2 Mutations
- Barium swallow Acute Pain
- CT Scan
Presence of abnormal cells within
- Biopsy
the tissues of the stomach.
- Assess characteristics of pain and
discomfort ; location, quality,
frequency, duration, etc.
GASTRIC CANCER - Reassure the patient that you
know, the pain is real and that you
will assist the patient in reducing
the pain.
- Collaboration in analgesic
administration to improve
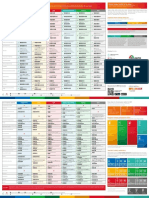
The cancer has grown into the The cancer has grown into the The cancer has grown through all The cancer of any size that has circulation within the optimal pain
Cancer is found only on the inner layer of the wall of the outer muscular layers of the wall of of the layers of the muscle into the spread to distant parts of the body prescription.
surface of the epithelium stomach the stomach connective tissue outside the in addition to the area around the - Teach the patient new strategies to
stomach and has grown into stomach relieve pain and discomfort with
nearby organs or structures. distraction, imagination, relaxation.
The cancer has not grown into any The cancer has grown through all
It has not spread to any lymph It has spread to 1 to 2 lymph
other layers of the stomach nodes or other organs nodes but not elsewhere of the layers of the muscle into the
connective tissue outside the
It may or may not have spread to 1 It has spread to 7 or more lymph
stomach It has not spread to any lymph
to 6 lymph nodes but not to distant nodes but not to other parts of the Stage IV
nodes or distant parts of the body body
Stage 0 parts of the body
Stage IA Stage IB
It has not grown into the peritoneal It has not grown into the peritoneal
lining or serosa. It has spread to 1 to 2 Stage IIIA Stage IIIB Stage IIIC
- Surgery (total or subtotal lining or serosa or spread to any lymph
nodes or surrounding organs lymph nodes but not elsewhere
gastrectomy)
- Endoscopic mucosal resection - Third-line palliative therapy
- Surgery (total or subtotal gastrectomy) - First-line palliative therapy - Second-line palliative (radiation therapy) with
- Endoscopic mucosal resection Stage IIA Stage IIB includes immunotherapy therapy includes: chemotherapy drugs
- Chemotherapy combined with chemotherapy: - Chemotherapy. - Endoluminal laser therapy
- Chemoradiation therapy - Chemotherapy drugs - Chemotherapy Drugs or endoluminal stent
- A clinical trial of chemoradiation therapy
- Surgery (total or subtotal gastrectomy)
- Endoscopic mucosal resection
- Chemotherapy
- Chemoradiation therapy
- A clinical trial of chemoradiation therapy
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Early Stages Advanced Stages
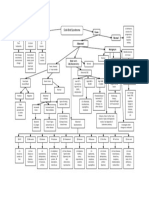
Cancer cells irritate the lining of The cancer can cause blockage in The cancer tends to Chemotherapy may alter
Chemotherapy and radiation to Tumor bleeding occurs The cancer cells spreads Swelling in the
the abdomen the stomach suppress appetite the normal bacterial flora
chest or upper abdomen to the liver organ oesophagus after surgery
that is present in the
intestines
Stops food from passing through Release hormones that Feces turns darker -
Lymph glands in the abdomen get may distort body's
Increased production of stomach the digestive system almost black Longer to chew and swallow, coughing
blocked and can't drain fluid perception of hunger Liver cells are damaged
acid Affects the digestion or choking while eating or drinking, or
properly
food sticking in your mouth or throat
Nausea Blood in the stool like a ball.
Indigestion and stomach
Unintentional weight loss
discomfort Buildup of fluid (ascites) in Stomach Pain Bilirubin level in the blood
the abdomen then increases
Dysphagia
Bloated Jaundice
Chemotherapy Drugs
- Surgery (total or subtotal gastrectomy) - Oxaliplatin plus 5-FU/leucovorin (FOLFOX), or
- Endoscopic mucosal resection Chemotherapy Drugs
oxaliplatin plus capecitabine (CAPOX) - Oxaliplatin plus 5-FU/leucovorin (FOLFOX), or
- Chemotherapy - FLOT (5-FU/leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel) - Third-line palliative therapy oxaliplatin plus capecitabine (CAPOX)
- Chemoradiation therapy - Physical exam and health history - First-line palliative therapy - Second-line palliative
- Docetaxel or paclitaxel plus either 5-FU or (radiation therapy) with - Cisplatin plus either 5-FU or capecitabine
- A clinical trial of chemoradiation therapy - Blood chemistry studies capecitabine includes immunotherapy therapy includes:
- Complete blood count chemotherapy drugs - Irinotecan plus 5-FU/leucovorin (FOLFIRI)
- Cisplatin plus either 5-FU or capecitabine combined with chemotherapy: - Chemotherapy. - Endoluminal laser therapy - Physical exam and health history
- Upper endoscopy - Paclitaxel plus either cisplatin or carboplatin
- Paclitaxel and carboplatin - Chemotherapy drugs - Chemotherapy Drugs or endoluminal stent - Blood chemistry studies
- Barium swallow - Docetaxel plus cisplatin
- Complete blood count
- CT Scan - Epirubicin, either cisplatin or oxaliplatin, and either
- Upper endoscopy
- Biopsy 5-FU or capecitabine
- Barium swallow
- Docetaxel, 5-FU, and either cisplatin, carboplatin, or
- CT Scan
oxaliplatin
- Tiredness - Biopsy
- Feeling and being sick
- Hair loss
- Infections - Tiredness
- Anaemia - Feeling and being sick
- Bruising and bleeding - Hair loss
- Sore mouth - Infections
- Loss of appetite - Anaemia
- Bruising and bleeding
- Sore mouth
- Loss of appetite
Chronic/ Acute Pain Imbalanced Nutrition : Anxiety
Less than body requirements
- Monitor the patient's activity - Teach the patient the following - Provide a relaxed environment and
tolerace things : avoid the sight, smell, non-threatening.
