Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsEndogenic Processes
Endogenic Processes
Uploaded by
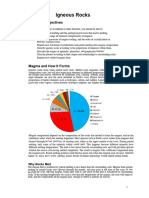
Jericho CarabidoMagma is molten rock found beneath Earth's surface that is less dense than solid rock, allowing it to rise. It is usually composed of elements like silicon, aluminum, iron, and oxygen. Magma has a very high temperature ranging from 800°C to 1400°C and can flow as it is a liquid, with its viscosity depending on factors like its silica content, gas content, and temperature.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Magma and Magma FormationDocument2 pagesMagma and Magma FormationAshlee EmongNo ratings yet
- How Magma Is FormedDocument21 pagesHow Magma Is FormedJAY ANDRESNo ratings yet
- Stem11a Group2Document32 pagesStem11a Group2fabbuddylizNo ratings yet
- Volcanic EruptionDocument2 pagesVolcanic EruptionLeo Cambaya Lascuña Jr.No ratings yet
- Characteristics of MagmaDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of MagmaCanggahNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesModule 3 ReviewerMikyla DulinNo ratings yet
- MagmaDocument4 pagesMagmaapi-3808551No ratings yet
- Magma, Lava and Pyroclastic MaterialsDocument9 pagesMagma, Lava and Pyroclastic MaterialsAdrienne BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Magma and Igneous RocksDocument17 pagesMagma and Igneous Rocksali karboubNo ratings yet
- Magma and Igneous RocksDocument17 pagesMagma and Igneous Rocksali karboubNo ratings yet
- ERUPTIONDocument3 pagesERUPTIONFerland James DelMar GumahinNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q3 Module 5Document4 pagesScience 9 Q3 Module 5Arthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- BeetDocument3 pagesBeetDariele BocadoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science - Volcanic EruptionDocument4 pagesQ3 Science - Volcanic EruptionAltheakim MacasadiaNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks: The Origins of MagmaDocument8 pagesIgneous Rocks: The Origins of MagmaLaxmi Kant PrasadNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument52 pagesEarth Materials and ProcessesMay Lyn BerondoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic EruptionsDocument20 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic Eruptionssuren kambleNo ratings yet
- Magma and Igneous RocksDocument14 pagesMagma and Igneous RocksANDREA DENISSENo ratings yet
- Magmatism Group 3Document29 pagesMagmatism Group 3MARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Q1 M7 Magma FormationDocument40 pagesQ1 M7 Magma FormationTheo AugustusNo ratings yet
- MagmatismDocument18 pagesMagmatismgardenshadow139No ratings yet
- Plutonism and VolcanismDocument42 pagesPlutonism and VolcanismAthenaNo ratings yet
- Science q3 Lecture 3Document38 pagesScience q3 Lecture 3jharealoNo ratings yet
- Nature and Generation of MagmaDocument42 pagesNature and Generation of MagmaMuzmmil MianNo ratings yet
- Geochemical CycleDocument13 pagesGeochemical CycleSOCKYNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaDocument12 pagesVolcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-1Document2 pagesAssignment 2-1Janet GawareNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption - Module 2Document18 pagesVolcanic Eruption - Module 2Ivy Grace Suarez CalipesNo ratings yet
- 01 Igneous PETROLOGY NotesDocument11 pages01 Igneous PETROLOGY NotesdaanaahishmaelsNo ratings yet
- Ultramafic, Mafic, Intermediate, or Felsic: - CompositionDocument13 pagesUltramafic, Mafic, Intermediate, or Felsic: - CompositionMilton Agustin GonzagaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANISMDocument27 pagesVOLCANISMeriantipuesto01750No ratings yet
- Q2 - Grade 11 - Lesson 3Document24 pagesQ2 - Grade 11 - Lesson 3Francheska AbandoNo ratings yet
- GLY 203 NotesDocument16 pagesGLY 203 Notesfortress generator servicesNo ratings yet
- Lava Flow: Baculao Buca DabloDocument12 pagesLava Flow: Baculao Buca DabloLol lolNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Week 3B: Magma Formation ObjectivesDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science - Week 3B: Magma Formation ObjectivesVernon100% (2)
- MagmaDocument2 pagesMagmaKaren DellosaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANISMDocument25 pagesVOLCANISMdave mahilumNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamLORENZ BLAISE GALVEZNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Lesson 1Document17 pagesMODULE 2 Lesson 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and Processes CMDocument28 pagesEarth Materials and Processes CMJaicelyn JarciaNo ratings yet
