Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scientific Method in The Social Sciences
Scientific Method in The Social Sciences
Uploaded by
Lemon Lakwatsera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pages1. Variables allow researchers to classify phenomena, measure characteristics, and explain relationships. There are different types of variables including independent, dependent, and intervening variables.
2. Quantitative research uses mathematics and statistics to systematically investigate social phenomena. It can be descriptive, correlational, causal-comparative, or experimental.
3. Variables are central to quantitative research and are used to classify subjects, measure attributes, and assess relationships between elements being studied.
Original Description:
HIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
Original Title
Scientific Method in the Social Sciences
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Variables allow researchers to classify phenomena, measure characteristics, and explain relationships. There are different types of variables including independent, dependent, and intervening variables.
2. Quantitative research uses mathematics and statistics to systematically investigate social phenomena. It can be descriptive, correlational, causal-comparative, or experimental.
3. Variables are central to quantitative research and are used to classify subjects, measure attributes, and assess relationships between elements being studied.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesScientific Method in The Social Sciences
Scientific Method in The Social Sciences
Uploaded by
Lemon Lakwatsera1. Variables allow researchers to classify phenomena, measure characteristics, and explain relationships. There are different types of variables including independent, dependent, and intervening variables.
2. Quantitative research uses mathematics and statistics to systematically investigate social phenomena. It can be descriptive, correlational, causal-comparative, or experimental.
3. Variables are central to quantitative research and are used to classify subjects, measure attributes, and assess relationships between elements being studied.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
through variables, we can
PRACTICAL RESEARCH describe the phenomenon or
population we are studying
through identifying possible
Scientific Method in the Social Sciences classifications.
1. Identify the research problem and state the research Measuring
questions. variables allows us to measure the frequency,
2. Review related literatures (RRL) magnitude, and impact among others of a particular
3. Formulate framework and hypothesis subject or concept.
4. Choose data collection method and analysis Explaining
5. Collect and Analyze data variables allows one to further understand the
6. Conclude and make recommendations existence, meaning, and purpose of certain
Quantitative Research phenomena.
the systematic empirical investigation of social Assessing Relationships
phenomena using tools of mathematics and statistics. variables are critical elements of the relationship
Systematic: follows a series of steps between the subjects and the phenomenon you are
Empirical: problems must possess observable investigating.
characteristics Types of Variables
Social phenomena: problems are concerned with Independent Variables
people/communities, organizations, behaviors, etc.
variables that cause changed in a situation or
Mathematics & Statistics: answers will be derived from
phenomenon.
equations and formulae
occurs prior to all variables.
Kinds of Quantitative Research
Dependent Variables
Descriptive Quantitative Research
variables which manifest the effects brought by the
to obtain information concerning the current status of
independent variables.
the phenomenon
outcome, effect or response variable
data is collected without changing the environment of
Intervening Variables
respondents
variables which are the link between dependent an
the variable is "as is, where is"
independent variables.
Correlational Research
shows the effect of the independent variable on the
to test relationships between variables
dependent variable.
data comprises of systematic relationships between
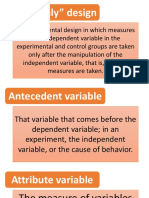
Antecedent Variables
descriptive parameters
variable which affects the link between the cause,
variables are observed first, then collected.
connecting, and effect variables.
Causal-Comparative Research
Categorial Variables
to unearth cause-and-effect relationships between
variables that may be classified into categories or
variables
may be placed in rank orders.
data are assigned in groups, then collected per group Nominal Variables
variables cannot be manipulated cannot be ordered in any particular way.
Experimental Research Ordinal Variables
to reveal cause-and-effect relationships by can be ordered from greatest to smallest.
manipulating one parameter, and observing its Numerical Variables
influence to another parameter
variables having absolute numerical values or
data is guided by, and manipulated through
measures.
hypothesis
Interval Variables
one variable is manipulated, another variable is set as
rank-ordered and have equal distances.
the standard/model.
do not have a "true zero" value.
