Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 viewsGraphic Organizer
Graphic Organizer
Uploaded by
Kenshin MedinaThe circulatory and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen and remove carbon dioxide throughout the body. The circulatory system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs through the arteries and returns deoxygenated blood to the lungs through veins. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, throat, lungs, and diaphragm. It brings air in through the nose and mouth, passes it through the throat and trachea into the lungs where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Surgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery Clinical Questions and Answers 3rd Edition 2022 PDFDocument589 pagesSurgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery Clinical Questions and Answers 3rd Edition 2022 PDFdat100% (1)
- 2023 - Ent Vivas FrcsDocument331 pages2023 - Ent Vivas FrcsPG ORL PUCENo ratings yet
- Sci9Q1M1 - Rev-Bait-it 2Document4 pagesSci9Q1M1 - Rev-Bait-it 2Realyn Delana OguisNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document10 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1RUTH PIANGNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 4Document8 pagesVIII Biology HO 4anousha1488No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Circulatory SystemCes GarceraNo ratings yet
- Superior Vena Cava: Right AtriumDocument3 pagesSuperior Vena Cava: Right AtriumMary SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Science Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesScience Respiratory and Circulatory SystemElisha Kate AmitNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemJpaw Kidman100% (1)
- Reviewer in Science 9..Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 9..nanami's ChildNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio MC1Document12 pagesAnaphysio MC1KRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- t2 S 427 Year 6 Human Body Circulatory System Lesson Teaching Powerpoint Ver 7Document8 pagest2 S 427 Year 6 Human Body Circulatory System Lesson Teaching Powerpoint Ver 7AyselNo ratings yet
- Function and Structure of Heart and LungsDocument2 pagesFunction and Structure of Heart and LungsClaChristinaNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Blood VesselsDocument20 pagesVisibleBody Blood VesselscascaveletteNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyDocument20 pagesBlood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyRoger RonconiNo ratings yet
- 6 - The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages6 - The Cardiovascular SystemKolea 2003No ratings yet
- Science 1.1Document42 pagesScience 1.1Ina SuzaraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemSakshi NijhawanNo ratings yet
- Heart Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesHeart Cardiovascular SystemKim Nae A. MasucolNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartPrince JenovaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemJovie Erma AtonNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions: AnswersDocument7 pagesGuide Questions: AnswersPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument87 pagesCare of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsQueen Jyil100% (1)
- Parts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaDocument3 pagesParts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Homework ManuelDocument4 pagesHomework ManuelFlorasela J. Fernández V.No ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument26 pagesDiscussionCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- Mang, Normal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMang, Normal PhysiologyThartea RokhumNo ratings yet
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDocument3 pagesReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Notes SLDocument1 pageCirculatory System Notes SLRathna PalaniappanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Lecture 1 2Document20 pagesScience 9 Lecture 1 2msraul917No ratings yet
- Ciculatory SystemDocument21 pagesCiculatory SystemSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument1 pageThe Heart and Blood VesselsozmanNo ratings yet
- Iii. Anatomy and Physiology The Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsDocument7 pagesIii. Anatomy and Physiology The Cardiovascular System: Arteries Veinskian5No ratings yet
- 0.8 Sec. The HeartDocument9 pages0.8 Sec. The Heartmary lee gumapacNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: The Body's Transport SystemDocument17 pagesCirculatory System: The Body's Transport SystemnoviNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNo ratings yet
- Activity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory System (CAARE)Document8 pagesActivity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory System (CAARE)Fheby ValerieNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1qprelimsDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 1qprelimsAlyanna SagcalNo ratings yet
- How The Heart WorksDocument2 pagesHow The Heart WorksNeel GamiNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesScience Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemMaribeth Villanueva100% (2)
- Heart and LungsDocument13 pagesHeart and LungsIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemJheyrick Casipe BaliguatNo ratings yet
- Vascular or Circulatory System RemhilDocument9 pagesVascular or Circulatory System Remhilremhil malicdemNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument37 pagesCardiovascular System - The HeartCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- 025735919Document3 pages025735919Vinz JaneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular - SummaryDocument18 pagesCardiovascular - Summarys.tinaja.marieantonetteNo ratings yet
