Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 14
CH 14
Uploaded by
JinHyung KimCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition CarlsonDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlsongainerhanukkah.zv28wx100% (29)
- Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N ButcherDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N Butcherforebodebelockjswp100% (49)
- Test Bank Abnormal Psychology 1st Edition Butcher PDFDocument60 pagesTest Bank Abnormal Psychology 1st Edition Butcher PDFRaiza BettinaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY (Carticiano) PDFDocument93 pagesINTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY (Carticiano) PDFJas John100% (2)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Quiz: The Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Quiz: The Biological Basis of Behaviorvadarsuperstar100% (1)
- PSY 101 Solved Quizs ComposedHuda ShahDocument14 pagesPSY 101 Solved Quizs ComposedHuda ShahMaya GeeNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy ManagementDocument76 pagesObstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy Managementphysio43100% (1)
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition CarlsonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlsonmarisgemma0j3vNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonPaula Smith100% (5)
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonDocument32 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonJoshuaGuerreropxmqg100% (41)
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1Document90 pagesPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1alicia100% (48)
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4Th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4Th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtommy.polkinghorn242100% (24)
- Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior 11th Edition by CarlsonDocument45 pagesTest Bank For Physiology of Behavior 11th Edition by CarlsonThomas White100% (31)
- Hooley 18e TB 114151617 Final-CombinedDocument201 pagesHooley 18e TB 114151617 Final-CombinedRUIJIE JiangNo ratings yet
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1Document36 pagesPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1jessicafinleytqspjcirof100% (33)
- 2021 Practice Test (Formative Assessment) Biological Psychology - Attempt ReviewDocument30 pages2021 Practice Test (Formative Assessment) Biological Psychology - Attempt ReviewMLNo ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument8 pagesGeneral InstructionsAbhishek PatilNo ratings yet
- PT 912 Anp 06 2018Document5 pagesPT 912 Anp 06 2018Arupkumar MeherNo ratings yet
- Dozois 5e Chapter01 TIFDocument32 pagesDozois 5e Chapter01 TIFrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Full Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9Th Edition Carlson Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument52 pagesFull Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9Th Edition Carlson Test Bank Online PDF All Chapterrebetombto100% (7)
- Physical Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood: Multiple ChoiceDocument28 pagesPhysical Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood: Multiple ChoiceTamarix76No ratings yet
- Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test BankDocument29 pagesFoundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test Bankxeniaeira98897% (38)
- Terminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)Document8 pagesTerminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)KES SCIENCE FYJC PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology Canadian 4th Edition Taylor Test BankDocument13 pagesHealth Psychology Canadian 4th Edition Taylor Test BankJosephWilliamsinaom100% (12)
- Exam Corner - Jan 2011 AnswersDocument4 pagesExam Corner - Jan 2011 Answersts8166No ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test BankDocument27 pagesAbnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test Bankisaacnorrisezwasfmtgi100% (34)
- Full Download Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N Butcher PDF Full ChapterDocument34 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N Butcher PDF Full Chapterpoleytallierbuj0cf100% (22)
- Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test BankDocument48 pagesAbnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test Bankxeniaeira988100% (19)
- Postreading Self Assessment and CME Test.23Document11 pagesPostreading Self Assessment and CME Test.23مجاهد إسماعيل حسن حسينNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Genetics 4th Edition Lynn B JordeDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Medical Genetics 4th Edition Lynn B Jorderoytuyenbau100% (1)
- Full Download Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test Bankextirper.unclean.xngl4100% (44)
- Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementDocument8 pagesChromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementReginaldNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Test Bank BN8e Selected 2021Document20 pagesCh07 Test Bank BN8e Selected 2021alzubairiyNo ratings yet
- Full Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5Th Edition Dozois Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument38 pagesFull Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5Th Edition Dozois Test Bank Online PDF All Chaptercatharfnechfttagonfan100% (5)
- Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition CarlsonDocument32 pagesTest Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition Carlsonchowryurduq0krhNo ratings yet
- Scientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test BankDocument66 pagesScientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test Bankbob joeNo ratings yet
- Ps 7Document8 pagesPs 7astaimanfNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition CarlsonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition Carlsonkempenoilsjuvbu100% (46)
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior, 10th Edition: Carlson All ChapterDocument55 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior, 10th Edition: Carlson All Chapterzyzomotesi100% (4)
- PendrinDocument157 pagesPendrinSatyakiranNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science II: I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science II: I. ObjectivesCarlo Sablaon CallosNo ratings yet
- Biology Science For Life With Physiology 4Th Edition Belk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesBiology Science For Life With Physiology 4Th Edition Belk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFCassieYangiosx100% (17)
- PHy 101 Solved MCQSDocument28 pagesPHy 101 Solved MCQSIྂqྂrྂaྂ MྂaྂhྂrྂoྂsྂhྂNo ratings yet
- Coursera Organ DonationDocument40 pagesCoursera Organ DonationQaphela MinenhleNo ratings yet
- 126Document16 pages126majedmalaeb66No ratings yet
- Reading QuizDocument5 pagesReading QuizMicah CookNo ratings yet
- Pathology Questions PDFDocument67 pagesPathology Questions PDFDhruva PatelNo ratings yet
- Ch5 TB PinelDocument31 pagesCh5 TB Pinelpixelpaisley12No ratings yet
- BHK 031Document13 pagesBHK 031FERNANDA CASTANEDA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition Feldman Test BankDocument30 pagesEssentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition Feldman Test BankEricFuentesfxgir100% (13)
- Dozois 5e Chapter04 TIFDocument30 pagesDozois 5e Chapter04 TIFrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Psychology SampQ WDocument25 pagesPsychology SampQ Wmicah deveralaNo ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2019 034974Document7 pagesBmjopen 2019 034974allyssa rahmadittaNo ratings yet
- Discovering Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics: Second EditionDocument8 pagesDiscovering Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics: Second EditionSuchetaNo ratings yet
- Class XII Biology (044) Theory Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument13 pagesClass XII Biology (044) Theory Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsAryanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 ExperimentDocument11 pagesWeek 4 ExperimentKomal KhanNo ratings yet