- Lectura N 1 Rxs. GneasDocument14 pagesLectura N 1 Rxs. GneasPatricia Del Carmen Guevara VasquezNo ratings yet
- How Does: Magma Formed?Document20 pagesHow Does: Magma Formed?Jho Mil ButacNo ratings yet
- Igneous RockDocument6 pagesIgneous Rocktajj_noor7900No ratings yet
- Petrography (I, M, S)Document29 pagesPetrography (I, M, S)MuhammadnasidiNo ratings yet
- Magma FormationDocument12 pagesMagma FormationAliyana Trisha HarunNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Internal Structure: Faculty of Agro Industry and Natural ResourcesDocument36 pagesThe Earth's Internal Structure: Faculty of Agro Industry and Natural ResourcesSandra ValdezNo ratings yet
- MagmaDocument22 pagesMagmaSherren NalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Textures & Structures of Igneous Rocks: This Document Last Updated On 15-Jan-2007Document14 pagesIntroduction & Textures & Structures of Igneous Rocks: This Document Last Updated On 15-Jan-2007api-19643403No ratings yet
- What Comes Out of A VolcanoDocument14 pagesWhat Comes Out of A VolcanoShiro NeroNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q3 Module2Document7 pagesSci9 Q3 Module2Gleziel Ann Sulima PacillosNo ratings yet
- 2 - Volcanic Eruptions Hazards 2017Document7 pages2 - Volcanic Eruptions Hazards 2017NitishNo ratings yet
- Science GroupingsDocument3 pagesScience GroupingsRemir Alfred QuianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Magma Characteristics and Types of Igneous RocksDocument18 pagesLecture 3 - Magma Characteristics and Types of Igneous RocksJoey Chienda (Baby Boy)No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentMuchael NipalNo ratings yet
- What Is A VolcanoDocument2 pagesWhat Is A VolcanoBrenda AurelliaNo ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument2 pagesRock CycleEdward John AlawagNo ratings yet
- Lava Flow DRRMDocument26 pagesLava Flow DRRMCyannah EcrivaineNo ratings yet
- Reporter No. 3Document13 pagesReporter No. 3alberto.deuna001No ratings yet
- 7 Features of The New WorldDocument2 pages7 Features of The New WorldJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- PR ConsentDocument5 pagesPR ConsentJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- DAYAWDocument3 pagesDAYAWJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument7 pagesBusiness PlanJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- PR CHAPTER I, 2,3 RevisedDocument35 pagesPR CHAPTER I, 2,3 RevisedJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Chart Entrep G1Document1 pageOrganizational Chart Entrep G1Jericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Possible QuestionsDocument1 pagePossible QuestionsJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
Endogenic Processes
Endogenic Processes
Uploaded by
Jericho Carabido0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageMagma is molten rock found beneath Earth's surface that is less dense than solid rock, allowing it to rise. It is usually composed of elements like silicon, aluminum, iron, and oxygen. Magma has a very high temperature ranging from 800°C to 1400°C and can flow as it is a liquid, with its viscosity depending on factors like its silica content, gas content, and temperature.
Original Description:
Disaster
Original Title
ENDOGENIC PROCESSES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMagma is molten rock found beneath Earth's surface that is less dense than solid rock, allowing it to rise. It is usually composed of elements like silicon, aluminum, iron, and oxygen. Magma has a very high temperature ranging from 800°C to 1400°C and can flow as it is a liquid, with its viscosity depending on factors like its silica content, gas content, and temperature.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageEndogenic Processes
Endogenic Processes
Uploaded by
Jericho CarabidoMagma is molten rock found beneath Earth's surface that is less dense than solid rock, allowing it to rise. It is usually composed of elements like silicon, aluminum, iron, and oxygen. Magma has a very high temperature ranging from 800°C to 1400°C and can flow as it is a liquid, with its viscosity depending on factors like its silica content, gas content, and temperature.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Rocks commonly found on the surface of Earth are in solid state.