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 pagesHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument3 pagesCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureDocument5 pagesVi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolDocument52 pagesCirculatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Human Heart StructureDocument9 pagesHuman Heart StructureSayali Patil100% (2)
- SIN Module IDocument4 pagesSIN Module IMeiane Ngojo MohamadNo ratings yet
- Cardio SystemDocument3 pagesCardio SystemAlowee AbelloNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument16 pagesCardiovascular SystemMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology PDFMelanie PrinceNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Action Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Action Rationale EvaluationJames Czar FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Clinico Diagnostic Studies On Traumatic Reticulopericarditis in Cattle - A Review of 56 CasesDocument11 pagesClinico Diagnostic Studies On Traumatic Reticulopericarditis in Cattle - A Review of 56 CasesSasikala KaliapanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and MidwiferyDocument13 pagesA Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and Midwiferyhsiria100% (2)
- Medical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanDocument5 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanNoreen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal CordDocument32 pagesBlood Supply of Brain and Spinal CordShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN KASUS - Stroke IskemikDocument22 pagesLAPORAN KASUS - Stroke IskemikMikhaNo ratings yet
- Onyx Frontier Physician Brochure A RevDocument8 pagesOnyx Frontier Physician Brochure A RevRedhwan Abdullah qaid AlshubiNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Structured Education Toolkit FinalDocument39 pagesStructured Education Toolkit Finaldoni spotifyNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of Diseases and DisordersDocument39 pagesPrevention and Control of Diseases and DisordersAprille Maye CayogNo ratings yet
- Vol 22 No 1 NeurologyDocument26 pagesVol 22 No 1 NeurologyVijay JainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OSPEDocument61 pagesAnatomy OSPEMusfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Oropharynx PPT VigneshDocument39 pagesOropharynx PPT VigneshsakthimuruganaravindNo ratings yet
- SDL DL BrochureDocument2 pagesSDL DL BrochureNanda Nabilah UbayNo ratings yet
- Recall 20-21 JunyDocument131 pagesRecall 20-21 JunyNicole VinnikNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269Document6 pages1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269KishoreNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- 345 - Hematology Physiology) PolycythemiasDocument3 pages345 - Hematology Physiology) PolycythemiasAro DanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SytemDocument56 pagesCardiovascular SytemlindapramusintaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Textbook of Critical Care PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Textbook of Critical Care PDFcharlotte.heckert523100% (29)
- Human Body Systems Essential VocabularyDocument6 pagesHuman Body Systems Essential Vocabularyapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Ventricular Tachycardia in The Ischemic HeartDocument57 pagesVentricular Tachycardia in The Ischemic Heartusfcards100% (3)
- Fccs - ShockDocument27 pagesFccs - ShockyuiflashNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Coagulation ObjectivesDocument14 pagesDrugs Affecting Coagulation ObjectiveslouradelNo ratings yet
- Thoracic IncisionsDocument10 pagesThoracic IncisionsRadioputro WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Visual Aid Suggested Detailing Story - 221229 - 093101Document26 pages2022 Visual Aid Suggested Detailing Story - 221229 - 093101sharma ramNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry: Presented By: Haya Mansour SLLE Exam 2022Document61 pagesClinical Chemistry: Presented By: Haya Mansour SLLE Exam 2022apdlh 99No ratings yet
Graphic Organizer
Graphic Organizer
Uploaded by
Kenshin Medina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views1 pageThe circulatory and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen and remove carbon dioxide throughout the body. The circulatory system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs through the arteries and returns deoxygenated blood to the lungs through veins. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, throat, lungs, and diaphragm. It brings air in through the nose and mouth, passes it through the throat and trachea into the lungs where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Original Description:
GO
Original Title
GRAPHIC ORGANIZER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe circulatory and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen and remove carbon dioxide throughout the body. The circulatory system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs through the arteries and returns deoxygenated blood to the lungs through veins. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, throat, lungs, and diaphragm. It brings air in through the nose and mouth, passes it through the throat and trachea into the lungs where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views1 pageGraphic Organizer
Graphic Organizer
Uploaded by
Kenshin MedinaThe circulatory and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen and remove carbon dioxide throughout the body. The circulatory system includes the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. The heart pumps oxygenated blood received from the lungs through the arteries and returns deoxygenated blood to the lungs through veins. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, throat, lungs, and diaphragm. It brings air in through the nose and mouth, passes it through the throat and trachea into the lungs where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves through tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Medina, Kaizen Drei M.
