Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eq - Lecture 7
Eq - Lecture 7
Uploaded by
عراقية KHOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eq - Lecture 7
Eq - Lecture 7
Uploaded by
عراقية KHCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept.
Equipment Design
3.8 Special Cases for Rectification Using McCabe-Thiele Method
a) Stripping-Column Distillation
In some cases the feed to be distilled is not supplied to an intermediate point in a column but is added
to the top of the stripping column as shown in Figure below. The feed is usually a saturated liquid at the
boiling point or subcooled and the overhead product VD is the vapor rising from the top plate, which
goes to a condenser with no reflux or liquid returned back to the tower. A very pure bottoms product can
be obtained but the vapor distillate will not be pure.
Assuming constant molar flow rates, a material balance of the more volatile component A around the
dashed line in figure below gives, on rearrangement,
Lm W xw
ym+1 = xm −
Vm+1 Vm+1
b) Enriching-Column Distillation
Enriching towers are also sometimes used, where the feed enters the bottom of the tower as a
superheated vapor or a saturated vapor. The overhead distillate is produced in the same manner as in a
complete fractionating tower and is usually quite rich in the more volatile component A ( very pure) but
the bottoms will not be very pure.
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 1
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
Note:Striping columns and enriching columns are used when a pure distillate or a pure bottoms,
respectively, is not needed.
Example 3.9: An enriching tower is fed 100 kg mol/h of a saturated vapor feed containing 40 mol %
benzene (A) and 60 mol % toluene (E) at 101.32 kPa abs. The distillate is to contain 90 mol % benzene.
The reflux ratio is set at 4.0 :1. Calculate the kg mol/h distillate D and bottoms Wand their compositions.
Also, calculate the number of theoretical plates required.
Solution
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 2
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
Example 3.10: A liquid feed at the boiling point of 400 kg mol/h containing 70 mol % benzene (A) and
30 mol % toluene (B) is fed to a stripping tower at 101.3 kPa pressure. The bottoms product flow is to
be 60 kg mol/h containing only 10 mol % A and the rest B. Calculate the kg mol/h overhead vapor, its
composition, and the number of theoretical steps required.
Solution
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 3
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
For a saturated liquid, the q line is vertical and is plotted in Fig. 11.4-15. The operating line is plotted
through the point y = xw = 0.1 and the intersection of yD = 0.806 with the q line. Stepping off the trays
from the top, 5.3 theoretical steps or 4.3 theoretical trays plus a reboiler are needed.
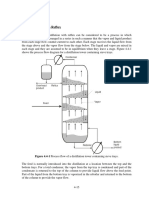
c) Steam Distillation
Steam distillation is a separation process in which live steam is blown through a liquid containing a
component A (usually having a low volatility and low solubility in water) when A vaporizes slowly
(depending upon its vapour pressure at the operating temperature) and leaves with the steam.
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 4
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
When an aqueous solution of more volatile A and water B is being distilled, the heat required may
be provided by the use of open steam injected directly at the bottom of the tower. The reboiler exchanger
is then not needed. The steam is injected as small bubbles into the liquid in the tower bottom, as shown
in Figure below. The vapor leaving the liquid is then in equilibrium with the liquid if sufficient contact
is obtained. Making an overall balance on the tower and a balance on A,
F+S=D+W
F xf + S ys = D xD + W xW
where S = mol/h of steam and ys = 0 = mole fraction of A in steam. The enriching operating-line
equation is the same as for indirect steam.For the stripping-line equation, an overall balance and a
balance on component A are asfollows:
Lm + S = Vm+1 + W
Lm xm + S (0) = Vm+1 ym+1 + W xW
Solving for ym+1
Lm W xW
ym+1 = xm −
Vm+1 Vm+1
For saturated steam entering, S = Vm+1 and henc, Lm = W. Substituting into above equation, the
stripping operating line is
W W
ym+1 = xm − x
S S W
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 5
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
Example 3.11: A liquid feed at the boiling point contains 3.3 mol % ethanol and 96.7 mol % water
and enters the top tray of a stripping tower. Saturated steam is injected directly into liquid in the
bottom of the tower. The overhead vapor which is withdrawn contains 99% of the alcohol in the feed.
