Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 2MACROCOMPUTERS
Lesson 2MACROCOMPUTERS
Uploaded by
Yasmin MachicadoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Unit 3-Types of Computers Revisado 1Document11 pagesUnit 3-Types of Computers Revisado 1Yasmin MachicadoNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Rad - Engleski JezikDocument20 pagesSeminarski Rad - Engleski Jezikjusufspa1997No ratings yet
- Computer TypesDocument6 pagesComputer TypesGarima GarimaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Microcomputers - 014644Document6 pagesBasic Concept of Microcomputers - 014644stevezubyik20No ratings yet
- Computer Applications: Chapter-IDocument34 pagesComputer Applications: Chapter-Imuskan smileNo ratings yet
- SupercomputerDocument5 pagesSupercomputerjshankar0108No ratings yet
- Name: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateDocument7 pagesName: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateKylie sheena MendezNo ratings yet
- Types of Computers I, Computer: DefinitionDocument5 pagesTypes of Computers I, Computer: DefinitionMenchie Ann Sabandal SalinasNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputerDocument23 pagesClassification of ComputerIDRISA NKUNYANo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument3 pagesClassification of ComputersRajeev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Computer Definition & Types of Computer. (Explained)Document6 pagesComputer Definition & Types of Computer. (Explained)elizabethternderNo ratings yet
- Computers Types: I, Computer: DefinitionDocument6 pagesComputers Types: I, Computer: Definitionராஜமாணிக்கம் பNo ratings yet
- MM 3 ComputersDocument4 pagesMM 3 Computersgood bye jungwoo with masks MariaNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Lesson 6Document5 pagesQ1 - Lesson 6JEROME DIAZNo ratings yet
- Computers Types: I, Computer: DefinitionDocument6 pagesComputers Types: I, Computer: DefinitionMesfene Tibebu FenNo ratings yet
- Classofication of Compuers: Shahzaib Imran Roll No:-51 Assignment:-001 Department:-BSITDocument6 pagesClassofication of Compuers: Shahzaib Imran Roll No:-51 Assignment:-001 Department:-BSITA Bundle Of knowledgeNo ratings yet
- Computer DevicesDocument23 pagesComputer DevicesRajashree RaviNo ratings yet
- C NotesDocument2 pagesC NotesMamta Mohit DhandaNo ratings yet
- CS 402Document3 pagesCS 402ebaadmalik653No ratings yet
- Grade 9 and 11 - Quarter 3 - Week 1Document2 pagesGrade 9 and 11 - Quarter 3 - Week 1Oliver C SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Allied EssentialsOfComputers 0bioinformaticsDocument156 pagesAllied EssentialsOfComputers 0bioinformaticssamikshajohn03No ratings yet
- Types of Computers I, Computer: Definition: Supercomputer and MainframeDocument4 pagesTypes of Computers I, Computer: Definition: Supercomputer and MainframeJeremias De la CruzNo ratings yet
- MST 1 SolutionDocument14 pagesMST 1 SolutionSumit JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument18 pagesChapter Threeaarka soomalidaNo ratings yet
- AMITY SUb2 - A1-Ans1Document3 pagesAMITY SUb2 - A1-Ans1Ashok PalNo ratings yet
- Ict Lab Task 3Document12 pagesIct Lab Task 3NOOB GAM1NGNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of ComputersHarry GillNo ratings yet
- Computer HierarchyDocument37 pagesComputer HierarchyRondo Hirohito67% (3)
- Computer - TypesDocument3 pagesComputer - TypesジョージNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument7 pagesClassification of ComputersscsdfvdgNo ratings yet
- Supercomputers Minicomputers Mainframes Workstations Personal Computers Least Powerful Most PowerfulDocument9 pagesSupercomputers Minicomputers Mainframes Workstations Personal Computers Least Powerful Most Powerfulsujit_ranjanNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument3 pagesTypes of ComputersKing ZuesNo ratings yet
- Gen Comp by T.MDocument11 pagesGen Comp by T.MErvin LinNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of ComputersMary Joy CanalanNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of Computerssweetktz789No ratings yet
- POP-module1 NotesDocument83 pagesPOP-module1 NotesrakshithatanNo ratings yet
- C Question BankDocument29 pagesC Question Bankdd0542469No ratings yet