- Phelan3e Testbank ch01Document24 pagesPhelan3e Testbank ch01Ahmed Maher Al-maqtariNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach, 8th Edition, Dee Unglaub Silverthorn, All ChapterDocument64 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach, 8th Edition, Dee Unglaub Silverthorn, All Chapterusulliarnoob100% (8)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo ISBN 1259024644 9781259024641Document36 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo ISBN 1259024644 9781259024641JacobFergusonrdbm100% (29)
- Edition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo Isbn 1259024644 9781259024641Document36 pagesEdition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo Isbn 1259024644 9781259024641kevin.huerta226100% (22)
- Siddha Applied Science InstituteDocument4 pagesSiddha Applied Science InstituteLagin DranNo ratings yet
- MEMO - RV RTPCR - MergedDocument5 pagesMEMO - RV RTPCR - MergedMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Holistic Thinking and Partial ThinkingDocument9 pagesThe Difference Between Holistic Thinking and Partial ThinkingPRIME SABER TIU57% (14)
- GPDocument3 pagesGPYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Rhinology Fellowship Revised Dec 2021 McMasterDocument3 pagesRhinology Fellowship Revised Dec 2021 McMasterStanley SuhermanNo ratings yet
- HAAD Exam (25-12-2018)Document7 pagesHAAD Exam (25-12-2018)Anisha Mary ThomasNo ratings yet
- Venous ThromboembolismDocument11 pagesVenous ThromboembolismKrsna Navera100% (1)
- Homeless Deaths ReportDocument102 pagesHomeless Deaths ReportCapital Public RadioNo ratings yet
- Knee ReplacementDocument2 pagesKnee ReplacementpahumbleNo ratings yet
- Daniela GarciaDocument8 pagesDaniela GarciaSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris 2Document7 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris 2azizah LasimpalaNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument2 pagesHigh Risk PregnancysamitbisenNo ratings yet
- Cristine Jane Marie V. AritaoDocument3 pagesCristine Jane Marie V. AritaoCristine Jane Marie AritaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PedodonticsDocument27 pagesIntroduction of PedodonticsSudeep M. ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Hawaii Health Department Fines NextHealth $58K, Orders Company To Stop COVID-19 Testing InboxDocument4 pagesHawaii Health Department Fines NextHealth $58K, Orders Company To Stop COVID-19 Testing InboxHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet
- Moot Court BrochureDocument16 pagesMoot Court BrochureAkashNo ratings yet
- Folio KerjayaDocument38 pagesFolio KerjayaamiqisNo ratings yet
- Fatigue: What Is Anemia?Document3 pagesFatigue: What Is Anemia?Annapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in OncologyDocument2 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in OncologyThe American Occupational Therapy Association100% (1)
- Implementation of Pathogen Reduction Technology in The Manufacture of Blood Components in Blood Establishments Questions and Answers Draft Guidance For IndustryDocument14 pagesImplementation of Pathogen Reduction Technology in The Manufacture of Blood Components in Blood Establishments Questions and Answers Draft Guidance For Industrydrsapta manNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDocument7 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDard TongNo ratings yet
- Intro To PTDocument709 pagesIntro To PTShoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma and OsteoarthritisDocument17 pagesOsteosarcoma and OsteoarthritisCricelle Rose CobreNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Muskaan BindalNo ratings yet
- Kumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Document7 pagesKumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Karki KedarNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Clinical SupervisorDocument52 pagesThe Role of The Clinical SupervisorDwi NopriyantoNo ratings yet
- Consolidated HIV Guidelines 2020Document245 pagesConsolidated HIV Guidelines 2020Esther AumaNo ratings yet
- Rajsthan All Surgical Distributor Data ListDocument33 pagesRajsthan All Surgical Distributor Data ListcatalogueNo ratings yet
- Quality and Safety in Compounding Non-Sterile PreparationsDocument5 pagesQuality and Safety in Compounding Non-Sterile PreparationsPruessada DeeyingNo ratings yet
CH 14
CH 14
Uploaded by
JinHyung KimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 14
CH 14
Uploaded by
JinHyung KimCopyright:
Available Formats
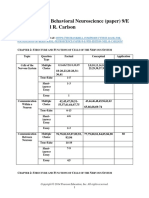
CHAPTER 14: NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
Topic Question Type Factual Conceptual Application
Tumors Multiple Choice 3,4,7-11,13 5,6 1,2,12
True-False 1-3
Short-Answer 1
Essay
Essay
Seizure Disorders Multiple Choice 18-23 14-17
True-False 4
Short-Answer 2
Essay
Essay
Cerebrovascular Multiple Choice 24-27,33,35 28,34 29-32
Accidents
True-False 5
Short-Answer 3,4
Essay
Essay 1
Disorders of Multiple Choice 36-47
Development
True-False 6-9
Short-Answer 5
Essay
Essay 2
Degenerative
Disorders Multiple Choice 48,50,52-58,61,68-73,75-78 49,512,63,64 59,60,62,74
True-False 10-15
Short-Answer 6
Essay
Essay 3,4
Disorders
Multiple 79,80,81,83 82,84
Caused by
Choice
Infectious
True-False 16
Diseases
Short-Answer 7,8
Essay
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
1
Essay
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
2
CHAPTER 14: NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
14.1 Multiple Choice
1) The seizure disorder suffered by Mrs R. in the chapter prologue was treated by
A) administration of tPa.
B) removal of a benign tumor from her brain.
C) administration of antiseizure medication.
D) removal of a malignant tumor from her brain.
E) electrical stimulation of her subthalamus.
Answer: B
Rationale: The seizure disorder suffered by Mrs R. in the chapter prologue was treated by removal of a
benign tumor from her brain.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 363 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
2) In the chapter prologue, Mrs. R. suffered from ________ brought on by ________.
A) tinnitus; a genetic disorder
B) seizures; alcoholism
C) seizures; a brain tumor
D) impaired vision; years of reading under low-light conditions
E) headaches; excessive caffeine intake
Answer: C
Rationale: In the chapter prologue, Mrs. R. suffered from seizures brought on by a brain tumor.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 363 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
3) Benign tumors (양성 종양)
A) spread rapidly through the process of metastasis.
B) are difficult to remove from brain tissue.
C) do not require treatment.
D) are likely to be fatal in very old persons.
E) have a distinct border.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 363 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
4) A ________ is a mass of cells without useful function that shows uncontrolled growth.
A) tumor
B) cyst
C) nodule
D) gland
E) polyp
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 363 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
5) Which of the following is not a characteristic of a benign tumor?
A) The tumor is harmless.
B) The tumor is encapsulated.
C) The tumor cells do not perform a useful function.
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
3
D) The tumor grows by infiltrating other brain regions.
베나인은 distinct border 있어서 그런가봄. 인필트레이션은 malignant tumor의 특징임.
E) The tumor has a distinct border.
Answer: D
Rationale: A benign tumor does not grow by infiltrating other brain regions.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 363 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
6) A key reason as to why malignant(악성) tumors are deadly is that such tumors
A) can compress liver and pancreatic cells.
B) can grow quickly.
C) are difficult to remove from gut
D) destroy other brain cells through apoptosis.
E) secrete toxic acids
Answer: B
Rationale: A key reason as to why malignant tumors are deadly is that such tumors can grow quickly.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 363-364 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
7) Which of the following tumors is most dangerous?