However, rocks also exist in
liquid state at certain locations deep inside Earth. The molten rocks that are found beneath
Earth's surface are called magma. They are less dense than the surrounding solid rock, and
therefore capable of rising the surface. When magma emerges at the surface, it is called lava.
Magma is usually composed of the abundant elements including silicon, aluminum, iron,
calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, hydrogen and oxygen. The compositional variation of
magma is expressed in terms of oxides such as SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, MgO, FeO and H2,O. The
most common component is silica (SiO2) at 45% to 75% by weight. Dissolved gases, primarily
water vapor and carbon dioxide, are also present, comprising 0.2 to 3% by weight.
Another property of magma is that it has very high temperature. The melting temperature
of rocks could range from 800°C to 1400°C. Magma also has the ability to flow since it is a
liquid. The degree of resistance to flow is called viscosity. The more viscous a substance is, the
less fluid it becomes. The viscosity of magma generally depends on its silica content. Magmas
with high silica are more viscous than low-silica magmas. Gas content and temperature also
affect the viscosity of magma. Generally, gas content is higher when the temperature is higher
and this makes the magma less viscous. For instance, lava that just came out of a volcano has
very high temperature and flows readily, but as the temperature decreases, it becomes more
viscous and eventually stops flowing.
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Magma and Magma FormationDocument2 pagesMagma and Magma FormationAshlee EmongNo ratings yet
- How Magma Is FormedDocument21 pagesHow Magma Is FormedJAY ANDRESNo ratings yet
- Stem11a Group2Document32 pagesStem11a Group2fabbuddylizNo ratings yet
- Volcanic EruptionDocument2 pagesVolcanic EruptionLeo Cambaya Lascuña Jr.No ratings yet
- Characteristics of MagmaDocument18 pagesCharacteristics of MagmaCanggahNo ratings yet
- Module 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesModule 3 ReviewerMikyla DulinNo ratings yet
- MagmaDocument4 pagesMagmaapi-3808551No ratings yet
- Magma, Lava and Pyroclastic MaterialsDocument9 pagesMagma, Lava and Pyroclastic MaterialsAdrienne BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Magma and Igneous RocksDocument17 pagesMagma and Igneous Rocksali karboubNo ratings yet
- Magma and Igneous RocksDocument17 pagesMagma and Igneous Rocksali karboubNo ratings yet
- ERUPTIONDocument3 pagesERUPTIONFerland James DelMar GumahinNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q3 Module 5Document4 pagesScience 9 Q3 Module 5Arthur CapawingNo ratings yet
- BeetDocument3 pagesBeetDariele BocadoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science - Volcanic EruptionDocument4 pagesQ3 Science - Volcanic EruptionAltheakim MacasadiaNo ratings yet
- Igneous Rocks: The Origins of MagmaDocument8 pagesIgneous Rocks: The Origins of MagmaLaxmi Kant PrasadNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument52 pagesEarth Materials and ProcessesMay Lyn BerondoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic EruptionsDocument20 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic Eruptionssuren kambleNo ratings yet
- Magma and Igneous RocksDocument14 pagesMagma and Igneous RocksANDREA DENISSENo ratings yet
- Magmatism Group 3Document29 pagesMagmatism Group 3MARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Q1 M7 Magma FormationDocument40 pagesQ1 M7 Magma FormationTheo AugustusNo ratings yet
- MagmatismDocument18 pagesMagmatismgardenshadow139No ratings yet
- Plutonism and VolcanismDocument42 pagesPlutonism and VolcanismAthenaNo ratings yet
- Science q3 Lecture 3Document38 pagesScience q3 Lecture 3jharealoNo ratings yet
- Nature and Generation of MagmaDocument42 pagesNature and Generation of MagmaMuzmmil MianNo ratings yet
- Geochemical CycleDocument13 pagesGeochemical CycleSOCKYNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaDocument12 pagesVolcanoes, Magma, and Volcanic Eruptions: Characteristics of Magma Types of MagmaJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-1Document2 pagesAssignment 2-1Janet GawareNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption - Module 2Document18 pagesVolcanic Eruption - Module 2Ivy Grace Suarez CalipesNo ratings yet