Assume equimolar overflow for this problem. Equilibrium data for mole fraction of alcohol arc as
follows at 10 1.32 kPa abs pressure (1 atm abs).
(a) For an infinite number of theoretical steps, calculate the minimum moles of steam needed per mole
of feed.
(b) Using twice the minimum moles of steam, calculate the number of theoretical steps needed, the
composition of the overhead vapor, and the bottoms composition.
Solution.
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 6
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 7
Chemical and Petrochemical Eng Dept. Equipment Design
M.Sc. Abdulrazzaq S. Abdullah 8
You might also like
- Nfpa 54 (Ansi Z223.1), 2021Document177 pagesNfpa 54 (Ansi Z223.1), 2021Dr kadhum shramaNo ratings yet
- Assig 2 Che422 Spring 2012Document3 pagesAssig 2 Che422 Spring 2012ⵃⴰⵎⵣⴰ ⵖⵉⵢⵜNo ratings yet
- Day 2 1 PDFDocument17 pagesDay 2 1 PDFChristianNo ratings yet
- R14 - Steam Power Cycles PDFDocument10 pagesR14 - Steam Power Cycles PDFnotoriousneal12No ratings yet
- Separation Process 1Document86 pagesSeparation Process 1hanisshi50% (4)
- 221 06Document25 pages221 06Fransiscus Leo ChandraNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column DesignDocument17 pagesDistillation Column DesignMazan ShaviNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Operations (ENV 425) Problem Set 4: Zewail City of Science and TechnologyDocument3 pagesMass Transfer Operations (ENV 425) Problem Set 4: Zewail City of Science and TechnologyMayar H. HaggagNo ratings yet
- Question bank-MASS TRANSFER-II MECDocument10 pagesQuestion bank-MASS TRANSFER-II MECkishore.21uchNo ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Absorption Problems 2020Document2 pagesGas Liquid Absorption Problems 2020vikyappleNo ratings yet
- AbsorptionDocument38 pagesAbsorptionzurina abidinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3deepika snehi0% (1)
- Probset4. EnergybalancesDocument4 pagesProbset4. EnergybalancesUmmu Qurratul Aini MansorNo ratings yet
- Teaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Document7 pagesTeaching 2912 25957 1653056232 1Solin HawreNo ratings yet
- Distillation: Unit Operations (Che 347/ 251)Document27 pagesDistillation: Unit Operations (Che 347/ 251)Amira KormainNo ratings yet
- BT Hoa Ly 1Document22 pagesBT Hoa Ly 1Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- CL405 2021 End Term ExaminationDocument4 pagesCL405 2021 End Term ExaminationArpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHE 312 Final Exam2013 - 2014 - RainDocument4 pagesCHE 312 Final Exam2013 - 2014 - RainChibuike CharlesNo ratings yet
- Numerical Unit1Document3 pagesNumerical Unit1Ayush DubeyNo ratings yet
- ERT 318/4 Unit Operations SEMESTER 1 (2013/2014) : Water Cooling TowerDocument18 pagesERT 318/4 Unit Operations SEMESTER 1 (2013/2014) : Water Cooling TowerNorzaifee NizamudinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Reactor Engineering - Problems PDFDocument75 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reactor Engineering - Problems PDFJojie-Ann Alabarca100% (1)
- INME 4045 - Chapter 3 - Suggested ProblemsDocument2 pagesINME 4045 - Chapter 3 - Suggested ProblemsAmanda SotoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11-ADocument19 pagesLecture 11-AChirag GargNo ratings yet
- Gate 1990Document12 pagesGate 1990Akhil TiwariNo ratings yet
- P Chem Homework 10Document3 pagesP Chem Homework 10Matthew RayNo ratings yet
- Bubble Cap Plate For Distillation ColumnDocument26 pagesBubble Cap Plate For Distillation Columnsanjukec100% (2)
- Distillation PresentationDocument61 pagesDistillation PresentationAli AmjadNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 AbsorptionDocument4 pagesSheet 4 AbsorptionMohamed FateemNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument124 pagesDistillationasharab70100% (1)
- 6-M-MassTransferI 20171125180514.014 X PDFDocument2 pages6-M-MassTransferI 20171125180514.014 X PDFMani SinghNo ratings yet
- Taller MasaDocument2 pagesTaller Masa__Caro26__No ratings yet
- MT IDocument5 pagesMT IParth Desai100% (1)