A) benign
B) gliomas
C) angiomas
D) blastocytes
E) neningioma
Answer: B
Rationale: The most dangerous tumor is a glioma.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
8) The process through which malignant brain tumors directly damage neurons is
A) the induction of hemorrhage.
B) excessive release of oxygen radicals.
C) compression and infiltration(압축과 침투).
D) the induction of seizure activity.
E) overstimulation of neuron activity.
Answer: C
Rationale: The process through which malignant brain tumors directly damage neurons is compression
and infiltration.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
9) A meningioma is a ________ tumor that arises from ________.
A) benign; astrocytes
B) benign; Schwann cells
C) malignant; Schwann cells
D) benign; dural or arachnoid cells 듀랄의 오그리마
E) malignant; dural or arachnoid cells
Answer: D
Rationale: A meningioma is a benign tumor that arises dural or arachnoid cells.
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
4
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
10) A tumor of the ________ type is dangerous because it ________.
A) neuroma; can compress neural tissue
B) benign; is malignant and fast growing
C) malignant; has an encapsulated border
D) glioma; is malignant and fast growing
E) benign; induced seizure activity.
Answer: D
Rationale: A tumor of the glioma type is dangerous because it is malignant and fast growing.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
11) Which of the following cells CANNOT give rise to a brain tumor?
A) meningeal cells
B) neurons
C) astrocytes
D) glial cells
E) ependymal cells
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
12) A tumor of the ________ type was removed from the brain of Mrs. R.
A) malignant
B) glioma
C) angioma
D) blastocyte
E) meningioma
Answer: E
Rationale: A tumor of the meningioma type was removed from the brain of Mrs. R.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
13) ________ involve(s) periodic bouts of overactivity of cerebral neurons.
A) Dementia
B) Metastases
C) Parkinson's disease
D) Seizure disorders
E) Strokes
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
14) Seizures that result in uncontrollable muscle contractions involve the
A) motor system.
B) hypothalamus.
C) cerebellum.
D) limbic system.
E) parietal cortex.
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
5
Answer: A
Rationale: Seizures that result in uncontrollable muscle contractions involve the motor system.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
15) Unlike other seizure disorders, a grand mal seizure
A) can produce convulsions, but not unconsciousness.
B) is an example of a simple partial seizure disorder.
C) is the most severe form of seizure disorder.
D) is usually localized to a small focus within the brain.
E) can dim consciousness, but does not produce motor convulsions.
Answer: C
Rationale: Unlike other seizure disorders, a grand mal seizure is the most severe form of seizure disorder.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 365 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
6
16) The distinction between ________ and ________ seizures relates to whether these originate from a
definite focus within the brain.
A) generalized; complex
B) simple; partial
C) simple; complex
D) partial; generalized
E) complex; epileptic
Answer: D
Rationale: The distinction between partial and generalized seizures relates to whether these originate
from a definite focus within the brain.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 365 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
17) The key distinction between ________ and ________ seizures relates to whether these involve most
of the brain.
A) simple; complex
B) complex; epileptic
C) generalized; other types of
D) partial; generalized
E) simple; partial
Answer: C
Rationale: The key distinction between generalized and other types of seizures relates to whether these
involve most of the brain.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 365 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 3.1
18) The initial phase of a grand mal seizure is termed the ________ and is denoted by ________.
A) clonic phase; relaxation of all muscles
B) tonic phase; rhythmic jerking movements of the body
C) aural phase; perception of music
D) tonic phase; forceful contraction of all muscles
E) aural phase; release of glycine within the spinal cord
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 365 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
19) ________ is the most common of the seizure disorders noted in children.
A) Petit mal disorder
B) Coma disorder
C) Simple partial seizure disorder
D) Absence
E) Status epilepticus
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 366 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
20) ________ is a condition in which a patient shows a series of seizures, but does not regain
consciousness.
A) Petit mal disorder
B) Coma disorder
C) Simple partial seizure disorder
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
7
D) Absence disorder
E) Status epilepticus. 의식이란 status가 돌아오지않으니까
Answer: E
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 366 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
21) What is the most common cause of seizures?
A) drug overdose
B) sudden withdrawal from barbiturates
C) scarring(흉터) produced by damage within the brain
D) exposure to toxic chemicals
E) long-term use of sleeping pills
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 366 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
22) An alcoholic who abruptly stops drinking may experience a seizure because
A) of a sudden release from the inhibiting effects of alcohol.
B) this abrupt withdrawal excites GABA receptors.
C) alcohol withdrawal induces hyposensitivity of glutamate receptors.
D) withdrawal leads to brain damage.
E) long-term alcohol abuse causes brain damage.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 366 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 3.1
23) Anticonvulsant drugs work by
A) directly inactivating motor neurons.
B) facilitating acetylcholine receptor sites.
C) increasing the effectiveness of inhibitory synapses in the brain.
D) blocking the activity of GABA sites in the brain.
E) causing the release of glutamate in brain.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 366 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
24) Another term for cerebrovascular accident is
A) apoptosis.
B) tumor growth.
C) epilepsy.
D) stroke.
E) seizure disorder.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 367 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
25) Obstructive strokes can be caused by
A) pressure from weakened blood vessels.
B) intracranial bleeding.
C) thrombi or emboli.
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
8
D) malformed blood vessels.
E) the weakening of blood vessels by toxic levels of glutamate.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 367 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
9
26) Which of the following will produce a hemorrhagic stroke?
A) bleeding within the brain
B) prevention of blood flow
C) the formation of an embolus in the lungs
D) the passage of a thrombus into the brain
E) release of glycine in brain.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 367 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
27) Which of the following statements about an embolus(색전) is correct?
A) It is composed of debris that travels in blood and eventually lodges in an artery.
B) It can consist of pieces of thrombi.
C) It can be caused by infection within the wall of the heart.
D) It is due to pressure exerted by a tumor.
E) An embolus secretes acids which destroy neurons.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 367 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
28) Which of the following is true regarding strokes?
A) Hemorrhagic strokes are associated with bleeding within the heart.
B) Ischemic strokes are related to excessive vasodilation of the brain blood vessels.
C) The risk of stroke increases with age.
D) Hemorrhagic strokes are associated with tumor compression of nerve tissue.
E) Ischemic stroke will eventually produce a hemorrhagic stroke.
Answer: C
Rationale: The risk of stroke increases with age.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 367 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
29) A key treatment for stroke involving weak and malformed blood vessels involves
A) medication to lower blood pressure.
B) administration of antibiotics.
C) administration of demoteplase.
D) brain surgery to seal off(봉인하다) the faulty vessels.
E) medication that speeds up the formation of blood clots.
Answer: D
Rationale: A key treatment for stroke involving weak and malformed blood vessels involves brain
surgery to seal off the faulty vessels.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 367 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
30) A key treatment for stroke caused by a thrombus involves
A) medication to lower blood pressure.