- Classification of Types of ComputerDocument8 pagesClassification of Types of Computershawai8009No ratings yet
- History of Computing Classification of Computers Types of ComputersDocument22 pagesHistory of Computing Classification of Computers Types of Computersdua tanveerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing PrelimDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Computing PrelimApril Jane AndresNo ratings yet
- Computers in EducationDocument9 pagesComputers in Educationkvsamy09No ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety Understanding ComputerDocument2 pagesOccupational Health and Safety Understanding ComputerRegina Fe EmpasNo ratings yet
- Computers TypesDocument4 pagesComputers TypesMuhammad Atif Qaim KhaniNo ratings yet
- TVL - Computer Systems Servicing 11: Let Us DiscoverDocument7 pagesTVL - Computer Systems Servicing 11: Let Us DiscoverFredilo Flores Jr.No ratings yet
- Basay, Rodilyn G. BSCE-2 GE-TFL TTH 3:00-4:30 PM 02-18-2020: Personal ComputerDocument3 pagesBasay, Rodilyn G. BSCE-2 GE-TFL TTH 3:00-4:30 PM 02-18-2020: Personal ComputerRodilyn BasayNo ratings yet
- Figure 6-1.-C1assification System of Memory.: Time Destructive ReadoutDocument7 pagesFigure 6-1.-C1assification System of Memory.: Time Destructive ReadoutVijay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics TextbookDocument103 pagesComputer Basics Textbookapi-19727066No ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.2: Types of ComputerDocument23 pagesInformation Sheet 1.2: Types of ComputerBerlin AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument10 pagesTypes of Computersmandy02scribdNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument19 pagesTypes of Computerkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument195 pagesComputer ArchitectureFahad AlamNo ratings yet
- Computer Awareness - Computer Awareness-1Document12 pagesComputer Awareness - Computer Awareness-1samskruti speaksNo ratings yet
- Is An Informal High-Level Description of The Operating Principle of A Computer Program or Other AlgorithmDocument4 pagesIs An Informal High-Level Description of The Operating Principle of A Computer Program or Other AlgorithmMary Charisse SandroNo ratings yet
- 0604 Advanced Computer ArchitectureDocument195 pages0604 Advanced Computer ArchitectureAdrian AdrNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument5 pagesClassification of ComputersTaha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cprogramming Module1Document42 pagesCprogramming Module1Haresh SNo ratings yet
- Ict ModuleDocument26 pagesIct ModuleSai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument4 pagesTypes of Computercutemano1311No ratings yet
- Makalah KomputerDocument16 pagesMakalah KomputerAbubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- ABAP ProfileDocument4 pagesABAP Profileteja chavaNo ratings yet
- Digi Connect Me 9210: Ultra-Compact High-Performance Embedded Modules For M2M Networking Combine On-Chip SecurityDocument5 pagesDigi Connect Me 9210: Ultra-Compact High-Performance Embedded Modules For M2M Networking Combine On-Chip SecurityVENKATESH KAMATHNo ratings yet
- MAGNET Ver 3.0.1 Release NotesDocument40 pagesMAGNET Ver 3.0.1 Release NotesNguyễn Thanh Hiền nguyenNo ratings yet
- ECE4007 Information Theory and Coding: DR - Sangeetha R.GDocument40 pagesECE4007 Information Theory and Coding: DR - Sangeetha R.GTanmoy DasNo ratings yet
- Data Platform and Analytics Foundational Training: (Speaker Name)Document10 pagesData Platform and Analytics Foundational Training: (Speaker Name)Kathalina SuarezNo ratings yet
- Flexible WorkflowDocument51 pagesFlexible WorkflowbasemffcamriNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide On Microsoft Excel For Data AnalysisDocument28 pagesA Comprehensive Guide On Microsoft Excel For Data AnalysisKhushi BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Sensor Network Applications in Smart GridDocument8 pagesWireless Sensor Network Applications in Smart GridTenda TiyNo ratings yet
- Handout 9800 MSF98001 Hands-OnDocument26 pagesHandout 9800 MSF98001 Hands-Onvuk vukanicNo ratings yet
- Manual HandbrakeDocument1 pageManual HandbrakeAndy LNo ratings yet