- Instruct the patient and family on sounds unpleasant in the - Encourage active participation of
appropriate prescribed and environment during meal times. the patient and family in care and
over-the-counter medications - Suggest eating preferred and well treatment decisions.
- Instruct the patient and family on tolerated by the patients, better - Instruct the patient to discuss
cardiac risk factor modification food with high content of calories / personal feelings with the
- Instruct the patient and family on protein. Respect the patient?s food supporters of such clergy if
the exercise regimen, including preferences based on ethnicity. desired.
warm-up,endurance, and - Encourage adequate fluid intake,
cool-down, as appropriate but limit fluids at mealtime.
- Promote bed rest and activity - Increase fluid levels with food can
limitation lead to a state of satiety. Consider
the cold food, if desired.
- Collaborative provision of
commercial liquid diet by way of
enteral feeding through a tube,
elemental diet.
Legends:
ETIOLOGY PREDISPOSING PRECIPITATING DISEASE PROCESS PATHOGENESIS CLASSIFICATIONS SIGNS & SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSTIC TEST MEDICATION SIDE EFFECTS MEDICAL MGT NURSING Dx NURSING INTERVENTIONS LABORATORY FINDINGS PREVENTIONS
SUBMITTED BY:
SANG-AN, DARWIN JAY L.
DABLIO, NIKKA
BSN - 3B
You might also like
- Utrecht Gender Dysphoria Scale PDFDocument16 pagesUtrecht Gender Dysphoria Scale PDFTherese EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Obesity Research PaperDocument10 pagesObesity Research PaperPaige-Hill88% (16)
- Syndromic Gastric PolypsDocument15 pagesSyndromic Gastric PolypsTheDrakairNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On Renal FailureDocument1 pageConcept Map On Renal FailureJessilda Damian VeranoNo ratings yet
- The Social Dilemma ReviewDocument5 pagesThe Social Dilemma ReviewNikkaDablio100% (1)
- Health and Fitness in Senior Years: Group MembersDocument35 pagesHealth and Fitness in Senior Years: Group MembersSiti Halimatus Saadiah100% (1)
- 0304 ConsultantoncallDocument4 pages0304 Consultantoncallnessimmounir1173No ratings yet
- Lacpacan Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLacpacan Breast Cancer Concept MapRIZI LACPACANNo ratings yet
- Group D Members:: Kidney Liver PancreasDocument1 pageGroup D Members:: Kidney Liver PancreasCourtney KateNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Document13 pagesPediatric Therapeutics: Eximius 2021Isabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Genome Poster 2009Document1 pageGenome Poster 2009ISAAC LEWNo ratings yet
- Gems Opt Select Brochure 2021 v6 3Document2 pagesGems Opt Select Brochure 2021 v6 3Bongani West VuthaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Amoeba - SarcodinaDocument14 pagesWeek 3 - Amoeba - SarcodinaShine CalarananNo ratings yet
- 5sample - Gastrointestinal System Notes - 3rd Ed OptimizedDocument28 pages5sample - Gastrointestinal System Notes - 3rd Ed OptimizedAlexis Tobar100% (2)
- GDM PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesGDM PathophysiologyShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- HZ SummaryDocument1 pageHZ SummaryPratzNo ratings yet
- All Charts Final Exam 1 PDFDocument294 pagesAll Charts Final Exam 1 PDFYasir RasoolNo ratings yet
- Azathioprine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAzathioprine Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado100% (1)
- Gynaecology Revision PDFDocument13 pagesGynaecology Revision PDFAadhi AadhiNo ratings yet
- DRUGDocument4 pagesDRUGPINKI DEBNo ratings yet
- Tables ProtozoaDocument14 pagesTables ProtozoaJanette Monica BarriosNo ratings yet
- Poster Caitlin BrennanDocument1 pagePoster Caitlin Brennansagun maharjanNo ratings yet
- Medical Prefixes and SuffixesDocument12 pagesMedical Prefixes and SuffixesKrishnanunni KLNo ratings yet
- Severe: Severe Persis4ng Symptoms of One or More Of: Gastrointes Nal SkinDocument2 pagesSevere: Severe Persis4ng Symptoms of One or More Of: Gastrointes Nal SkinSanjuy GarzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document23 pagesChapter 5ozmanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesWeek 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Colorect: Patient's Name: F.V Age: 64 Years OldDocument3 pagesColorect: Patient's Name: F.V Age: 64 Years OldGenynne Ragasa100% (1)
- Biowords v2Document3 pagesBiowords v2Hiezeyl Ymana GuntangNo ratings yet
- Drug To Xi CitiesDocument1 pageDrug To Xi CitiesGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Trematodes ScheduleDocument1 pageTrematodes ScheduleDr-positive EnergyNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea-Vomiting Pathway-Primary Care MAY 2015Document2 pagesDiarrhoea-Vomiting Pathway-Primary Care MAY 2015nimraNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13Document6 pages2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13A HNo ratings yet