Variables
Ratio Variables
is a variation within a class of objects.
has all the characteristics of nominal, ordinal, and
Constant: a characteristic with no variations within a
interval measures.
class of objects.
have "true zero" value.
central idea in quantitative research
Sources of Research Topics
Mass media communication
books, internet, peer-reviewed journals. Government
publications
measurable attributes or characteristics that can vary professional periodicals
for different cases. general periodicals
at lease 2 distinct categories. previous reading assignments in your other subjects
Uses of Variables work experience
Classifying Research Problem
definite or clear expression about an area ofconcern, Observe proper grammar and capitalization
a condition to be improved upon, a difficulty to be capitalize the first words in your title.
eliminated, or a troubling question that points to a all nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs
need for meaningful understanding and deliberate that appear between the first and last words of the
investigation. title are also capitalized.
Statement of the Problem Cite properly
used in research work as a claim that outlines the when including a quote as part of the title, the source
problem addressed by a study of the quote is cited, indicated by an asterisk or a
focal point of any research footnote beside the word/s or phrase
Research Question Related Review Literature (RRL)
defined as specific questions about behavior, event, a comprehensive summary of previous research on a
or phenomena of interest that you wish to seek topic.
answer for your research. should enumerate, describe, summarize, objectively
Characteristics of Good RQs evaluate and clarify this previous research.
1. It should clarify what information needs to be relates your study to a larger body of literature
gathered. sets the context of the study and explains the
2. It should be empirical significance of your research problem
3. It should be complex and not terminal List of Scholarly Sources
4. It should be relevant 1. Scholarly Journal: often take the form of literature
5. It should be practical reviews, book reviews, or research studies.
Introduction of the Study 2. Books: either readers; collection of scholarly and
to give readers an overview of what the entire study expert essay; annual research books containing
is all about studies and reports.
aims to introduce the research topic and research a.) Reader - an edited and synthesized collection of original
problem to the readers research reports.
includes the background of the study, the research b.) Compendium - contains articles and essays
questions or objectives, the significance of the study, organized around a particular topic.
and scope and limitation c.) Annual Reports - have a volume number specific for a
Background of the Study certain year and underline a general research idea.
to provide readers with the context and explain the 3. Thesis and Dissertation: most postgraduate students
circumstances that led to the study. are required to complete their individual research.
provides insights to the motivation and perspective of 4. Government Documents: government units conduct
the researchers. or commission studies and publish official reports.
5. Policy Reports and Presented Paper – professional
Significance of the Study organizations in academic fields annually hold
impact of the study to: institution, students, meetings and conferences.
researchers, body of knowledge/discipline Characteristics of Cited Materials
Scope and Limitation of the Study must be recent as possible
short section where you clarify what your study must be objective and unbiased as possible
covers based on your research topic must be relevant to the study
the possible limitations of your study must not too few but not too many
how the study is constrained by particular factors that Literature Review Process
you encountered in the research process 1. Select a Topic
Research Title 2. Select and choose literature
conveys the central idea behind your research 3. Analyze and interpret literature
reflects the critical points of your research 4. Write the review.
Effective Research Titles Elements of RRL
Two-part title: the first part is a snappy phrase 1. Introduction: briefly describes the content of the
intended to catch the audience's attention. The second section and how it' s organized
part is more descriptive. 2. Topic 1: must review scholarly literature related to
Provide the necessary information the independent variable
indicate the subject of the study. 3. Topic 2: similar procedures must be observed when
include the scope of your study by mention the discussing dependent variables and the subsidiary
setting measured utilized
Choose the appropriate wording 4. Topic 3: explains why the independent and dependent
variables are related
play with words when crafting a research title to
5. Summary/Synthesis: highlights major themes,
stimulate the reader's interest.
explain the major and seminal studies on your topic,
refrain from using abbreviations and/or jargons,
identify the gap that needs to be addressed.
unless these terms are commonly known
Plagiarism
Be mindful of the length
limit your research title to 10 to 15 substantive words
is an act of quoting or copying the exact words of the methodological in nature
writer and passing the quoted words off as your own illustrating the methodological process that the
words research will follow
Types of Plagiarism Input - Process – Output
Cut and Paste Plagiarism Theoretical Framework
Mosaic Plagiarism the "blueprint" or guide for a research (Grant &
Misattribution Plagiarism Osanloo, 2014)
Self-plagiarism the specific theory or theories about aspects of human
Avoiding Plagiarism endeavor that can be useful to the study of events
Integral Citation (Brondizio, Leemans, & Solecki, 2014)
one way of citing or referring to the author whose theoretical principles, constructs, concepts, and
ideas appear in your work tenants of a theory
Non-Integral Citation Importance of Theoretical Framework
downplays strength of the writer's personal guides a researcher's choice of research design and
characteristics data analysis plan.