- EDUP 2082 Psikologi Pendidikan: Perbezaan Individu Dan PembelajaranDocument31 pagesEDUP 2082 Psikologi Pendidikan: Perbezaan Individu Dan PembelajaranNur Farahin AliasNo ratings yet
- Collaborate. Communicate. Concentrate.: Logitech Zone Wireless HeadsetsDocument2 pagesCollaborate. Communicate. Concentrate.: Logitech Zone Wireless HeadsetsraviezsoftNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 CAAGAY MARIMEL P BSEDSCI3A.Introtech2Document8 pagesCHAPTER 4 CAAGAY MARIMEL P BSEDSCI3A.Introtech2Kay LagunaNo ratings yet
- Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery DatasheetDocument2 pagesCommvault Complete Backup and Recovery DatasheetitnetmanNo ratings yet
- Informational Influence in Organizations: An Integrated Approach To Knowledge AdoptionDocument26 pagesInformational Influence in Organizations: An Integrated Approach To Knowledge AdoptionAnne AfrianiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1Document42 pagesAdvanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1Mustafamna Al Salam0% (1)
- Introduction To Software Testing Engineering Criteria For TechnologiesDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Software Testing Engineering Criteria For TechnologiesNurma Ayu WigatiNo ratings yet
- Resify Website UpdatesDocument12 pagesResify Website UpdatesChathura JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Big-O Algorithm Complexity Cheat Sheet (Know Thy Complexities!) @ericdrowellDocument9 pagesBig-O Algorithm Complexity Cheat Sheet (Know Thy Complexities!) @ericdrowelldungNo ratings yet
- Information SiloDocument3 pagesInformation Silokatherine976No ratings yet
- Release 13 Using The Transaction ConsoleDocument26 pagesRelease 13 Using The Transaction ConsoleMahesh VeluruNo ratings yet
- Example On Bresenhams Line Drawing AlgorithmDocument2 pagesExample On Bresenhams Line Drawing AlgorithmPunam Patil60% (30)
- Question Papers AllDocument64 pagesQuestion Papers AllAbdulBasit ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Order Statistic NotesDocument7 pagesOrder Statistic NotesKoustab BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision and Graphics PDFDocument3 pagesComputer Vision and Graphics PDFAkash SinhaNo ratings yet
- World Handwriting ContestDocument2 pagesWorld Handwriting Contestclassicintrovert897No ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics (BDAG 19-5) : Quiz: GMP - 2019 Term VDocument2 pagesBig Data Analytics (BDAG 19-5) : Quiz: GMP - 2019 Term VdebmatraNo ratings yet
- Raquel V. Cepillo: Mobile No. 0956-354-5034Document3 pagesRaquel V. Cepillo: Mobile No. 0956-354-5034Allan Ahadi UsmanNo ratings yet
- Modbus Manual v1 7 PDFDocument59 pagesModbus Manual v1 7 PDFHoangtnt NguyenNo ratings yet
- Permutation GroupDocument12 pagesPermutation GroupHarshitaNo ratings yet
Lesson 2MACROCOMPUTERS
Lesson 2MACROCOMPUTERS
Uploaded by
Yasmin MachicadoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 2MACROCOMPUTERS
Lesson 2MACROCOMPUTERS
Uploaded by
Yasmin MachicadoCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 2 MACROCOMPUTERS
Pre-reading
TASK 1. Match column A with column B.
A B
a. capable _____ 1. users, customers
b. type _____ 2. very big
c. public _____ 3. important
d. large _____ 4. kind
e. main _____ 5. able to
f. research _____ 6. investigate
TASK 2 READING
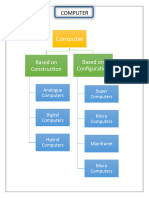
MACROCOMPUTERS
The term originally referred to the servers, workstations, and personal
large cabinets called "mainframes," computers.
which housed the central processing
unit and main memory of early
computers. They are larger and have
more processing power than other
kinds of computers: minicomputers,
In the hierarchy of computers, mainframes are just below supercomputers, which
are the most powerful computers in the world, a mainframe can usually run many
programs simultaneously at high speed, while supercomputers are designed for a
single process. Currently, the main mainframe manufacturers are IBM and Unisys.
Mainframe computers first appeared
in the 1940s, with ENIAC being the
first general-purpose electronic
computer.
The size of modern mainframe is
considerably smaller than older about
the size of a large refrigerator.