B) administration of a drug that dissolves clots.
C) administration of demoteplase.
D) brain surgery to seal off the faulty vessels.
E) medication that speeds up the formation of blood clots.
Answer: B
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
10
Rationale: A key treatment for stroke caused by a thrombus involves administration of a drug that
dissolves clots.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 368 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.1 APA 3.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
11
31) The death of neurons following a stroke is caused by
A) over-stimulation of nerve cells by abnormally high levels of glutamate.
B) neuronal firing produced by compression.
C) interruption of glycogen delivery to the cell.
D) enhanced release of the inhibitory transmitter GABA.
E) loss of oxygen radicals.
Answer: A
Rationale: The death of neurons following a stroke is caused by over-stimulation of nerve cells by
abnormally high levels of glutamate.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 368 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
32) Which of the following represents a potential therapy for stroke?
A) drugs that promote inflammatory reactions
B) drugs that inactivate GABA receptors
C) drugs that block glutamate receptors / 스트로크가 글루타밋으로 overstimulation하니까
막아버리는거.
D) introduction of free radicals into the affected brain region
E) drugs that excite glutamate receptors
Answer: C
Rationale: Drugs that block glutamate receptors represent a potential therapy for stroke.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 368 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 3.1
33) Which of the following represents a therapy for non-hemorrhagic ischemic stroke?
A) drugs that activate GABA receptors
B) drugs that block glutamate receptors
C) drugs that block inflammatory reactions
D) tPa
E) the anticoagulant desmoteplase
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 368 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
34) The impact of ________ within the internal carotid artery is serious because this artery ________.
A) tPa; supplies blood to the gut
B) neurofibrillary tangles; supplies blood to the heart
C) atherosclerotic plaque; supplies blood to the brain
D) tPa; absorbs CSF from the brain
E) atherosclerotic plaque; supplies blood to the gut
Answer: C
Rationale: The impact of atherosclerotic plaque within the internal carotid artery is serious because this
supplies blood to the brain.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 369 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
35) Which of the following is a risk factor for stroke?
A) stress
B) low blood pressure
C) high blood levels of cholesterol
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
12
D) marijuana smoking
E).yoga
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 368-369 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 3.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
13
36) What causes the impaired fetal development induced by rubella?
A) The virus induces key cells to form a 23rd chromosome.
B) toxins produced by the rubella virus 루벨라는 루벨라 바이러스지.
C) alteration of chromosome number by the virus
D) induction of an error of metabolism within key brain cells
E) deletion of key enzymes within the brain
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 371 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
37) A mother who contracts rubella during her pregnancy may deliver a child that suffers from
A) phenylketonuria.
B) fetal alcohol syndrome.
C) Moebius syndrome.
D) mental retardation.
E) Tay-Sachs syndrome.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 371 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
38) ________ is(are) a primary symptom or sign of fetal alcohol syndrome.
A) Grand mal seizures
B) Swelling of the brain
C) An immature immune system
D) Abnormal facial development 엄마가 술마시면 애 얼굴&retardation
E) Motor tics of the hands and arms
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 371 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
39) Fetal alcohol syndrome can result
A) from chronic paternal alcoholism.
B) from as little as a single drinking binge during a critical period of fetal development. 약간이라도.
C) from the combined effects of alcohol and other drugs.
D) only from chronic maternal alcoholism.
E) from a single exposure to a beer consumed by the mother.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 371 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
40) Phenylketonuria is caused by
A) an inherited lack of an enzyme.
B) neurofibrillary tangles.
C) toxic chemicals released by a virus.
D) accumulation of waste products in the brain.
E) prenatal exposure to rubella.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 372 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
14
41) Treatment for phenylketonuria consists of early diagnosis and
A) a diet low in thyroxine.
B) a complete blood transfusion at birth.
C) a shift to diet low in phenylalanine.
D) lifelong supplemental phenylalanine.
E) daily injections of the precursor of phenylalanine.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 372 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.1 APA 3.1
42) Tay-Sachs disease is characterized by
A) accumulation of waste products within brain neurons. / 다른 삭스도 쓰레기죠
B) damage to lysosomes contained within neurons.
C) interference with the chemical signals that control normal brain development.
D) faulty migration of cells to the cortex during development.
E) incomplete myelinization.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 372 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
43) The term congenital(선천적인) refers to
A) a condition present at birth.
B) the fact that a fetus has both male and female internal reproductive structures.
C) a neurological condition that appears during puberty.
D) a mismatch between gender identity and gender morphology.
E) a genetic metabolic error of the brain.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 372 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
44) Which of the following is NOT a congenital disorder?
A) phenylketonuria
B) galactosemia
C) Tay-Sachs disease
D) Down syndrome
E) Parkinson’s disease
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 372-373 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
45) Down syndrome is caused by
A) improper migration of brain cells during brain development.
B) an inherited faulty gene.
C) a genetic error in which a vital enzyme is missing in the brain.
D) the presence of an extra twenty-first chromosome.
E) obstetric difficulties at the time of birth.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 373 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
15
46) Abnormal microscopic structures develop in the brains of older persons with Down syndrome and
those suffering from
A) Tay-Sachs disease.
B) Alzheimer's disease.
C) Korsakoff's syndrome.
D) Parkinson's disease.
E) status epilepticus.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 373 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
47) People with Down syndrome
A) have brains that are approximately 10 percent lighter than those of normal people.
B) suffer from augmented activity of the frontal lobe.
C) often fail to learn to talk.
D) have no distinguishing physical characteristics.
E) hace an extra Y chromosome.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 373 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
48) The brain damage noted in a human who has contracted BSE ("Mad Cow Disease") is caused by a
A) type of protein known as a prion.
B) virus.
C) bacterium.
D) deficiency in blood levels of calcium.
E) kuru virus.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 373 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.2 APA 1.1
49) The disorder known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy results in
A) degeneration of the brain.
B) shrinking of the brain ventricles.
C) anomalies of the face.
D) nausea.
E) greater cortical weight.
Answer: A
Rationale: The disorder known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy results in degeneration of the
brain.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 374 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.3 APA 1.1
50) A disease condition is considered to be sporadic(산발적인) if it
A) occurs often.
B) is seen in many parts of the world.
C) is not caused by heredity(유전).
D) cannot be traced to a specific cause.
E) is easily treated using drugs.
Answer: C
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
16
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 374 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.3 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
17
51) Misfolded prion proteins may be toxic to brain cells because these
A) can be passed from neuron to neuron.
B) trigger apoptosis in a neuron.
C) overstimulate glutamate receptors.
D) block sodium currents through the neuron membrane.
E) damage lysosomes leading to neuron swelling.