TAKING CARE OF RESPIRATORY AND
IX- LUIS AGUADO
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Blood vessels Mouth and nose: Openings that pull air from
outside your body into your respiratory system.
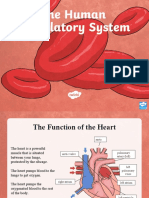
Arteries The heart
Blood vessels have a
Sinuses: Hollow areas between the bones in your
head that help regulate the temperature and
Oxygenated blood is range of different sizes The heart pumps blood around the body.
humidity of the air you inhale.
pumped from the heart and structures, It sits inside the chest, in front of the lungs
depending on their role and slightly to the left side. The heart is Pharynx (throat): Tube that delivers air from your
along arteries, which are
in the body. actually a double pump made up of four mouth and nose to the trachea (windpipe).
muscular. Arteries divide
chambers, with the flow of blood going in Trachea: Passage connecting your throat and lungs.
like tree branches until one direction due to the presence of the
they are slender. The heart valves. The contractions of the Bronchial tubes: Tubes at the bottom of your
largest artery is the aorta, chambers make the sound of heartbeats. windpipe that connect into each lung.
which connects to the Lungs: Two organs that remove oxygen from the air
heart and picks up The right side of the heart
and pass it into your blood.
oxygenated blood from the
left ventricle. The only The right upper chamber (atrium) takes in From your lungs, your bloodstream delivers oxygen to all your
artery that picks up deoxygenated blood that is loaded with organs and other tissues. Muscles and bones help move the air you
deoxygenated blood is the carbon dioxide. The blood is squeezed down inhale into and out of your lungs. Some of the bones and muscles in
pulmonary artery, which into the right lower chamber (ventricle) and the respiratory system include your:
runs between the heart taken by an artery to the lungs where the
and lungs. carbon dioxide is replaced with oxygen.
Diaphragm: Muscle that helps your lungs pull in air and
Capillaries The left side of the heart push it out.
Ribs: Bones that surround and protect your lungs and
The arteries eventually The oxygenated blood travels back to heart.
divide down into the smallest the heart, this time entering the left
blood vessel, the capillary. upper chamber (atrium). It is pumped
Capillaries are so small that into the left lower chamber (ventricle) When you breathe out, your blood carries carbon dioxide and other
blood cells can only move and then into the aorta (an artery). The waste out of the body. Other components that work with the lungs
through them one at a time. blood starts its journey around the body and blood vessels include:
Oxygen and food nutrients once more.
pass from these capillaries Veins
to the cells. Capillaries are
also connected to veins, so Veins have one-way valves instead of Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of
wastes from the cells can be muscles, to stop blood from running oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place.
transferred to the blood. back the wrong way. Generally, veins Bronchioles: Small branches of the bronchial tubes that lead
carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the alveoli.
Blood pressure
to the heart, where it can be sent to the Capillaries: Blood vessels in the alveoli walls that move
lungs. The exception is the network of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
pulmonary veins, which take oxygenated Lung lobes: Sections of the lungs — three lobes in the right
Blood pressure refers to the amount of
blood from the lungs to the heart. lung and two in the left lung.
pressure inside the circulatory system as the
blood is pumped around. Pleura: Thin sacs that surround each lung lobe and separate
your lungs from the chest wall.
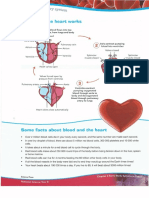
Some common problems of the circulatory system include:
Some of the other components of your respiratory system include:
Aneurysm – a weak spot in the wall of an artery
Atherosclerosis – a narrowing of the arteries caused by plaque deposits Cilia: Tiny hairs that move in a wave-like motion to filter dust and other irritants out of your
airways.