Mainframes are accessed and controlled primarily through terminals, which are
workstations similar to a standard computer, but do not have their own CPU.
Instead, they are red-connected to the mainframe and act as an access point for
users, only the terminals connected to them are capable of accessing the
information.
Distributed mainframes can be accessed from computers outside the mainframe,
allowing users to access material from their homes or via the Internet.
E-Business, (Banking institutions, brokerage houses, insurance agencies and
fortune companies are some examples of the public and private sectors that
transfer data through mainframe computers), military use, academic use and
research. Many of the busiest web sites store their production databases on a
mainframe.
Post-reading
TASK 3. Answer the following questions:
1. What is the difference between supercomputers and macrocomputers?
………………………………………………………………………………………
2. Which kind of computers have more hierarchy macrocomputers or
supercomputers?
………………………………………………………………………………………
3. Are mainframes and macrocomputers the same kind?
………………………………………………………………………………………
4. When did mainframes appear?
………………………………………………………………………………………
5. Who are the main users of macrocomputers?
………………………………………………………………………………………
TASK 4 Circle these words in the text and the Word they are modifying.
Then, translate into Spanish.
Example: modern modern mainframe una mainframe moderna
1.smaller ………………………………. ………………………………..
2. larger ………………………………. ………………………………..
3. modern ………………………………. ………………………………..
4. smaller ………………………………. ………………………………..
5. older ………………………………. ………………………………..
6. large ………………………………. ………………………………..
You might also like
- Unit 3-Types of Computers Revisado 1Document11 pagesUnit 3-Types of Computers Revisado 1Yasmin MachicadoNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Rad - Engleski JezikDocument20 pagesSeminarski Rad - Engleski Jezikjusufspa1997No ratings yet
- Computer TypesDocument6 pagesComputer TypesGarima GarimaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Microcomputers - 014644Document6 pagesBasic Concept of Microcomputers - 014644stevezubyik20No ratings yet
- Computer Applications: Chapter-IDocument34 pagesComputer Applications: Chapter-Imuskan smileNo ratings yet
- SupercomputerDocument5 pagesSupercomputerjshankar0108No ratings yet
- Name: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateDocument7 pagesName: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateKylie sheena MendezNo ratings yet
- Types of Computers I, Computer: DefinitionDocument5 pagesTypes of Computers I, Computer: DefinitionMenchie Ann Sabandal SalinasNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputerDocument23 pagesClassification of ComputerIDRISA NKUNYANo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument3 pagesClassification of ComputersRajeev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Computer Definition & Types of Computer. (Explained)Document6 pagesComputer Definition & Types of Computer. (Explained)elizabethternderNo ratings yet
- Computers Types: I, Computer: DefinitionDocument6 pagesComputers Types: I, Computer: Definitionராஜமாணிக்கம் பNo ratings yet
- MM 3 ComputersDocument4 pagesMM 3 Computersgood bye jungwoo with masks MariaNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Lesson 6Document5 pagesQ1 - Lesson 6JEROME DIAZNo ratings yet
- Computers Types: I, Computer: DefinitionDocument6 pagesComputers Types: I, Computer: DefinitionMesfene Tibebu FenNo ratings yet
- Classofication of Compuers: Shahzaib Imran Roll No:-51 Assignment:-001 Department:-BSITDocument6 pagesClassofication of Compuers: Shahzaib Imran Roll No:-51 Assignment:-001 Department:-BSITA Bundle Of knowledgeNo ratings yet
- Computer DevicesDocument23 pagesComputer DevicesRajashree RaviNo ratings yet
- C NotesDocument2 pagesC NotesMamta Mohit DhandaNo ratings yet
- CS 402Document3 pagesCS 402ebaadmalik653No ratings yet
- Grade 9 and 11 - Quarter 3 - Week 1Document2 pagesGrade 9 and 11 - Quarter 3 - Week 1Oliver C SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Allied EssentialsOfComputers 0bioinformaticsDocument156 pagesAllied EssentialsOfComputers 0bioinformaticssamikshajohn03No ratings yet