- Viii. PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesViii. Pathophysiologymacedon145377No ratings yet
- Chapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney DisordersDocument40 pagesChapter54 Management of Patients With Kidney Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Abdominal PainDocument4 pagesApproach To Abdominal PainShamen KohNo ratings yet
- HISTORY & EXAMINATION Edited 228Document11 pagesHISTORY & EXAMINATION Edited 228Saurabh LamkhadeNo ratings yet
- 01 Sick Bird SyndromeDocument1 page01 Sick Bird SyndromeAli BakNo ratings yet
- MUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3Document1 pageMUGOT - DEMENTIA CONCEPT MAP - Page 3MICHELLIN VAN MUGOTNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal DisordersJerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- T2 DM Seizure 1Document1 pageT2 DM Seizure 1Mika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- Hypoparathyroidism Care MapDocument1 pageHypoparathyroidism Care MapDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Ashap Medical Terminology Chapter 1Document1 pageAshap Medical Terminology Chapter 1Lorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- Legend: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageLegend: PathophysiologyMikhail LamayoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm 2: Diarrhea: Signalment/History/Exam Polyuria DiarrheaDocument1 pageAlgorithm 2: Diarrhea: Signalment/History/Exam Polyuria DiarrheaAli BakNo ratings yet
- NUR 3032 Pancreatic, Biliary, and Hepatic Disorders Study PlanDocument6 pagesNUR 3032 Pancreatic, Biliary, and Hepatic Disorders Study PlanThalia FortuneNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Document32 pagesBacteria Chart FINAL 3 2Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument4 pagesDrug Study FormRhea LaplanaNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0923753419544970Document6 pagesPi Is 0923753419544970AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis Aguda Guías ClínicasDocument1 pagePancreatitis Aguda Guías Clínicaslbritez7No ratings yet
- DRUG - NDocument1 pageDRUG - NaizatiangcoNo ratings yet
- A3 Plant KingdomDocument1 pageA3 Plant KingdomMeenakshi VermaNo ratings yet
- Skema AnalisaDocument2 pagesSkema AnalisaAhmad MukhlisNo ratings yet
- Histopathological Features in Anemia DisordersDocument1 pageHistopathological Features in Anemia Disorderskoki74No ratings yet
- Drug Study Camillus MabiniDocument5 pagesDrug Study Camillus MabiniJonh Carlo LopezNo ratings yet
- Parasites High YoieldDocument4 pagesParasites High Yoieldnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Animals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)Document5 pagesAnimals Study Guide - Yeshen a. (2-4)krisamikaela1123No ratings yet
- NoteDocument9 pagesNote65O6O78 ฐิติพันธ์ เพชรกระจายแสงNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMuhammad Jefri LukmanNo ratings yet
- PGI Reyes StomachDocument124 pagesPGI Reyes StomachMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- AmebasDocument3 pagesAmebasNaomi NicoleNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology 1: - Non MotileDocument27 pagesBacteriology 1: - Non MotileYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- En DoDocument2 pagesEn Dofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesDocument11 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Trends and IssuesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- OB WorkbookDocument13 pagesOB WorkbookNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Theories of AgingDocument4 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Theories of AgingNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- TFN - BennerDocument1 pageTFN - BennerNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Physiologic ChangesDocument25 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Physiologic ChangesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patients With Pneumonia and Pulmonary EmbolismDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patients With Pneumonia and Pulmonary EmbolismNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- 19th Century RizalDocument2 pages19th Century RizalNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument27 pagesPsoriasisNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Sihay - Ang Silid NG BuhayDocument5 pagesSihay - Ang Silid NG BuhayNikkaDablio100% (1)
