Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LESSON 5 T-Test FOR INDEPENDENT (Or SINGLE) SAMPLES
LESSON 5 T-Test FOR INDEPENDENT (Or SINGLE) SAMPLES
Uploaded by
Carmy Faith BaclayoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 5 T-Test FOR INDEPENDENT (Or SINGLE) SAMPLES
LESSON 5 T-Test FOR INDEPENDENT (Or SINGLE) SAMPLES
Uploaded by
Carmy Faith BaclayoCopyright:
Available Formats
Psych 2 – Psychological Statistics LABORATORY WORKSHEET usa.edu.
ph
LESSON 5: t-Test FOR INDEPENDENT (or SINGLE) SAMPLES
What is the t-test for independen t samples?
The t-test is a test of difference between two independent groups. The means are being compared
x̄1 against x̄2.
When to use the t-test for indepe ndent samples?
The t-test for independent sampl es is used when we compare means of two indepe ndent groups.
- the distribution is normally distributed,
- Sk= 0 and Ku = .265.
- we use interval or ratio data.
- the sample is at least n=30.
Why do we use the t-test for inde pendent sample?
The t-test is used for independent sample because it is a more powerful test compa red with
other tests of difference of two indepen dent groups.
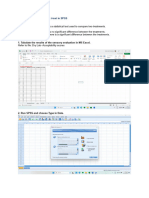
SPSS P rocedure for Independent Samples t-test
1. Click on Data View located at the lowest left corner of your data editor.
2. Enter the number ‘cod es’ for your groupings in one column of the data editor, var00001
or var1. On the second column, enter the scores or your dependent variable var00002
or var2.
3. From the menu bar at the top click on: Analyze, then click on Compare Means, then on
Independent Sample s t-test.
4. Move the dependent v ariable (e.g., time) into the area labeled Test Variable(s).
5. Move the independen t variable (e.g., eater) into the section labeled Gro uping Variable.
6. Click on Define group s and type in the numbers used in the data set to code each
group. In the current sample file 1 = normal weight, 2 = mega weight, therefore in the
Group 1 box, type ‘1’; and in the Group 2 box, type ‘2’.
7. Click on Continue an d then OK.
Psych 2 – Psychological Statistics LABORATORY WORKSHEET usa.edu.ph
Example:
Dr. Vill Mah wishes to test the hypothesis that mega-weight individuals tend to eat faster than
normal weight individuals. To test this hypothesis, she has two assistants sit in a MacDowel’s
restaurant and identify individuals who order the Big Mack Special for lunch. The Big Mackers, as
the assistants affectionately call them are classified as mega-weight and normal weight. The
assistants identify 9 overweight and 9 normal weight Big Mackers. The assistants record the
amount of time it takes for the individuals to complete their Big Mack special meals. Data collected
are presented below:
Normal weight Mega-weight
23 24
12 7
24 7
30 29
30 13
41 3
50 16
44 14
34 30
1. State the null hypothesis.
4. What is the significance or probability
associated with the obtained t value?
