Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MODULE6
MODULE6
Uploaded by
Diana Calderon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesThe document discusses air pollution and air quality. It defines air pollution as the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alter the natural atmosphere. Common sources of air pollution include combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities, forest fires, and indoor sources like cooking and cleaning. Major outdoor air pollutants that impact public health are particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. The document also discusses air pollution sources, pollutants, effects on health and the environment, and approaches to air pollution control.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses air pollution and air quality. It defines air pollution as the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alter the natural atmosphere. Common sources of air pollution include combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities, forest fires, and indoor sources like cooking and cleaning. Major outdoor air pollutants that impact public health are particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. The document also discusses air pollution sources, pollutants, effects on health and the environment, and approaches to air pollution control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesMODULE6
MODULE6
Uploaded by
Diana CalderonThe document discusses air pollution and air quality. It defines air pollution as the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by chemical, physical, or biological agents that alter the natural atmosphere. Common sources of air pollution include combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities, forest fires, and indoor sources like cooking and cleaning. Major outdoor air pollutants that impact public health are particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. The document also discusses air pollution sources, pollutants, effects on health and the environment, and approaches to air pollution control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
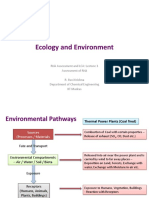
Air Pollution and Air Quality
DISCUSSION: • Cooking and heating
Air pollution refers to the • Building materials
contamination of the indoor or outdoor • Office machines
environment by any chemical, physical • Furnishings
or biological agent that modifies the • Household cleaning
natural characteristics of the substances
atmosphere. Household combustion • Street dust/garden soil
devices, motor vehicles, industrial • Biological agents
facilities, and forest fires are common • Tobacco smoke
sources of air pollution. Pollutants of • Industrial operations
major public health concern include
particulate matter, carbon monoxide, Major Air Pollutants
ozone, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur
dioxide. Outdoor and indoor air pollution • Primary air pollutants -
cause respiratory and other diseases and emitted from identifiable
is an important source of morbidity and sources ( e.i. particulate
mortality (WHO.org) matter, carbon monoxide,
nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur
Air Pollution Sources dioxide)
• Secondary air pollutants -
Outdoor (Ambient) results from the suspension of
some primary pollutants (e.i.
• Fuel combustion
ozone, PAN)
• Industrial operations
• Solid waste disposal FATE OF AIR POLLUTANTS
• Nuclear devices
• Smoking 1. Photochemical reactions
• Miscellaneous sources -
volcanic eruptions, typhoons, 2. Scavenging processes or
fires, construction disposal reactions
3. Dilution, diffusion, and
Indoor dispersion
AIR POLLUTANTS AND THEIR DISPOSAL REACTIONS
Pollutant Disposal reactions
CO Soil organisms
SO2 Oxidation to sulfate
Soluble: stays in the air for only a few minutes. May undergo intermediate processes and beco
Reducing agent H2SO4 that can cause acid rain
NO/NO2
Oxidation to nitrate
Soluble: stays in the air for only a few minutes.
Photosynthesis
CO2
Absorption in oceans
HC Photochemical reaction
Processes that will terminate their existence in
Particulate matter
absorption, adsorption, rainout or wash out
Air Pollution Effects • Superficial physical damage
(e.i. sensory irritations,
1. Environmental Effects Discomfort, impairment of
➢ Land visibility)
• Indirect effects (e.i mental
• Adverse effects on soil and well-being)
other surfaces • death
➢ Water
• Adverse effects of acid gases AIR POLLUTION CONTROL
on marine life and vegetation
• Settling of air particles in 1. Technological air pollution control (
water causes water pollution e.i. filters, scrubbers, chimney)
2. Administrative air pollution control (e.
➢ Vegetation i. rules, regulations, standards, laws)
• Chlorosis – discoloration ADDITION LECTURE VIDEO
• Necrosis – drying up
• Abscission – premature falling Reminders:
out of flowers
• Please prepare for a quiz next
• Plasmolysis – disturbance in
meeting. Also, research for
the water balance
examples of technological and
2. Health Effects administrative air pollution
control.