Answer: B
Rationale: Misfolded prion proteins may be toxic to brain cells because these trigger apoptosis in a
neuron.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 375 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.3 APA 1.1
52) A common element for neurodegenerative diseases is
A) an infection related to the prion bacterium.
B) suppression of apoptosis within the brain.
C) the presence of misfolded proteins within brain cells.
D) the inactivation of caspase-12 within neurons.
E) the inactivation of caspase-12 within glia.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 375 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.3 APA 3.1
53) Which of the following is true of Parkinson's disease (PD)?
A) PD is a rare neurodegenerative syndrome.
B) Nigrostriatal neurons die in PD.
C) Most cases of PD are inherited..
D) Muscle flacidity is a PD symptom.
E) Early intervention can cure PD.
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 375-376 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
54) Tracing the cause of Parkinson's disease is difficult because PD is
A) an inherited disorder. .
B) can be caused by drugs of abuse such as caffeine.
C) an unrecognized infectious disorder.
D) can be caused by environmental toxins.
E) .is a sporadic disorder.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 376 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 3.1
55) Parkinson's disease has been traced to
A) overproduction of dopamine within the basal ganglia.
B) degeneration of dopamine neurons within the nigrostriatal system.
C) loss of cholinergic neurons within the frontal cortex.
D) overproduction of GABA within the caudate nucleus.
E) overactivation of serotonin neurons in the hippocampus.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 376 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
18
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
19
56) Abnormal or misfolded intracellular proteins are tagged by ________ molecules, which targets them
for destruction by the ________.
A) parkin; ubiquitin
B) α-synuclein; parkin
C) ubiquitin; proteasomes
D) parkin; Lewey bodies
E) ubiquitin; neurofilaments
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 376 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
57) ________ is caused by degeneration of dopamine-secreting neurons of the substantia nigra.
A) Multiple sclerosis
B) Parkinson's disease 파킨슨은 니그로~
C) Acute anterior poliomyelitis
D) Encephalitis
E) Dowen syndrome
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 375 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
58) Which of the following represents a current therapy for Parkinson's disease?
A) stereotaxically guided destruction of the internal division of the globus pallidus
B) administration of an immune factor against β-amyloid
C) administration of amphetamine or cocaine
D) stereotaxically guided destruction of the internal division of the primary motor cortex
E) administration of haloperidol
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 377 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 3.1
59) The standard drug treatment for Parkinson's disease is administration of
A) haloperidol.
B) belladonna.
C) L-DOPA.
D) apomorphine.
E) cocaine and amphetamine.
Answer: C
Rationale: The standard drug treatment for Parkinson's disease is administration of L-DOPA.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 377 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
60) Administration of ________ may prevent the further development of Parkinson's disease. .
A) L-DOPA
B) deprenyl
C) MPTP
D) L-DOPA
E) hydrogen peroxide
Answer: B
Rationale: Administration of deprenyl may prevent the further development of Parkinson's disease.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 377 Objective: Applied
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
20
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
21
61) Surgical removal of portions of the ________ can alleviate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
A) caudate nucleus
B) orbitofrontal cortex
C) putamen
D) basal ganglia
E) globus pallidus
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 377 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
62) ________ is a recent treatment 전기자극 for Parkinson's disease that allows patients to suppress their
motor symptoms..
A) Electrical stimulation of the primary motor region
B) Intracranial administration of the drug haloperidol
C) Administration of reserpine into the spinal cord
D) Deep electrical stimulation of the subthalamic region
E) Infusion of GABA into the locus coeruleus
Answer: D
Rationale: Deep electrical stimulation of the subthalamic region is a recent treatment for Parkinson's
disease that allows patients to suppress their motor symptoms.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 377 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.4 APA 2.1
63) Which of the following is true of Huntington's disease (HD)?
A) HD is characterized by a poverty of movement.
B) HD can be cured using pallidotomy.
C) People who develop HD at a younger age have shorter stretches of glutamine.
D) HD is a hereditary disorder involving chromosome 4.
E) HD involves degeneration of the mesolimbic DA system.
Answer: D
Rationale: HD is a hereditary disorder involving chromosome 4.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 378 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
64) Parkinson's disease ________, but Huntington's disease ________.
A) is characterized by a poverty of movement; is characterized by uncontrollable movement
파킨슨은 못 움직이고.. 헌팅턴은 통제할 수 없는 움직임..
B) cannot be controlled; can be cured using pallidotomy
C) is a hereditary disorder; does not usually have genetic origins
D) usually occurs in the twenties and thirties; almost always occurs in the fifties and sixties
E) can be cured with drug treatment or surgery; can only be controlled
Answer: A
Rationale: Parkinson's disease is characterized by a poverty of movement, but Huntington's disease is
characterized by uncontrollable movement.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 376,378 Objective: Conceptual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
65) A common treatment for Huntington's disease is
A) L-DOPA.
B) stereotaxic removal of the putamen.
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
22
C) avoiding alcohol during pregnancy.
D) electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus.
E) There is no current treatment for this disorder.
Answer: E
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 379 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
23
66) ________ is a rare motor disorder is caused by a defective gene on chromosome 4.
A) Phenylketonuria
B) Huntington's disease 헌팅턴은 4번 유전자.
C) Tay-Sachs disease
D) Rabies
E) Alzheimer's disease
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 379 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
67) The first signs of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease involve loss of
A) neurons involved in the synthesis of nitrous oxide.
B) dopamine-secreting neurons of the nigrostriatal system.
C) neurons involved in glucose metabolism.
D) GABAergic neurons of the putamen. G다음이 H니까 가바가 H의 first sign이야.
E) cholinergic neurons in the pons.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 379 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.4 APA 1.1
68) The term dementia refers to
A) impaired cell functioning caused by viral toxins.
B) deterioration of intellectual abilities caused by an organic brain disorder.
C) the appearance of hallucinations and delusions.
D) demyelinization by autoimmune responses.
E) loss of neurons in the cerebral cortex and cells surrounding the third ventricle.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 379 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
69) The memory deficit noted in Alzheimer's disease involves
A) loss of spiny neurons in the putamen.
B) a form of retrograde amnesia.
C) anterograde amnesia similar to that of Korsakoff's syndrome. 암네시아.
D) loss of dopaminergic cells with the striatum.
E) a severe degeneration of the parietal cortex.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 379 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
70) An example of an early symptom of Alzheimer's disease is
A) difficulty in remembering appointments.
B) an inability to rise from bed in the morning.
C) mood swings.
D) trembling of the hands and feet.
E) muscle stiffness.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 380 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
24
71) Dying neurons that contain accumulations of amyloid and twisted protein filaments are called
A) neurofibrillary tangles. / 트위스티드니까 탱글스.
B) neuritic plaques.
C) free radicals.
D) beta amyloid precursor proteins.