- 11 PEME330101 S 1Document6 pages11 PEME330101 S 1Shammus SultanNo ratings yet
- Problems - Chapter 12 Introduction To Compressible FlowDocument52 pagesProblems - Chapter 12 Introduction To Compressible FlowbrayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.2 Gas Absorption ProcessDocument31 pagesChapter 7.2 Gas Absorption Processamira nabillaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Test PaperDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Test PaperKrishnaKishoreReddyNo ratings yet
- Distillation 2Document3 pagesDistillation 2roxette100% (2)
- Ex03 PDFDocument10 pagesEx03 PDFafendiNo ratings yet
- 8-Plant Design - Separation Units Part 4Document189 pages8-Plant Design - Separation Units Part 4MrHemFunNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Part 6Document11 pagesDistillation - Part 6SyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- IV B. TECH (Chemical Engineering) I SemesterDocument14 pagesIV B. TECH (Chemical Engineering) I SemesterPiyush AmbulgekarNo ratings yet
- Basic ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesBasic ThermodynamicsVivek VermaNo ratings yet
- 619PT304Document4 pages619PT304arpit gargNo ratings yet
- Rawr PDFDocument3 pagesRawr PDFGrazel MDNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument22 pagesReviewerRobert DelfinNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer With/Without Chemical Rection (Solid-Liquid System)Document7 pagesMass Transfer With/Without Chemical Rection (Solid-Liquid System)Sameep JainNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument19 pagesExercisesNhật MinhNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer With/Without Chemical Rection (Solid-Liquid System)Document7 pagesMass Transfer With/Without Chemical Rection (Solid-Liquid System)Sameep JainNo ratings yet
- Thermo Quiz 1 (OAC)Document4 pagesThermo Quiz 1 (OAC)SHUSWABHIT SHADANGINo ratings yet
- Gate 1990Document16 pagesGate 1990KapilSahuNo ratings yet
- Chap4 4 PDFDocument8 pagesChap4 4 PDFroxetteNo ratings yet
- Two Marks CH 6603 Mass TransferDocument17 pagesTwo Marks CH 6603 Mass Transfersampathkumar100% (1)
- Taller MasaDocument3 pagesTaller MasaAna Maria VallejoNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems in Absorption and HumidificationDocument4 pagesPractice Problems in Absorption and HumidificationJenna BraszNo ratings yet
- Murphy DisDocument19 pagesMurphy DisMurphy MofeNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2021 1013529Document10 pagesMUCLecture 2021 1013529mugentsukiyomi31No ratings yet
- CHE 430 Fa21 - HW#1 (27-August-2021)Document2 pagesCHE 430 Fa21 - HW#1 (27-August-2021)Charity QuinnNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Examples Control SystemDocument42 pagesExamples Control Systemعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- Logic OperationDocument4 pagesLogic Operationعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- 4 Material Balance On ReactersDocument21 pages4 Material Balance On Reactersعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- شيماء عبدالباري يونسDocument4 pagesشيماء عبدالباري يونسعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ReactionDocument17 pagesChemical Engineering Reactionعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- Chemical EngineeringDocument6 pagesChemical Engineeringعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- Lectures of Second Semester ChemicalDocument53 pagesLectures of Second Semester Chemicalعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- اسألة 2021 كورس اول ، ثاني ، فاينل دور اول ، دور ثانيDocument43 pagesاسألة 2021 كورس اول ، ثاني ، فاينل دور اول ، دور ثانيعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Curve Fitting: Curve Fitting: Is The Process of Constructing A Curve, or Mathematical FunctionDocument13 pagesChapter Five: Curve Fitting: Curve Fitting: Is The Process of Constructing A Curve, or Mathematical Functionعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- انتقال حرارةDocument15 pagesانتقال حرارةعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- تقرير التدريب الصيفيDocument5 pagesتقرير التدريب الصيفيعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- 6 ENTRAIN TT3 Basics of Flue Gas Cleaning AEE RamerstorferDocument15 pages6 ENTRAIN TT3 Basics of Flue Gas Cleaning AEE Ramerstorferعراقية KHNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of Heat Enhancement in Internally Helical GroovedDocument102 pagesCFD Simulation of Heat Enhancement in Internally Helical GroovedTHE SEZARNo ratings yet