stress is given to the piece of information rather than provides a common worldview or lens from which to
the ideas support one's thinking on the problem and analysis of
Patterns of Citation data
Summary Conceptual Framework
shortened version of the original text that's expressed a structure which the researcher believes could best
in own language explain the natural progression of the phenomenon to
picking out the most important ideas or aspects of the be studied
text offers a logical structure of connected conceptsnthat
Paraphrase help provide a picture or visual display of hownideas
explains what the text means in own words in a study relate to one another
it's possible that the explanations may decrease or
exceed the number of words of original text
Short Direct Quotation
you'll need to include the author, year, and page
number of the reference ("p." - single page; "pp." -
span of multiple pages)
Long Direct Quotation, Block Quotation, or Extract
makes you copy the author's exact words from 40-
100 words
under APA, limit is eight lines
placed at the center with no indentation, the copied
lines look like a composed stanza of a poem
Tense of verbs for reporting
active verbs to use in reporting authors' idea
present ideas in present, simple past, or present
perfect tenses
in APA, must use present perfect tense
NOTE!: Publication Manual suggest that authors
should use past tense/present perfect tense for signal
phrases that occur in RRL, while contexts other than MURFE, SANDARA A. STEM 12-02
traditionally-structured research can use simple
present tense
Theoretical
must be an established theory
explains the relationships between variables
a guide for data analysis and development of
instrument
Conceptual
can be used on several existing theory
illustrate the relationship between variable
guided by logical intuition and previous findings in
making connections between kay concepts
Rule of thumb
Operational
You might also like
- PR 2Document5 pagesPR 2Eissa SamanoNo ratings yet
- Research Methods For Architecture Module 5Document3 pagesResearch Methods For Architecture Module 5Bill Ely BalagotNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document37 pagesResearch 1Keith MoradaNo ratings yet
- Exp Psych Midterm RevDocument4 pagesExp Psych Midterm RevNathalie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mind Map FinalDocument1 pageMind Map FinalGinielle Gem Atim BelarminoNo ratings yet
- SHS RESEARCH BASICS. - Identifying-Research-VariablesDocument17 pagesSHS RESEARCH BASICS. - Identifying-Research-Variablesalabmyself100% (1)
- PR For PTDocument3 pagesPR For PTAbbyjane MadlangsakayNo ratings yet
- Donato, Edwin 12-Sapphire (Electronics) Weeks 11-14 ResearchDocument6 pagesDonato, Edwin 12-Sapphire (Electronics) Weeks 11-14 ResearchEdwin DonatoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5: Identifying VariablesDocument1 pageCHAPTER 5: Identifying Variablesalia.delareineNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesPractical Research 2 ReviewerM e g u m iNo ratings yet
- Types of Quantitative Research VariablesDocument1 pageTypes of Quantitative Research VariablesHannah R. NavarroNo ratings yet
- The Kinds and Types of Variables, and Level of Measurement VariableDocument4 pagesThe Kinds and Types of Variables, and Level of Measurement Variablehyacinth buenaventuraNo ratings yet
- RMM NotesDocument177 pagesRMM NotesVahni SinghNo ratings yet
- Handouts 1Document4 pagesHandouts 1Ken DumpNo ratings yet
- Field Methods 1Document6 pagesField Methods 1Angelika PadawanNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesPractical Research 2 ReviewerlotoizzyaliyahNo ratings yet
- Variables and HypothesisDocument2 pagesVariables and HypothesisMercedes CandelonNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerKit DyNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 ReviewerMaria Christine OgenaNo ratings yet
- LESSON - Quantitative Research DesignsDocument16 pagesLESSON - Quantitative Research DesignsHomer Kurt BugtongNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ReviewerGabby GargantosNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics: Paper #6Document11 pagesAdvanced Statistics: Paper #6Precious NosaNo ratings yet
- Q1. W3. The Nature of VariablesDocument3 pagesQ1. W3. The Nature of VariablesDazzleNo ratings yet
- Li'izza Diana Manzil - Summary On Topic 16Document2 pagesLi'izza Diana Manzil - Summary On Topic 16Diana ManzilNo ratings yet