E) amyloid plaques.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 380 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
72) A critical intracellular trigger for the development of Alzheimer's disease is
A) overproduction of the short form of the β-amyloid protein.
B) reduced amounts of the tau protein in brain cells.
C) overproduction of the long form of the β-amyloid protein.
D) an unfolding of the long form of the β-amyloid protein.
E) induction of apoptosis within hippocampal neurons.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 380 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
73) Which of the following is true about Alzheimer's disease (AD)?
A) Opiate exposure is a cause of AD.
B) Early detection is critical for arresting the progress of AD. .
C) Most forms of AD may be hereditary.
D) The disease may be treated by blocking the formation of β-amyloid.
파킨슨은 L-DOPA. 알츠하이머는 B Amyloid
E) The disease is congenital.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 380-381 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
74) A promising approach for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease involves
A) an antagonist of glutamate receptors in brain.
B) infusion of L-DOPA into the brain ventricles.
C) a drug that blocks the immune system.
D) a vaccine that passively stimulates the immune system to destroy β-amyloid.
E) the use of the opiate MPTP.
Answer: D
Rationale: A promising approach for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease involves a vaccine that
passively stimulates the immune system to destroy β-amyloid.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 382 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.5 APA 3.1
75) Which of the following is NOT true of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)?
A) Most ALS cases are sporadic.
B) ALS is a degenerative disease.
C) The cause of death in ALS is failure of respiration.
D) Spinal cord and cranial motor neurons are destroyed in ALS.
E) ALS is caused by damage to Beta-amyloid in nerve cells. B는 알츠하이머다. 그렇게 외우자.
Answer: E
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
25
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 383 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
26
76) ________ is considered to be an autoimmune demyelinating disease.
A) Moebius syndrome
B) Alzheimer's disease
C) Multiple sclerosis / sclerosis라는 말 자체가 왠지 myelin을 깎는느낌
D) Parkinson's disease
E) Huntington's disease
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 383 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
77) Which of the following is true of multiple sclerosis (MS)?
A) MS is most likely to develop in a person over the age of 65.
B) The cortex is the target of MS.
C) MS is caused by misfolded prion proteins.
D) People who live close to the equator are most likely to develop MS.
E) MS is more common in people born during the late winter and early spring.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 383 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
78) An important cause of multiple sclerosis involves
A) a lack of an enzyme needed for myelinization.
B) the formation of neurofibrillary tangles.
C) the conversion of MPTP to MPP+.
D) damage to myelin induced by the person's immune system.
E) low levels of the β-amyloid protein.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 383 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.5 APA 1.1
79) The most common infectious diseases likely to produce neurological damage are ________ and
________.
A) AIDS; polio
B) poliomyelitis; AIDS
C) multiple sclerosis; Alzheimer's disease
D) encephalitis; meningitis
E) rabies; herpes simplex
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 385 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.6 APA 1.1
80) Acute anterior poliomyelitis is a(n)
A) form of viral encephalitis.
B) bacterial infection.
C) congenital disorder.
D) immune system disease.
E) degenerative disease.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 385 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.6 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
27
81) Rabies is a type of
A) hoof and mouth disease.
B) viral encephalitis.
C) autoimmune disorder.
D) bacterial infection.
E) disorder related to environmental toxins.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 385 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.6 APA 1.1
82) Having a stiff and painful neck is one of the most important symptoms of meningitis because this is
associated with
A) release of excitotoxins by astrocytes.
B) excessive pressure on the carotid artery.
C) painful stretching of inflamed meninges.
D) damage to the motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord.
E) damage to myelin.
Answer: C
Rationale: Having a stiff and painful neck is one of the most important symptoms of meningitis because
this is associated with painful stretching of inflamed meninges.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 386 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.6 APA 3.1
83) The most severe form of meningitis is
A) bacterial.
B) viral.
C) caused by the herpes simplex virus.
D) caused by the rabies virus.
E) associated with use of heroin.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 386 Objective: Factual
LO: 14.6 APA 1.1
84) An effective treatment for bacterial meningitis involves administration of
A) interferon β.
B) NMDA agonists.
C) antibiotics.
D) L-DOPA.
E) GABA antagonists.
Answer: C
Rationale: An effective treatment for bacterial meningitis involves administration of antibiotics.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 386 Objective: Applied
LO: 14.6 APA 1.1
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
28
14.2 True-False
1) Tumors that arise from glial cells are usually benign.
Answer: FALSE 그냥 외워
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364
2) Benign tumors have a distinct border.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364
3) Seizures that result in convulsion involve the motor system.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364
4) The most common cause of seizures is scarring of the brain.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 366
5) An embolus is a blood clot that obstructs a blood vessel.
Answer: FALSE embolus는 혈관이 아니라 동맥(artery)막음.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 367
6) A single drinking episode rarely results in fetal alcohol syndrome.
Answer: FALSE 한번만 마셔도 fetal alcohol syndrome
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 371
7) Phenylketonuria can be treated by placing an infant on a diet low in phenylalanine.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 372
8) Down syndrome is a congenital disorder.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 373
9) A disorder that one is born with is called a congenital disorder.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 373
10) A sporadic disease is both frequent and related to heredity.
Answer: FALSE 산발적인 질병은 heredity 아님.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 374
11) The standard treatment for Parkinson's disease is transplantation of fetal dopamine cells into caudate.
Answer: FALSE 파킨슨 치료는 L-DOPA
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 377
12) Parkinson's disease can be induced by drugs such as MPTP.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 376
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
29
13) Huntington's disease involves uncontrollable movements of the limbs.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 378
14) A key symptom of Huntington's disease is anterograde amnesia.
Answer: FALSE 암네시아는 알츠하이머였음. 아무것도 안보이는거지. 헌팅턴은 통제불가능한
움직임. 파킨슨은 못움직임.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 377-378
15) Huntington's disease is a sporadic disease.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 379
16) Interferon β treatment can reduce the symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 383
17) The most common source of encephalitis is a mosquito bite.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 385
14.3 Short-Answer Essay
1) Differentiate between a benign and a malignant tumor.
Answer: A benign tumor is harmless and has a distinct. A malignant tumor has no distinct border; it
harms patient through compression and infiltration.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 363-364
2) Explain the differences between partial and generalized seizures.
Answer: A partial seizure acts in the limited region of the brain. A generalized seizure can involve wide
area of the brain.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 364-365
3) Explain the differences between hemorrhagic and obstructive cerebrovascular accidents. What are
common causes of each?
Answer: Hemorrhagic strokes are caused by bleeding within the brain related to a malformed blood vessel
or a high blood pressure. Obstructive cerebrovascular accidents are caused by thrombi or emboli.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 367-368
4) Explain what causes neuronal death when the blood supply to a region of the brain is interrupted.