- Nikka Dablio - ACTIVITY 1 The Paradox of Our TimeDocument1 pageNikka Dablio - ACTIVITY 1 The Paradox of Our TimeNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University: Department of BiologyDocument4 pagesCentral Mindanao University: Department of BiologyNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Datasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersDocument14 pagesDatasheet On Factors Affecting BuffersNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Map of Region IIIDocument8 pagesMap of Region IIINikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabia Written ReportDocument3 pagesSaudi Arabia Written ReportNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Patterns of StrugglesDocument2 pagesPatterns of StrugglesNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Vijaya DiagnosticsDocument3 pagesVijaya DiagnosticssampathNo ratings yet
- Women The Skilled Architect of The SocietyDocument4 pagesWomen The Skilled Architect of The SocietyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Space Closure Using Simple Mechanics in Compromised First Molar Extraction Spaces: Case SeriesDocument9 pagesOrthodontic Space Closure Using Simple Mechanics in Compromised First Molar Extraction Spaces: Case SeriesHabeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- 2048 Wal LA Clarification Deficiency CA FSHC PKTDocument7 pages2048 Wal LA Clarification Deficiency CA FSHC PKTJuliana GallardoNo ratings yet
- Resume of DR Pramod Nanda - Manager in Health Care Professional 2021Document10 pagesResume of DR Pramod Nanda - Manager in Health Care Professional 2021Dr Pramod NandaNo ratings yet
- The Paediatric Voice Clinic: Ian Smillie, Kirsy Mcmanus, Wendy Cohen, Elizabeth Lawson, David Macgregor WynneDocument5 pagesThe Paediatric Voice Clinic: Ian Smillie, Kirsy Mcmanus, Wendy Cohen, Elizabeth Lawson, David Macgregor WynneCarolina UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Pilar College of Zamboanga City, IncDocument14 pagesPilar College of Zamboanga City, IncIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Alternative FeedingDocument36 pagesAlternative FeedingEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- History of MedicineDocument24 pagesHistory of MedicineРоман КравецьNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip Palate TherapyDocument5 pagesCleft Lip Palate TherapyNathalieCaracaNo ratings yet
- English Project 2Document34 pagesEnglish Project 2HARSHNo ratings yet
- OralcholecystographyDocument13 pagesOralcholecystographySuman PokhrelNo ratings yet
- FS Nicotine Mouth SprayDocument11 pagesFS Nicotine Mouth SprayAdnan DugonjicNo ratings yet
- 06 AQU347 Course Notes Chapter 1Document13 pages06 AQU347 Course Notes Chapter 1Nurul Syafiqah Binti ShaidanNo ratings yet
- PDF Hypertension A Companion To Braunwalds Heart Disease 3Rd Edition George L Bakris Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Hypertension A Companion To Braunwalds Heart Disease 3Rd Edition George L Bakris Ebook Full Chapteriris.russell843100% (3)
- Antimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeDocument35 pagesAntimicrobial Drugs: Powerpoint Presentations Prepared by Bradley W. Christian, Mclennan Community CollegeTiffany Jane Huertas100% (1)
- 2021 Examining The Black U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate and How ToDocument2 pages2021 Examining The Black U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate and How ToCece JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ab Omas A L Ulceration Andtympanyofcalves: Tessa S. MarshallDocument12 pagesAb Omas A L Ulceration Andtympanyofcalves: Tessa S. Marshallana lauraNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Complications and Prognosis LastDocument42 pagesBreast Cancer Complications and Prognosis Lastalalmaee1No ratings yet
- Spinal ShockDocument82 pagesSpinal ShockPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- Big Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseDocument7 pagesBig Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseHernán GiménezNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology CH 8Document139 pagesMedical Terminology CH 8ياسين المسطوNo ratings yet
- DEVPSY Reviewer - Chapters 1-6Document17 pagesDEVPSY Reviewer - Chapters 1-6Charmaine FloresNo ratings yet
- Development and Testing of ATime Resolved Personal Ozone MonitorDocument80 pagesDevelopment and Testing of ATime Resolved Personal Ozone MonitorJijo SagaiNo ratings yet
- A Study On Work From Home, Motivation & Productivity of Employees in Indian Population During COVID-19 PandemicDocument15 pagesA Study On Work From Home, Motivation & Productivity of Employees in Indian Population During COVID-19 Pandemicمعن الفاعوريNo ratings yet
- Laporan Bulanan Pasien CT - Scan 2016Document165 pagesLaporan Bulanan Pasien CT - Scan 2016Fera NurrizaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing Must Knows by Dr. Chris G. SorongonDocument2 pagesOncology Nursing Must Knows by Dr. Chris G. SorongonAleandro DizonNo ratings yet