- PR2 Topic 4 - Variables and Scales of MeasurementDocument23 pagesPR2 Topic 4 - Variables and Scales of Measurementibrahim coladaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research Design: by Erica L. Canon-Teacher 1 (SHS)Document46 pagesQuantitative Research Design: by Erica L. Canon-Teacher 1 (SHS)Erica CanonNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ResearchDocument19 pagesQuantitative ResearchMelisa PontónNo ratings yet
- Math 1F - 4 StatisticsDocument8 pagesMath 1F - 4 StatisticsJay-pNo ratings yet
- Variablesandmeasurementscales 090604032334 Phpapp02Document34 pagesVariablesandmeasurementscales 090604032334 Phpapp02ihtishamNo ratings yet
- Research Quiz 1Document5 pagesResearch Quiz 1Ellen CatedralNo ratings yet
- Terms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsDocument13 pagesTerms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsMichael JubayNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Introduction To StatisticsDocument28 pagesCh1 Introduction To StatisticshectorNo ratings yet
- Summar Quant Designs ChartDocument1 pageSummar Quant Designs ChartYoni MacNo ratings yet
- Correlational & Quasi Experimental DesignsDocument52 pagesCorrelational & Quasi Experimental DesignsFerdinand PagaranNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Process SkillDocument7 pagesIntegrated Science Process Skillcikgu gio80% (15)
- Regression AnalysisDocument14 pagesRegression AnalysisMadhura RaoNo ratings yet
- FrameworksDocument54 pagesFrameworksKaren RoseNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument16 pagesThe Nature of Inquiry and ResearchElenear De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Research Approaches and Data Collection MethodsDocument25 pagesResearch Approaches and Data Collection Methodsjumanhamdan4No ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignsDocument16 pagesQuantitative Research Designsapi-339611548100% (15)
- Concept Construct and VariableDocument8 pagesConcept Construct and VariableMegha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 6 Bab V Variabel Dan Desain Riset AkuntansiDocument15 pagesPertemuan 6 Bab V Variabel Dan Desain Riset AkuntansiSusanto ChNo ratings yet
- 1 Quantitative Research VariablesDocument37 pages1 Quantitative Research Variablescatherine abaoNo ratings yet
- Types - of - Quantitative - Research - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''Types of Quantitative ResearchDocument16 pagesTypes - of - Quantitative - Research - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''Types of Quantitative ResearchCris VillarNo ratings yet
- PR Notes Unit 1Document4 pagesPR Notes Unit 1Alyssa MacamayNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quarter 2 Module 1Document18 pagesPractical Research 2 Quarter 2 Module 1renierpardz09No ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: QUARTER 2-MODULE 4: Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataDocument27 pagesPractical Research 2: QUARTER 2-MODULE 4: Understanding Data and Ways To Systematically Collect DataKaye Antonette FloresNo ratings yet
- Types of VariableDocument26 pagesTypes of VariablePauline Chavez - AmorsoloNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1Document72 pagesA Guide To Writing Thesis and Dissertation 1louella repolloNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument2 pagesResearch ReviewerJoseline SisonNo ratings yet
- Key Elements of A Research Proposal Quantitative DesignDocument3 pagesKey Elements of A Research Proposal Quantitative DesignHilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.No ratings yet
- The VariableDocument3 pagesThe VariableYmme LouNo ratings yet
- HyDocument31 pagesHyHiba NaseerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantitative Research NCM111 Lec 2PDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Quantitative Research NCM111 Lec 2PMary Queenie TulinNo ratings yet
- BRM AkashDocument15 pagesBRM Akashuday bansalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFDocument36 pagesLESSON 1 - Nature of Inquiry and Research PDFKent SalmorinNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document4 pagesWeek 3Raidon JantanataNo ratings yet
- STATPSY ReviewerDocument15 pagesSTATPSY ReviewerVincent Miguel BastieroNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Algorithms in C++: Data Patterns and Algorithms for Modern ApplicationsFrom EverandData Mining Algorithms in C++: Data Patterns and Algorithms for Modern ApplicationsNo ratings yet