Answer: Interruption of blood flow depletes the region’s oxygen and glucose. This leads to release of
glutamate, and cells overstimulated by glutamate die.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 368
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
30
5) What causes fetal alcohol syndrome? What are the symptoms of this disorder?
Answer: Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is caused by consumption of alcohol by a mother during
pregnancy. The symptoms are mental retardation, and abnormal facial development.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 371
6) Explain the significance of prions for neurological disorders.
Answer: Prions are "protein infectious agents." Prions are three-dimensional proteins that when misfolded
can accumulate in a neuron leading to toxicity and death of the cell. Prions cannot be destroyed with heat,
and can transmitted to others (transplantation of infected prion tissue).
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 374-375
7) Describe the causes and symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
Answer: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is infected by virus. The symptom is demyelination.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 383-384
8) What are the most common forms of viral encephalitis?
Answer: Infection of the brain by virus, mostly carried by mosquitos..
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 385-386
14.4 Essay
1) Describe the risk factors for stroke.
Answer : Major risk factors are smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 368-369
2) Describe the symptoms and causes of phenylketonuria and Tay-Sachs disease. How are these
diseases related to one another?
Answer: Each of these diseases is an example of an inherited metabolic disorder. Phenylketonuria is an
inherited lack of an enzyme that results in the buildup in blood of a toxic metabolite of phenylalanine
(resulting in severe mental retardation). During a critical period of postnatal brain development, the PKU
child is placed on a low phenylalanine diet. Tay-Sachs disease is a disease in which the lysosomes are
unable to destroy certain cellular waste products, which accumulate to toxic levels.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 372-373
3) Describe the etiology and symptoms of Huntington's disease and of Parkinson's disease. How do both
these diseases of the basal ganglia differ from one another?
Answer: Huntington's disease is caused by degeneration of the caudate nucleus and the putamen. It
causes uncontrolled movements. Parkinson's disease is associated with neurodegeneration of the
nigrostrial dopamine system and causes muscle rigidity.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 378-379
4) Describe the neuroanatomical changes that accompany Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. In
what way are these diseases similar to each other? How do they differ from one another?
Answer: Down syndrome is a congenital disorder involving profound mental retardation. The disorder is
induced by the presence of an additional twenty-first chromosome. After age 30, a Down's person will
experience brain atrophy and degeneration (a similarity to that of Alzheimer's disease). Alzheimer's
disease (AD) involves dementia, which first appears as a memory difficulty. AD is associated with severe
degeneration of brain structures such as the hippocampus and neurocortex. Both disorders are
characterized by abnormal intracellular abnormalities.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 373,379-381
Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
31
You might also like
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition CarlsonDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlsongainerhanukkah.zv28wx100% (29)
- Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N ButcherDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N Butcherforebodebelockjswp100% (49)
- Test Bank Abnormal Psychology 1st Edition Butcher PDFDocument60 pagesTest Bank Abnormal Psychology 1st Edition Butcher PDFRaiza BettinaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY (Carticiano) PDFDocument93 pagesINTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY (Carticiano) PDFJas John100% (2)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Quiz: The Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Quiz: The Biological Basis of Behaviorvadarsuperstar100% (1)
- PSY 101 Solved Quizs ComposedHuda ShahDocument14 pagesPSY 101 Solved Quizs ComposedHuda ShahMaya GeeNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy ManagementDocument76 pagesObstructive Disease of Lung and Physiotherapy Managementphysio43100% (1)
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition CarlsonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlsonmarisgemma0j3vNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonPaula Smith100% (5)
- Test Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonDocument32 pagesTest Bank For Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience Paper 9 e 9th Edition Neil R CarlsonJoshuaGuerreropxmqg100% (41)
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1Document90 pagesPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1alicia100% (48)
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4Th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4Th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtommy.polkinghorn242100% (24)
- Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior 11th Edition by CarlsonDocument45 pagesTest Bank For Physiology of Behavior 11th Edition by CarlsonThomas White100% (31)
- Hooley 18e TB 114151617 Final-CombinedDocument201 pagesHooley 18e TB 114151617 Final-CombinedRUIJIE JiangNo ratings yet
- Psychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1Document36 pagesPsychology From Inquiry To Understanding 4th Edition Lilienfeld Test Bank 1jessicafinleytqspjcirof100% (33)
- 2021 Practice Test (Formative Assessment) Biological Psychology - Attempt ReviewDocument30 pages2021 Practice Test (Formative Assessment) Biological Psychology - Attempt ReviewMLNo ratings yet
- General InstructionsDocument8 pagesGeneral InstructionsAbhishek PatilNo ratings yet
- PT 912 Anp 06 2018Document5 pagesPT 912 Anp 06 2018Arupkumar MeherNo ratings yet
- Dozois 5e Chapter01 TIFDocument32 pagesDozois 5e Chapter01 TIFrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Full Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9Th Edition Carlson Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument52 pagesFull Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9Th Edition Carlson Test Bank Online PDF All Chapterrebetombto100% (7)
- Physical Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood: Multiple ChoiceDocument28 pagesPhysical Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood: Multiple ChoiceTamarix76No ratings yet
- Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test BankDocument29 pagesFoundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test Bankxeniaeira98897% (38)
- Terminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)Document8 pagesTerminal Exam Answer Key (Biology)KES SCIENCE FYJC PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology Canadian 4th Edition Taylor Test BankDocument13 pagesHealth Psychology Canadian 4th Edition Taylor Test BankJosephWilliamsinaom100% (12)
- Exam Corner - Jan 2011 AnswersDocument4 pagesExam Corner - Jan 2011 Answersts8166No ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test BankDocument27 pagesAbnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test Bankisaacnorrisezwasfmtgi100% (34)
- Full Download Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N Butcher PDF Full ChapterDocument34 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Abnormal Psychology 15th Edition James N Butcher PDF Full Chapterpoleytallierbuj0cf100% (22)
- Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test BankDocument48 pagesAbnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5th Edition Dozois Test Bankxeniaeira988100% (19)