2. State the alternative hypothesis.
5. What do the results indicate?
3. What is the obtained t value?
The output generated from this procedure is shown below:
Group Statistics
Type of Eater N Mean Std. Std. Error
Deviation Mean
Normal
Time it takes the eater to Weight 9 32.00 11.758 3.919
finish the burger
Mega Weight 9 15.89 9.829 3.276
Independent Samples Test
Levene's Test for
Equality of Variances t-test for Equality of Means
95% Confidence
Interval of the
Mean Std. Error Difference
F Sig. t df Sig. (2-tailed) Difference Difference Lower Upper
timeEqual variances
assumed .191 .668 3.154 16 .006 16.111 5.108 5.282 26.940
Equal variances
not assumed 3.154 15.512 .006 16.111 5.108 5.254 26.968
You might also like
- Splunk 8.2 Fundamentals Part 2Document349 pagesSplunk 8.2 Fundamentals Part 2redirete123No ratings yet
- Final - Module 4 BDocument61 pagesFinal - Module 4 BJohn Emmanuel TulayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inferential Statistics & Important Statistical TestsDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Inferential Statistics & Important Statistical Testsadeel_khan_48No ratings yet
- Assignment: 1. Perform The Following StepsDocument3 pagesAssignment: 1. Perform The Following StepsXuehua GuanNo ratings yet
- Spss ASSIGNMENT 2Document4 pagesSpss ASSIGNMENT 2Mohamad Hilman Al-KelantaniNo ratings yet
- Herman Karanja Mwangi Final Submission PDFDocument112 pagesHerman Karanja Mwangi Final Submission PDFcyrusNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 T-Test FOR DEPENDENT (Or CorrelatedPairedMatched) SAMPLESDocument3 pagesLESSON 6 T-Test FOR DEPENDENT (Or CorrelatedPairedMatched) SAMPLESCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- CRJ 503 PARAMETRIC TESTS DifferencesDocument10 pagesCRJ 503 PARAMETRIC TESTS DifferencesWilfredo De la cruz jr.No ratings yet
- Research Methadolgy AssignmentDocument7 pagesResearch Methadolgy AssignmentAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Bus101 Wk11 Ws Ttests Anova Bv2Document11 pagesBus101 Wk11 Ws Ttests Anova Bv2Ansariah CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 2 Hypothesis Testing and Test of DifferencesDocument13 pagesUnit 7 2 Hypothesis Testing and Test of Differencesedselsalamanca2No ratings yet
- AE 108 Handout No.1Document8 pagesAE 108 Handout No.1hambalos broadcastingincNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis TestingDocument36 pagesHypothesis TestingIsaiah Shane PinedaNo ratings yet
- Xaviers - 7 - Independent Sample T TestDocument24 pagesXaviers - 7 - Independent Sample T TestNitish KumarNo ratings yet
- Nama: Suryaningtyas Dharma Putri NRP: 150114390 1. Uji Beda Between Design Eksperimen Kontrol 3 2 4 3 6 2 8 2Document9 pagesNama: Suryaningtyas Dharma Putri NRP: 150114390 1. Uji Beda Between Design Eksperimen Kontrol 3 2 4 3 6 2 8 2Suryaningtyas Dharma PutriNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Study On Independent T-TestDocument6 pagesAn Empirical Study On Independent T-Testryan james amistosoNo ratings yet
- Part I. Give Your Answer Based On Your Basic Understanding in StatisticsDocument18 pagesPart I. Give Your Answer Based On Your Basic Understanding in Statisticsnemwel capolNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Sport and Exercise TestingDocument37 pagesResearch Methods in Sport and Exercise TestingZe MelieNo ratings yet
- T-Tests & Chi2Document35 pagesT-Tests & Chi2JANANo ratings yet
- QRM Seminar 2 - CanvasDocument50 pagesQRM Seminar 2 - Canvasrxh6kp5pp9No ratings yet
- Sample of Action Research ResultDocument4 pagesSample of Action Research ResultNick Cris GadorNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 and 3 MemoDocument11 pagesPractical 2 and 3 MemomabotjasefudiNo ratings yet
- Tests For Mean and ProportionDocument34 pagesTests For Mean and ProportionSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 19Document6 pagesTutorial 19Dewi RahmasariNo ratings yet
- Nota T-TestDocument27 pagesNota T-Testhamidah2No ratings yet
- Inferential Statistics: Draw Inferences About The Larger GroupDocument60 pagesInferential Statistics: Draw Inferences About The Larger GroupPoverty 304No ratings yet
- Samples Tests in SSPS: 1.0 One Sample T-TestDocument12 pagesSamples Tests in SSPS: 1.0 One Sample T-TestKakeeto MosesNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Continuous and Categorical Variables: January 28, 2020Document31 pagesAnalysis of Continuous and Categorical Variables: January 28, 2020Nour MusharbashNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 Experiment DesignDocument15 pagesHandout 1 Experiment DesignFleming MwijukyeNo ratings yet