- Types of Computers I, Computer: Definition: Supercomputer and MainframeDocument4 pagesTypes of Computers I, Computer: Definition: Supercomputer and MainframeJeremias De la CruzNo ratings yet
- MST 1 SolutionDocument14 pagesMST 1 SolutionSumit JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument18 pagesChapter Threeaarka soomalidaNo ratings yet
- AMITY SUb2 - A1-Ans1Document3 pagesAMITY SUb2 - A1-Ans1Ashok PalNo ratings yet
- Ict Lab Task 3Document12 pagesIct Lab Task 3NOOB GAM1NGNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of ComputersHarry GillNo ratings yet
- Computer HierarchyDocument37 pagesComputer HierarchyRondo Hirohito67% (3)
- Computer - TypesDocument3 pagesComputer - TypesジョージNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument7 pagesClassification of ComputersscsdfvdgNo ratings yet
- Supercomputers Minicomputers Mainframes Workstations Personal Computers Least Powerful Most PowerfulDocument9 pagesSupercomputers Minicomputers Mainframes Workstations Personal Computers Least Powerful Most Powerfulsujit_ranjanNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument3 pagesTypes of ComputersKing ZuesNo ratings yet
- Gen Comp by T.MDocument11 pagesGen Comp by T.MErvin LinNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of ComputersMary Joy CanalanNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of Computerssweetktz789No ratings yet
- POP-module1 NotesDocument83 pagesPOP-module1 NotesrakshithatanNo ratings yet
- C Question BankDocument29 pagesC Question Bankdd0542469No ratings yet
- Classification of Types of ComputerDocument8 pagesClassification of Types of Computershawai8009No ratings yet
- History of Computing Classification of Computers Types of ComputersDocument22 pagesHistory of Computing Classification of Computers Types of Computersdua tanveerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing PrelimDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Computing PrelimApril Jane AndresNo ratings yet
- Computers in EducationDocument9 pagesComputers in Educationkvsamy09No ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety Understanding ComputerDocument2 pagesOccupational Health and Safety Understanding ComputerRegina Fe EmpasNo ratings yet
- Computers TypesDocument4 pagesComputers TypesMuhammad Atif Qaim KhaniNo ratings yet
- TVL - Computer Systems Servicing 11: Let Us DiscoverDocument7 pagesTVL - Computer Systems Servicing 11: Let Us DiscoverFredilo Flores Jr.No ratings yet
- Basay, Rodilyn G. BSCE-2 GE-TFL TTH 3:00-4:30 PM 02-18-2020: Personal ComputerDocument3 pagesBasay, Rodilyn G. BSCE-2 GE-TFL TTH 3:00-4:30 PM 02-18-2020: Personal ComputerRodilyn BasayNo ratings yet
- Figure 6-1.-C1assification System of Memory.: Time Destructive ReadoutDocument7 pagesFigure 6-1.-C1assification System of Memory.: Time Destructive ReadoutVijay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics TextbookDocument103 pagesComputer Basics Textbookapi-19727066No ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.2: Types of ComputerDocument23 pagesInformation Sheet 1.2: Types of ComputerBerlin AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument10 pagesTypes of Computersmandy02scribdNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument19 pagesTypes of Computerkaplan abateNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument195 pagesComputer ArchitectureFahad AlamNo ratings yet
- Computer Awareness - Computer Awareness-1Document12 pagesComputer Awareness - Computer Awareness-1samskruti speaksNo ratings yet
- Is An Informal High-Level Description of The Operating Principle of A Computer Program or Other AlgorithmDocument4 pagesIs An Informal High-Level Description of The Operating Principle of A Computer Program or Other AlgorithmMary Charisse SandroNo ratings yet
- 0604 Advanced Computer ArchitectureDocument195 pages0604 Advanced Computer ArchitectureAdrian AdrNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument5 pagesClassification of ComputersTaha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cprogramming Module1Document42 pagesCprogramming Module1Haresh SNo ratings yet
- Ict ModuleDocument26 pagesIct ModuleSai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument4 pagesTypes of Computercutemano1311No ratings yet