• acute and chronic diseases • Recorded synchronous will be
posted on a separate page.
• Changes in important
physiological functions (CO
poisoning)
Environmental Health
DISCUSSION: • Biological - Disease organisms
present in food and water
According to the • Physical - Noise, ionizing and
WHO, health pertains to a state of non-ionizing radiation
complete physical, mental and social • Socioeconomic - Poor access
well-being and not merely the absence to safe and sufficient health
of disease or infirmity. The main factors care
that influence our health would include • Psychological - Anxiety,
genetics, personal behavior and lifestyle, overcrowding, isolation, and
and environment. The environment is anomie
further believed to be grouped as
physical, biological, and social & cultural. Levels of Concern for Environmental
Environmental health is said to Quality by Winthrop (1968)
include aspects of human health that are
determined by physical, biological, social, • Bare survival – control of
and psychosocial factors in the major disease epidemics and
environment. It also involves the theory violent death; minimum food
and practice of assessing, correcting, and water
controlling, and preventing factors in the • Control of disease and injury –
environment that can adversely affect control of endemic and
the health of present and future dietary disease and accidental
generations. injury
The Basic Requirements for a Healthy • Efficient performance –
Environment adequate and proper diet;
maintenance of environment
• Clean air for efficient use of manpower
• Safe and sufficient water • Comfort – stimulating
• Safe and adequate food environment; aesthetic
• Safe and peaceful settlements satisfaction and comfort
• Stable global environment control
Types of Environmental Hazards • Survival of human species
Hazards are anything (things or Environmental Engineering
situations) that has the potential to
cause harm or injury to an individual. Branch of engineering concerned with:
• Chemical - Air pollutants, • Protection of human
toxins, pesticides, and volatile populations from the effects
organic compounds (VOCs)
of adverse environmental SELF-CHECK ACTIVITY:
factors
• Protection of the environment 1. Research for examples and list them
from potentially deleterious down In your notebook.
effects of human activities
• Improvement of • Types of environmental
environmental quality for hazards
human health and well-being • Examples of diseases and
disorders
** Recorded synchronous lecture to be • Environmental engineering
posted on a separate page.
You might also like
- Construction of A Grey Water Recycling SystemDocument8 pagesConstruction of A Grey Water Recycling SystemvigyanashramNo ratings yet
- Community and Public Health: Summer A.Y. 2020 - 2021Document8 pagesCommunity and Public Health: Summer A.Y. 2020 - 2021MwaeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Process Technology Dr. Tran Le LuuDocument221 pagesEnvironmental Process Technology Dr. Tran Le Luuanon_824105482No ratings yet
- Environmental Science Module 13-16Document41 pagesEnvironmental Science Module 13-16Ranzel SerenioNo ratings yet
- L-4 Environmental PollutionDocument11 pagesL-4 Environmental PollutionSwaral NaikNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument2 pagesNOTESMary Joy Heraga PagadorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Environmental EngineeringDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Environmental EngineeringAbdul Wafiy NaqiuddinNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution PDFDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Pollution PDFSwaral NaikNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution L2Document3 pagesAir Pollution L2wenah29472No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Environmental Pollution (1) NewDocument249 pagesUnit 2 Environmental Pollution (1) NewVinit TandelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Pollution and PollutantsDocument59 pagesChapter 1 Pollution and PollutantsHanane TRACHENo ratings yet
- Polluion ReportDocument14 pagesPolluion ReportJanele QuitosNo ratings yet