- Example Independent Sample T Test PDFDocument3 pagesExample Independent Sample T Test PDFYamuna GovindarajNo ratings yet
- IE005 Lab Exercise 1 and 2mnDocument7 pagesIE005 Lab Exercise 1 and 2mnApril Dawates100% (1)
- Anova-1Document27 pagesAnova-1Iftitah AkbarNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: Ervin C. ReyesDocument15 pagesHypothesis Testing: Ervin C. ReyesReyes C. ErvinNo ratings yet
- Independent Samples T-Test: Module No. 2Document9 pagesIndependent Samples T-Test: Module No. 2Ash AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Surigao State College of Technology - Malimono Campus Learning ModuleDocument4 pagesSurigao State College of Technology - Malimono Campus Learning ModuleElla Clent moralesNo ratings yet
- Test of Hypothesis - T and Z Tests. Chi-Square Test. F Test.Document15 pagesTest of Hypothesis - T and Z Tests. Chi-Square Test. F Test.Barath RajNo ratings yet
- Confidence IntervalsDocument18 pagesConfidence IntervalsDeniseJade LeguardaNo ratings yet
- Stat Activity 6 Inferential StatDocument4 pagesStat Activity 6 Inferential StatCHRIS ARWIEL PENALESNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method NotesDocument8 pagesScientific Method NoteschaiiiNo ratings yet
- SPSS T Test Lab AnswersDocument4 pagesSPSS T Test Lab AnswersSOMASUNDARAM RNo ratings yet
- S1 To N4 Physics Practice Question Book AnswersDocument35 pagesS1 To N4 Physics Practice Question Book Answersnguyen.tat.thang.1957.2020No ratings yet
- Biostatistics HandoutsDocument108 pagesBiostatistics HandoutsSalah SaeedNo ratings yet
- Comparing The Means Using The TtestDocument25 pagesComparing The Means Using The TtestAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Measures of DisperstionDocument19 pagesChapter-4 - Measures of DisperstionKebede HaileNo ratings yet
- 5 Chapter Five ANOVADocument9 pages5 Chapter Five ANOVADenaw AgimasNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics: Test The Difference Between The Two MeansDocument8 pagesApplied Statistics: Test The Difference Between The Two Meansiiyousefgame YTNo ratings yet
- PSYC 3990 Lab: Final Assessment (40 PTS) : NameDocument5 pagesPSYC 3990 Lab: Final Assessment (40 PTS) : NamemicahgaffneyNo ratings yet
- Inferential StatisticsDocument22 pagesInferential StatisticsTrixie MengulloNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No 3BDocument6 pagesLaboratory Exercise No 3BMichael AbeledaNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemDocument10 pagesAnalytical ChemMeerab 242-bh-chem-19No ratings yet
- 5 Single Sample T JASPDocument10 pages5 Single Sample T JASPInês MendesNo ratings yet
- Science Research Iii: Second Quarter-Module 6 Hypothesis Testing For The Means - Two Sample (Independent Sample)Document9 pagesScience Research Iii: Second Quarter-Module 6 Hypothesis Testing For The Means - Two Sample (Independent Sample)marc marcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Experimental Design and HahaDocument46 pagesChapter 13 Experimental Design and Hahamannsahil72No ratings yet
- Kubsa Guyo Advance BiostatisticDocument30 pagesKubsa Guyo Advance BiostatistickubsaNo ratings yet
- CH 8 Independent Measures T-TestDocument8 pagesCH 8 Independent Measures T-TestMatthew ShawNo ratings yet
- Kuis Biostatistik Ii T-Test: Nama: Richie Junianto Prodi: K3 Semesester IV Sore NPM: 172410032Document3 pagesKuis Biostatistik Ii T-Test: Nama: Richie Junianto Prodi: K3 Semesester IV Sore NPM: 172410032richie juniantoNo ratings yet
- ANOVA & T-Test PresentationDocument46 pagesANOVA & T-Test PresentationdatumNo ratings yet
- How To Analyze Data Using T-Test in SPSSDocument6 pagesHow To Analyze Data Using T-Test in SPSSGaily Jubie HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Paired T TestDocument21 pagesPaired T TestDaxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Testing Accuracy and Precision in Using A MicropipettorDocument4 pagesExperiment 1: Testing Accuracy and Precision in Using A MicropipettorRosheenNo ratings yet
- Biology UNIT 3X EMPA Revision GuideDocument23 pagesBiology UNIT 3X EMPA Revision Guideyk_60375325No ratings yet