- 01 Igneous PETROLOGY NotesDocument11 pages01 Igneous PETROLOGY NotesdaanaahishmaelsNo ratings yet
- Ultramafic, Mafic, Intermediate, or Felsic: - CompositionDocument13 pagesUltramafic, Mafic, Intermediate, or Felsic: - CompositionMilton Agustin GonzagaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANISMDocument27 pagesVOLCANISMeriantipuesto01750No ratings yet
- Q2 - Grade 11 - Lesson 3Document24 pagesQ2 - Grade 11 - Lesson 3Francheska AbandoNo ratings yet
- GLY 203 NotesDocument16 pagesGLY 203 Notesfortress generator servicesNo ratings yet
- Lava Flow: Baculao Buca DabloDocument12 pagesLava Flow: Baculao Buca DabloLol lolNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Week 3B: Magma Formation ObjectivesDocument8 pagesEarth and Life Science - Week 3B: Magma Formation ObjectivesVernon100% (2)
- MagmaDocument2 pagesMagmaKaren DellosaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANISMDocument25 pagesVOLCANISMdave mahilumNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamLORENZ BLAISE GALVEZNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Lesson 1Document17 pagesMODULE 2 Lesson 1Anne Rose CoderiasNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and Processes CMDocument28 pagesEarth Materials and Processes CMJaicelyn JarciaNo ratings yet
- Lectura N 1 Rxs. GneasDocument14 pagesLectura N 1 Rxs. GneasPatricia Del Carmen Guevara VasquezNo ratings yet
- How Does: Magma Formed?Document20 pagesHow Does: Magma Formed?Jho Mil ButacNo ratings yet
- Igneous RockDocument6 pagesIgneous Rocktajj_noor7900No ratings yet
- Petrography (I, M, S)Document29 pagesPetrography (I, M, S)MuhammadnasidiNo ratings yet
- Magma FormationDocument12 pagesMagma FormationAliyana Trisha HarunNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Internal Structure: Faculty of Agro Industry and Natural ResourcesDocument36 pagesThe Earth's Internal Structure: Faculty of Agro Industry and Natural ResourcesSandra ValdezNo ratings yet
- MagmaDocument22 pagesMagmaSherren NalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Textures & Structures of Igneous Rocks: This Document Last Updated On 15-Jan-2007Document14 pagesIntroduction & Textures & Structures of Igneous Rocks: This Document Last Updated On 15-Jan-2007api-19643403No ratings yet
- What Comes Out of A VolcanoDocument14 pagesWhat Comes Out of A VolcanoShiro NeroNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q3 Module2Document7 pagesSci9 Q3 Module2Gleziel Ann Sulima PacillosNo ratings yet
- 2 - Volcanic Eruptions Hazards 2017Document7 pages2 - Volcanic Eruptions Hazards 2017NitishNo ratings yet
- Science GroupingsDocument3 pagesScience GroupingsRemir Alfred QuianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Magma Characteristics and Types of Igneous RocksDocument18 pagesLecture 3 - Magma Characteristics and Types of Igneous RocksJoey Chienda (Baby Boy)No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentMuchael NipalNo ratings yet
- What Is A VolcanoDocument2 pagesWhat Is A VolcanoBrenda AurelliaNo ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument2 pagesRock CycleEdward John AlawagNo ratings yet
- Lava Flow DRRMDocument26 pagesLava Flow DRRMCyannah EcrivaineNo ratings yet
- Reporter No. 3Document13 pagesReporter No. 3alberto.deuna001No ratings yet
- 7 Features of The New WorldDocument2 pages7 Features of The New WorldJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- PR ConsentDocument5 pagesPR ConsentJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- DAYAWDocument3 pagesDAYAWJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument7 pagesBusiness PlanJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- PR CHAPTER I, 2,3 RevisedDocument35 pagesPR CHAPTER I, 2,3 RevisedJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Organizational Chart Entrep G1Document1 pageOrganizational Chart Entrep G1Jericho CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Possible QuestionsDocument1 pagePossible QuestionsJericho CarabidoNo ratings yet