- Env. Health I - Air & Ventilaiton DRFMQDocument28 pagesEnv. Health I - Air & Ventilaiton DRFMQamir khanNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY-Energy & Environmental Engineering Subject Code-ES - 401 Topic-Environmental Pollution B.Tech Civil 4 SemDocument34 pagesACTIVITY-Energy & Environmental Engineering Subject Code-ES - 401 Topic-Environmental Pollution B.Tech Civil 4 SemShivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Ecological ConceptsDocument68 pagesModule 1 - Ecological ConceptsAbegailNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument57 pagesIntroductionইসলামিক টিভিNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management System .Document18 pagesEnvironmental Management System .G-IOSH International-Pvt LTDNo ratings yet
- 26 BOT 101 Ecology Lecture 3-1Document29 pages26 BOT 101 Ecology Lecture 3-1samuelogunsola005No ratings yet
- Final Pa Print - JammmDocument4 pagesFinal Pa Print - JammmMary Joy Heraga PagadorNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University PhilippinesDocument9 pagesSt. Paul University PhilippinesAshley DayagNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument51 pagesIntroductionইসলামিক টিভিNo ratings yet
- Pollution: Submitted To: Prof - Abeer Submitted By: Ibtasam Mohsin Roll No: B1Fi8Asoc005Document14 pagesPollution: Submitted To: Prof - Abeer Submitted By: Ibtasam Mohsin Roll No: B1Fi8Asoc005Dark GardianNo ratings yet
- Learning Module GE Envi Sci - Module 3 - MmoDocument14 pagesLearning Module GE Envi Sci - Module 3 - MmoHarold AmbidNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution 2021Document20 pagesEnvironmental Pollution 2021Agaba MartinNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 Environmental Pollution Envt Policies and Practices WNcVRhIzKxDocument55 pagesModule - 3 Environmental Pollution Envt Policies and Practices WNcVRhIzKxSUNG-JINN WOONo ratings yet
- BEC 210: Introduction To Environmental Engineering: Chapter 1: Environmental Management and Sustainable DevelopmentDocument18 pagesBEC 210: Introduction To Environmental Engineering: Chapter 1: Environmental Management and Sustainable DevelopmentAstiger IshakNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument49 pagesEnvironmental PollutionAria PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Pollutionموسى جعفر احمد محمدNo ratings yet
- MPM 721 Chapter 1Document63 pagesMPM 721 Chapter 1NAZRAWI GETACHEWNo ratings yet
- NREE - CHapter 5Document23 pagesNREE - CHapter 5Yohanis TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Module IvDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Module IvAlondra RanaNo ratings yet
- More Carbon Dioxide (CO) Being Released in The Atmosphere Traps More HeatDocument3 pagesMore Carbon Dioxide (CO) Being Released in The Atmosphere Traps More HeatNicoleNo ratings yet
- Pollution: 1. Pollution Caused by Solid WastesDocument3 pagesPollution: 1. Pollution Caused by Solid WastesBogart MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Environmetal Health: Dr. Ezzadin FrankaDocument34 pagesEnvironmetal Health: Dr. Ezzadin FrankaHannan AliNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument33 pagesPollutionAPDG CCNo ratings yet
- CENG241 - Lecture 1 - Introduction - HamdanDocument48 pagesCENG241 - Lecture 1 - Introduction - HamdanTaleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document19 pagesTopic 4Jomari TawatNo ratings yet
- Air Quality: by Dr. Abdullah BostajiDocument53 pagesAir Quality: by Dr. Abdullah Bostajiاسامة الصبحيNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Environmental PollutionDocument32 pagesUNIT 3 - Environmental PollutionsamarthdahibhateNo ratings yet
- Impacts On Air Environment: Prediction and Assessment ofDocument42 pagesImpacts On Air Environment: Prediction and Assessment ofDhruv YadavNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument31 pagesEnvironmental PollutionAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- HEA 101 Lecture # 3 Section # 2Document36 pagesHEA 101 Lecture # 3 Section # 2mahfuzNo ratings yet
- CHE61203 Pollution Control: Principles of Sustainable Development and Environmental Pollution and EthicsDocument44 pagesCHE61203 Pollution Control: Principles of Sustainable Development and Environmental Pollution and EthicsPorkkodi SugumaranNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Environmental Science Pollution and Its FactorsDocument22 pagesWeek 15 Environmental Science Pollution and Its FactorsReine Jholo BagaipoNo ratings yet