- Postreading Self Assessment and CME Test.23Document11 pagesPostreading Self Assessment and CME Test.23مجاهد إسماعيل حسن حسينNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Genetics 4th Edition Lynn B JordeDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Medical Genetics 4th Edition Lynn B Jorderoytuyenbau100% (1)
- Full Download Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Foundations of Behavioral Neuroscience 9th Edition Carlson Test Bankextirper.unclean.xngl4100% (44)
- Chromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementDocument8 pagesChromosome Mutations Variation in Number and ArrangementReginaldNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Test Bank BN8e Selected 2021Document20 pagesCh07 Test Bank BN8e Selected 2021alzubairiyNo ratings yet
- Full Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5Th Edition Dozois Test Bank Online PDF All ChapterDocument38 pagesFull Abnormal Psychology Perspectives Update Edition 5Th Edition Dozois Test Bank Online PDF All Chaptercatharfnechfttagonfan100% (5)
- Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition CarlsonDocument32 pagesTest Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition Carlsonchowryurduq0krhNo ratings yet
- Scientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test BankDocument66 pagesScientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test Bankbob joeNo ratings yet
- Ps 7Document8 pagesPs 7astaimanfNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition CarlsonDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Physiology of Behavior 10th Edition Carlsonkempenoilsjuvbu100% (46)
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior, 10th Edition: Carlson All ChapterDocument55 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Physiology of Behavior, 10th Edition: Carlson All Chapterzyzomotesi100% (4)
- PendrinDocument157 pagesPendrinSatyakiranNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science II: I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science II: I. ObjectivesCarlo Sablaon CallosNo ratings yet
- Biology Science For Life With Physiology 4Th Edition Belk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesBiology Science For Life With Physiology 4Th Edition Belk Test Bank Full Chapter PDFCassieYangiosx100% (17)
- PHy 101 Solved MCQSDocument28 pagesPHy 101 Solved MCQSIྂqྂrྂaྂ MྂaྂhྂrྂoྂsྂhྂNo ratings yet
- Coursera Organ DonationDocument40 pagesCoursera Organ DonationQaphela MinenhleNo ratings yet
- 126Document16 pages126majedmalaeb66No ratings yet
- Reading QuizDocument5 pagesReading QuizMicah CookNo ratings yet
- Pathology Questions PDFDocument67 pagesPathology Questions PDFDhruva PatelNo ratings yet
- Ch5 TB PinelDocument31 pagesCh5 TB Pinelpixelpaisley12No ratings yet
- BHK 031Document13 pagesBHK 031FERNANDA CASTANEDA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition Feldman Test BankDocument30 pagesEssentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition Feldman Test BankEricFuentesfxgir100% (13)
- Dozois 5e Chapter04 TIFDocument30 pagesDozois 5e Chapter04 TIFrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Psychology SampQ WDocument25 pagesPsychology SampQ Wmicah deveralaNo ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2019 034974Document7 pagesBmjopen 2019 034974allyssa rahmadittaNo ratings yet
- Discovering Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics: Second EditionDocument8 pagesDiscovering Genomics, Proteomics, and Bioinformatics: Second EditionSuchetaNo ratings yet
- Class XII Biology (044) Theory Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDocument13 pagesClass XII Biology (044) Theory Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsAryanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 ExperimentDocument11 pagesWeek 4 ExperimentKomal KhanNo ratings yet
- Phelan3e Testbank ch01Document24 pagesPhelan3e Testbank ch01Ahmed Maher Al-maqtariNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of Test Bank For Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach, 8th Edition, Dee Unglaub Silverthorn, All ChapterDocument64 pagesFull Download PDF of Test Bank For Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach, 8th Edition, Dee Unglaub Silverthorn, All Chapterusulliarnoob100% (8)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo ISBN 1259024644 9781259024641Document36 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo ISBN 1259024644 9781259024641JacobFergusonrdbm100% (29)
- Edition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo Isbn 1259024644 9781259024641Document36 pagesEdition by Feldman Catney Cavanagh and Dinardo Isbn 1259024644 9781259024641kevin.huerta226100% (22)
- Siddha Applied Science InstituteDocument4 pagesSiddha Applied Science InstituteLagin DranNo ratings yet
- MEMO - RV RTPCR - MergedDocument5 pagesMEMO - RV RTPCR - MergedMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Holistic Thinking and Partial ThinkingDocument9 pagesThe Difference Between Holistic Thinking and Partial ThinkingPRIME SABER TIU57% (14)
- GPDocument3 pagesGPYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Rhinology Fellowship Revised Dec 2021 McMasterDocument3 pagesRhinology Fellowship Revised Dec 2021 McMasterStanley SuhermanNo ratings yet
- HAAD Exam (25-12-2018)Document7 pagesHAAD Exam (25-12-2018)Anisha Mary ThomasNo ratings yet
- Venous ThromboembolismDocument11 pagesVenous ThromboembolismKrsna Navera100% (1)
- Homeless Deaths ReportDocument102 pagesHomeless Deaths ReportCapital Public RadioNo ratings yet
- Knee ReplacementDocument2 pagesKnee ReplacementpahumbleNo ratings yet
- Daniela GarciaDocument8 pagesDaniela GarciaSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris 2Document7 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris 2azizah LasimpalaNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument2 pagesHigh Risk PregnancysamitbisenNo ratings yet
- Cristine Jane Marie V. AritaoDocument3 pagesCristine Jane Marie V. AritaoCristine Jane Marie AritaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PedodonticsDocument27 pagesIntroduction of PedodonticsSudeep M. ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Hawaii Health Department Fines NextHealth $58K, Orders Company To Stop COVID-19 Testing InboxDocument4 pagesHawaii Health Department Fines NextHealth $58K, Orders Company To Stop COVID-19 Testing InboxHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet
- Moot Court BrochureDocument16 pagesMoot Court BrochureAkashNo ratings yet
- Folio KerjayaDocument38 pagesFolio KerjayaamiqisNo ratings yet
- Fatigue: What Is Anemia?Document3 pagesFatigue: What Is Anemia?Annapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- The Role of Occupational Therapy in OncologyDocument2 pagesThe Role of Occupational Therapy in OncologyThe American Occupational Therapy Association100% (1)
- Implementation of Pathogen Reduction Technology in The Manufacture of Blood Components in Blood Establishments Questions and Answers Draft Guidance For IndustryDocument14 pagesImplementation of Pathogen Reduction Technology in The Manufacture of Blood Components in Blood Establishments Questions and Answers Draft Guidance For Industrydrsapta manNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDocument7 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus ClosureDard TongNo ratings yet
- Intro To PTDocument709 pagesIntro To PTShoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Osteosarcoma and OsteoarthritisDocument17 pagesOsteosarcoma and OsteoarthritisCricelle Rose CobreNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2Muskaan BindalNo ratings yet
- Kumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Document7 pagesKumri-In Goat :A Laboratory Epidemiological Outbreak Investigation in Banke District of Mid-Western Region of Nepal.Karki KedarNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Clinical SupervisorDocument52 pagesThe Role of The Clinical SupervisorDwi NopriyantoNo ratings yet
- Consolidated HIV Guidelines 2020Document245 pagesConsolidated HIV Guidelines 2020Esther AumaNo ratings yet
- Rajsthan All Surgical Distributor Data ListDocument33 pagesRajsthan All Surgical Distributor Data ListcatalogueNo ratings yet
- Quality and Safety in Compounding Non-Sterile PreparationsDocument5 pagesQuality and Safety in Compounding Non-Sterile PreparationsPruessada DeeyingNo ratings yet