- Hema Lab Module 10Document7 pagesHema Lab Module 10Carmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 MODULE 2 LecDocument28 pagesHema 2 MODULE 2 LecCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4. The Existential and Humanistic Approach To Counseling PsychotherapyDocument23 pagesMODULE 4. The Existential and Humanistic Approach To Counseling PsychotherapyCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- HemaLec MLS3D Module1.1Document9 pagesHemaLec MLS3D Module1.1Carmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Variables and Measurements Activity (2) BaclayoDocument1 pageLesson 1 Variables and Measurements Activity (2) BaclayoCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 STANDARD SCORES z-SCORESDocument3 pagesLESSON 4 STANDARD SCORES z-SCORESCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 T-Test FOR DEPENDENT (Or CorrelatedPairedMatched) SAMPLESDocument3 pagesLESSON 6 T-Test FOR DEPENDENT (Or CorrelatedPairedMatched) SAMPLESCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- Final Kahilwayan TrainingModuleDocument10 pagesFinal Kahilwayan TrainingModuleCarmy Faith BaclayoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Module 1Document28 pagesPractical Research 2 Module 1ShirleyNo ratings yet
- Zhang Et Al. (2016)Document43 pagesZhang Et Al. (2016)prempatilNo ratings yet
- Section1 7 PDFDocument8 pagesSection1 7 PDFجنيسة مؤنا100% (1)
- Data Analysis Is The Process of Systematically Applying Statistical andDocument7 pagesData Analysis Is The Process of Systematically Applying Statistical andkebonyeNo ratings yet
- ANOVA - Activity 2Document11 pagesANOVA - Activity 2Roadend PaspasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Sampling and Sample SizeDocument16 pagesLecture On Sampling and Sample SizePRITI DASNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Islamiyya Teachers in Promoting Morality Among Muslim YouthDocument65 pagesContribution of Islamiyya Teachers in Promoting Morality Among Muslim Youthabdullahiyusufwuyo8No ratings yet
- UBD Lesson Plan Grade 7 MathDocument20 pagesUBD Lesson Plan Grade 7 Mathrosalynrendon1004No ratings yet
- Cyberbullying Detection Through Sentiment AnalysisDocument6 pagesCyberbullying Detection Through Sentiment AnalysisZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marine Policy: Mary E. DavisDocument6 pagesMarine Policy: Mary E. DavisIrma YantiNo ratings yet
- ASTM E 178 Dealing With Outlying ObservationsDocument11 pagesASTM E 178 Dealing With Outlying Observationsiel84749No ratings yet
- BiostatsDocument17 pagesBiostatsKIRTI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Answer Demand Forecasting & ABC Analysis (Exercise 2)Document18 pagesAnswer Demand Forecasting & ABC Analysis (Exercise 2)Asep Rahmatullah50% (2)
- Research Chapter 3Document23 pagesResearch Chapter 3Halil DandunNo ratings yet
- Shore, B. Operations Management.Document569 pagesShore, B. Operations Management.IsabelNo ratings yet
- ArtikelDocument7 pagesArtikelaisyah nabilaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Research (2 Semester, 2020-2021) Pedrito Jose V. Bermudo, Edd PHD ProfessorDocument154 pagesMethods of Research (2 Semester, 2020-2021) Pedrito Jose V. Bermudo, Edd PHD ProfessorYuriiNo ratings yet
- Research MethodoloyDocument13 pagesResearch MethodoloyNivedita SolankeNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I - Basics of Modelling - SCH1401: School of Bio and Chemical Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument111 pagesUNIT - I - Basics of Modelling - SCH1401: School of Bio and Chemical Department of Chemical EngineeringSaurabh KinareNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Trade Before and After The WTO: A Case Study of IndiaDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Trade Before and After The WTO: A Case Study of IndiaChandanNo ratings yet
- Stat Cluster SamplingDocument22 pagesStat Cluster SamplingbldhakaNo ratings yet
- Neyman Pearson LemmaDocument2 pagesNeyman Pearson Lemmaamiba45No ratings yet
- Stat 250 Gunderson Lecture Notes Relationships Between Categorical Variables 12: Chi Square AnalysisDocument17 pagesStat 250 Gunderson Lecture Notes Relationships Between Categorical Variables 12: Chi Square AnalysisDuckieNo ratings yet
- Pelatihan Kader: Lampiran Uji StatistikDocument2 pagesPelatihan Kader: Lampiran Uji StatistikSiti Hidayatul FitriNo ratings yet
- Ann Rec054Document1 pageAnn Rec054YASHWANTHj58No ratings yet
- Bap 20 Sem.i Iii V PDFDocument16 pagesBap 20 Sem.i Iii V PDFConfucius Immortal RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Regression Fitting Lines To DataDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Regression Fitting Lines To Dataapi-367364282100% (1)
- Assessing The Impact of Service Quality Dimensions On Customer Satisfaction in Commercial Banks of MauritiusDocument12 pagesAssessing The Impact of Service Quality Dimensions On Customer Satisfaction in Commercial Banks of MauritiusDheeraj Ku. RajakNo ratings yet