- Ecology and EnvironmentDocument19 pagesEcology and EnvironmentDimpi ShahNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Kesmavet & One Health-Sumber Pencemaran Udara Dan Dampaknya Terhadap Kesehatan TubuhDocument44 pagesKuliah Kesmavet & One Health-Sumber Pencemaran Udara Dan Dampaknya Terhadap Kesehatan Tubuhzidandzikru01No ratings yet
- Impact On Air EnvDocument42 pagesImpact On Air EnvSangeeth ThomasNo ratings yet
- What Is The Meaning of Environment ?Document9 pagesWhat Is The Meaning of Environment ?CYNTIANDRNNo ratings yet
- Environmental and Occupational Health Part 1Document36 pagesEnvironmental and Occupational Health Part 1ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Unit XIVDocument47 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Unit XIVsalmanNo ratings yet
- 20u03060 MidDocument38 pages20u03060 MidCHETANYA PRATAPNo ratings yet
- Environmental HealthDocument56 pagesEnvironmental HealthibrahimNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution Solid Waste Management: Disaster Management: Global Climate Change and Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion Problem Acid RainDocument28 pagesEnvironmental Pollution Solid Waste Management: Disaster Management: Global Climate Change and Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion Problem Acid RainRiajiminNo ratings yet
- Unit 2a-Environmental PollutionDocument67 pagesUnit 2a-Environmental PollutionKunal GautamNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Pollutionchinedumpeters31No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3ARPITA MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - PollutionDocument54 pagesUnit 5 - PollutionRadhika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Course: Subject Unit Title Topic BYDocument49 pagesCourse: Subject Unit Title Topic BYShobana Ramesh100% (2)
- Unit 4 - FC - EVSDocument15 pagesUnit 4 - FC - EVSPek yyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science & Disaster ManagementDocument131 pagesEnvironmental Science & Disaster ManagementJyothis T SNo ratings yet
- GB Oral PresentationDocument9 pagesGB Oral PresentationDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- The Oval Painting ActivityDocument2 pagesThe Oval Painting ActivityDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0Document3 pagesChapter 0Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Italian LiteraureDocument3 pagesItalian LiteraureDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Short StoriesDocument4 pagesShort StoriesDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Middle Eastern and African LiteratureDocument3 pagesMiddle Eastern and African LiteratureDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- 5 Qualities of A Health WorkerDocument4 pages5 Qualities of A Health WorkerDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Literature (1) - 1Document9 pagesIntroduction To Literature (1) - 1Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- 3 Health StatisticsDocument7 pages3 Health StatisticsDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- 4 Community Health Care Development ProcessDocument7 pages4 Community Health Care Development ProcessDiana Calderon100% (1)
- 1 Nature of Community Health DevelopmentDocument9 pages1 Nature of Community Health DevelopmentDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document3 pagesModule 7Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Health Care Ethics Introduction To Bioethics Ethical Schools of Thought (Part A)Document4 pagesWeek 1: Health Care Ethics Introduction To Bioethics Ethical Schools of Thought (Part A)Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document5 pagesModule 4Diana CalderonNo ratings yet
- W5: Solidarity Moral Discernment Professional RelationshipDocument4 pagesW5: Solidarity Moral Discernment Professional RelationshipDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Overview of Nursing Profession NotesDocument2 pagesOverview of Nursing Profession NotesDiana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Application Filed by The Industry / Organization OnDocument9 pagesApplication Filed by The Industry / Organization Onkrish659No ratings yet