- Makalah KomputerDocument16 pagesMakalah KomputerAbubakar AdeniNo ratings yet
- ABAP ProfileDocument4 pagesABAP Profileteja chavaNo ratings yet
- Digi Connect Me 9210: Ultra-Compact High-Performance Embedded Modules For M2M Networking Combine On-Chip SecurityDocument5 pagesDigi Connect Me 9210: Ultra-Compact High-Performance Embedded Modules For M2M Networking Combine On-Chip SecurityVENKATESH KAMATHNo ratings yet
- MAGNET Ver 3.0.1 Release NotesDocument40 pagesMAGNET Ver 3.0.1 Release NotesNguyễn Thanh Hiền nguyenNo ratings yet
- ECE4007 Information Theory and Coding: DR - Sangeetha R.GDocument40 pagesECE4007 Information Theory and Coding: DR - Sangeetha R.GTanmoy DasNo ratings yet
- Data Platform and Analytics Foundational Training: (Speaker Name)Document10 pagesData Platform and Analytics Foundational Training: (Speaker Name)Kathalina SuarezNo ratings yet
- Flexible WorkflowDocument51 pagesFlexible WorkflowbasemffcamriNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide On Microsoft Excel For Data AnalysisDocument28 pagesA Comprehensive Guide On Microsoft Excel For Data AnalysisKhushi BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Sensor Network Applications in Smart GridDocument8 pagesWireless Sensor Network Applications in Smart GridTenda TiyNo ratings yet
- Handout 9800 MSF98001 Hands-OnDocument26 pagesHandout 9800 MSF98001 Hands-Onvuk vukanicNo ratings yet
- Manual HandbrakeDocument1 pageManual HandbrakeAndy LNo ratings yet
- EDUP 2082 Psikologi Pendidikan: Perbezaan Individu Dan PembelajaranDocument31 pagesEDUP 2082 Psikologi Pendidikan: Perbezaan Individu Dan PembelajaranNur Farahin AliasNo ratings yet
- Collaborate. Communicate. Concentrate.: Logitech Zone Wireless HeadsetsDocument2 pagesCollaborate. Communicate. Concentrate.: Logitech Zone Wireless HeadsetsraviezsoftNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 CAAGAY MARIMEL P BSEDSCI3A.Introtech2Document8 pagesCHAPTER 4 CAAGAY MARIMEL P BSEDSCI3A.Introtech2Kay LagunaNo ratings yet
- Commvault Complete Backup and Recovery DatasheetDocument2 pagesCommvault Complete Backup and Recovery DatasheetitnetmanNo ratings yet
- Informational Influence in Organizations: An Integrated Approach To Knowledge AdoptionDocument26 pagesInformational Influence in Organizations: An Integrated Approach To Knowledge AdoptionAnne AfrianiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1Document42 pagesAdvanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1Mustafamna Al Salam0% (1)
- Introduction To Software Testing Engineering Criteria For TechnologiesDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Software Testing Engineering Criteria For TechnologiesNurma Ayu WigatiNo ratings yet
- Resify Website UpdatesDocument12 pagesResify Website UpdatesChathura JayasingheNo ratings yet
- Big-O Algorithm Complexity Cheat Sheet (Know Thy Complexities!) @ericdrowellDocument9 pagesBig-O Algorithm Complexity Cheat Sheet (Know Thy Complexities!) @ericdrowelldungNo ratings yet
- Information SiloDocument3 pagesInformation Silokatherine976No ratings yet
- Release 13 Using The Transaction ConsoleDocument26 pagesRelease 13 Using The Transaction ConsoleMahesh VeluruNo ratings yet
- Example On Bresenhams Line Drawing AlgorithmDocument2 pagesExample On Bresenhams Line Drawing AlgorithmPunam Patil60% (30)
- Question Papers AllDocument64 pagesQuestion Papers AllAbdulBasit ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Order Statistic NotesDocument7 pagesOrder Statistic NotesKoustab BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision and Graphics PDFDocument3 pagesComputer Vision and Graphics PDFAkash SinhaNo ratings yet
- World Handwriting ContestDocument2 pagesWorld Handwriting Contestclassicintrovert897No ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics (BDAG 19-5) : Quiz: GMP - 2019 Term VDocument2 pagesBig Data Analytics (BDAG 19-5) : Quiz: GMP - 2019 Term VdebmatraNo ratings yet
- Raquel V. Cepillo: Mobile No. 0956-354-5034Document3 pagesRaquel V. Cepillo: Mobile No. 0956-354-5034Allan Ahadi UsmanNo ratings yet
- Modbus Manual v1 7 PDFDocument59 pagesModbus Manual v1 7 PDFHoangtnt NguyenNo ratings yet
- Permutation GroupDocument12 pagesPermutation GroupHarshitaNo ratings yet