- Drafts Andchimney PDFDocument3 pagesDrafts Andchimney PDFEric PaderNo ratings yet
- Expertise Contracting Company Project Name: Contract No: Expertise Welder'S Performance Qualification Test ReportDocument15 pagesExpertise Contracting Company Project Name: Contract No: Expertise Welder'S Performance Qualification Test ReportBALAKRISHANANNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing Systems and Cell DesignDocument87 pagesLean Manufacturing Systems and Cell Designluizbandeira100% (2)
- Valve Case StudyDocument3 pagesValve Case StudyAnoopNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Diameter For Methanol-IPA System (Continuous) - Top Boil Up PropertiesDocument3 pagesCalculation of Diameter For Methanol-IPA System (Continuous) - Top Boil Up PropertiesBagadi AvinashNo ratings yet
- Heat & Mass TransferDocument11 pagesHeat & Mass TransferBen JoeNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and Mechanisms POGILDocument6 pagesKinetics and Mechanisms POGILElainaNo ratings yet
- Line Sizing Using HysysDocument4 pagesLine Sizing Using HysysRandomNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Temperature ProfileDocument3 pagesPressure and Temperature ProfileFalom BanderNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Review 2 TermodinamikaDocument8 pagesJurnal Review 2 TermodinamikaFitriani -No ratings yet
- Ceng 426 Project FinalDocument23 pagesCeng 426 Project FinalDuaa SalehNo ratings yet
- Flame Propagation in Swirilng FlwsDocument34 pagesFlame Propagation in Swirilng FlwsmohammadNo ratings yet
- ME8351-Manufacturing Technology-IDocument12 pagesME8351-Manufacturing Technology-IDayon MathewNo ratings yet
- List of Product Must Sold To Customers: Products Guide For Feed, Lead and SoldDocument1 pageList of Product Must Sold To Customers: Products Guide For Feed, Lead and SoldFendy ShirahNo ratings yet
- CHEN3009 Final Exam - Example PaperDocument4 pagesCHEN3009 Final Exam - Example PaperRosario QFNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Principles and Applications by BK Dutta 5 PDF FreeDocument134 pagesHeat Transfer Principles and Applications by BK Dutta 5 PDF Freesudhanshu.sbt22No ratings yet
- CH 07Document99 pagesCH 07Larissa Albunio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Ameer Hakeem Primus100% (1)
- Sicurezza Antincendio: Titolo Presentazione SottotitoloDocument15 pagesSicurezza Antincendio: Titolo Presentazione Sottotitoloahsan ahmadNo ratings yet
- C4 Chemical KineticsDocument92 pagesC4 Chemical KineticsaliesyaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics SIMP-2023Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics SIMP-2023Bharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 - FlocculationDocument20 pagesChapter 3.2 - FlocculationHanif NifNo ratings yet
- FPSO Flow Meter Fits Just RightDocument1 pageFPSO Flow Meter Fits Just RightJuan JaramilloNo ratings yet
- 212 Series RegulatorDocument2 pages212 Series RegulatorkicsnerNo ratings yet
- Guseva 2021 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1083 012083Document8 pagesGuseva 2021 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1083 012083Amit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet V-152 Relief Valve: Important Receiving InformationDocument14 pagesInstruction Sheet V-152 Relief Valve: Important Receiving InformationRODRIGO RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Bunger ValveDocument31 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Howell-Bunger ValveEng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document9 pagesExperiment 5Dr.AhmedNo ratings yet