Heart disease – lack of blood supply to the heart because of narrowed
arteries Epiglottis: Tissue flap at the entrance to the trachea that closes when you swallow to keep
High blood pressure – can be caused by obesity (among other things) food and liquids out of your airway.
Varicose veins – problems with the valves that stop blood from running Larynx (voice box): Hollow organ that allows you to talk and make sounds when air moves in
backwards. and out.
You might also like
- Surgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery Clinical Questions and Answers 3rd Edition 2022 PDFDocument589 pagesSurgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery Clinical Questions and Answers 3rd Edition 2022 PDFdat100% (1)
- 2023 - Ent Vivas FrcsDocument331 pages2023 - Ent Vivas FrcsPG ORL PUCENo ratings yet
- Sci9Q1M1 - Rev-Bait-it 2Document4 pagesSci9Q1M1 - Rev-Bait-it 2Realyn Delana OguisNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document10 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1RUTH PIANGNo ratings yet
- VIII Biology HO 4Document8 pagesVIII Biology HO 4anousha1488No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Circulatory SystemCes GarceraNo ratings yet
- Superior Vena Cava: Right AtriumDocument3 pagesSuperior Vena Cava: Right AtriumMary SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Science Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesScience Respiratory and Circulatory SystemElisha Kate AmitNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemJpaw Kidman100% (1)
- Reviewer in Science 9..Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 9..nanami's ChildNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio MC1Document12 pagesAnaphysio MC1KRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- t2 S 427 Year 6 Human Body Circulatory System Lesson Teaching Powerpoint Ver 7Document8 pagest2 S 427 Year 6 Human Body Circulatory System Lesson Teaching Powerpoint Ver 7AyselNo ratings yet
- Function and Structure of Heart and LungsDocument2 pagesFunction and Structure of Heart and LungsClaChristinaNo ratings yet
- VisibleBody Blood VesselsDocument20 pagesVisibleBody Blood VesselscascaveletteNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyDocument20 pagesBlood Vessels: Blood Vessels Are How Blood Travels Through The BodyRoger RonconiNo ratings yet
- 6 - The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages6 - The Cardiovascular SystemKolea 2003No ratings yet
- Science 1.1Document42 pagesScience 1.1Ina SuzaraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemSakshi NijhawanNo ratings yet
- Heart Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesHeart Cardiovascular SystemKim Nae A. MasucolNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument1 pageHeartPrince JenovaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemIra Lavigne De VillaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemJovie Erma AtonNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions: AnswersDocument7 pagesGuide Questions: AnswersPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument87 pagesCare of Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsQueen Jyil100% (1)
- Parts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaDocument3 pagesParts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNo ratings yet
- Homework ManuelDocument4 pagesHomework ManuelFlorasela J. Fernández V.No ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument26 pagesDiscussionCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- Mang, Normal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMang, Normal PhysiologyThartea RokhumNo ratings yet
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDocument3 pagesReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Notes SLDocument1 pageCirculatory System Notes SLRathna PalaniappanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Lecture 1 2Document20 pagesScience 9 Lecture 1 2msraul917No ratings yet
- Ciculatory SystemDocument21 pagesCiculatory SystemSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- The Heart and Blood VesselsDocument1 pageThe Heart and Blood VesselsozmanNo ratings yet
- Iii. Anatomy and Physiology The Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsDocument7 pagesIii. Anatomy and Physiology The Cardiovascular System: Arteries Veinskian5No ratings yet
- 0.8 Sec. The HeartDocument9 pages0.8 Sec. The Heartmary lee gumapacNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: The Body's Transport SystemDocument17 pagesCirculatory System: The Body's Transport SystemnoviNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNo ratings yet
- Activity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory System (CAARE)Document8 pagesActivity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory System (CAARE)Fheby ValerieNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1qprelimsDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer 1qprelimsAlyanna SagcalNo ratings yet