- Sewer TunnelDocument10 pagesSewer TunnelshahqazwsxNo ratings yet
- Fkasa - Nurul Masliana BT Khairil Anuar (CD9323) - Chap 1 PDFDocument3 pagesFkasa - Nurul Masliana BT Khairil Anuar (CD9323) - Chap 1 PDFAlexsandra GulaneNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Lesson 3: Changes in Matter and Its Effect in The EnvironmentDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Lesson 3: Changes in Matter and Its Effect in The EnvironmentTEAM KnightzNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment HWDocument2 pagesPhysico-Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment HWmsinsigneNo ratings yet
- Listening and Speaking 2unit 7 Student Book Answer KeyDocument3 pagesListening and Speaking 2unit 7 Student Book Answer KeyNguyễn Thanh TúNo ratings yet
- Advanced Oxidation Processes and Their Application in PDFDocument21 pagesAdvanced Oxidation Processes and Their Application in PDFTalles BarcelosNo ratings yet
- Ganga River PollutionDocument8 pagesGanga River PollutionDr. Nitish Priyadarshi75% (4)
- Inter Generational Responsibility For The Marilao-Meycauayan-Obando River SystemDocument18 pagesInter Generational Responsibility For The Marilao-Meycauayan-Obando River SystemAgnes CayabanNo ratings yet
- Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004Document7 pagesPhilippine Clean Water Act of 2004nilereverofNo ratings yet
- 12.5 Hypo Rho Rite Solution MSDSDocument11 pages12.5 Hypo Rho Rite Solution MSDSmaheenkapadia4612No ratings yet
- Other Regulations Affecting Protective Coatings: Bernard R. ApplemanDocument20 pagesOther Regulations Affecting Protective Coatings: Bernard R. ApplemanNgô Trung NghĩaNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution Management Training Manual PDFDocument176 pagesWater Pollution Management Training Manual PDFJaspal SinghNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Standard Construction DrawingsDocument98 pagesAppendix B Standard Construction DrawingsSubashini JaganathanNo ratings yet
- Ready Mix Concrete Industry LEED Reference GuideDocument86 pagesReady Mix Concrete Industry LEED Reference Guidemirza057No ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument42 pagesSolid Waste ManagementKathir RaviNo ratings yet
- Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0175453 A1Document8 pagesPatent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0175453 A1Dnyaneshwar Dattatraya PhadatareNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic PrecipitatorDocument2 pagesElectrostatic PrecipitatorPrasad KhambeteNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument26 pagesPPTRashi GargNo ratings yet
- M.E Group 3 ReportDocument43 pagesM.E Group 3 ReportDimple LapuzNo ratings yet
- MarEnv Annex IV Regulation For The Prevention of Pollution by Sewage From ShipsDocument50 pagesMarEnv Annex IV Regulation For The Prevention of Pollution by Sewage From ShipsBurento DesuNo ratings yet
- Salinometer With 3 Way ValveDocument36 pagesSalinometer With 3 Way ValveParthivNo ratings yet
- Name: Baron Cathy Leoncia C. Course: Bsed Science Yr - Section: 2 ADocument7 pagesName: Baron Cathy Leoncia C. Course: Bsed Science Yr - Section: 2 AKa-ell Surb SorenNo ratings yet
- Folleto HYBAS-IFASDocument2 pagesFolleto HYBAS-IFASMaria Alejandra Colonia MoyaNo ratings yet
- Zarjis Composite Knit Ind LTD PDFDocument3 pagesZarjis Composite Knit Ind LTD PDFMd. Suruz ZamanNo ratings yet
- Zooplankton and White Goby (Glossogobius Giuris Hamilton 1822) : Correlation and Fishers' Perception in Selected Sites in Laguna de Bay, Luzon Island, PhilippinesDocument18 pagesZooplankton and White Goby (Glossogobius Giuris Hamilton 1822) : Correlation and Fishers' Perception in Selected Sites in Laguna de Bay, Luzon Island, PhilippinesMutya, Rosemarie Kate N.No ratings yet
- Piping BOQ (13 Jul)Document25 pagesPiping BOQ (13 Jul)Mubashir100% (2)
- Kochi: City Sanitation Plan ForDocument32 pagesKochi: City Sanitation Plan Forapinku1002No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Drinking-Water Quality - Second Edition - Volume 1 - RecommendationsDocument11 pagesGuidelines For Drinking-Water Quality - Second Edition - Volume 1 - RecommendationsJin SiclonNo ratings yet