- How The Heart WorksDocument2 pagesHow The Heart WorksNeel GamiNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesScience Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemMaribeth Villanueva100% (2)
- Heart and LungsDocument13 pagesHeart and LungsIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory SystemJheyrick Casipe BaliguatNo ratings yet
- Vascular or Circulatory System RemhilDocument9 pagesVascular or Circulatory System Remhilremhil malicdemNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument37 pagesCardiovascular System - The HeartCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- 025735919Document3 pages025735919Vinz JaneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular - SummaryDocument18 pagesCardiovascular - Summarys.tinaja.marieantonetteNo ratings yet
- Heart and CirculationDocument12 pagesHeart and CirculationEizelle Zabyne VerzosaNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument3 pagesCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureDocument5 pagesVi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Circulatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolDocument52 pagesCirculatory / Transport System: For 1O Grade Igcse Semesta Bilingual Boarding SchoolThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Human Heart StructureDocument9 pagesHuman Heart StructureSayali Patil100% (2)
- SIN Module IDocument4 pagesSIN Module IMeiane Ngojo MohamadNo ratings yet
- Cardio SystemDocument3 pagesCardio SystemAlowee AbelloNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument16 pagesCardiovascular SystemMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology PDFMelanie PrinceNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Action Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Action Rationale EvaluationJames Czar FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Clinico Diagnostic Studies On Traumatic Reticulopericarditis in Cattle - A Review of 56 CasesDocument11 pagesClinico Diagnostic Studies On Traumatic Reticulopericarditis in Cattle - A Review of 56 CasesSasikala KaliapanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and MidwiferyDocument13 pagesA Case Study of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVD) : School of Nursing and Midwiferyhsiria100% (2)
- Medical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanDocument5 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanNoreen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal CordDocument32 pagesBlood Supply of Brain and Spinal CordShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN KASUS - Stroke IskemikDocument22 pagesLAPORAN KASUS - Stroke IskemikMikhaNo ratings yet
- Onyx Frontier Physician Brochure A RevDocument8 pagesOnyx Frontier Physician Brochure A RevRedhwan Abdullah qaid AlshubiNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Structured Education Toolkit FinalDocument39 pagesStructured Education Toolkit Finaldoni spotifyNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of Diseases and DisordersDocument39 pagesPrevention and Control of Diseases and DisordersAprille Maye CayogNo ratings yet
- Vol 22 No 1 NeurologyDocument26 pagesVol 22 No 1 NeurologyVijay JainNo ratings yet
- Anatomy OSPEDocument61 pagesAnatomy OSPEMusfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Oropharynx PPT VigneshDocument39 pagesOropharynx PPT VigneshsakthimuruganaravindNo ratings yet
- SDL DL BrochureDocument2 pagesSDL DL BrochureNanda Nabilah UbayNo ratings yet
- Recall 20-21 JunyDocument131 pagesRecall 20-21 JunyNicole VinnikNo ratings yet
- 1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269Document6 pages1-Diabetes Package - PO2693771771-269KishoreNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- 345 - Hematology Physiology) PolycythemiasDocument3 pages345 - Hematology Physiology) PolycythemiasAro DanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SytemDocument56 pagesCardiovascular SytemlindapramusintaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Textbook of Critical Care PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Textbook of Critical Care PDFcharlotte.heckert523100% (29)
- Human Body Systems Essential VocabularyDocument6 pagesHuman Body Systems Essential Vocabularyapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Ventricular Tachycardia in The Ischemic HeartDocument57 pagesVentricular Tachycardia in The Ischemic Heartusfcards100% (3)
- Fccs - ShockDocument27 pagesFccs - ShockyuiflashNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Coagulation ObjectivesDocument14 pagesDrugs Affecting Coagulation ObjectiveslouradelNo ratings yet
- Thoracic IncisionsDocument10 pagesThoracic IncisionsRadioputro WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Visual Aid Suggested Detailing Story - 221229 - 093101Document26 pages2022 Visual Aid Suggested Detailing Story - 221229 - 093101sharma ramNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry: Presented By: Haya Mansour SLLE Exam 2022Document61 pagesClinical Chemistry: Presented By: Haya Mansour SLLE Exam 2022apdlh 99No ratings yet